biomolecules - honors biology 10
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
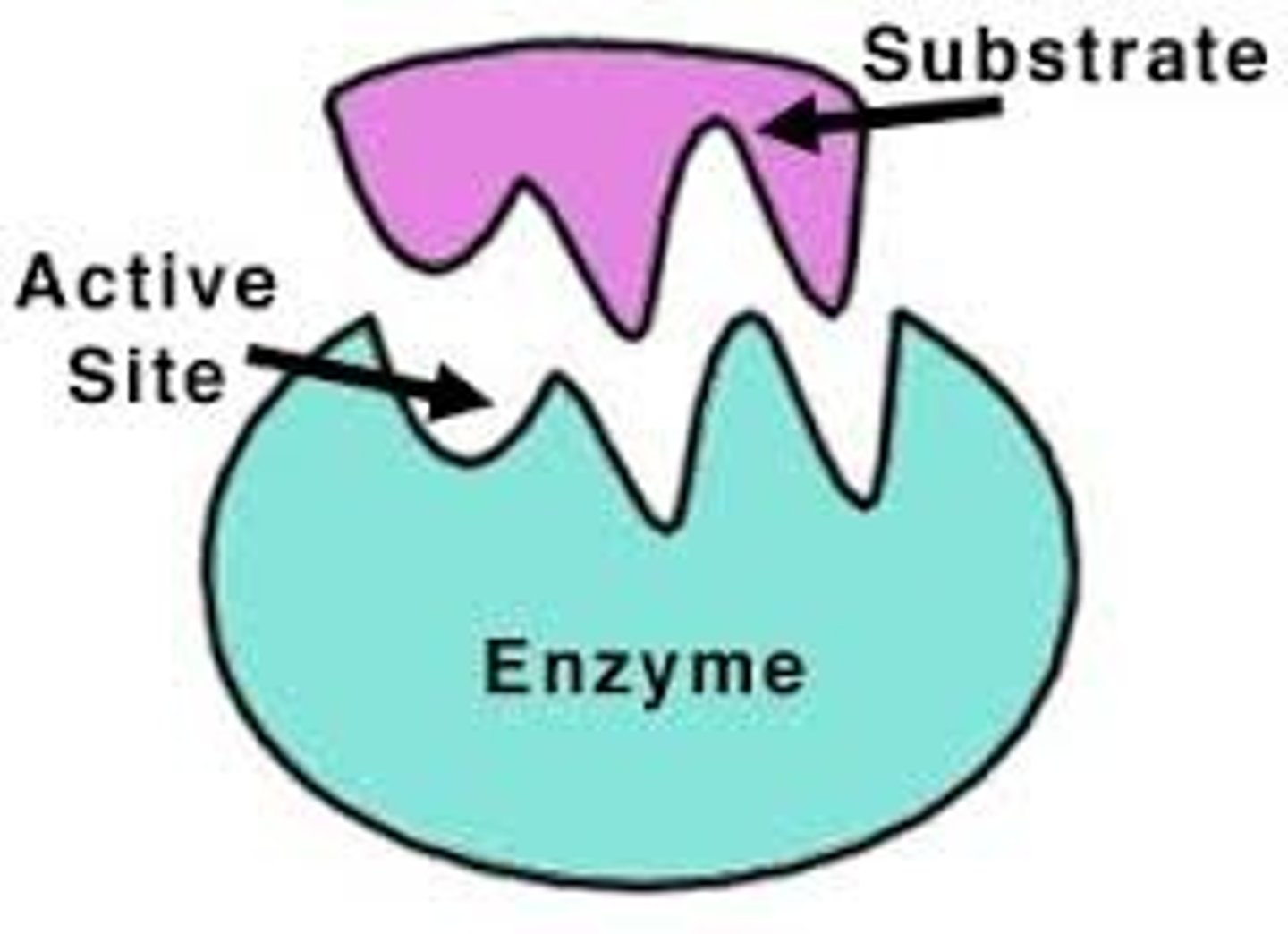
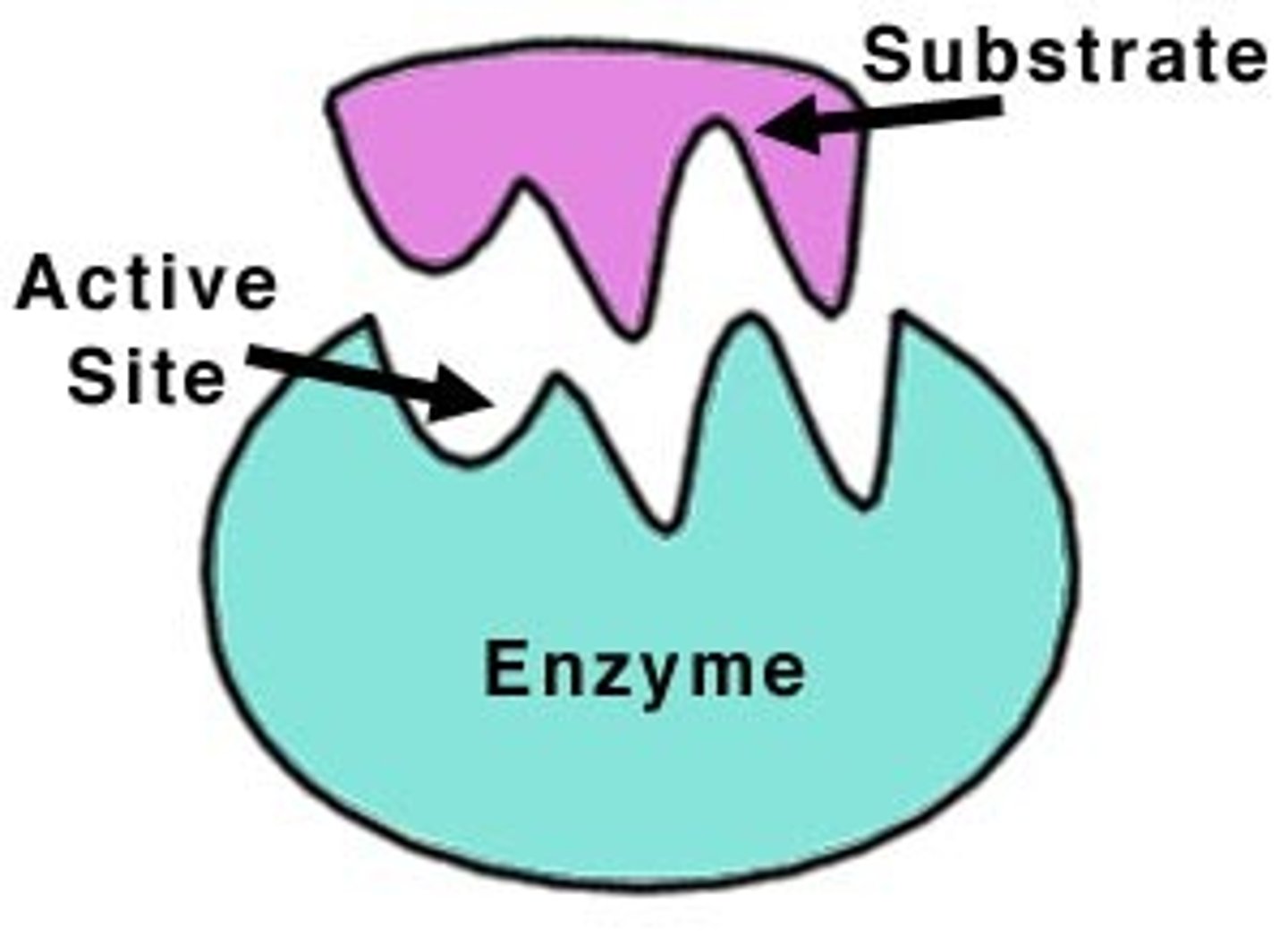
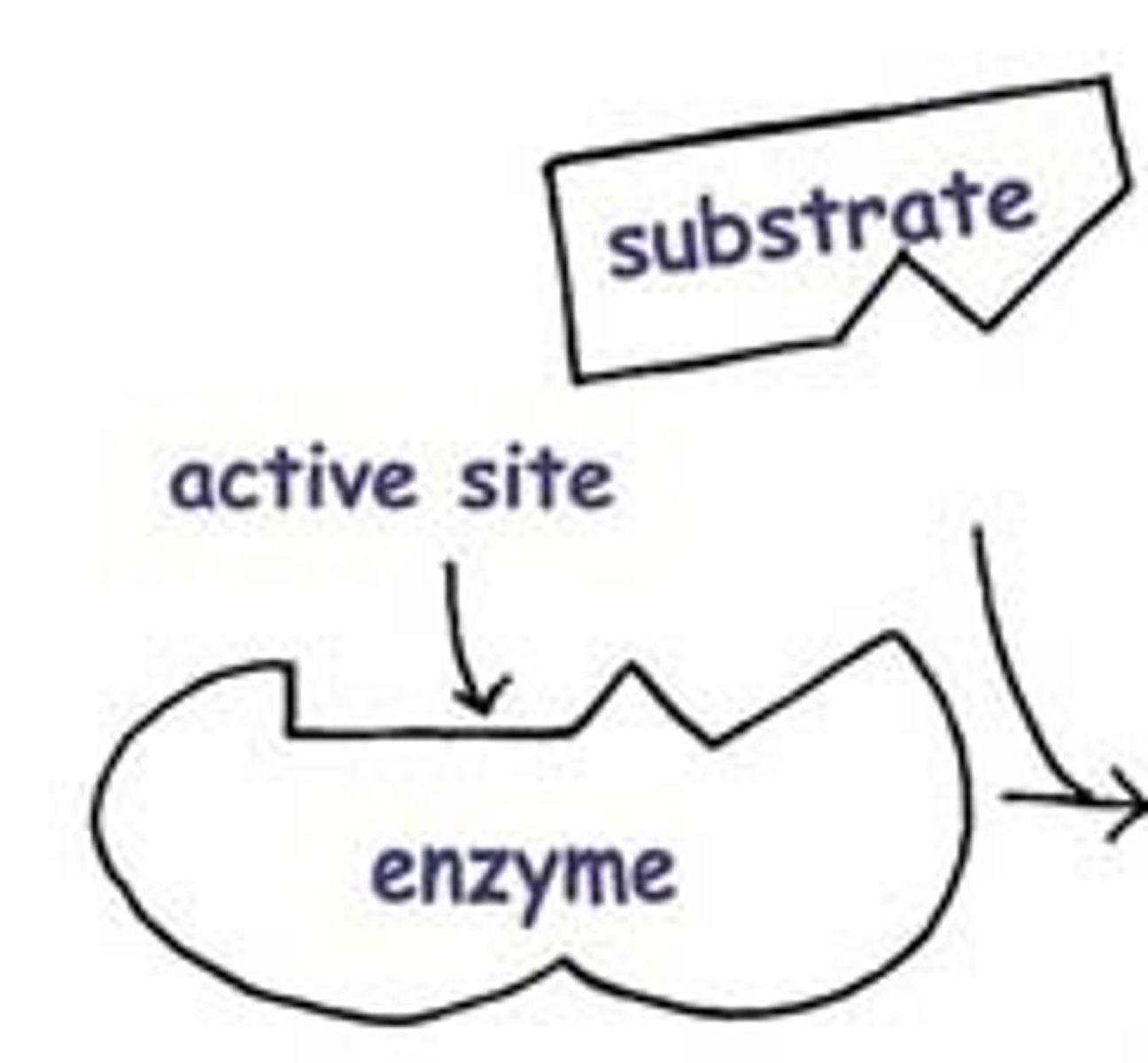
What is an active site?
The region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate.
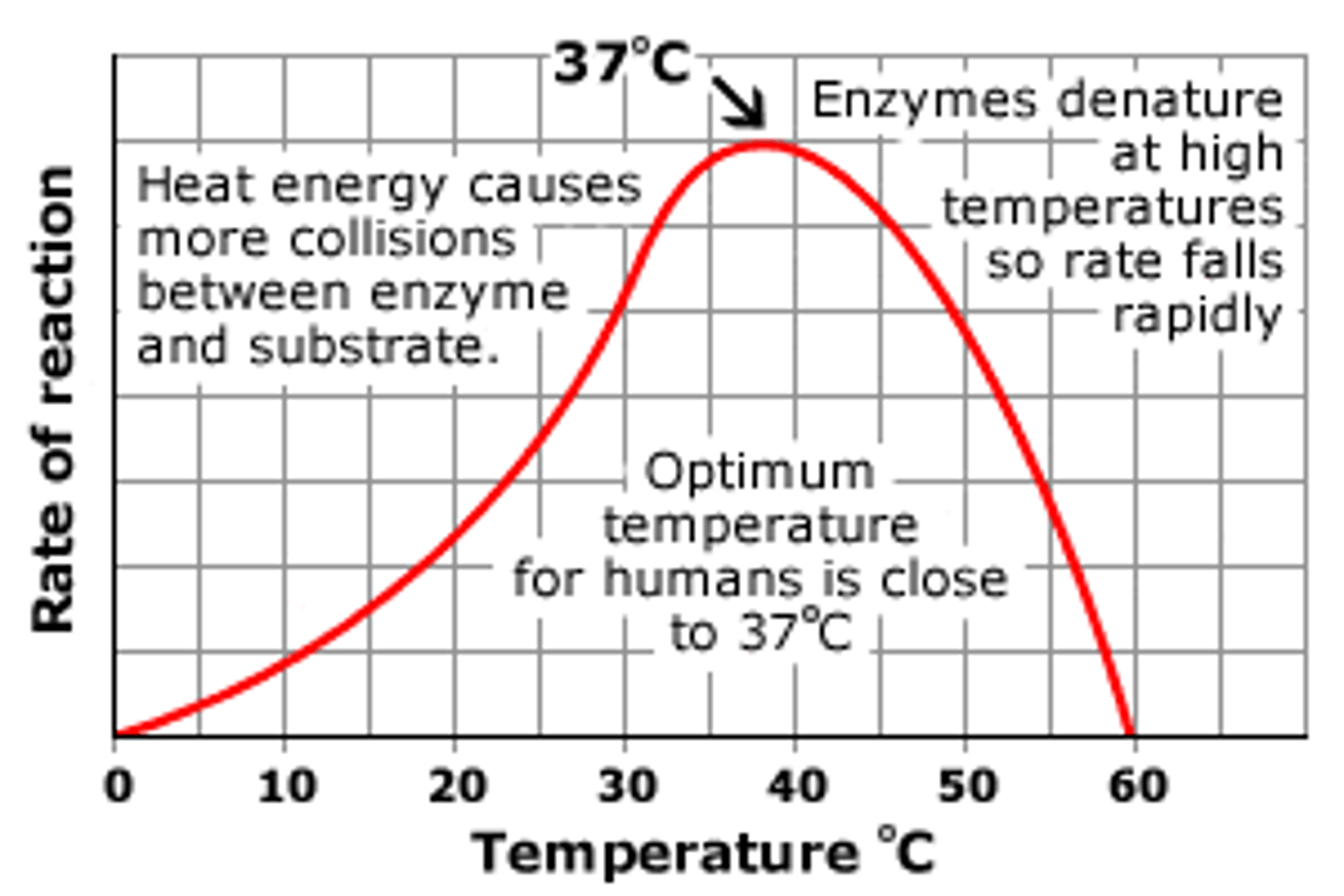
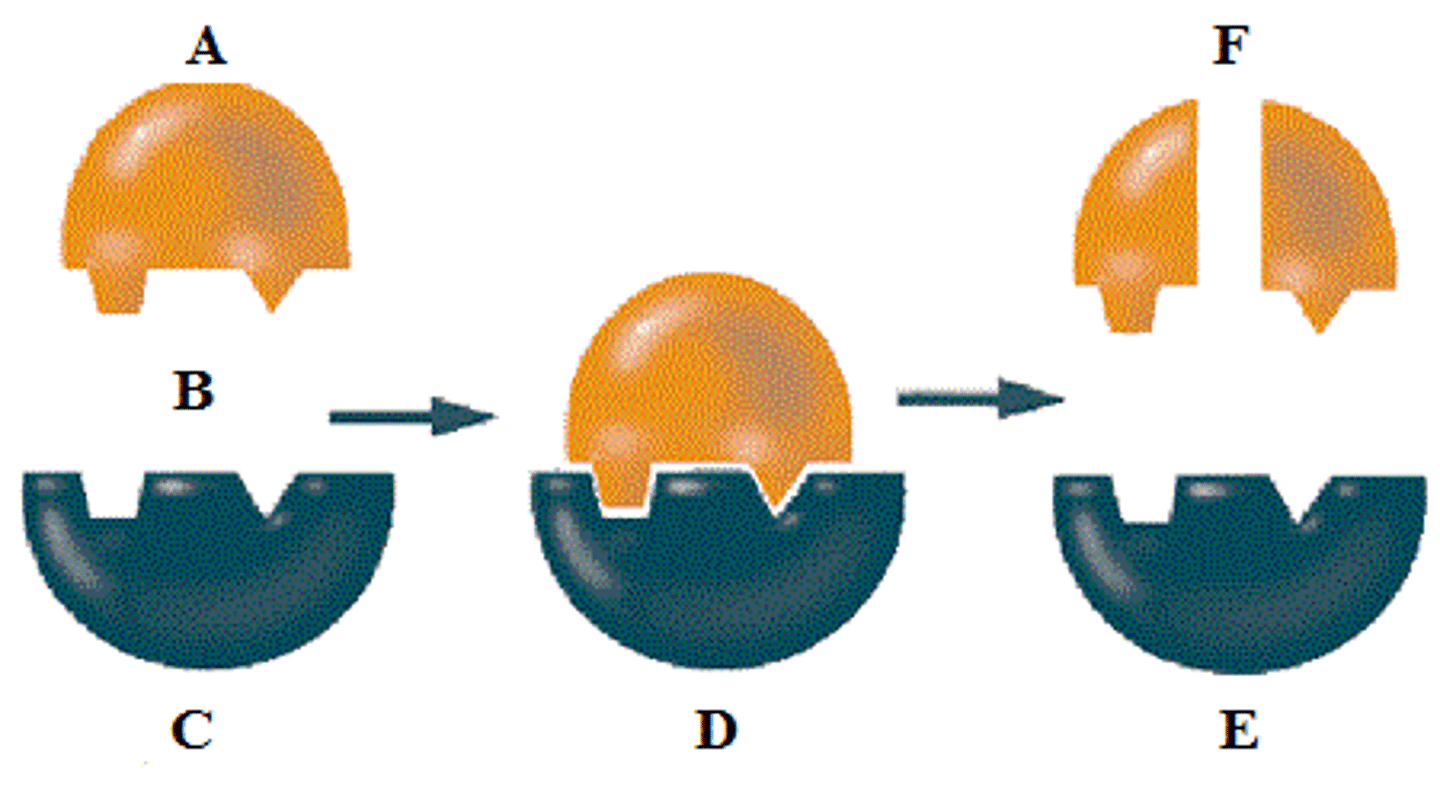
Why has this enzyme activity decreased so much?
The enzyme has become denatured.
Which building blocks are correctly matched to the macromolecule they form?
Amino acids make proteins.
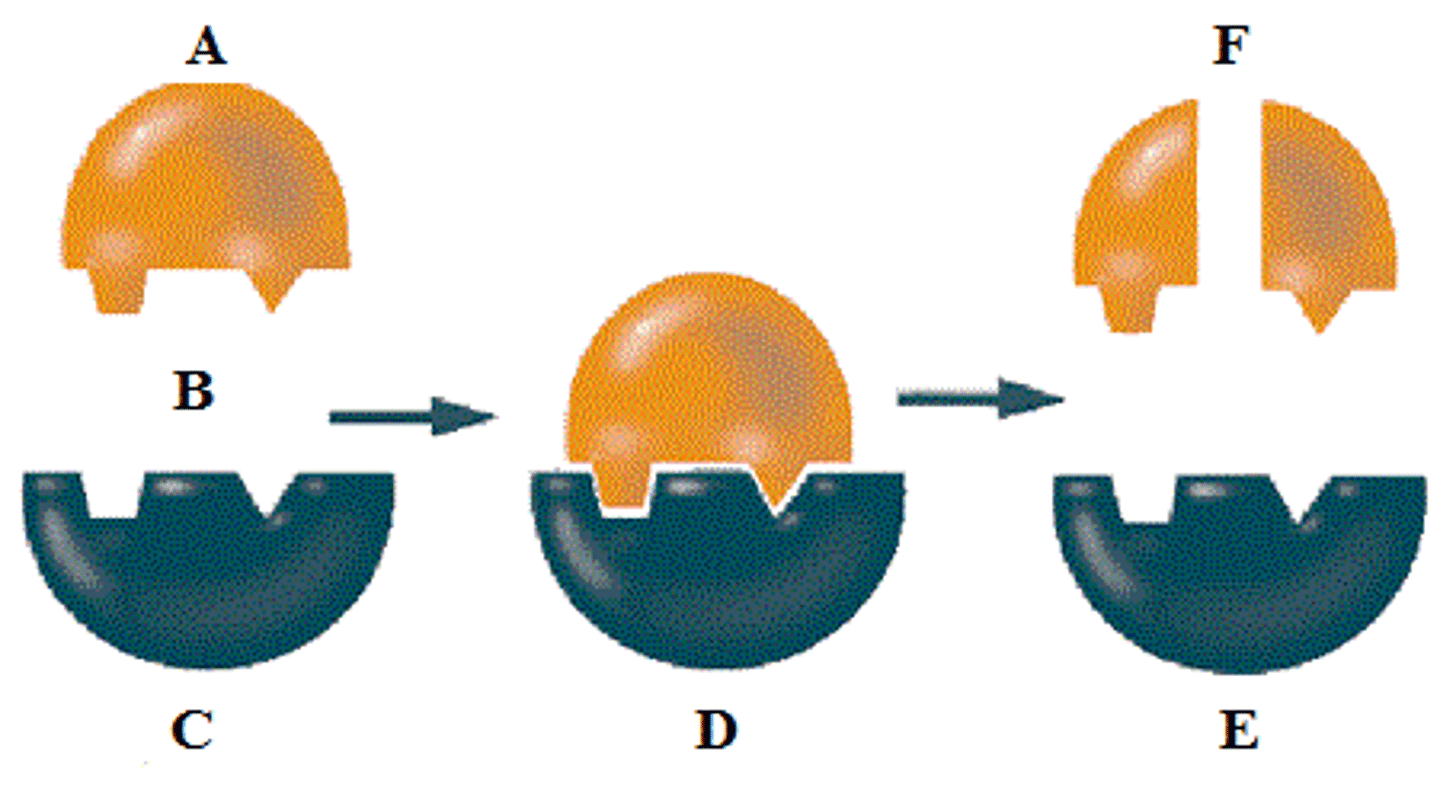
What is the purple piece?
The substrate.
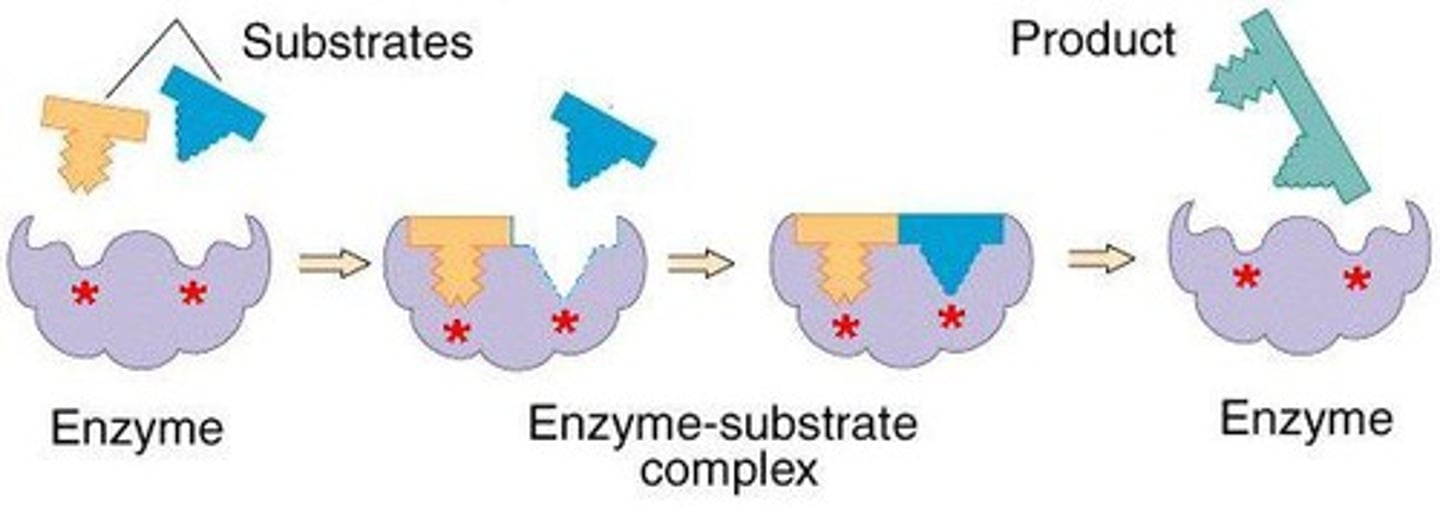
What is the second photo?
An enzyme-substrate complex.
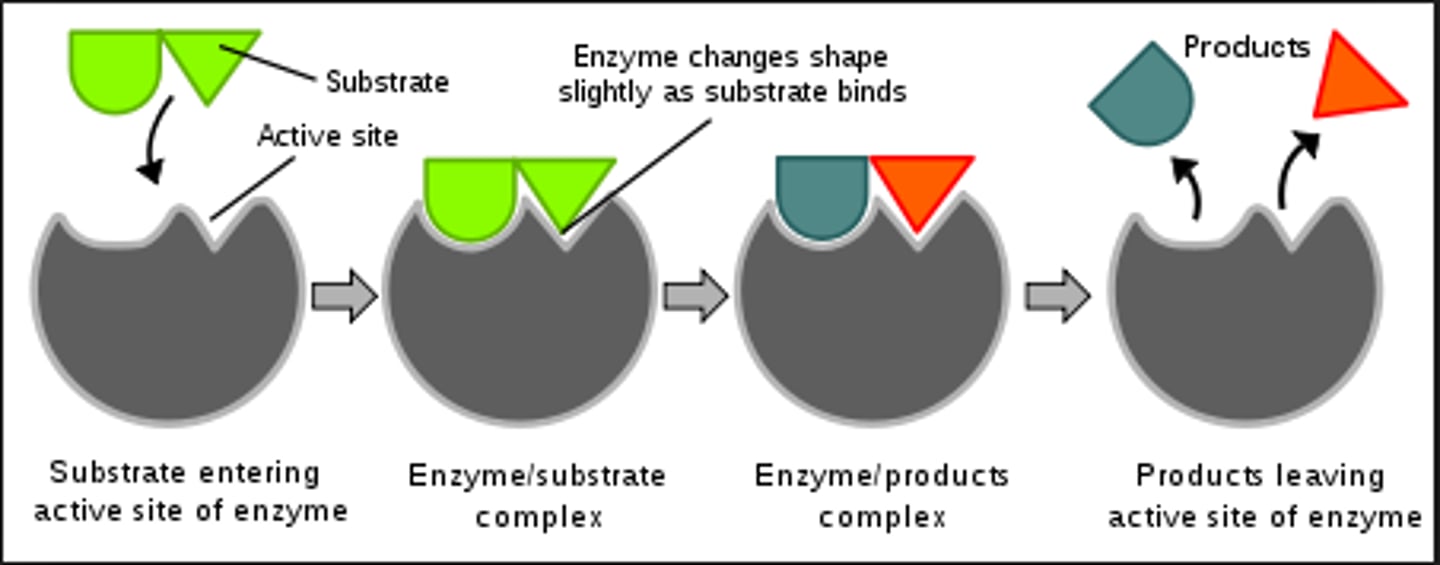
Substrate. . .
A reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
The protein (a) _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ breaks down the carbohydrate (b) _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
a. Galactase.
b. Galactose.
Type of lipid that sends messages throughout the body, is usually 4 carbon rings, and hydrophobic.
Steroid.
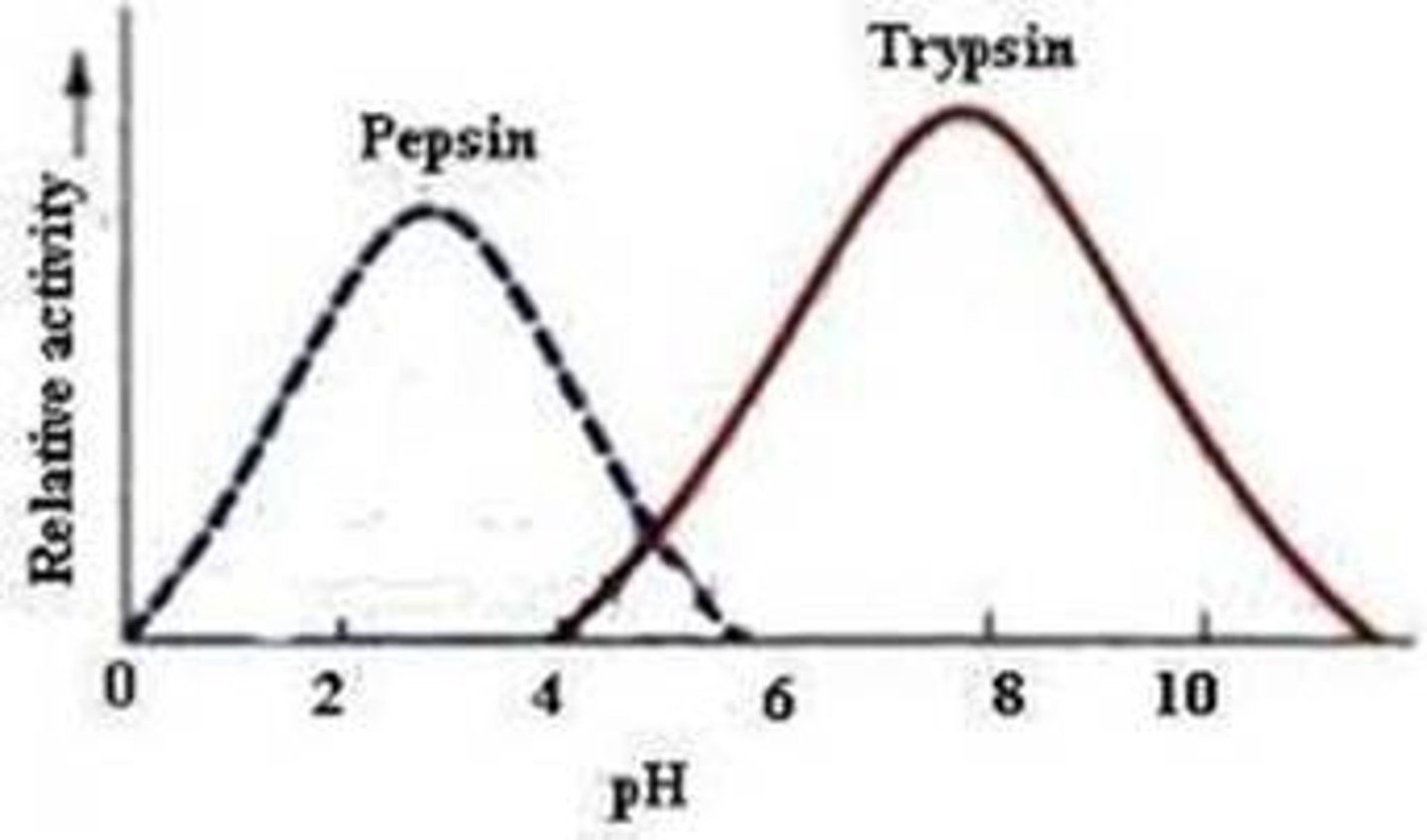
What happens to the pepsin enzyme in alkaline conditions
The enzyme will denature and no longer work.
The four organic compounds found in all living things are?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids.
Which best describes how the shape of an enzyme affects its function?
It determines the specific reaction it will catalyze.
What is the function of proteins?
Build skin, hair, nails, muscles.
What is the substrate?
The reactant that an enzyme acts on.
Most enzymes end in the following suffix:
Ase.
Which macromolecule is structured this way?
Lupid.
Nucleotides are the building blocks (monomers) of. . .
Nucleic Acids.
A student is preparing to run in a school track competition. For the quickest source of energy, the student should eat a food that contains a high percentage of?
Carbohydrates.
What happens to an enzyme when it is denatured?
It loses its shape.
What happens to an enzyme after it has completed a reaction?
The enzyme is reused.
The building blocks (monomers) or proteins are. . .
Amino Acids.
Match the biomolecule with the example:
Lupids.
Fats, oils, and waxes.
___________ are many monomers bonded together that form a larger molecule.
Polymers.
Why are nucleic acids important to humans?
Nucleic acids store heredity information.
Which function could best be substituted for an enzyme?
Speeds up chemical reactions.
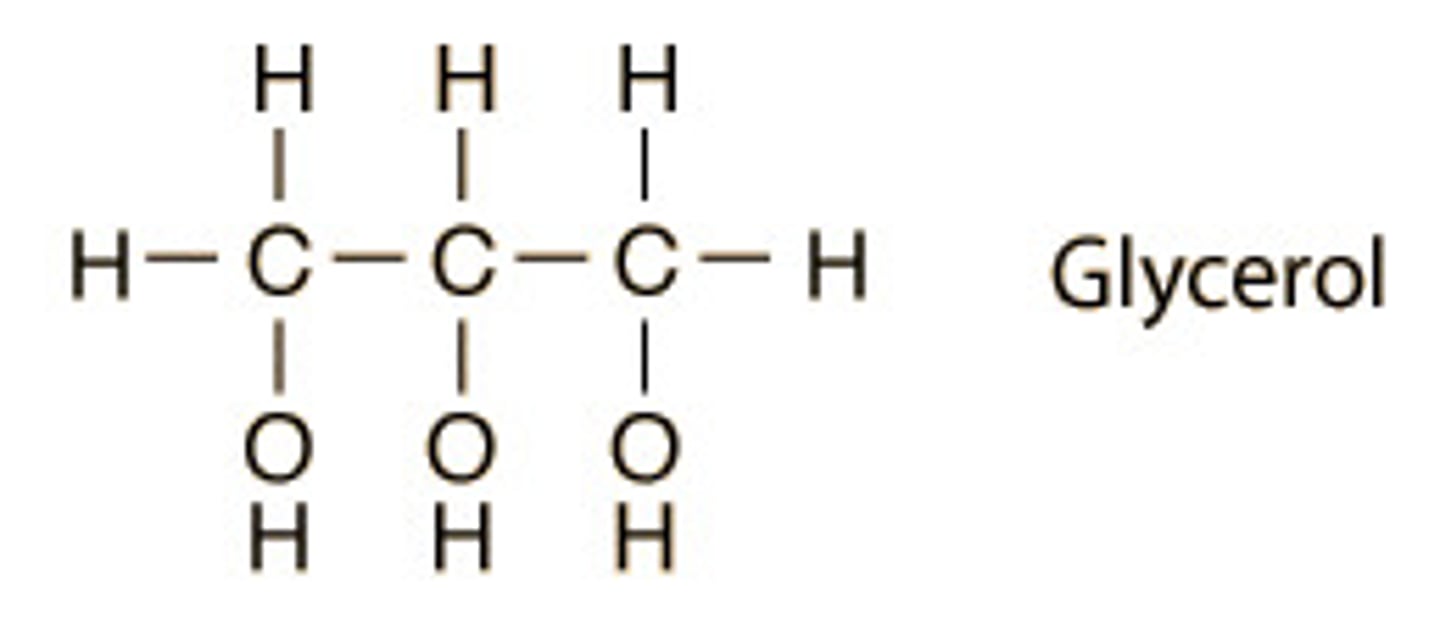
A lipid is made up of...?
1 glycerol, 3 fatty acids.
Sugars, starches and chitin are examples of. . .
Carbohydrates.
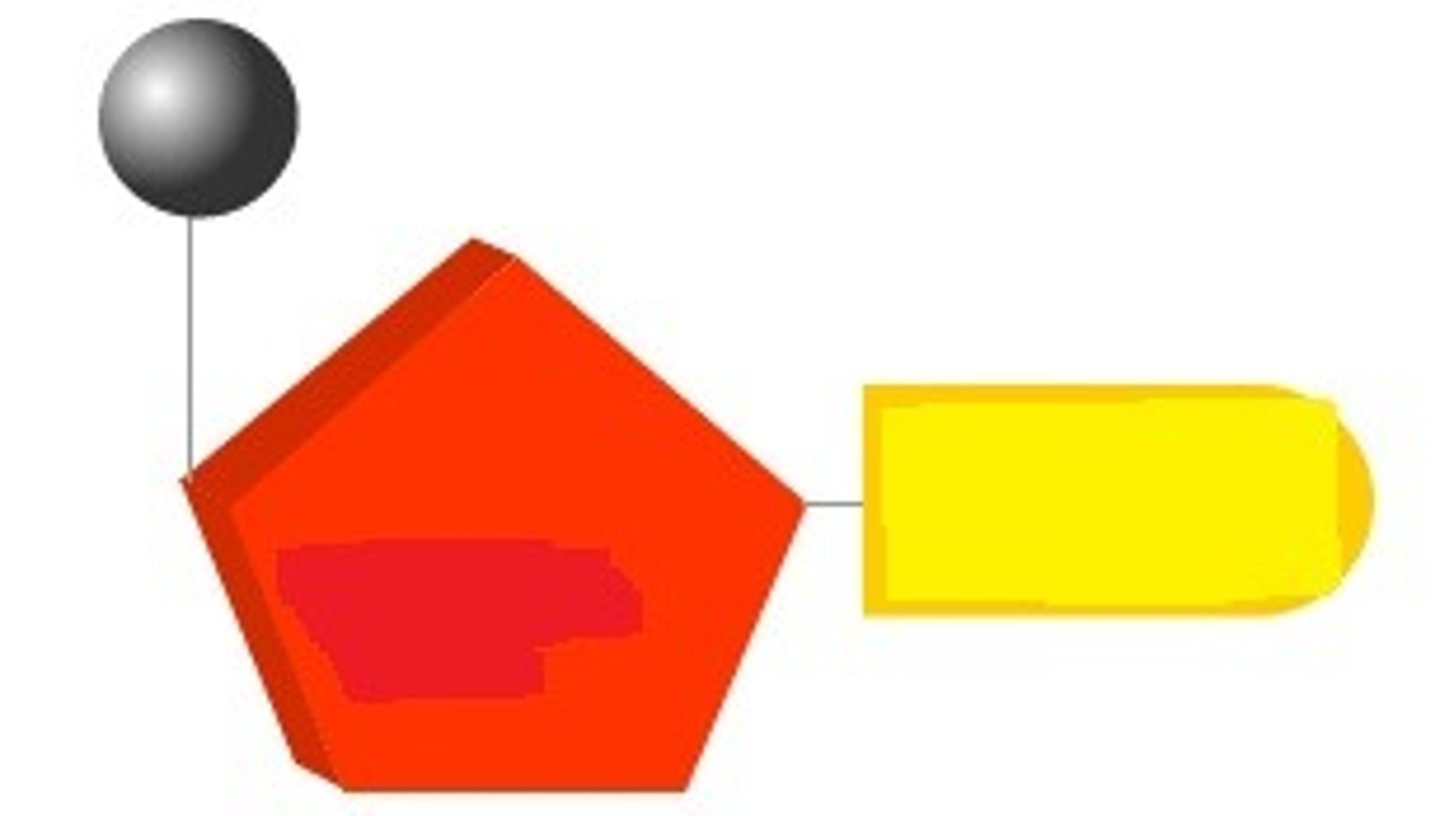
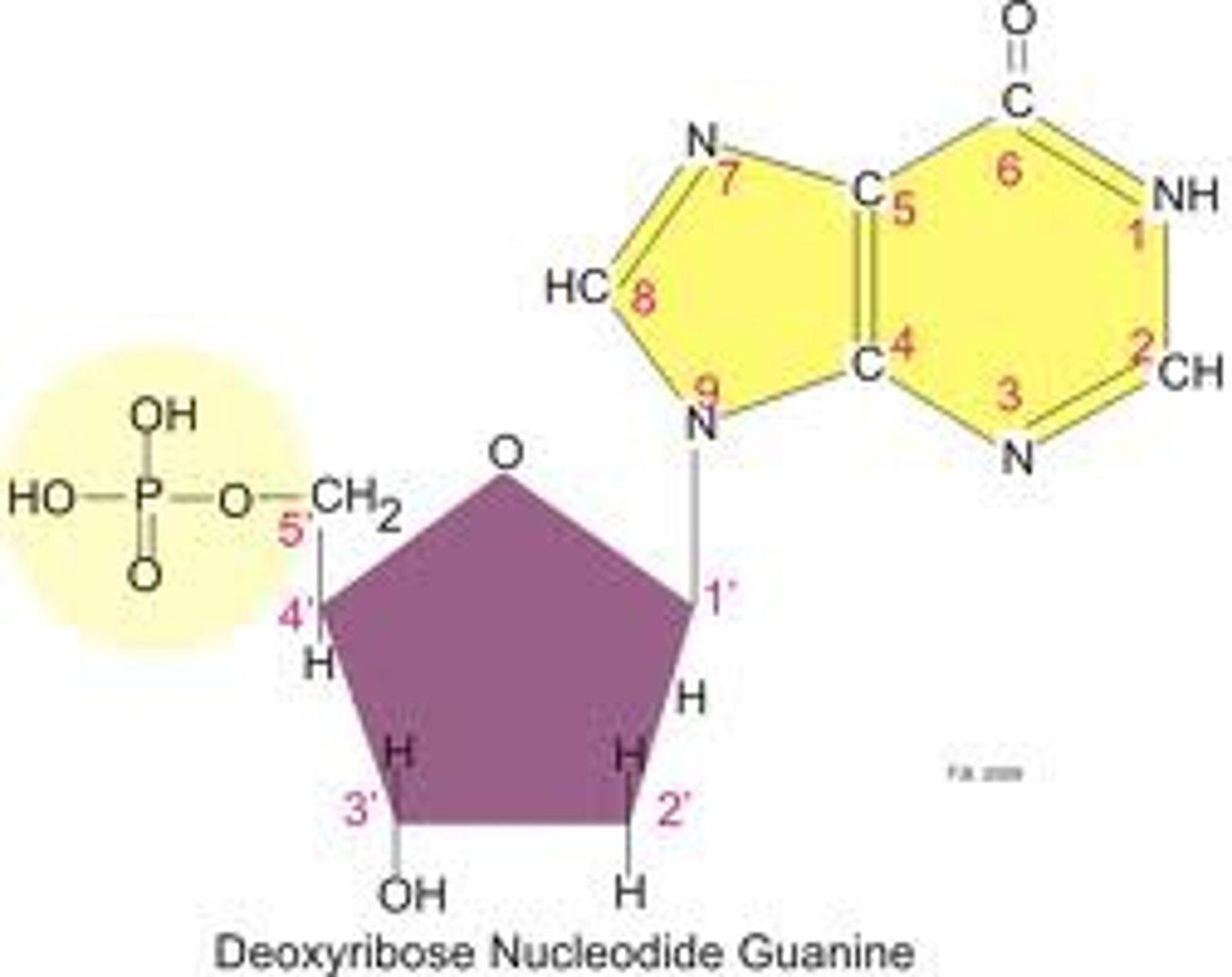
What are the parts of a nucleotide?
Circle - Phosphate.
Rectangle - Base.
Hexagon - Sugar.
A monomer of lupid is a. . .
Fatty Acid.
A monomer of Carb is a. . .
Monosaccharide.
A monomer of protein is a. . .
Amino Acid.
A monomer of nucleic Acid is a. . .
Nucleotide.
My building blocks are nucleotides.
Nucleic Acids.
Which is an example of a carbohydrate?
Cellulose.
Denature.
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
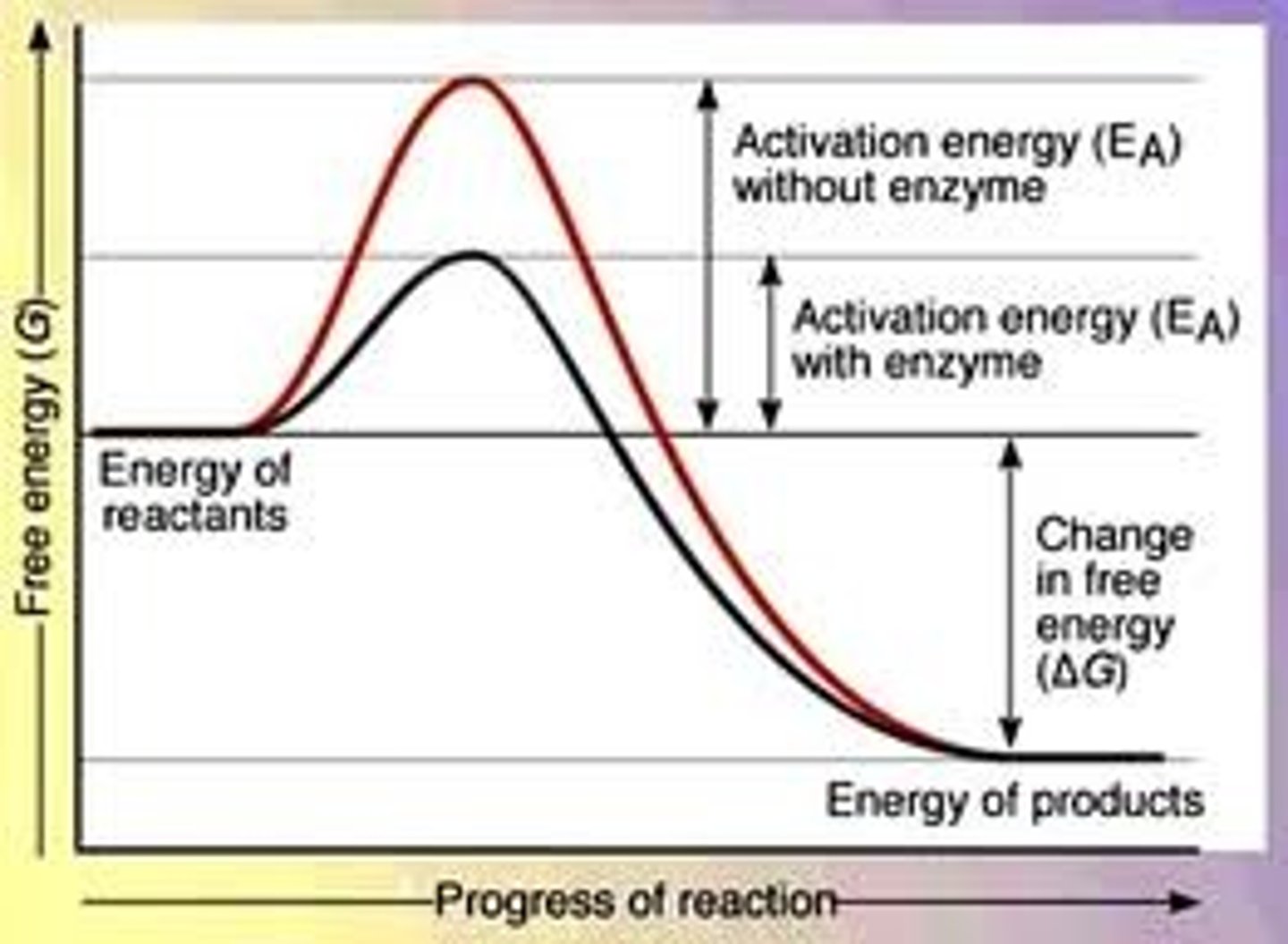
An enzyme speeds up a reaction by. . .
Lowering the activation energy.
An example of lupid is. . .
Phospholipid.
An example of carb is. . .
Glucose.
An example of protein is. . .
Lactase.
An example of nucleic acid is. . .
DNA.
Examples of nucleic acids are. . .
DNA and RNA.
Label the numbers.
a. Enzymes.
cde. Substrate
f. Products.
Letter f are. . .
Products.
What is the building block molecule of starch?
Simple Sugar.
This macromolecule has amino acids as building blocks.
Proteins.
If the effective temp ranges of enzymes are 20-27 degrees, what temperature would it most likely be denatured?
89 degrees; very big changes in temperature.
A lipid characteristic is that. . .
They don't mix with water.
A carb characteristic is that. . .
They are long, complex chains.
A protien characteristic is that. . .
They fold into shapes.
A nucleic ccid characteristic is that. . .
Their bases make a code.
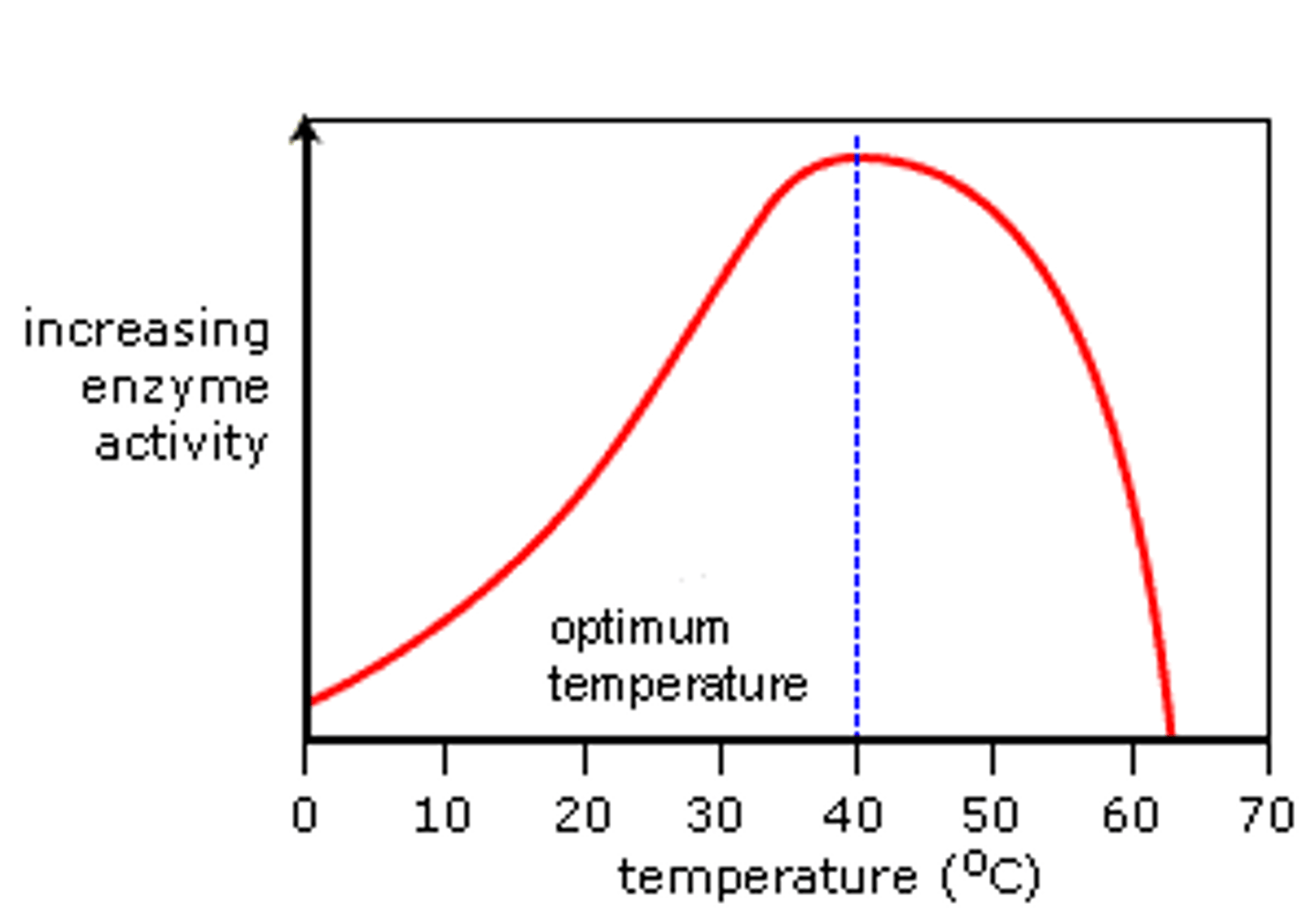
Based on the graph, what is the optimal temperature for this enzyme?
40 degrees.
What is a substance called if it speeds up a chemical reaction?
A catalyst.
What is the monomer for a protein called?
Amino acid.
How does the structure of nucleic acids differ from the structure of proteins?
Nucleic acids contain nucleotides, and proteins contain amino acids.
Substances that are changed during a chemical reaction.
Reactants.
Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?
APT.
Muscle cells need to convert energy from food molecules into a usable form quickly. For this reason, which of the following do muscle cells have in greater numbers than most other types of cells?
Mitochondria.
My building blocks are glycerol and fatty acids. What macromolecule am I?
Lupid.
What is the active site?
...
How does glycogen compare with starch?
Glycogen is carbohydrate storage in animals, while starch is
carbohydrate storage in plants.
Enzymes are an example of. . .
Protein.
Each enzyme only has 1 substrate that will fit its active site. What is this called?
Specific.
What is the function of carbohydrates?
Store energy (short-term).
What are the building blocks of carbohydrates?
Simple sugars (glucose).
An example of protein is. . .
Enzymes.
All carbohydrates are compounds that contain the elements. . .
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
What is an enzyme?
...
Which line represents an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
Line green.
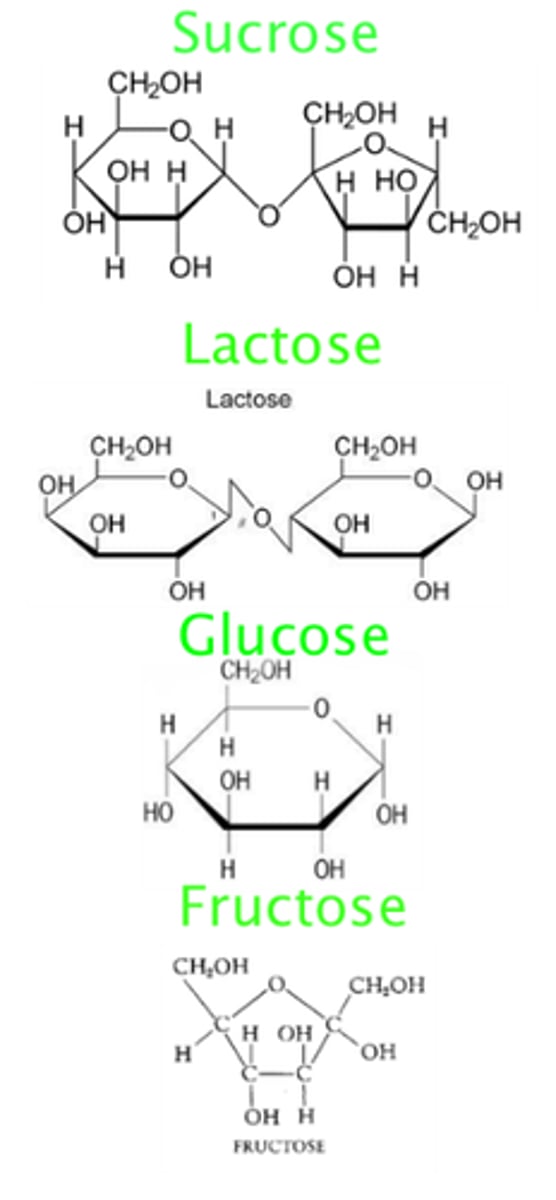
Lupid stores. . .
Long-term energy.
Carbs store. . .
Short-term energy.
Proteins controls. . .
Reactions.
Nucleic acids store. . .
Information.
Carb structure:
...
Lupid structure:
...
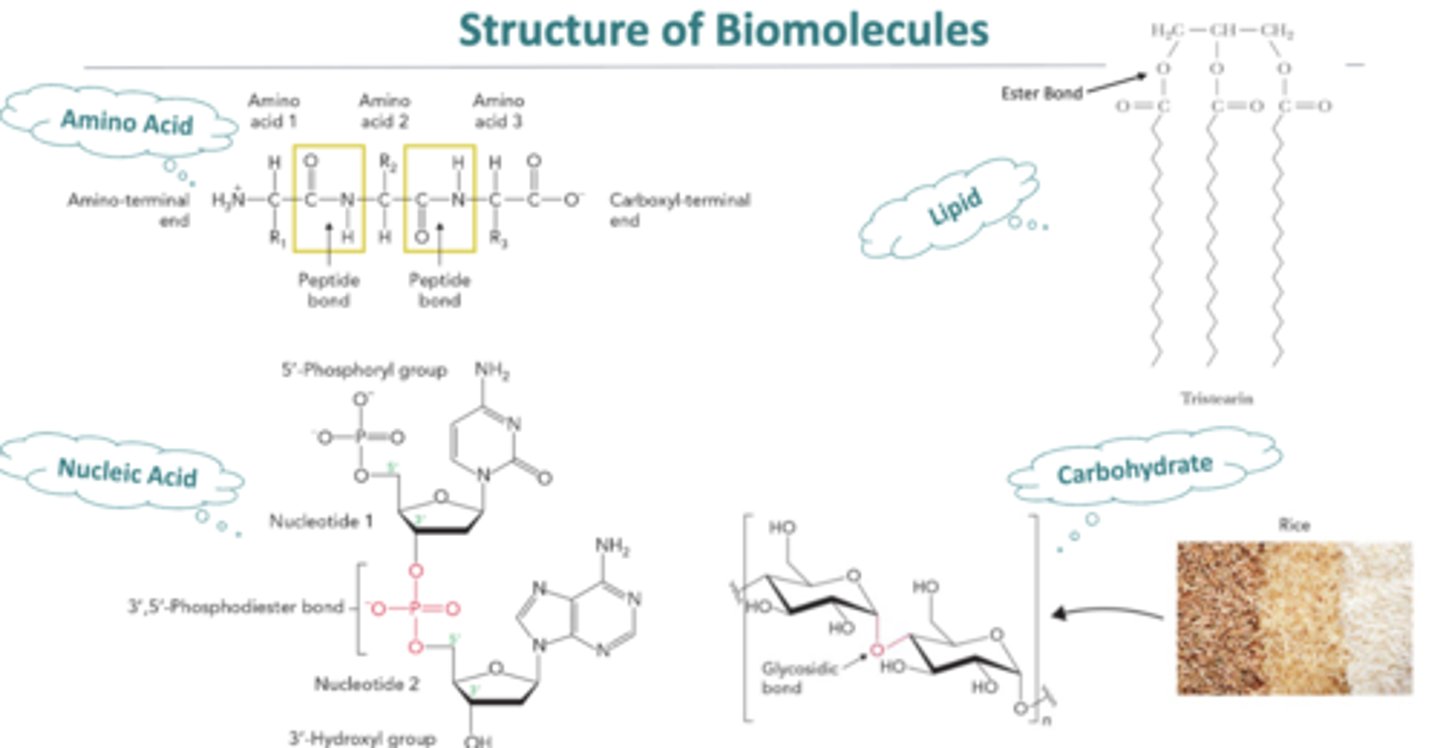
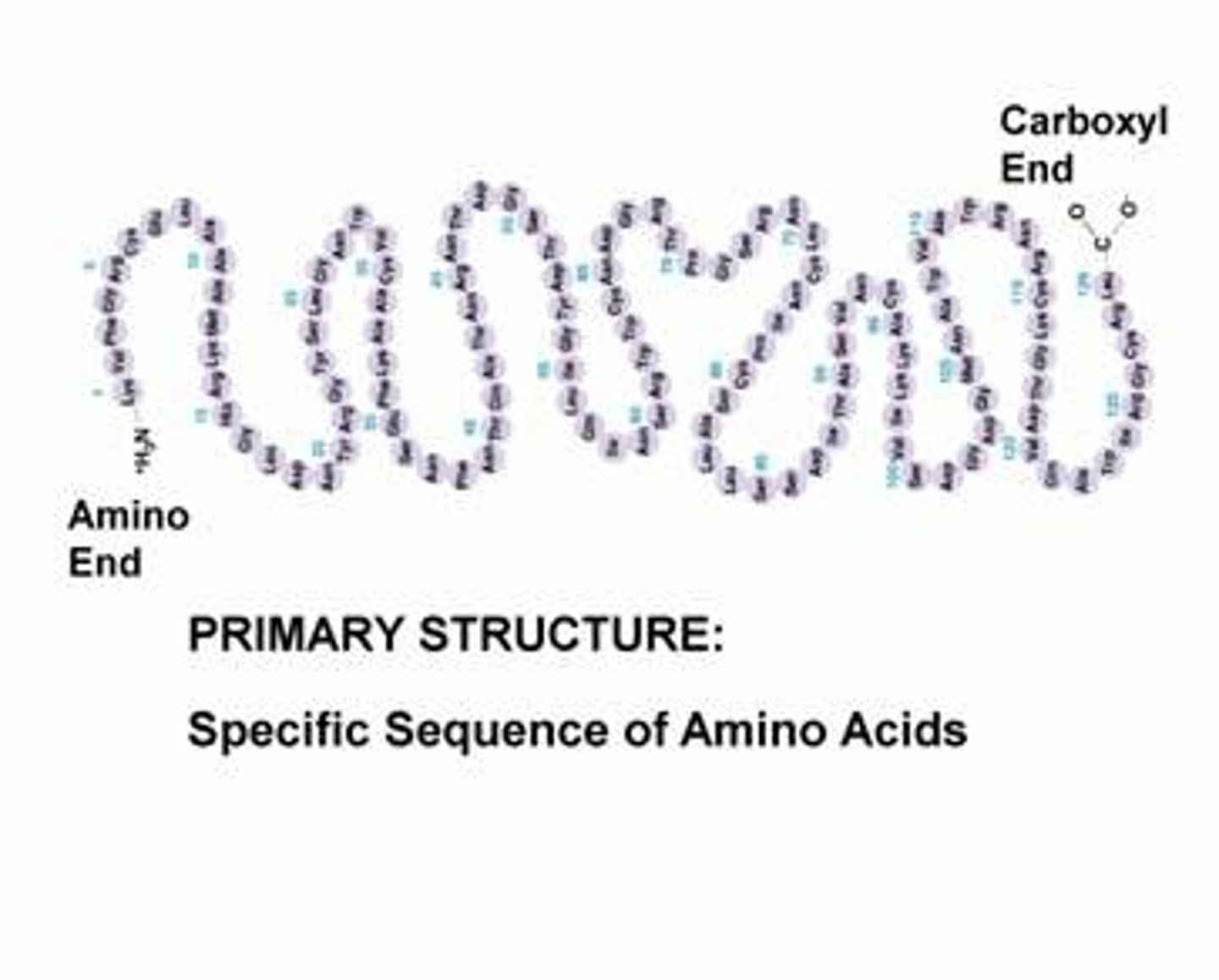
Protein structure:
...
Nucleic acid structure:
...
Which of the following is an inorganic molecule?
H2O
Which of the following can be used to determine the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
Rate of disappearance of the substrate
The basic unit of life is a. . .
Cell.
Which compound is a polysaccharide?
Starch.
In which organic molecules is nitrogen a component?
Protein and nucleic acid.
The diagram shows a reaction that forms a polymer from two monomers. What is this type of reaction called?
Dehydration synthesis.
DNA is a polymer consisting of repeating units known as. . .
Nucleotides.
What happens when enzymes are heated to a high temperature?
The shape of the enzyme are changed and it denatures.
Which elements are found in all organic molecules?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Glucose is a building block of carbohydrates. Which of these best describes glucose?
Monosaccharide.
Another word for a building block is a. . .
Monomer.
How are monosaccharides and polysaccharides different?
Polysaccharides are made up of two or more monosaccharides bonded together.
Examples of a carbohydrate.
Glucose.
What is cellulose used by. . . to?
Used by plants to build their structures (stems, trunks, etc).
What is starch used by. . . to?
Used by plants for their short term energy storage.
What is protein used by. . . to?
Used by animals to build their structures
What is glycogen used by. . . to?
Used by animals for their short term energy storage.
What is glucose used by. . .to?
Used by plants and animals to recharge their ATP energy carrier molecule.
What is an active site?
...