W11- Mutations
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is a mutation?
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a genome
List the two types of mutations
Small-scale mutations
Large-scale mutations
How is mutation determined to be either harmful, beneficial, or neutral?
It is determined by the environmental conditions present at the time
List the two ways mutations can arise.
Spontaneous mutations
Induced mutations
How can spontaneous mutation arise?
Arise occasionally in all cells in the absence of any added agent
How can spontaneous mutation be caused?
Errors during DNA replication
How can Induced mutations arise?
Arise due to exposure to a mutagen
Define mutagen
It is either a physical or chemical agent that interacts with DNA to cause a mutation
Give an example of physical mutagen agent
UV radiation
Can induce mutations by damaging the bases in DNA. Causes incorrect base pairing during replication
Give an example of a chemical mutagen agent
Ethidium bromide which acts by inserting itself between the stacked bases of the helix. Causing a single nucleotide insertion or deletion
List two types of small-scale mutations
Nucleotide-pair substitutions
Insertions and deletions
Describe nucleotide-pair substituition
It is the replacement of one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides.
List the types of nucleotide-pair substituition
Silent mutation
Missense mutation
nonsense mutation
Describe what a silent mutation is.
Occurs when a nucleotide is changed in the DNA, but it does not cause a change in the amino acid that will be added to the polypeptide.
Describe what missense mutation is.
A type of nucleotide-pair substitution which a change in the nucleotide sequence DOES change the amino acid sequence of polypeptide.
Is there a way missense mutation may not be harmful, despite changing the amino acid of the polypeptide?
Yes, if the mutation changes an amino acid in the polypeptide that is not essential for function, then it might not have any effect.
Also, if the mutation is replaced with another amino acid that had similar properties there may also not be much a difference in terms of protein.
Describe Nonsense mutation
A type of nucleotide-pair substitution mutation that results in the formation of a stop codon. This results in a premature termination of a polypeptide chain, which usually results in a non-functional protein.
Describe Insertions and Deletions
A type of small-scale mutation which occurs when one or two base pairs are added or deleted to a coding region of a gene.
What results in a shift in the reading frame?
Addition or deletion of fewer than three nucleotides
Define Frameshift mutation
A type of Insertion or deletion smale-scale mutation……….
What is a large-scale mutation?
A type of mutation where chromosomal rearrangements affect long segment of DNA
What may cause Large-scale mutation?
Errors that occur during meiosis
Exposure of DNA to damaging agents
What can large-scale mutations cause?
A change in the chromosome structure
OR
A change in the chromosome number
List the 4 types of changes in chromosome structure can occur.
Deletion
Duplications
Inversions
Translocations
Describe Deletion of a Large-scale mutation
Occurs when a chromosomal fragment is lost, resulting in missing genes.

Describe Duplication of large-scale mutation
A chromosomal fragment that may arise following breakage of chromosome. May join to a sister or nonsister chromatid of homologous pair
UNDERSRAND THIS and ADD PIC FROM SLIDE 47

During which stage does deletions and duplications arise?
During BLANK, when unequal-sized DNA segment are sometimes exchanged, lading to one chromosome with a deletion and one with a duplication
Describe Insertions of a large-scale mutation
A chromosomal fragment after breakage may reattach to the original chromosome, but in the reverse direction
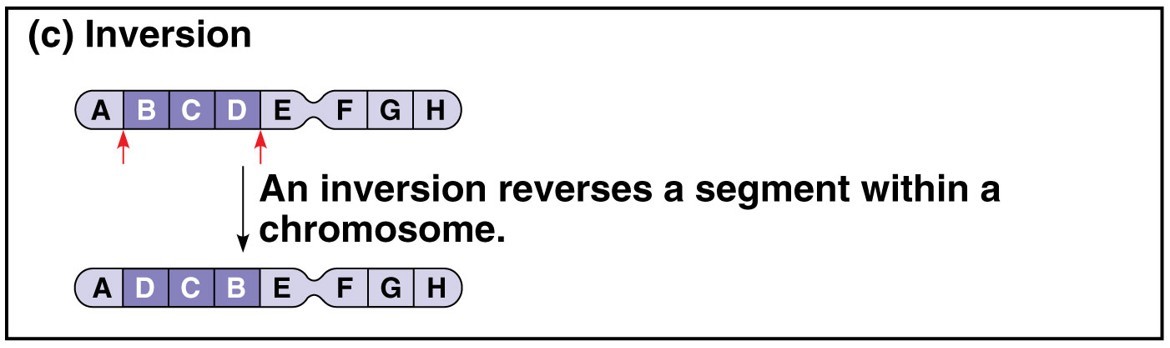
Describe Translocation of the large-scale mutation
The chromosome fragment after breakage may join a nonhomologous chromosome
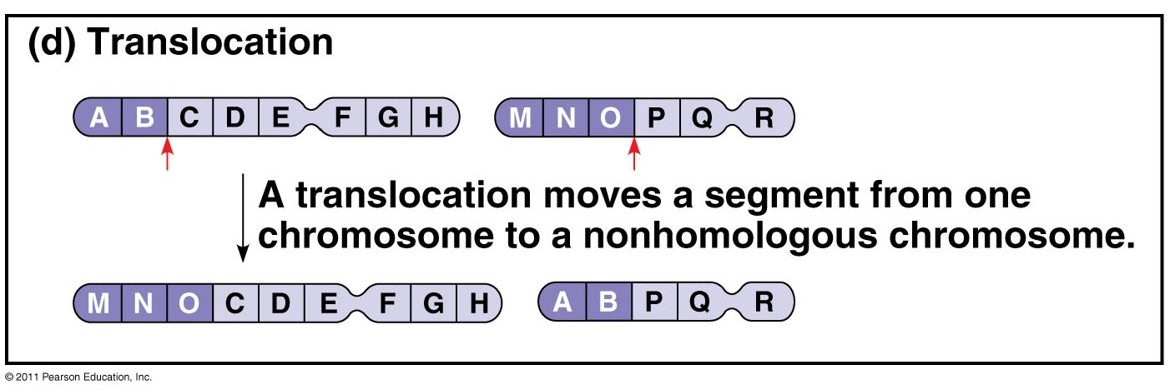
What are the consequences of Chromosomal rearrangements? Are they harmful or not?
All are generally harmful. Large deletions are ordinarily lethal
Describe a change in the chromosome number of the large-scale mutations
May arise due to a mistake during meiosis called non-disjunction
What is non-disjunction?
Failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis(either in I or II)
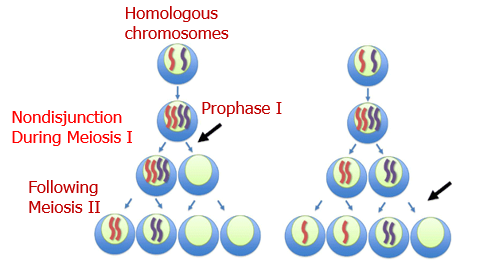
Describe the result at the end of each gametes on the left
Two gametes have an extra copy of the chromosome
Two gametes do not have a copy of the chromosome
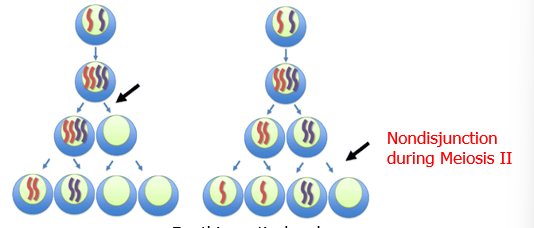
Describe the result at the end of each gametes on the right
One gamete has an extra copy of the chromosome
One gamete does not have a copy of the chromosome
Two normal gametes
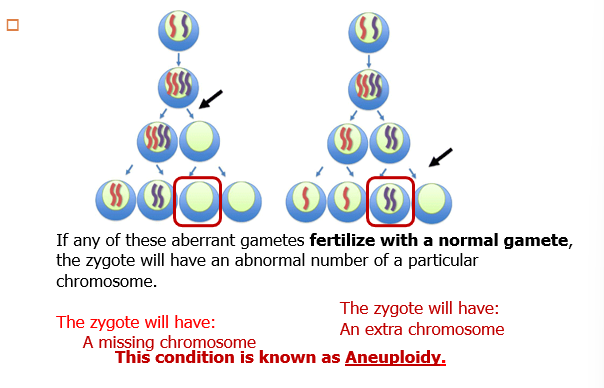
UNDERSTAND THIS
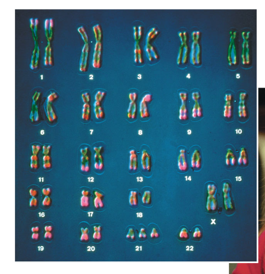
What is an example of aneuploid condition?
Down syndrome results from the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21
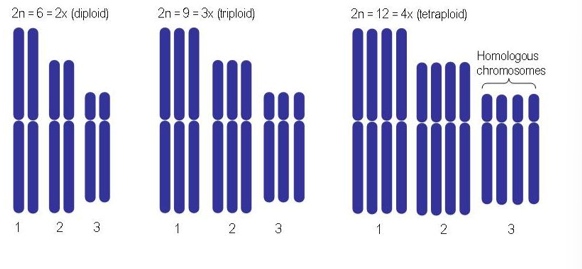
What is polyploidy?
When organisms have more than two complete chromosomal sets.