ionic compounds, covalent bonding & simple molecular substances
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
structure of ionic compound
giant ionic lattice
What is a giant ionic lattice
positive ion is surrounded by negative ion
what is a regular lattice structure
very strong electrostatic forces of attraction between opposite charge ions in all direction
what is sodium chloride
salt, has one giant ionic lattice, na+ and cl- ions held together in a regular lattice
properties of ionic compounds
high melt and boil points cus strong bonds between ions, when solid they cant conduct, when melted ions move free and carry charge, some dissolve in water
formula of ionic compound if given dot and cross diagram
count how many atoms of each element
formula for ionic compound if given 3d diagram of ionic lattice
work out what ions are in compound, balance charges of ions so overall charge of compound is 0
covalent bonds
share electrons
what happens when non metal atoms bond together
share pairs of different electron make covalent bonds, positive nuclei bond to atoms to share a pair of electrons, electrostatic forces, strong bond
different ways of drawing covalent bonds
dot and cross diagram, formula, 3D model
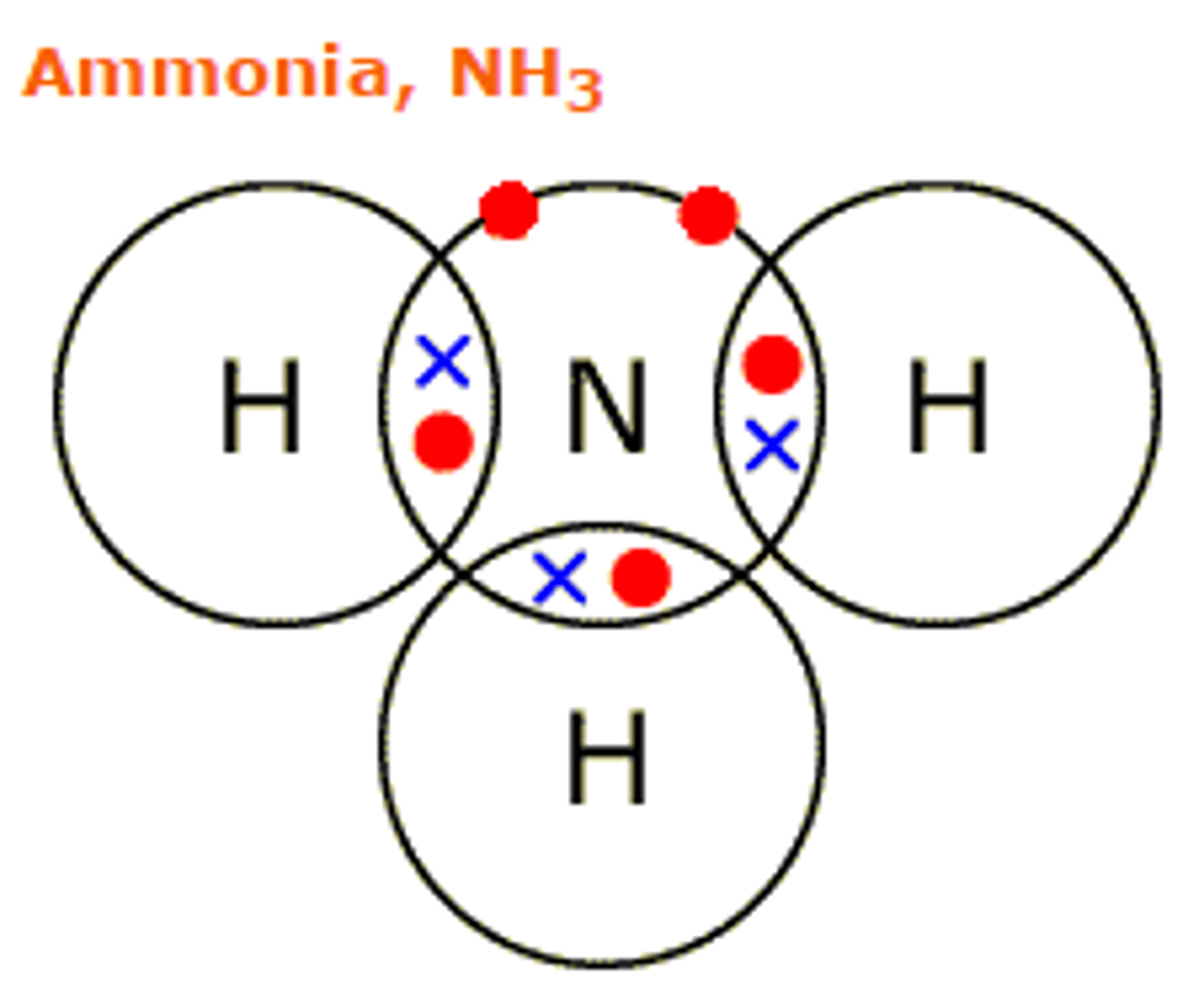
Dot and cross diagram
electrons drawn in overlap between outer shells of two atoms are shared between those atoms
formula
shows bonds as lines between atoms
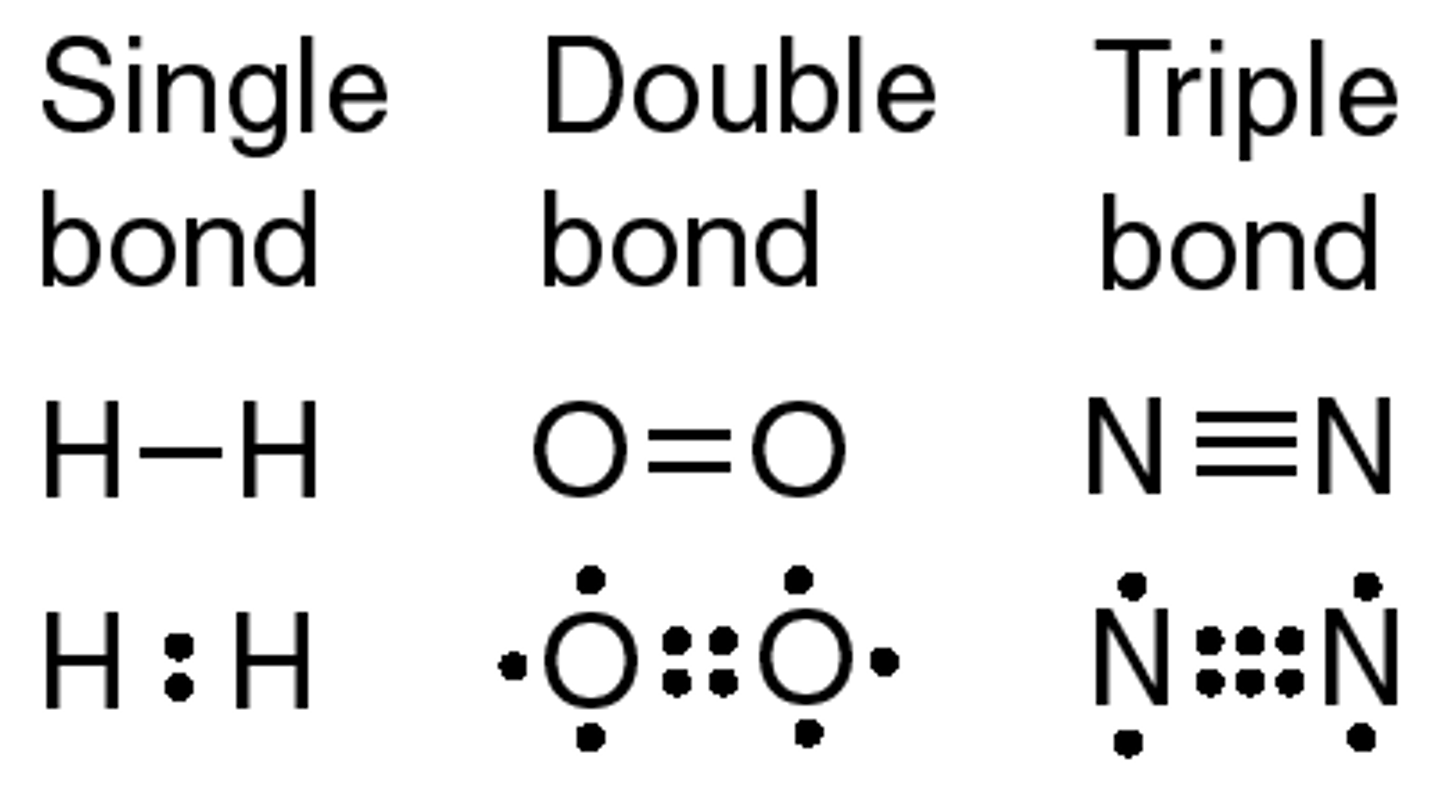
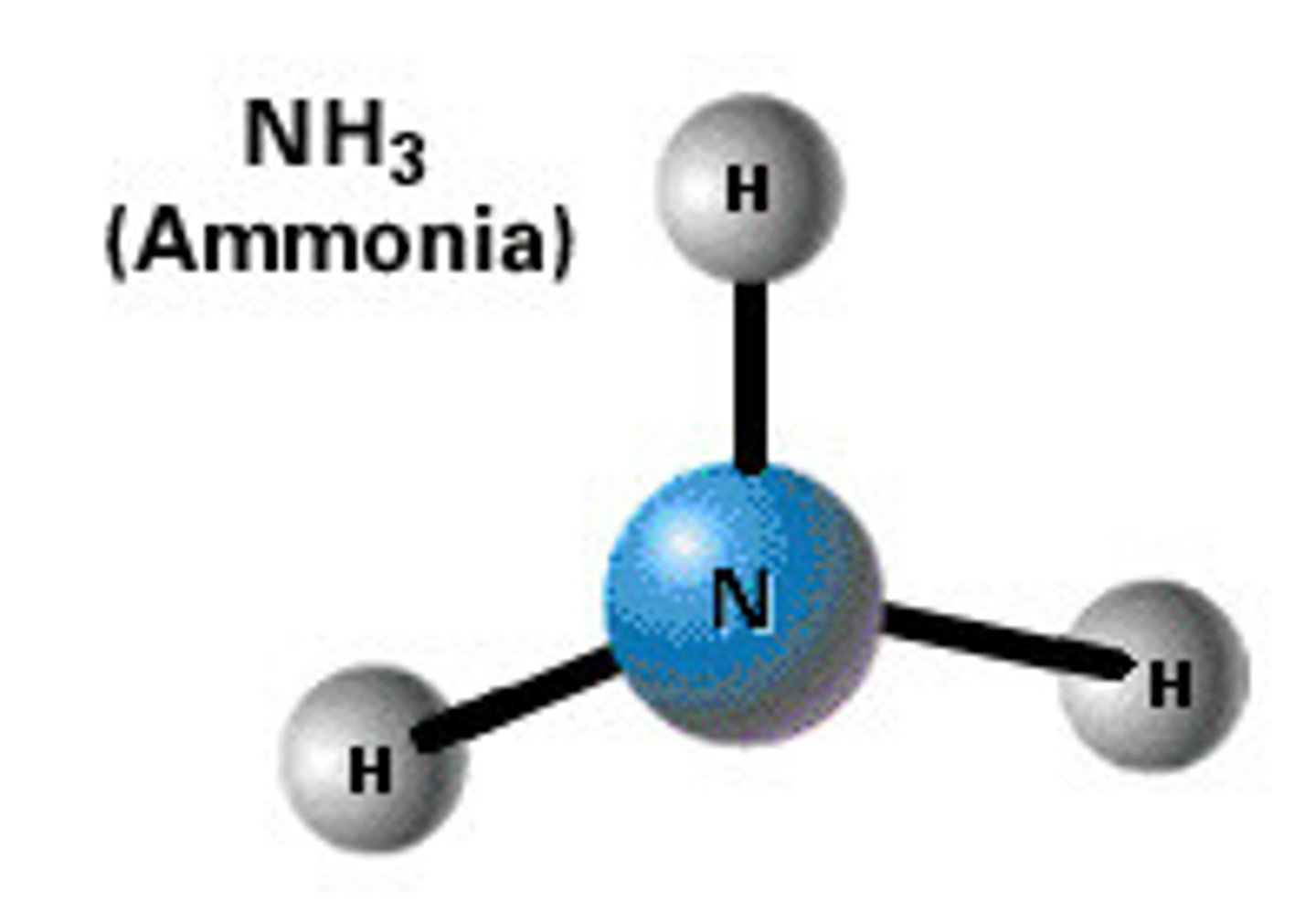
3d model
scaled representation of covalent bonds
examples of simple molecular substances
hydrogen, chlorine, hydrogen chloride, methane, ammonia, water, nitrogen, oxygen
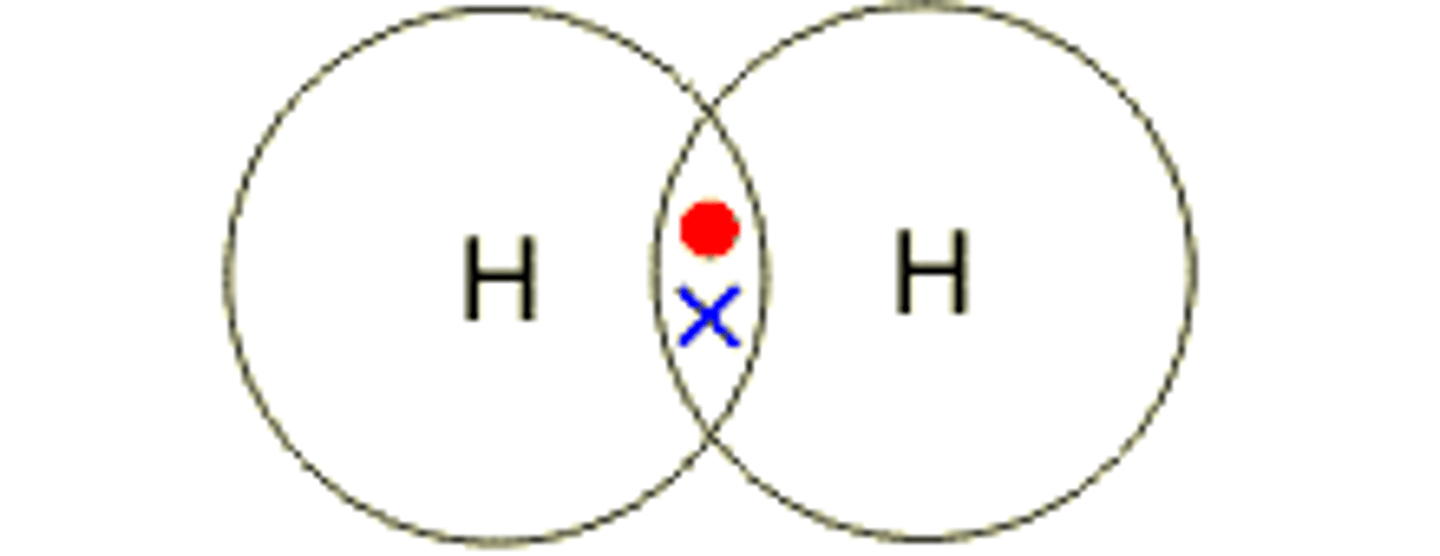
hydrogen- H2
atom has 1 electron, needs 1 more to complete shell, forms covalent bond with other hydrogen atom or elements
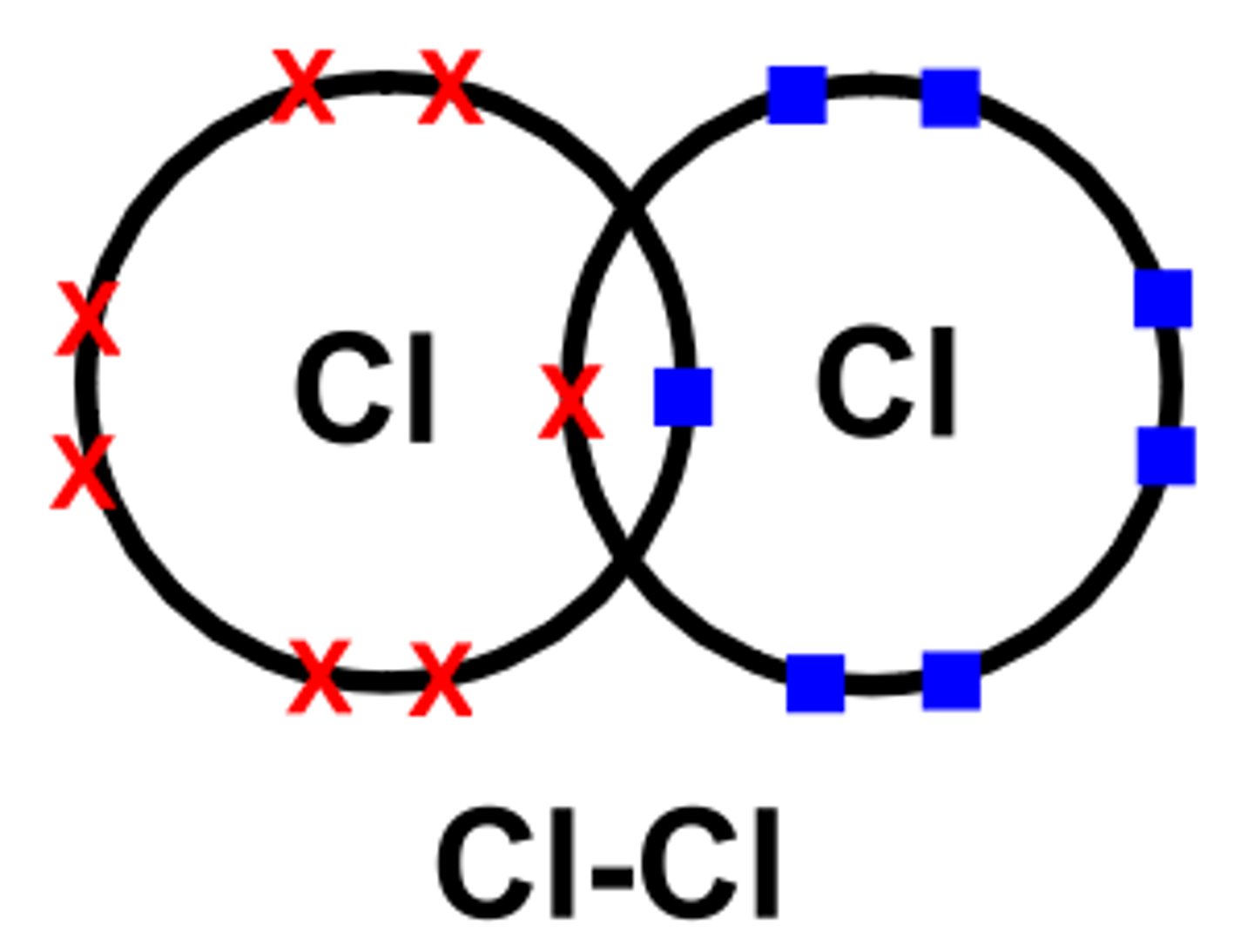
chlorine- Cl2
2 chlorine atoms share pair of electron and form a single covalent bond
oxygen- O2
needs 2 more electrons, oxygen atoms share 2 pairs of electron, makes double covalent bond
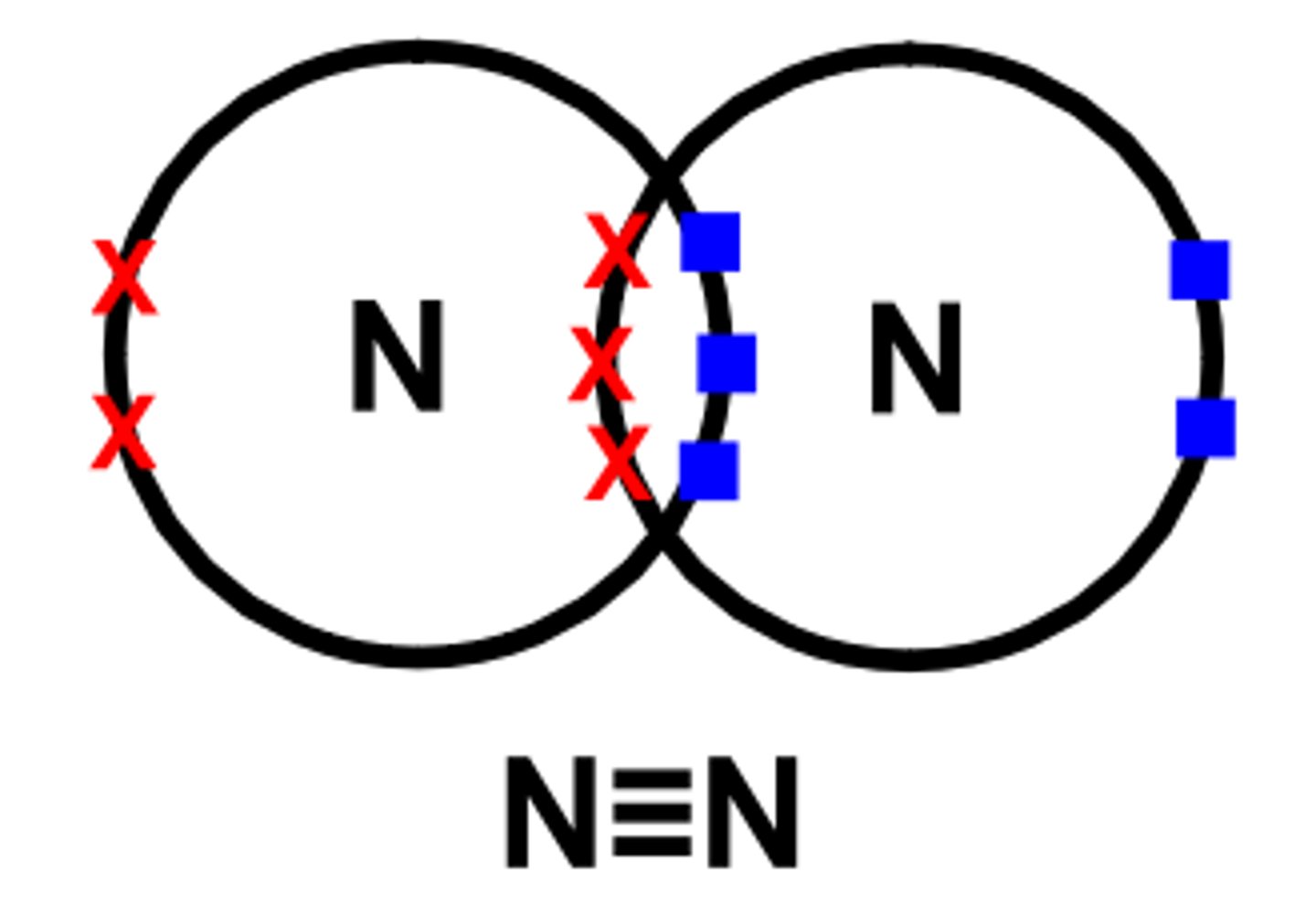
nitrogen- N2
needs 3 more electrons, 2 nitrogen atoms share 3 pairs of electron, makes triple bond
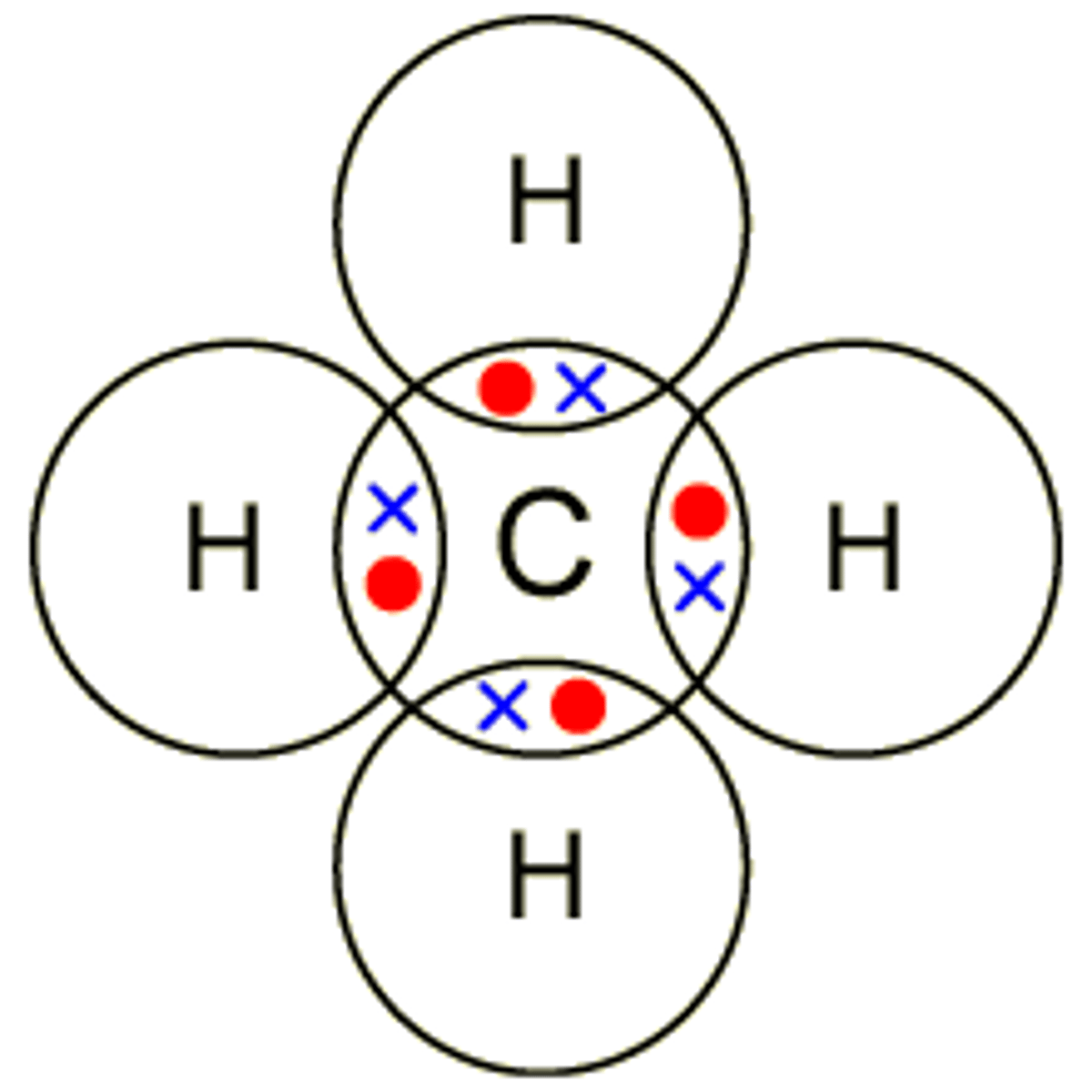
methane- CH4
carbon has 4 outer electrons, forms 4 covalent bonds with hydrogen
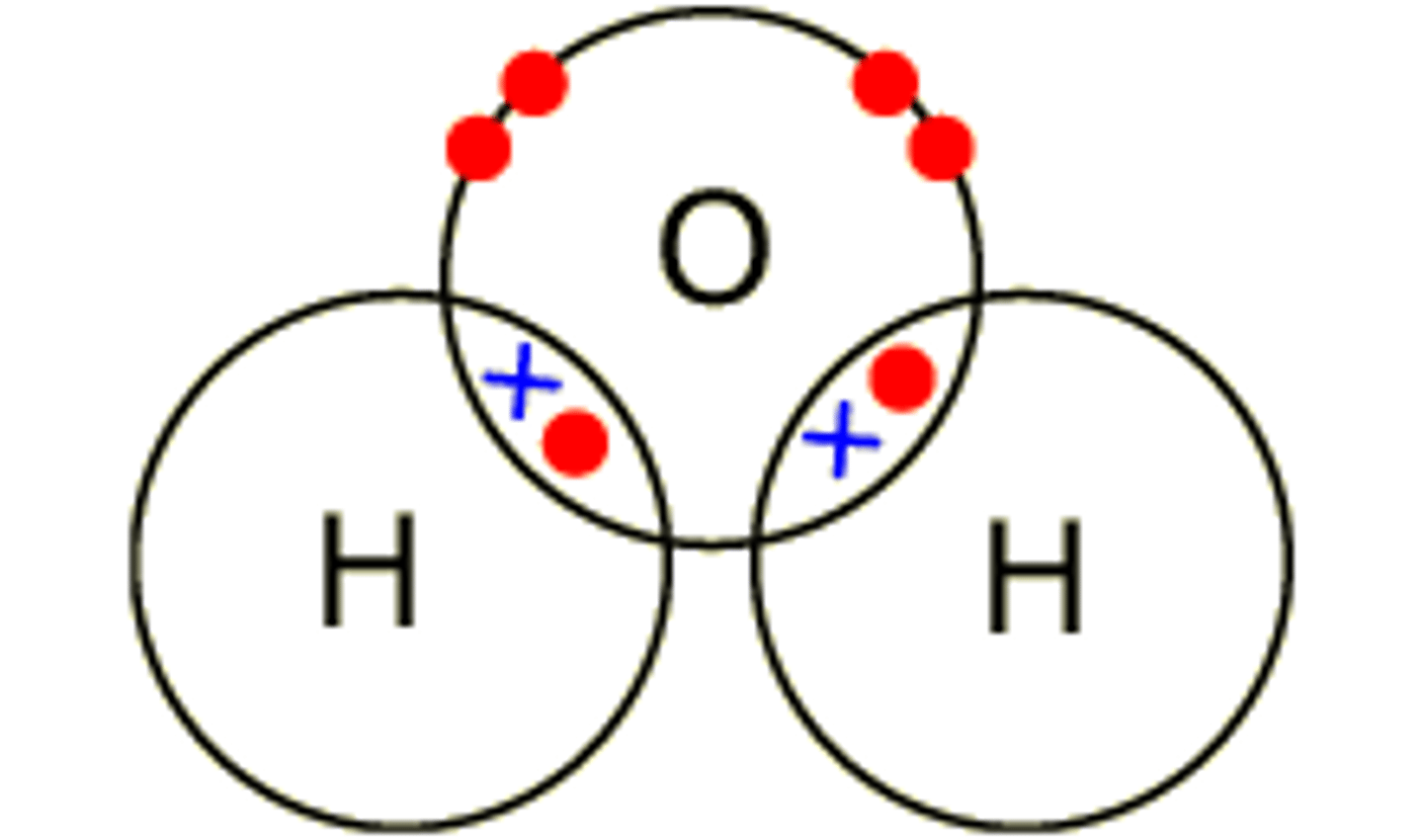
water- H2O
oxygen shares a pair of electron with 2 hydrogen atom, forms 2 single covalent bond
hydrogen chloride- HCl
both atoms need 1 more electron to complete outer shell
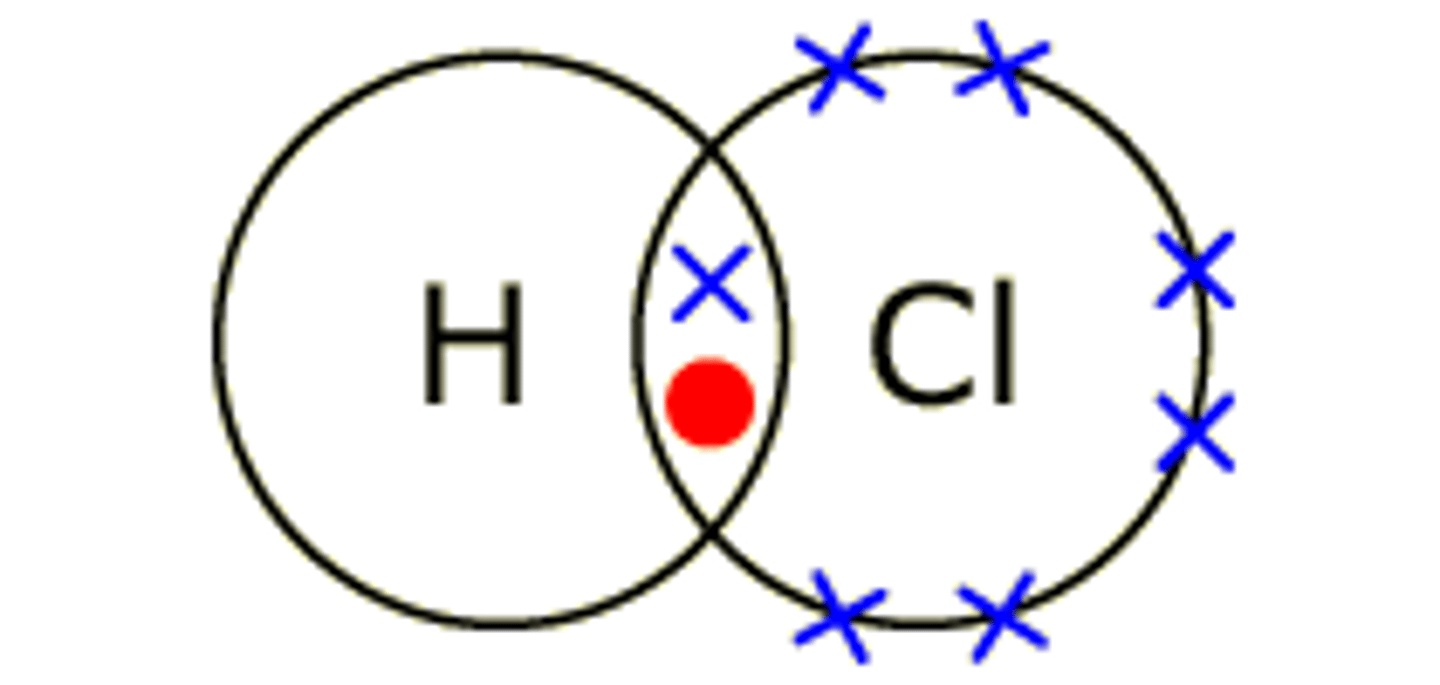
what are atoms within molecules held by
very strong covalent bonds means forces of attraction between molecules is weak
what do you need to do to melt or boil simple molecular compounds
break feeble intermolecular forces and not bonds
at room temp what state are molecular forces
liquid or gas
what happens when molecules get bigger
strength of intermolecular forces increases, so more energy need to break them, melt and boil point increases
why cant molecular compounds conduct electricity
not charged, no free electrons or ions