BIMM 120 WEEK ONE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
What are the three domains of life? What type of cell are the organisms in each domain made up of?
Eukarya, bacteria, archea. Eukarya are made of eukaryotic cells and bacteria and archaea are made of prokaryotic cells.
2
New cards
Name one reason why microbes are important ecologically.
\
Microbes produce oxygen, they are decomposers, they provide nutrients to plants, and they’re also important as pathogens.
Microbes produce oxygen, they are decomposers, they provide nutrients to plants, and they’re also important as pathogens.
3
New cards
How are mycorrhizae important for plant growth?
They facilitate uptake of minerals and water from the soil, they seek out tiny pockets of phosphate in the soil and increase the surface area of the plant root.
4
New cards
If we want to visualize a living microbe under the microscope, what type of mount would we use?
Wet mount
5
New cards
This picture likely came from which type of microscope?
\
\
TEM
6
New cards
What is the main reason we stain cells? How does the stain bind to the cell?
To see them better, otherwise they are clear. Stains are positively charged, allowing them to bind to negatively charged cell components.
7
New cards
What is culture media made of? Who invented it?
Agar, nutrients, (and water). Angelina Fannie Hess.
8
New cards
What is a microbial colony on a culture plate?
One cell that landed on the culture media and divided hundreds of times to become a clump of visible cells.
9
New cards
Describe why spontaneous generation is not true.
\
Microbes do not spontaneously pop into existence and cause food to spoil. Rather, they float down from the air and land on food.
Microbes do not spontaneously pop into existence and cause food to spoil. Rather, they float down from the air and land on food.
10
New cards
What is the main point of germ theory? What are Koch’s postulates?
Specific microbes cause specific diseases. Postulates: 1) The suspicious microbe is found only in the diseased organisms, 2) the microbe is cultured from the diseased organism, 3) the culture is injected into a healthy organism that then develops disease symptoms, 4) the same microbe is cultured from the diseased organism.
11
New cards
The cell membrane is a __________ bilayer. Make a simple drawing of a cell membrane.
Phospholipid
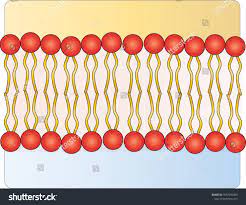
12
New cards
Draw the word you filled in above and label its main parts.
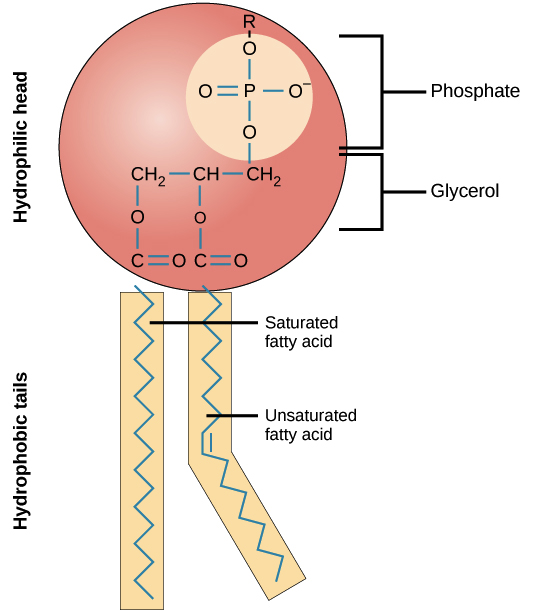
13
New cards
How are active and passive transport different?
In passive transport solutes move from a high to a low concentration of themselves, so no energy is needed because the solute naturally wants to diffuse to a low concentration area. In active transport solutes move from a low to a high concentration of themselves, so energy is required.
14
New cards
The bacterial cell wall is made up of _________________.
Peptidoglycan.
15
New cards
How are gram negative and gram positive cells structurally different?
Gram negative: have an outer membrane and have a thin cell wall. Gram positive: don’t have an outer membrane and have a thick cell wall.
16
New cards
Why do gram negative and gram positive cells stain the way they do?
Cells with thick walls appear purple and are called “gram positive” because their wall readily absorbs the purple dye like a sponge. Cells with thin walls and an outer membrane appear pink and are called “gram negative”. This is because the alcohol wash stage dissolves the outer cell membrane, causing the purple dye to leak out of the thinner peptidoglycan wall. These cells need to be counterstained with pink dye, so they appear pink.
17
New cards
How are inclusions and gas vesicles different?
Inclusions are for storing extra compounds like carbon, sulfur, etc. while vesicles are little bubbles of air meant to keep the cell buoyant.
18
New cards
What do bacterial cells use to form a biofilm? What is one impact of biofilms?
Slime layer, capsid, pili, and/or fimbriae. They can form on internal organs and be lethal.
19
New cards
Why do cells form endospores?
If bacteria find themselves in unfavorable conditions, they form an endospore to survive heat, chemicals, or radiation.