Chapter 27: Male and Female Reproductive Systems
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What are the primary components of the male reproductive system?
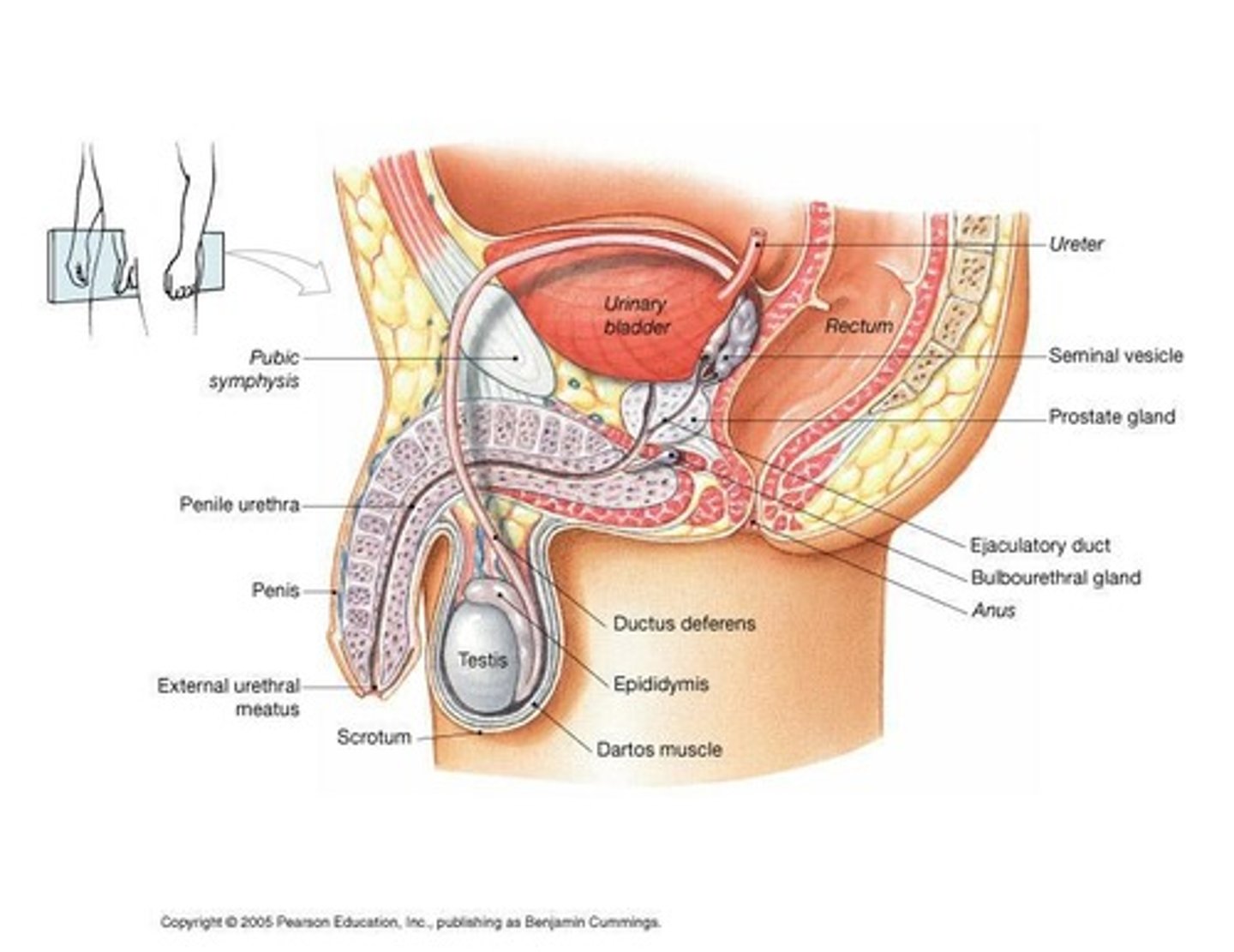
Scrotum, Testis, Male sex ducts, Male sex glands, Penis.
What are the primary components of the female reproductive system?
Ovary, Female sex ducts, Uterine tube, Uterus, Vagina.
What is the primary function of the gonads in the reproductive system?
They produce sex cells (gametes) and secrete sex hormones.
What are the secondary sex organs in the male reproductive system?
Sex ducts (Epididymis, Vas Deferens, Ejaculatory Ducts, Urethra) and Accessory Sex Glands (Seminal Vesicles, Prostate, Bulbourethral Glands).
What is the role of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
The scrotum supports the testes and regulates their temperature, which is essential for sperm production.
What condition is characterized by the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum?
Cryptorchidism.
What are the two types of cells found in the seminiferous tubules of the testis?
Spermatocytes (which produce sperm) and Interstitial (Leydig) cells (which secrete testosterone).
What is spermatogenesis?
The process by which the seminiferous tubules of the testes produce sperm through meiosis.
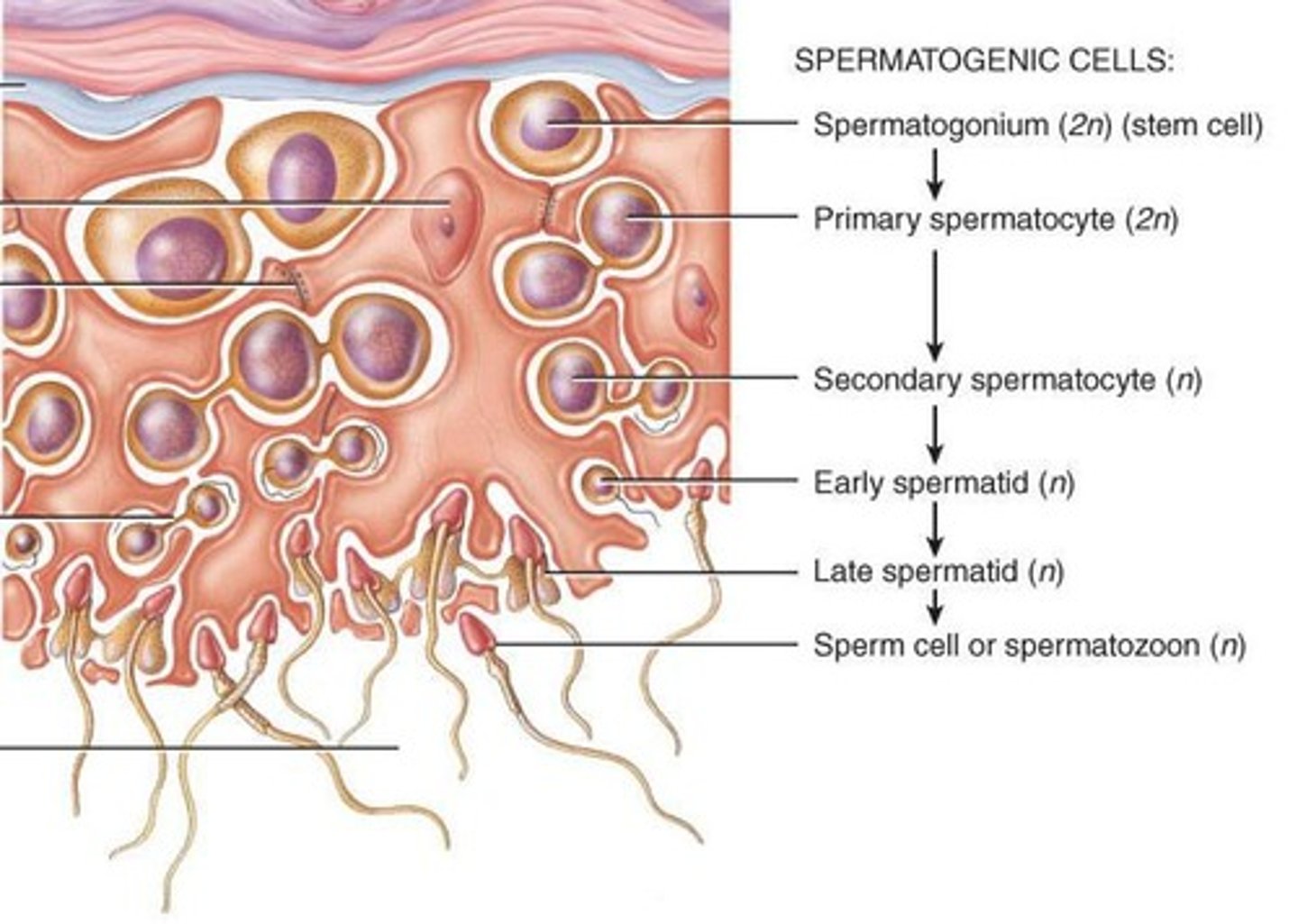
Describe the process of spermatogenesis starting from spermatogonia.
Spermatogonia undergo mitosis to reserve stem cells and form primary spermatocytes, which then undergo meiosis I to form secondary spermatocytes, followed by meiosis II to form spermatids that mature into sperm.
What is the significance of the scrotal temperature being lower than body temperature?
It is essential for optimal sperm production.
What are the two layers of the endometrium in the female reproductive system?
The functional layer and the basal layer.
What changes occur in the ovary and uterus during the female reproductive cycles?
The ovary undergoes changes in hormone levels and follicle development, while the uterus prepares for potential implantation of a fertilized egg and sheds its lining if fertilization does not occur.
What is the function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
The ovaries produce eggs (ova) and secrete hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
What structures are involved in the male external genitalia?
Scrotum and Penis.
What is the role of the accessory sex glands in the male reproductive system?
They produce secretions that nourish and transport sperm.
What is the anatomical structure that divides the scrotum into two sacs?
A vertical septum.
What is the process of maturation in spermatogenesis?
Spermatids mature into sperm after undergoing morphological changes.
What is the primary sex organ in the male reproductive system?
The testes.
What is the pathway of sperm from the testes to the outside of the body?
Testes → Epididymis → Vas Deferens → Ejaculatory Duct → Urethra.
What is the primary male sex hormone secreted by the interstitial cells?
Testosterone.
What are the functions of the uterine tubes in the female reproductive system?
They transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and are the site of fertilization.
What is the structure of the penis and its role in the male reproductive system?
The penis is the external organ used for sexual intercourse and urination, facilitating the delivery of sperm.
What is spermiogenesis?
The maturation of spermatids into sperm cells, where spermatids lose excess cytoplasm and form a flagellum and many mitochondria.
What are the main components of sperm morphology?
The head contains the nucleus and acrosome, the midpiece contains mitochondria, and the tail is a flagellum used for movement.
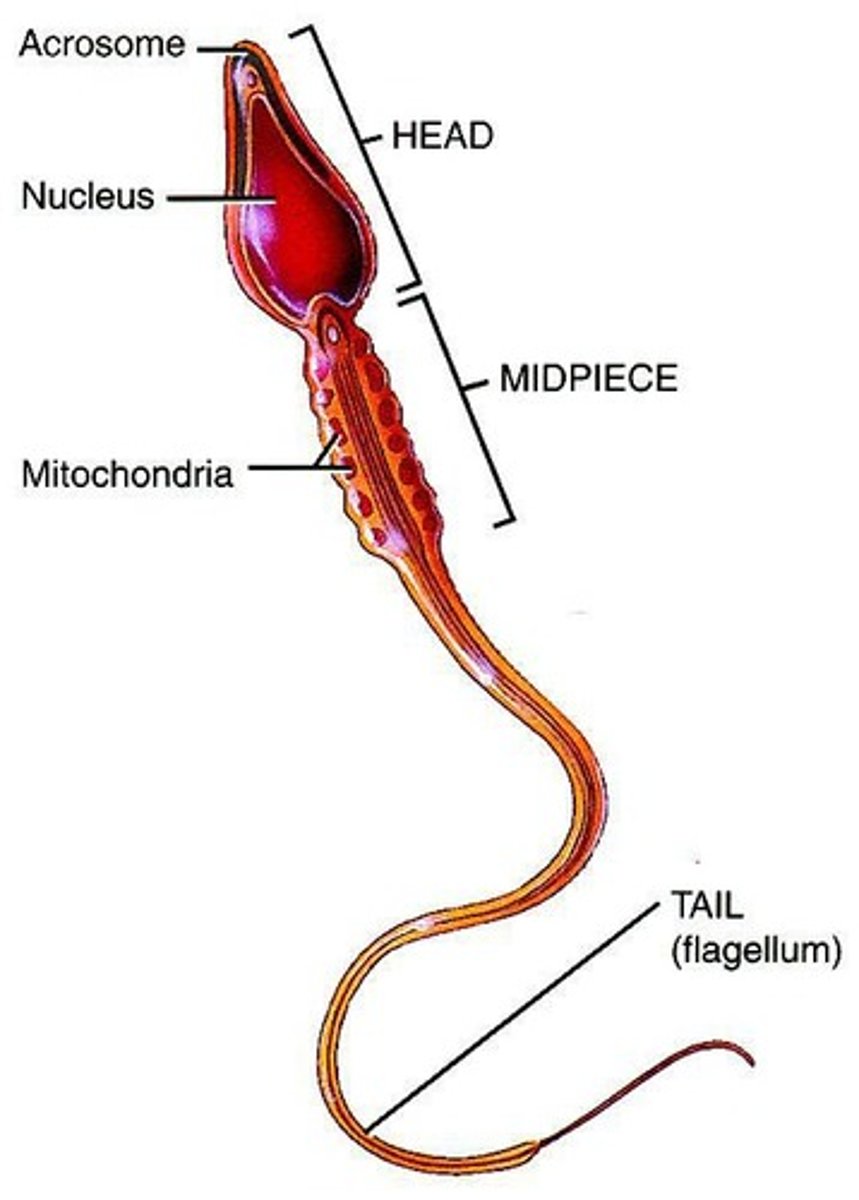
What does the acrosome of a sperm do?
It covers the head and contains enzymes to penetrate the egg.
How many sperm are produced per day?
About 300 million.
How long can sperm live within the female reproductive tract after ejaculation?
Up to 48 hours.
What hormone stimulates spermatogenesis?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
What does luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulate in males?
It stimulates the interstitial cells to secrete testosterone.
What are the functions of testosterone in males?
It controls growth, development, and functions of male sex organs, stimulates bone growth, protein anabolism, sperm maturation, and development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
What are some secondary sexual characteristics stimulated by testosterone?
Increased body hair, thick muscles and bones, sebaceous gland secretion, deep voice, broad shoulders, and narrow hips.
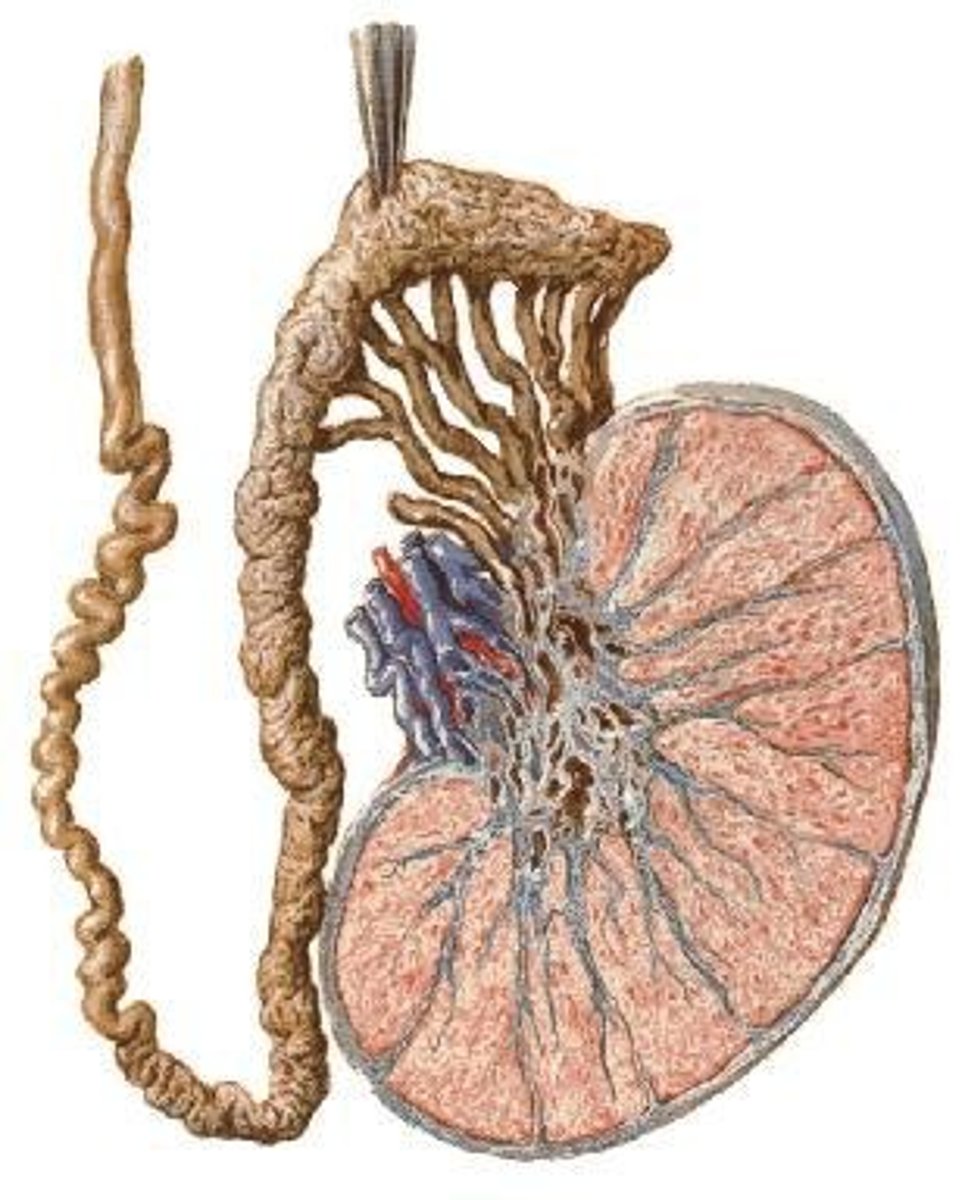
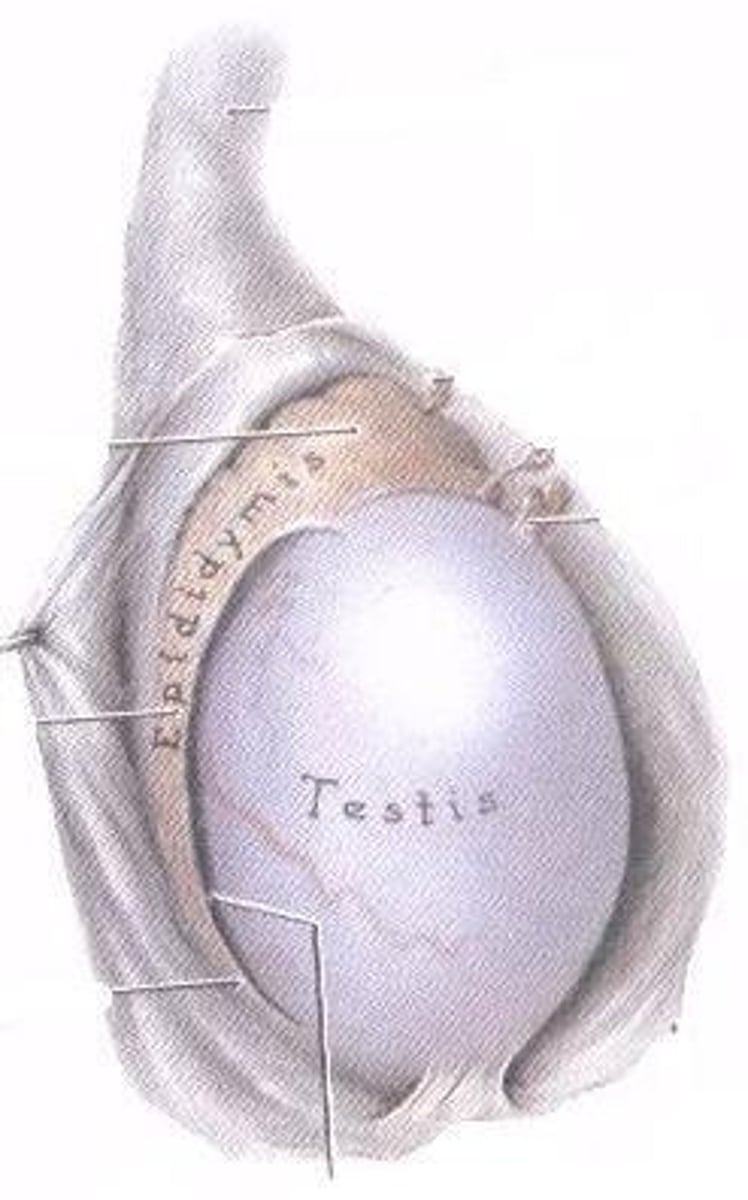
What is the epididymis and what is its function?
The epididymis is located behind the testis and is divided into head, body, and tail; it is where sperms mature, become mobile, and are stored.
What is the vas deferens and its role in the male reproductive system?
The vas deferens is a continuation of the tail of the epididymis, passing through the inguinal canal to enter the pelvic cavity and joining the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct.
What is a vasectomy?
A surgical procedure for male sterilization where the two vas deferens are cut and tied or sealed.
What forms the ejaculatory duct?
The union of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle.
What is the role of the seminal vesicles?
They secrete an alkaline, viscous fluid containing fructose that nourishes sperm and helps in ATP production.
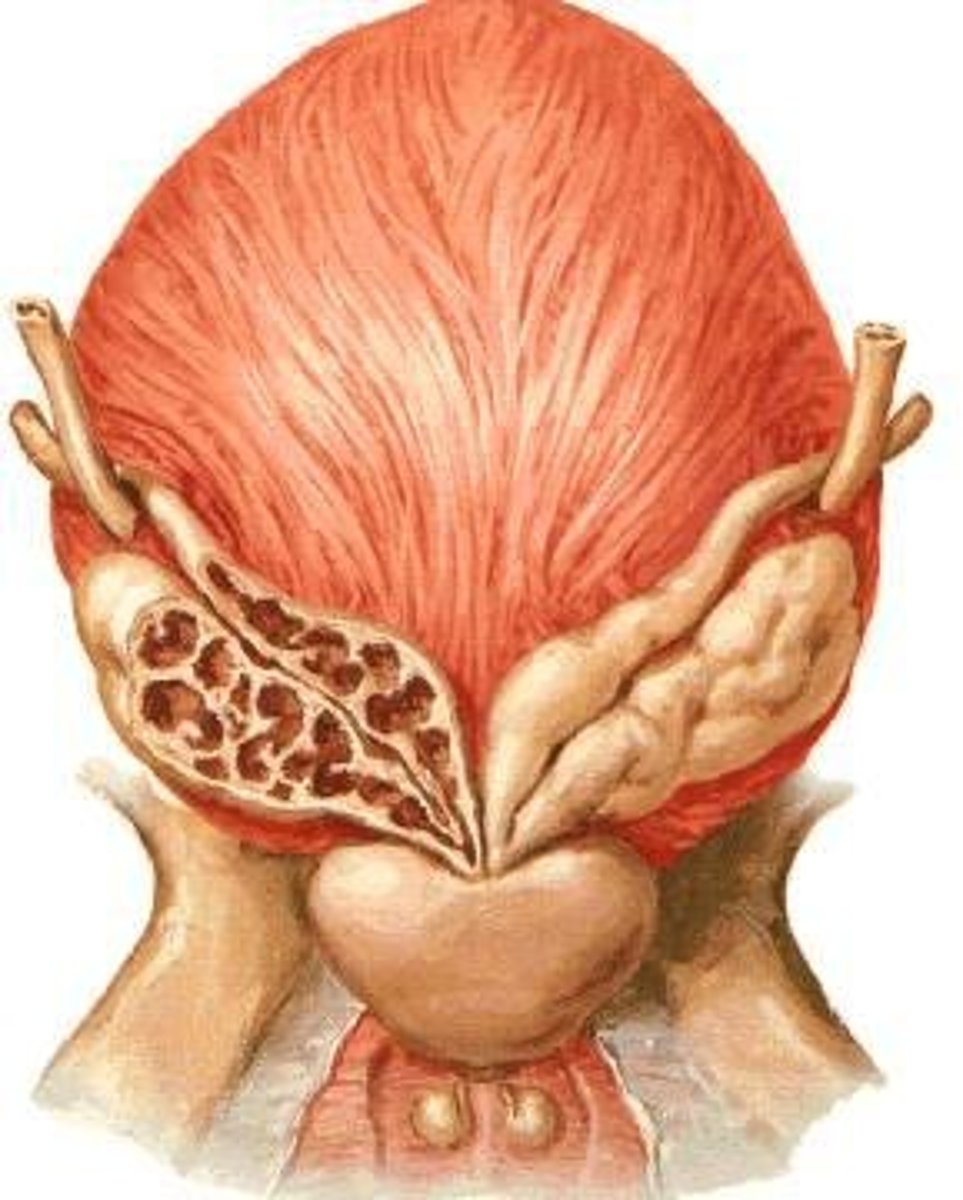
Why is the fluid secreted by the seminal vesicles alkaline?
To neutralize the acidity in the male urethra and the female reproductive tract.
What do the bulbourethral glands secrete?
Mucus for lubrication.
Where is the prostate gland located?
Inferior to the neck of the urinary bladder.
What is the function of the prostate gland?
It secretes fluid that is part of semen and is traversed by the prostatic urethra and the ejaculatory ducts.
What is the significance of the midpiece of the sperm?
It contains mitochondria that supply energy to the tail for movement.
What is the structure of the sperm's tail?
The tail is a flagellum used for movement in the female reproductive system.
What is the relationship between the vas deferens and the spermatic cord?
The vas deferens forms the spermatic cord with other structures connected to the testis.
What happens to sperm as they pass through the epididymis?
They mature, become mobile, and are stored.
How does the ejaculatory duct function in sperm transport?
It allows sperm to pass through different parts of the urethra to the outside.
What fluid does the gland secrete that contains clotting enzymes?
A milky white fluid that coagulates and liquefies semen.
Where are the testes located?
In the scrotum.
What glands contribute to the formation of seminal fluid?
The seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands.
What is the shape and location of the perineum?
A diamond-shaped area located between the thighs, inferior to the pelvis, containing external genitalia and the anus.
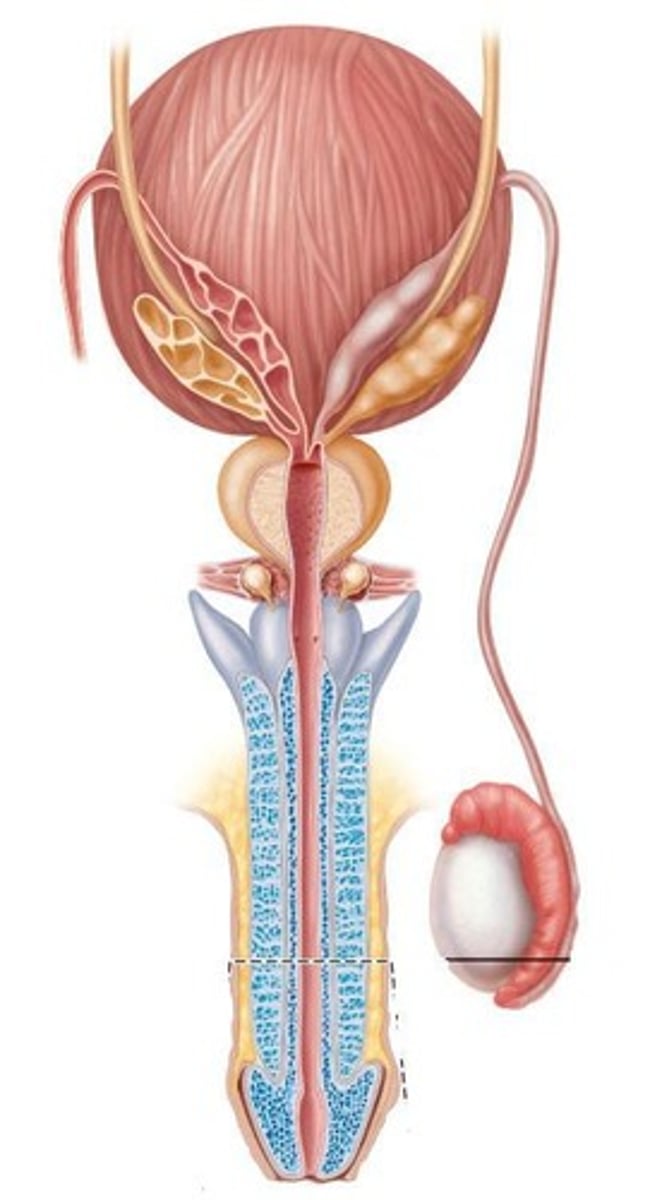
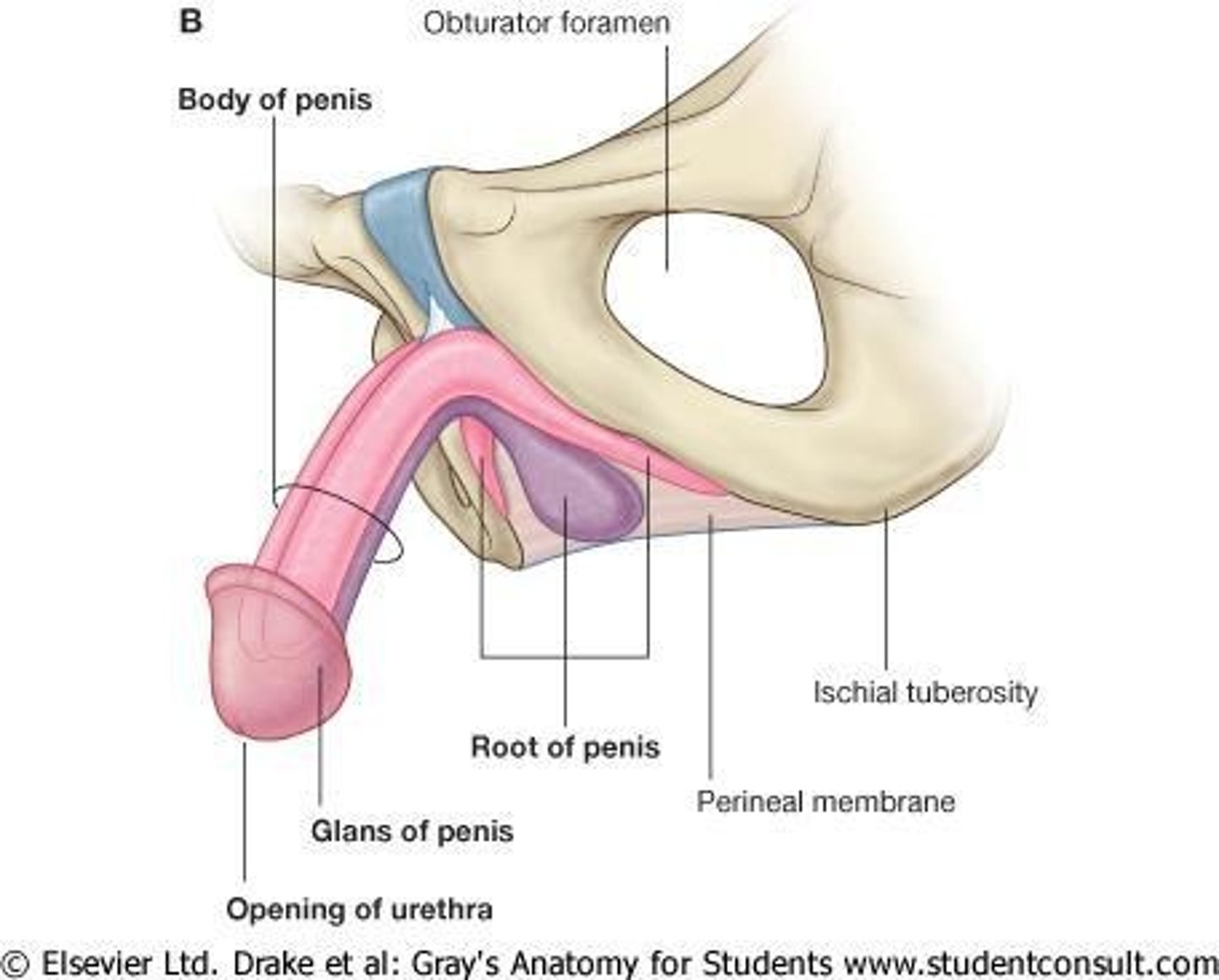
What are the two main parts of the penis?
Root (located in the perineum) and Body (the free part of the penis).
What forms the root of the penis?
A bulb in the middle and two crura laterally.
What are the three elongated erectile bodies of the penis?
Corpus spongiosum (posteriorly) and two corpora cavernosa (anteriorly).
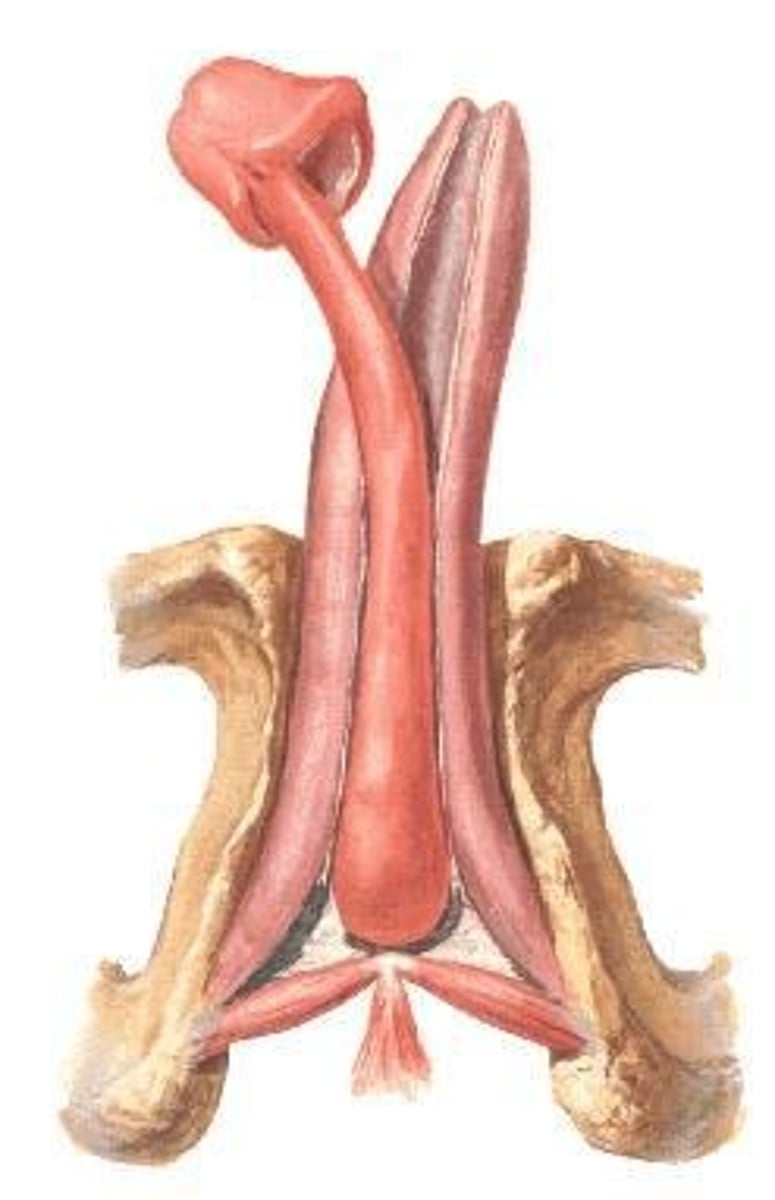
What is the function of the corpus spongiosum?
It is traversed by the penile urethra and its anterior end forms the glans penis.
What is the prepuce?
A loose fold of skin covering the glans penis, removed during circumcision.
What happens to the erectile tissue during erection?
Blood fills the spaces in the erectile tissue, causing distension.
What type of reflex is responsible for erection?
A parasympathetic reflex.
What mediates local vasodilatation during an erection?
Nitric oxide.
What type of reflex is responsible for ejaculation?
A sympathetic reflex.
What prevents urine flow during ejaculation?
Muscle contraction closes the internal urethral sphincter.
What actions propel semen into the penile urethra during ejaculation?
Peristaltic contractions in the vas deferens, seminal vesicles, ejaculatory ducts, and prostate.
What is the role of the internal urethral sphincter in males?
It prevents urine flow during ejaculation.
What is the role of the external urethral sphincter in males?
It allows voluntary control over urination.
How do the internal and external urethral sphincters differ?
The internal sphincter is involuntary and prevents urine flow during ejaculation, while the external sphincter is voluntary and controls urination.
What is the bulb of the penis?
The posterior expanded part of the corpus spongiosum.
What are the crura of the penis?
They are continuous with the corpora cavernosa and are located laterally.
What are the two types of urethral sphincters and their characteristics in males?
The internal urethral sphincter is involuntary and made of smooth muscles, located at the neck of the bladder. The external urethral sphincter is voluntary and made of skeletal muscles, surrounding the membranous urethra.
What is the function of the internal urethral sphincter during ejaculation?
It contracts to prevent the flow of urine from the bladder to the urethra.
What is semen composed of and what is its average volume?
Semen is a mixture of sperms and secretions from the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands, with an average volume of 2.5 - 5.0 mL.
What is the sperm concentration in semen, and what is the significance of this number?
The sperm concentration is 50 - 150 million sperms/mL, and only one sperm can fertilize an egg.
What conditions are indicated by oligospermia and azoospermia?
Oligospermia is a low sperm count below 20 million/mL of semen, while azoospermia indicates no sperm at all in the semen.
What are the functions of semen?
Semen nourishes sperms, transports sperms, neutralizes acidity of the male urethra and female vagina, lubricates the reproductive tract during intercourse, and prevents infection due to antibacterial proteins.
What are the primary sex organs in the female reproductive system?
The primary sex organs are the two ovaries.
What are the secondary sex organs in the female reproductive system?
The secondary sex organs include the two uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina.
What hormones do the ovaries secrete, and what is their significance?
The ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone, which are the female sex hormones important for reproductive functions.
Where are the ovaries located in the female body?
The two ovaries are located laterally in the pelvic cavity.
What are the uterine tubes also known as, and what is their function?
The uterine tubes are also called fallopian tubes or oviducts, and they are the site of fertilization where sperm fertilizes the egg.
What is the role of fimbria in the female reproductive system?
Fimbria are finger-like extensions at the end of the uterine tubes that contact the ovary and help carry the egg into the tube.
What is a tubal pregnancy and its consequences?
A tubal pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg cannot make its way through the fallopian tube into the uterus, leading to potential abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, which can be fatal if untreated.
What is the primary function of the uterus?
The uterus is the site of implantation and development of the embryo during pregnancy.
What are the three parts of the uterus?
The three parts of the uterus are the fundus (upper rounded part), body (extends from uterine tube to isthmus), and cervix (lower part projecting into the vagina).
Where is the uterus located in relation to other pelvic organs?
The uterus is located between the urinary bladder anteriorly and the rectum posteriorly.
What ligaments provide stability to the uterus?
The broad ligament attaches the uterus and uterine tube to the side wall of the pelvis, while the ovarian ligament attaches the ovary to the lateral angle of the uterus.
What are the three layers of the uterine wall?
The three layers are the perimetrium (outer layer of peritoneum), myometrium (thick layer of smooth muscles), and endometrium (inner mucosal lining).
What is the uterine cavity and cervical canal?
The uterine cavity is the cavity of the body of the uterus, while the cervical canal is the cavity of the cervix.
What are the internal os and external os?
The internal os is the opening of the cervical canal into the body of the uterus, and the external os is the opening of the cervical canal into the vagina.
What are the two layers of the endometrium lining the uterus?
Stratum functionalis and Stratum basalis.
What is the function of the stratum functionalis?
It grows during the menstrual cycle to prepare for a fertilized egg and is shed during menstruation if fertilization does not occur.
What is the role of the stratum basalis?
It is the deep layer of the endometrium that is never shed and replaces the stratum functionalis each month through mitosis.
What happens to the egg after ovulation?
The egg is drawn into the fallopian tube by the fimbriae and can be fertilized within 24 hours.
What is the term for the fertilized egg?
Zygote.
What is the morula?
A 16-cell stage that forms as the zygote grows by mitotic divisions before moving to the uterus for implantation.
What is the vaginal fornix?
The upper end of the vagina surrounding the cervix, opening into the cervical canal and vaginal vestibule.
What is the pH of vaginal secretion and what neutralizes it?
The vaginal secretion is acidic, and the alkaline nature of semen neutralizes this acidity to increase sperm viability.
List three functions of the vagina.
1. Pathway for sperm during sexual intercourse. 2. Pathway for menstruation. 3. Birth canal.
What initiates the female reproductive cycles?
They start at puberty and continue throughout the reproductive years.
What is the typical length of the female reproductive cycle?
28 days, with the first day of menstrual flow considered the first day of the cycle.
What are the two main cycles involved in the female reproductive cycle?
The ovarian cycle and the menstrual (uterine) cycle.
What occurs during the ovarian cycle?
A series of events associated with the maturation of the egg in the ovary leading to ovulation.
What happens during the menstrual (uterine) cycle?
Endometrial changes in the uterus prepare to receive a fertilized egg; if fertilization does not occur, the stratum functionalis is shed.
What is oogenesis?
The production of eggs in the ovaries, involving two reduction divisions (meiosis I & II) to form haploid sex cells.