Biology: 4.5.2.3/4 - The human nervous system (the eye) (control of body temperature)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
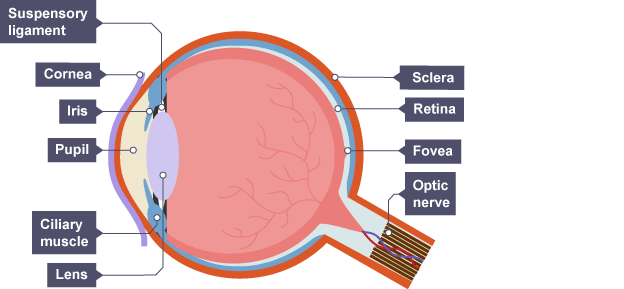
The eye
Sense organ with receptors sensitive to light intensity and colour which has many structures allowing the shape to change
Retina
layer of light sensitive cells at the back of the eye
light hits retina → impulses sent to the brain
Optic nerve
nerve connecting eye and brain carrying impulses
Sclera
white outer layer that supports structures inside the eye
strong to prevent damage
Cornea
see-through layer at the front of the eye
lets light through
focuses light onto retina
Iris
muscles surrounding the pupil
in bright light - makes pupil smaller to avoid damage
→ circular muscles contract
→ radial muscles relax
in dim light - enlarges pupil to allow more light in
→ circular muscles relax
→ radial muscles contract
Ciliary muscles & suspensory ligaments
control the shape of lens
Focus on a near object
ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligaments loosen
lens becomes thicker and more curved
light refracts more
Focus on a distant object
ciliary muscles relax
suspensory ligaments tighten
lens becomes thinner
light refracts less
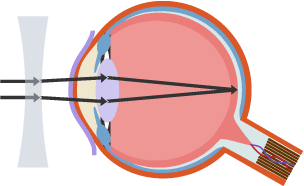
Myopia
Short-sightedness where lens is too curved. So a concave lens is used.
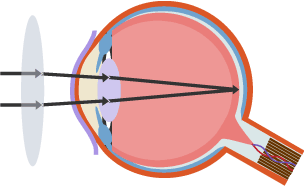
Hyperopia
Long-sightedness where lens is too flat. So a convex lens is used.
Laser eye surgery
reduces thickness of cornea so less light is refracted for myopia
changes cornea curvature so light is refracted strongly for hyperopia
Replacement lens
natural lens is replaced with an artificial on
may damage retina
cataracts can develop
Thermoregulatory centre
found in the brain
controls body temperature
contains receptors sensitive to blood temperature
receives impulses from temp receptors in skin
More than 37.5°C
sweat is produced from sweat glands
vasodilation where blood vessels dilate
both cause transfer of energy from skin to environment
Less than 37.5°C
sweating stops
shivering - skeletal muscles contract
hairs stand on end for insulation
vasoconstriction where blood vessels constrict