Human A&P 4: Cells
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Study of Cells
Cytology
4 Things Cells Have in Common
Building blocks for all plants/animals
Come from division of pre-existing cells
Smallest units that perform all the vital physiological functions
Each cell maintains homeostasis on cellular level
3 Things Cells need to be able to do
Produce energy from nutrients and release wastes
Reproduce when necessary
Have all information necessary to carry out functions
3 Main Parts of the Cell
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
2 Types of Cells
Sex Cells
Somatic Cells
5 Types of Somatic Cells
Nerve Cell
Muscle Cell
Bone Cell
Blood Cell
Gland Cell
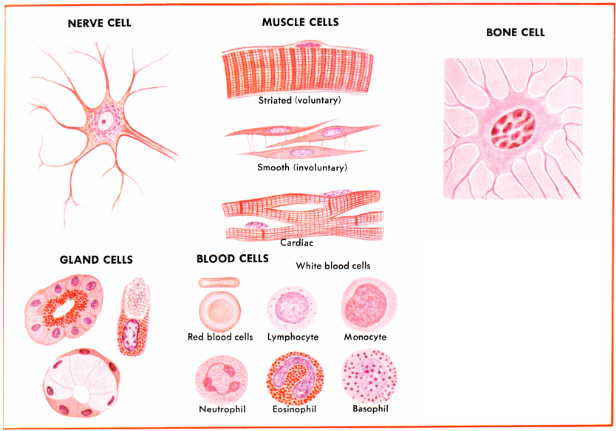
Variations in Human Cells
Red blood cells have no nucleus
Striated muscle cells are multinucleated
Columnar Epithelial cell: simple shape
Neurons are highly branched
3 Extracellular Fluids
Interstitial fluid: cell submersed
Blood plasma: blood fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid: surrounds nervous organs
Extracellular Materials
Extracellular Fluids
Cellular Secretions: saliva, mucus etc
Extracellular Matrix: “glue”
4 Main Functions of Plasma Membrane
Physical Isolation: Barrier
Regulation of Exchange with the Environment: ions, nutrients, wastes, secretions
Sensitivity to Environment: 1st part of the cell affected by change in environment
Structural Support: Specialized connections, tissue stability
Phospholipid Bilayer
Main component of cell membrane
Phosphate heads are hydrophilic
Lipid tails are hydrophobic
Membrane Proteins
Integral Proteins: span width of membrane at least once
Peripheral Proteins: bound to either side of membrane surface
3 Transport Mechanisms Through Plasma Membrane
Diffusion
Carrier Mediated Transport
Vesicular Transport
Active/Passive Processes
P: Substance moves down concentration gradient
A: Uses cellular energy, usually ATP, against concentration gradient
Diffusion (Overview)
Movement of ions, molecules down gradient
Important in body fluids
CO2 moves freely through PM[CO2] → cell > ECF > circulating blood
3 Types:
Simple
Channel-Mediated
Osmosis
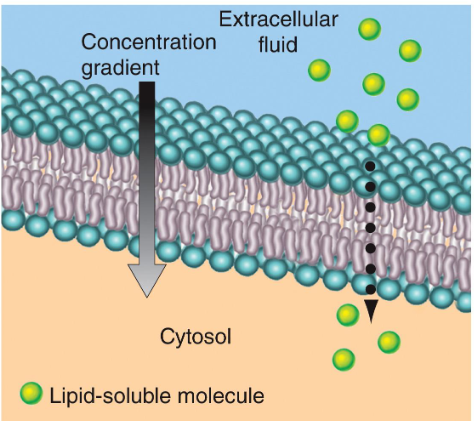
Simple Diffusion
Substances that can diffuse through bilayer
Alcohol
Fatty acids
Steroids
O2, CO2
Lipid soluble drugs
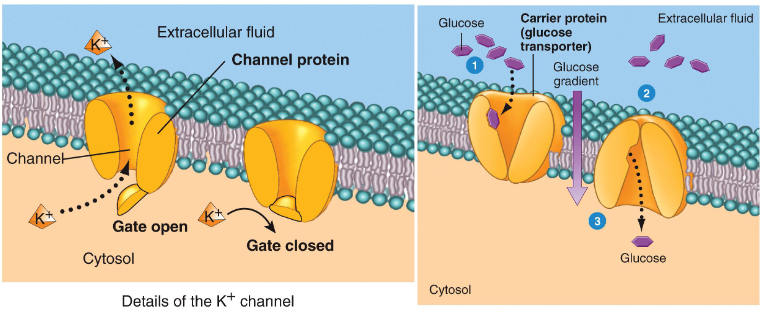
Channel Mediated (Facilitated) Diffusion
Small channels (0.8 nm in diameter) exist in the membrane. Small ions and molecules may diffuse through via these channels.
Facilitated by Protein Channels: The protein channels facilitate the transport of polar or charged substances, which cannot easily pass through the hydrophobic lipid bilayer of the cell membrane
Certain factors influence diffusion rate:
size & charge of ion
size of hydration sphere
interactions between the ion and channel wall
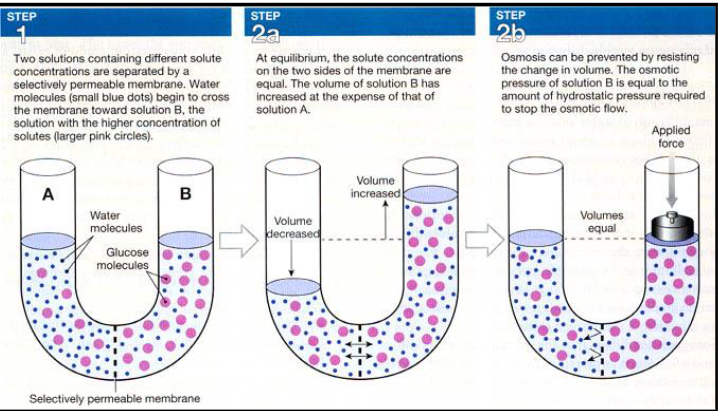
Osmosis
Movement of water molecules across selectively permeable membrane from low to higher solute concentration
Total solute concentration is osmotic pressure
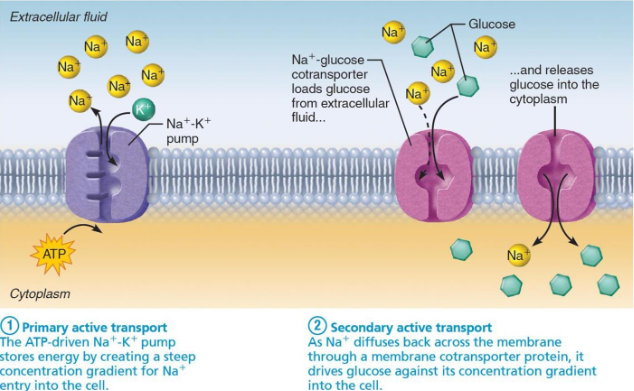
Carrier Mediated Transport (Active Transport)
Movement of substances against gradient
Requires ATP
Primary AT
Secondary AT
Vesicular Transport
Materials move in/out of cells in vesicles
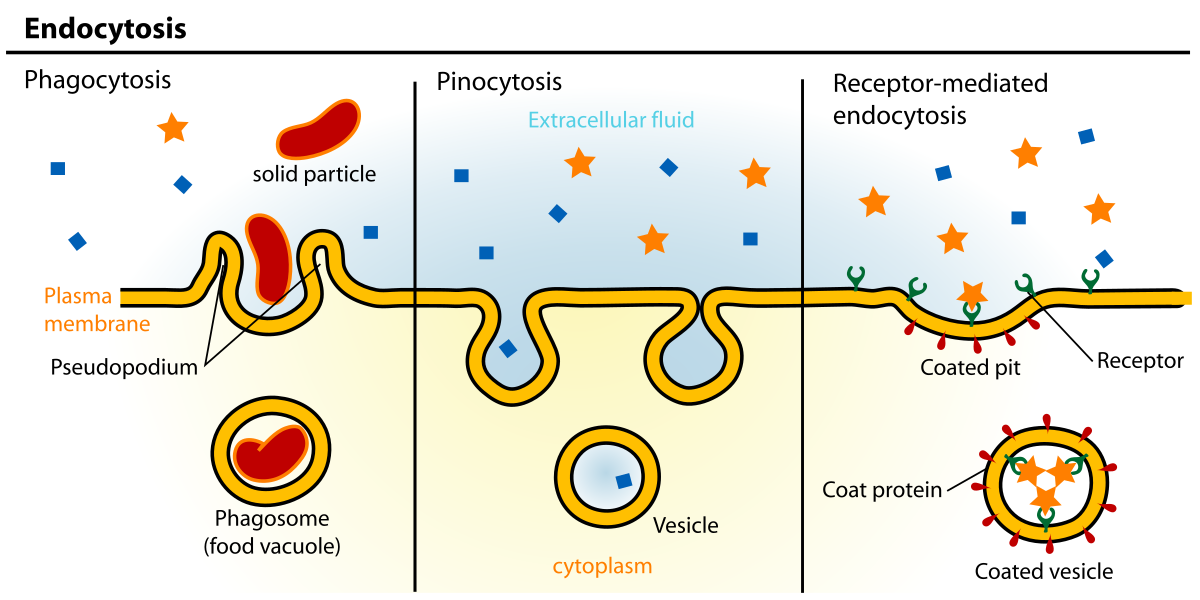
Endocytosis
Pinocytosis
Phagocytosis/Exocytosis
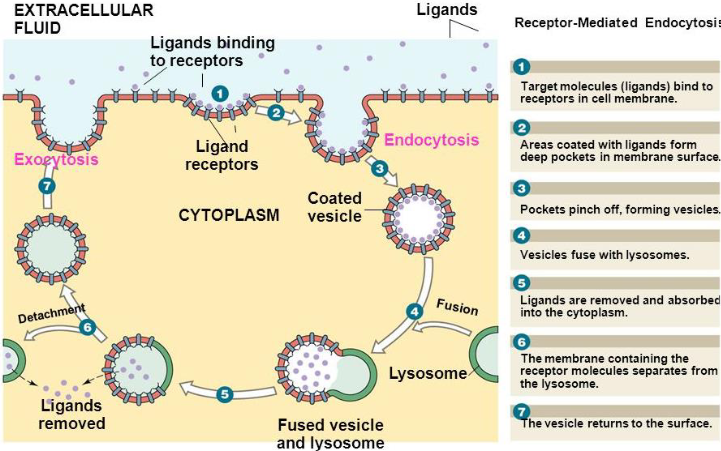
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis (7 Steps)
Extracellular materials packaged in vesicles at cell surface and brought into cell
Pinocytosis
A cellular process where a cell engulfs liquid and small particles from its surroundings.
Plays a crucial role in nutrient uptake and cellular homeostasis.
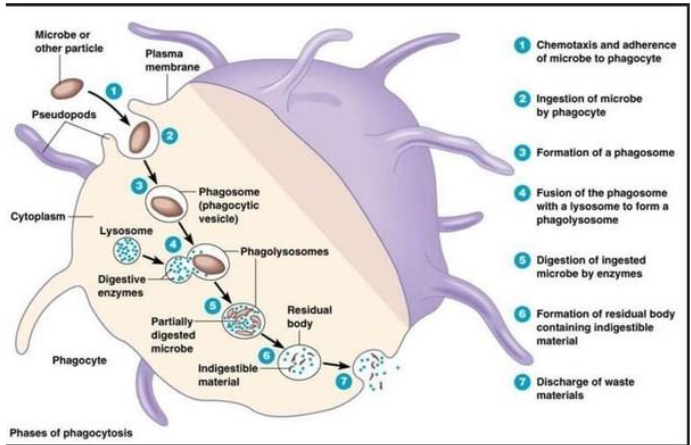
Phagocytosis (7 Steps)
Cytoplasm
All material inside cell
Cytosol
Organelles
Cytosol
Intracellular fluid
Dissolved nutrients, ions, proteins, wastes
2 Classifications of Organelles
Nonmembranous
Not completely enclosed by membranes
Some contact with cytosol
Membranous
Isolated from cytosol by membranes
6 Nonmembranous Organelles
Cytoskeleton
Microvilli
Centrioles
Cilia
Ribosomes
Proteasomes
6 Membranous Organelles
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Cytoskeleton
Nonmembranous organelle
Provides internal framework
Microfilaments
Intermediate Filaments
Thick Filaments
Microtubules
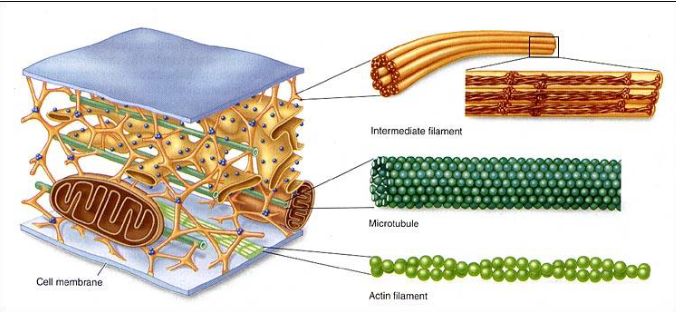
Microfilaments (Actin Filaments)
Thinnest part of cytoskeleton
Made of actin
Functions:
Anchors cytoskeleton to integral proteins
Determines consistency of cytoplasm
Actin & myosin produce active movement
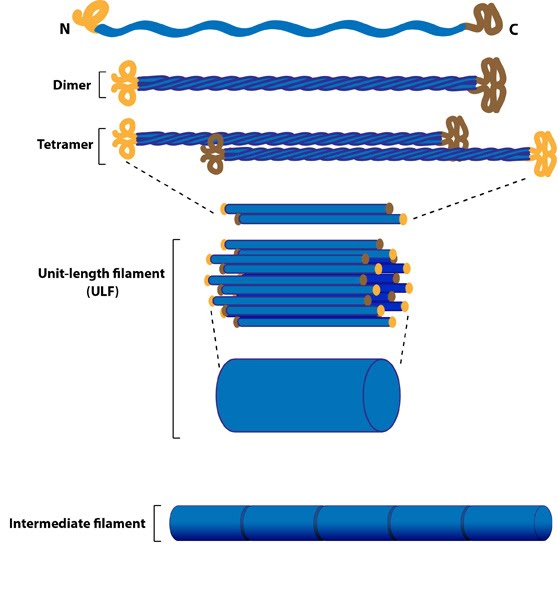
Intermediate Filaments
Composition varies
7-11 nm
Functions:
Strengthens cell/maintains shape
Stabilizes organelles
Stabilize wall position
Thick Filament
Made of Myosin
15 nm
Muscle cells only
Interact with actin for muscle contractions
Microtubules
Tubulin
25 nm
Extend from centrosome
Functions:
Cell rigidity
Change cell shape through disassembly
Monorail: can move vesicles & organelles
Mitosis: form spindles
Form centrioles and cilia
Microvilli
Increases surface area of cell exposed to extracellular environment
Small, finger-shaped projections
Actively absorbing - GI tract
Connects cytoskeleton to microfilaments
Centrioles
Organizes cytoskeletal microtubules
All animal cells capable of division have them
Cylindrical, short microtubules
Associated with centrosome
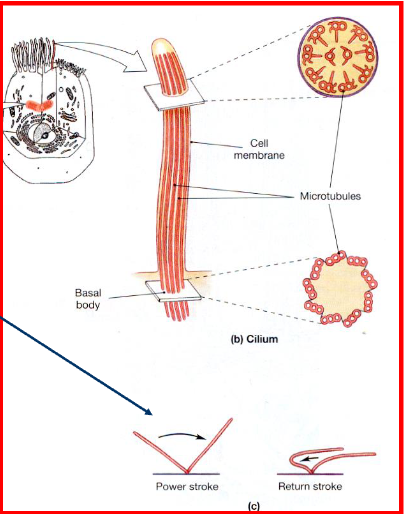
Cilia
Long, slender extensions of cell membrane
Found in the respiratory tract, reproductive tract
Anchored to basal body found just beneath the cell’s
surface“Beat” rhythmically – move fluids, secretions across
the cell’s surfacestiff during the power stroke, and flexible during
return stroke
Smoking: damages cilia
- can’t clear irritants away
Ribosomes
Fixed ribosomes: attached to RER, produces plasma membrane/ secretory proteins
Free ribosomes: Scattered throughout cytoplasm
Protein synthesis
Small & large subunit
Contain special proteins & rRNA
Uses mRNA to produce protein
Proteasomes
Responsible for removing/recycling damaged or denatured proteins, and breaking down abnormal proteins
Attach Ubiquitin tag to proteins that need to be recycled
Tagged proteins broken down in proteasome and released
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of intra-cellular membranes connected to nuclear envelope
Hollow tubes, flattened sheets, cisternae
Functions:
Synthesizes proteins, carbs, lipids
Stores synthesized molecules
Allows for transport of materials
Detoxification: toxins neutralized by enzymes within
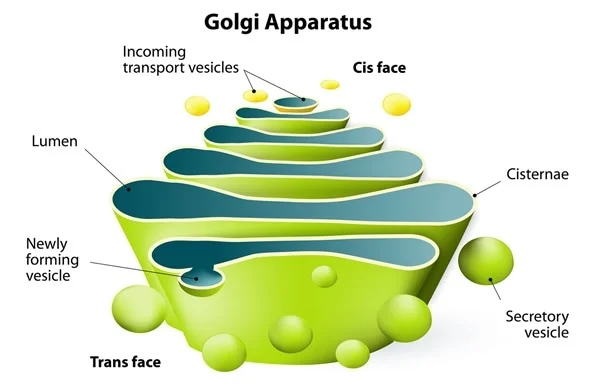
Golgi Apparatus
Transport vesicle with new proteins goes to golgi from ER
Membranous organelle
Functions:
Modifies and packages secretions
Renews or modifies plasma membranes
Packages special enzymes for cytosol
Lysosome
Functions:
Primary lysosomes: inactive enzymes that activate when fused with damaged organelles
Secondary lysosomes: break down contents
Destroy bacteria & dead/damaged cells
Cleanup and recycling functions inside cell
Peroxisomes
Functions:
Absorb & break down fatty acids & organic compounds, results in H2O2 production
Enzymes break down H2O2, produces water & O2
Cell is protected from potentially damaging effects of the free radicals produced during catabolism
Mitochondrion
Cellular respiration
Double membraned (cristae)
Reactions release energy in mitochondria
Activities that require energy occur in cytoplasm
Semi-autonomous organelle, divides via fission
Nucleus
Control center of cell
Stores “blueprints” for synthesizing more than 100,000 different proteins
Cells with nucleus have longer life span
Contains:
Nuclear Envelope: Separates from cytosol, double layered
Nucleolus: Synthesize rRNA
Nucleoplasm: Fluid contents of nucleus
Nuclear Pore: Channels between nucleus and cytosol, allows for exchange of ions & small molecules