25 - Oxidation of fatty acids: β-oxidation of fatty acids with odd- and even number of carbon atoms. Carnitine shuttle. Energy balance. Regulation.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
sections
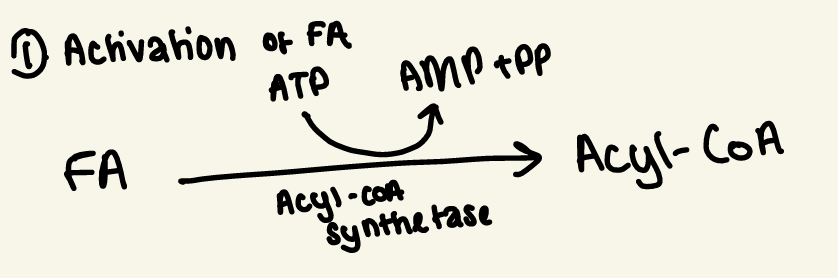
activation of FA
regulation
enzyme defects
beta oxidation even and odd number
canitine shuttle
energy yield
oral box
activation of FA
regulation
Inhibited by malonyl-CoA (blocks CPT-I)
Stimulated by fasting, glucagon, epinephrine
Inhibited by insulin and high ATP/acetyl-CoA
enzyme defects
deficiency of hepatic CPT1 - decrease oxidation of fatty acid in liver → hypoglycaemia, decreased ketogenesis
Deficiency in muscle CPT2 - muscle pain and fatigue and myoglobinuria
beta oxidation even and odd number
Occurs in mitochondria
Even-numbered FAs → broken into acetyl-CoA units
Odd-numbered FAs → last 3 carbons form propionyl-CoA → converted to succinyl-CoA (enters TCA cycle)
carnitine shuttle
Needed to transport long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria
Steps:
Fatty acyl-CoA → Fatty acyl-carnitine (CPT-I)
Transport across inner membrane
Reconversion to fatty acyl-CoA (CPT-II)
energy yield
Example: Palmitate (C16) → 106 ATP
(via 7 cycles: 8 acetyl-CoA, 7 NADH, 7 FADH₂)
oral box
