Biology unit 1 Exam
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
What’s a DV (dependent variable)
the variable that will (or may) change because you changed the independent variable
What’s a IV (independent variable)
The variable that your changing in order to test the effect
What’s the purpose of a CV (control variable)
to ensure that only the independent variable can be causing a change in the dependent variable
increases validity of the experiment
What is a controlled variable
factor in an experiment that is kept constant to ensure that the results are reliable and accurate
What’s precision
How close all the data is to each other
What’s accuracy
How close the data is to the true value
What’s validity
how well an experiment or investigation actually measures what it is supposed to measure
Difference between quantitative and qualitative data
‘Quali(ty)’tative- describing
‘Quan(tity)’titative- numbers, data
What information needs to be included in a hypothesis?
How you expect the IV to affect the DV
including the direction of change
Advantages of larger surface area to volume ratio (SA:V)
Faster diffusion rates
allows cells and organisms to exchange nutrients, gases, and waste products with their environment more efficiently
Does SA:V affect rate of diffusion or efficiency?
yes, lower SA:V means it will take longer for nutrients or waste to absorb therefore being less efficient
When a cell grows, does the SA:V increase?
no, it decreases because volume of the cell increases faster than its surface area
What is surface area to volume ration a measure of?
compares the surface area of an object to its volume
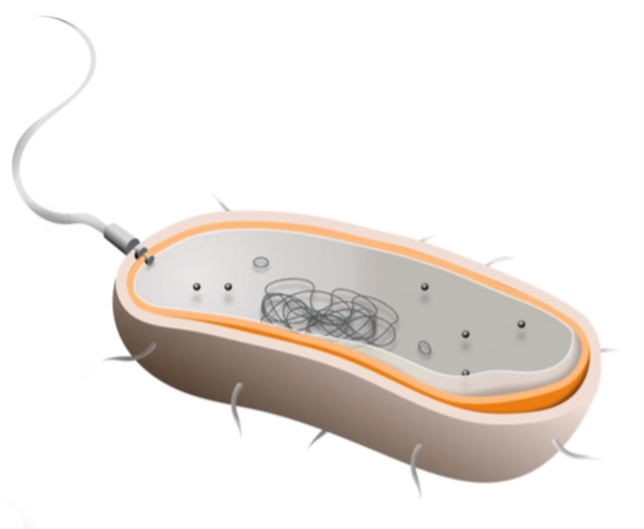
Prokaryote cell features
Lack membrane-bound organelles
has no nucleus
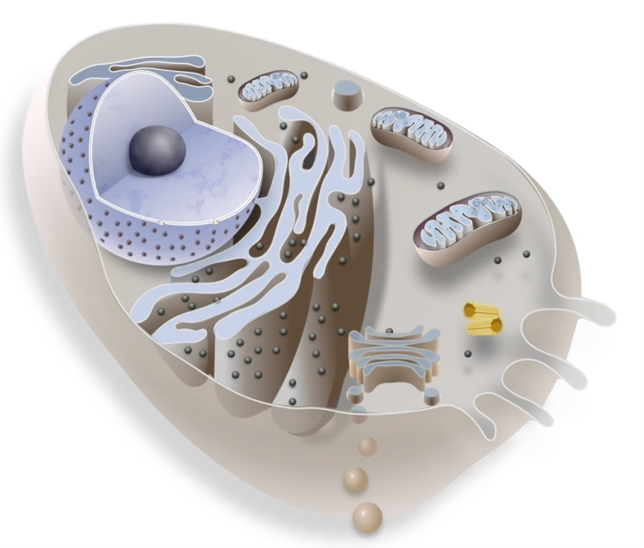
Eukaryote cell features
membrane-bound nucleus & organelles
bigger than prokaryotic cells
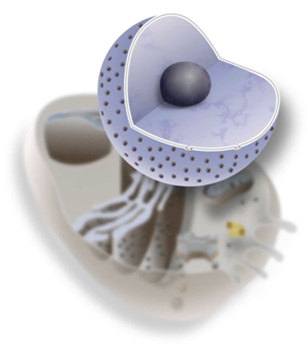
What’s the function of the Nucleus
To contain most of the genetic material (DNA) of the cell
regulates protein synthesis and cell division
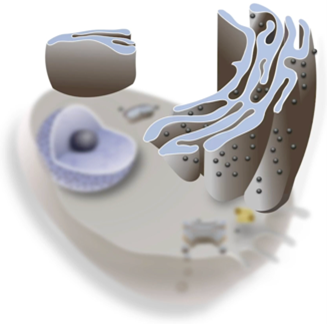
What’s the function of the Endoplasmic reticulum
To transport materials such as proteins and lipids
What’s the function of the Golgi body
Modifies and packages proteins to be exported from the cell
What’s the function of ribosomes
read the genetic code from mRNA
What’s the function of chloroplast
site of photosynthesis in plant cells
contain chlorophyll
What’s the function of the mitochondria
to do aerobic respiration
What’s the function of large vacuoles
to help plant maintain its structure with turgor (swelling) pressure
stores metabolic wastes from the cell
What’s the structure of the Nucleus
surrounded by a nuclear envelope that has two layers of membrane
pierced with nuclear pores
What’s the structure of the Endoplasmic reticulum
network of membrane channels
What’s the structure of the Golgi body
stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs

What’s the structure of ribosomes
not membrane bound
made of 60% rRNA and 40% protein
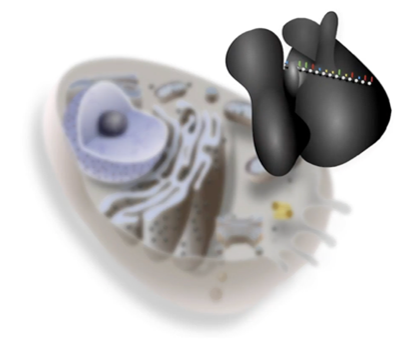
What’s the structure of chloroplast
bound by two layers of membrane
smaller structures called thylakoids, each membrane-bound
thylakoids stacked are grana

What’s the structure of the mitochondria
double membrane-bound
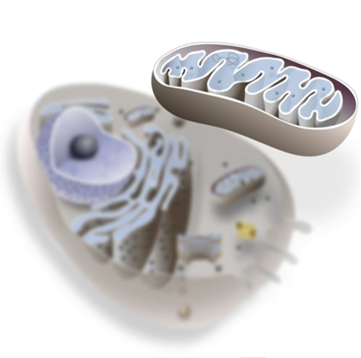
What’s the structure of large vacuoles
membrane bound sac
What’s anaerobic respiration
metabolic process that generates energy (ATP) in the absence of oxygen
What’s aerobic respiration
metabolic process that utilizes oxygen to convert glucose into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water
What’s the equation for anaerobic respiration
Glucose → Lactic Acid + Energy (ATP)
What’s the equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
What’s the purpose of aerobic respiration
produce energy in the form of ATP for cells to use
What’s the purpose of an anaerobic respiration
provide energy in the absence of oxygen, allows glycolysis to continue producing ATP
What are the limiting factors of aerobic respiration
oxygen concentration, glucose concentration, and temperature. influence the efficiency and speed of biochemical reactions in breaking down glucose to produce energy
What are the limiting factors of anaerobic respiration
oxygen deficiency
Examples of anaerobic respiration
alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation and in decomposition of organic matter
Examples of aerobic respiration
Krebs cycle
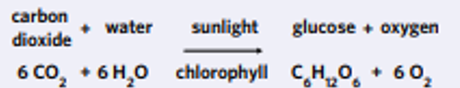
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
What do plant cells look like

What do animal cells look like
What’s diffusion
molecules dispersing between a membrane until they have reaches equilibrium
What’s osmosis
passive net movement of free water molecules through a semi permeable membrane
What’s a hypertonic solution
having a higher osmolality (concentration of solutes) than the extracellular fluid
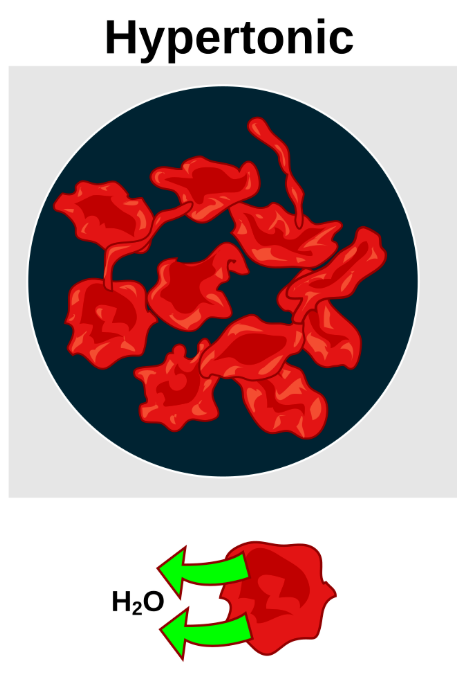
What’s a hypotonic solution
having a lower osmolality (concentration of solutes) than the extracellular fluid
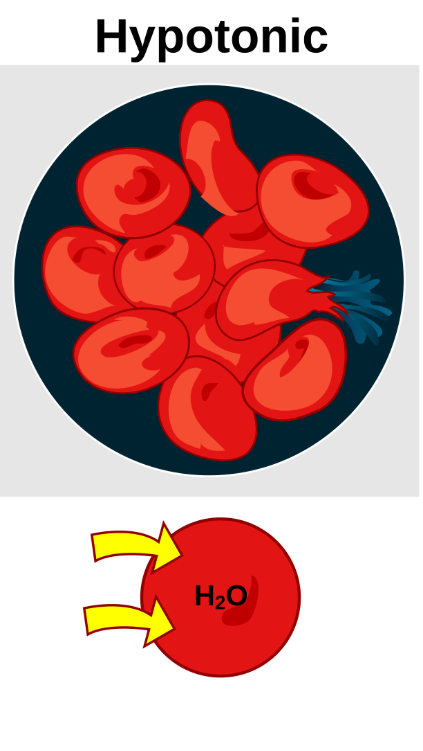
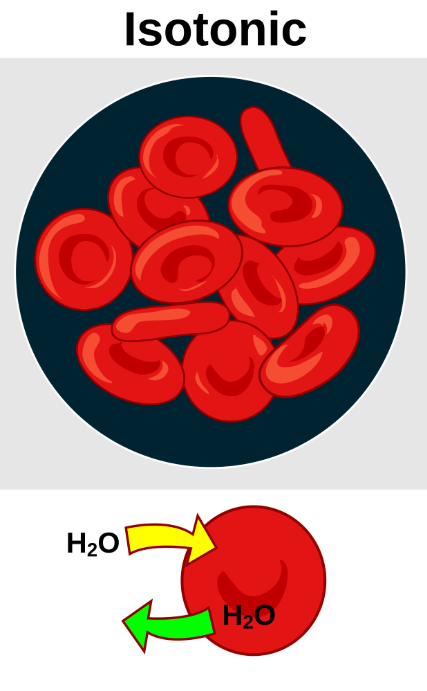
What’s an isotonic solution
having the same osmotic pressure as the extracellular fluid
What’s passive transport (Include examples)
transport though the membrane that doesn’t require energy
e.g oxygen, carbon dioxide, salts, ethanol
What’s facilitated diffusion (Include examples)
passive transport through the cells that does NOT require energy
e.g glucose, amino acids, and certain ions like sodium, potassium, and chloride
What’s endocytosis
cell takes in substances from its surrounding environment by forming a vesicle
essentially "eating" the external material
type of active transport that requires energy
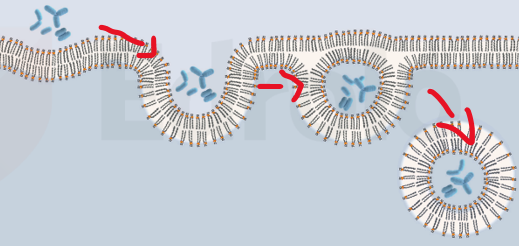
What’s exocytosis
substances are released from inside a cell to the external environment
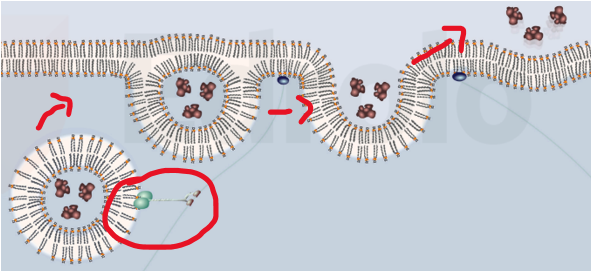
What’s a hydrophobic molecule
repels or doesn't mix well with water
e.g flour
What’s a hydrophilic molecule
one that readily dissolves in water or other polar solvents
What are polar molecules
molecules that have a separation of electric charge
one end of molecule slightly positive and the other end slightly negative
water, ethanol, ammonia
What are non-polar molecules (Include example)
molecules that lack an overall electric charge
co2, methane, most molecules containing carbon
What’s the function of the plasma membrane
act as a barrier, separating the cell's internal environment from the external one
role in regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell
Diagram of the plasma membrane

Parts of the plasma membrane
phosphate head
fatty acid tails
carbohydrate chains
glycoprotein
transport proteins
Difference between simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and active transport
Simple diffusion involves small, nonpolar molecules moving directly through the lipid bilayer
Facilitated diffusion uses membrane proteins to aid the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient, doesn't require energy
Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy and specific membrane proteins
Difference between eukaryote and prokaryotic cells
presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
What are unipotent cells
a specialized stem cell that can only differentiate into one type of cell
e.g Epidermal stem cells, Muscle stem cells
What are pluripotent cells
embryonic stem cell that can differentiate into any cell type found within the three primary germ layers of the body
ectoderm - skin, nervous system
mesoderm - muscle, bone, blood, urogenital
endoderm - lungs, gastrointestinal
What order to stem cells develop in
TPMOU Toti-pluri-multi-oli-uni
What are multipotent cells
The ability of a stem cell to differentiate into multiple, but limited, cell types within a specific lineage.
e.g blood stem cells, capable of giving rise to all blood cell types, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
What are totipotent cells
capable of developing into any cell type in a complete organism, including both embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues (like the placenta)
How do uni-, pluri-, multi-, toti- potent cells differ from each other
toti- can give rise to all cell types in the embryo and extra-embryonic tissue
pluri- can differentiate into all cell types within the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) but not extra-embryonic tissues.
multi-can differentiate into multiple cell types within their specific lineage
toti-can only differentiate into a single cell type
Difference between binary fission and mitosis
Binary fission is the primary method of cell division in prokaryotes, while mitosis is the primary method in eukaryotic cells
Phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle
mitosis (PMAT)
interphase (cytokenesis, G1, Synthesis, G2)
= 2 daughter cells
Where do checkpoints appear in mitosis
Metaphase - chromosome spindle attachment
G1 - Nutrients, growth factors, DNA damage
G2
What type of errors do checkpoints look for in mitosis and how do they fix the errors
DNA damage, incomplete DNA replication, or chromosomes not properly attached to the spindle.
fix errors by pausing the cell cycle to allow repair
if the problem can't be fixed, the cell will self-destruct through apoptosis
What is apoptosis?
programmed cell death
What is Necrosis?
uncontrolled cell death
How are living things organized?
Cell, tissue, organ, system, organism
What are the systems in the body?
skeletal
muscular
nervous
endocrine
respiratory
digestive
urinary
reproductive
What organs are in the digestive system
mouth
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
rectum
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
What’s the function of the digestive system
break down food into smaller molecules that the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and repair
What organs are in the excretory system
kidneys
ureters
bladder
urethra
What’s the function of the excretory system
eliminate waste products and excess fluids from the body maintaining homeostasis
What’s the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion
Mechanical digestion involves physically breaking down food into smaller pieces without altering its chemical composition
Chemical digestion uses enzymes and other chemicals to chemically break down food into smaller molecules.
What’s mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces without altering its chemical composition
What’s chemical digestion
enzymes break down large food molecules into smaller, absorbable components. This process occurs in the digestive tract
Examples of mechanical digestion
chewing, churning in the stomach
Examples of chemical digestion
protein/fat digestion, nucleic acid digestion
What organs are in the endocrine system
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
thyroid gland
pancreas
What’s the function of the endocrine system
regulate and coordinate various bodily functions through the secretion of hormones
What’s the structure of Xylem

What’s the function of Xylem
transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, including the stems and leaves
What’s the structure of Phloem
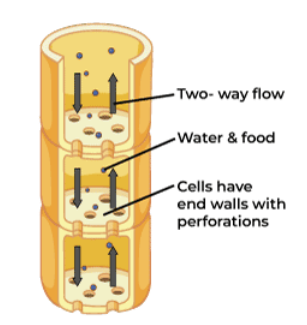
What’s the function of Phloem
to transport sugars and other organic molecules throughout a plant
Describe water movement into roots
happens through osmosis
Water moves from areas of higher water potential (like the soil) to areas of lower water potential (inside the root cells)
Describe water movement into stems
facilitated by the specialized xylem tissue, which acts like a network of tiny tubes extending from the roots up the stem and into the leaves
Describe water movement into leaves
transpiration
What’s a cell
smallest unit capable of carrying out all the functions of life
What’s a tissue
group of similar cells and their surrounding matrix, working together to perform a specific function
What’s an organ
a collection of tissues that structurally form a functional unit specialized to perform a particular function
What’s a system
related components-such as organs, tissues, cells, or molecules-that interact and work together as a unified whole to perform specific biological functions
What’s homeostasis?
body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions
e.g body temperature, blood sugar levels, and fluid balance
What’s osmoregulation?
regulates the balance of water and electrolytes (like salt) within its body fluids to maintain a stable osmotic pressure
What’s the stimulus response model?

How is high body temperature regulated?
STIMULUS: body temperature reises above 37 degrees
RECEPTOR: Increase detected by thermoreceptors in skin, organs & hypothalamus
CONTROL CENTER: Hypothalamus sends signals via nerve and hormones to effectors
EFFECTORS: sweat glands, blood vessels in skin, cerebral cortex, body cells
RESPONSE: increase in swelling, vasodilation of skin vessels, behavioral cortex, decreased metabolic rate