Self-Protective Features of the Dentition & Handout #3
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
• Primary function of the teeth: prepare food for swallowing
• Facilitate digestion
• Teeth have respective form to facilitate their function: incision, holding, tearing, grinding and trituration of the food.
• The shapes of the anterior and posterior teeth are related to to the function they perform.
• Aid in Speech
• Esthetics
Form & Function of the Permanent Dentition:
Each tooth has specific contours that has a functional role, and it is important to reproduce these contours to allow for proper function for mastication, phonetics, and esthetics.
Why is it important to preserve the shape of a tooth?
1. The nature of the biologic tissues themselves.
2. The shapes of the teeth.
3. The way the shapes of the teeth relate to one another.
Important features of teeth that help reserve their existence:
2mm
What is the approximate biological width?
CEJ
Identify the structure in the blue box
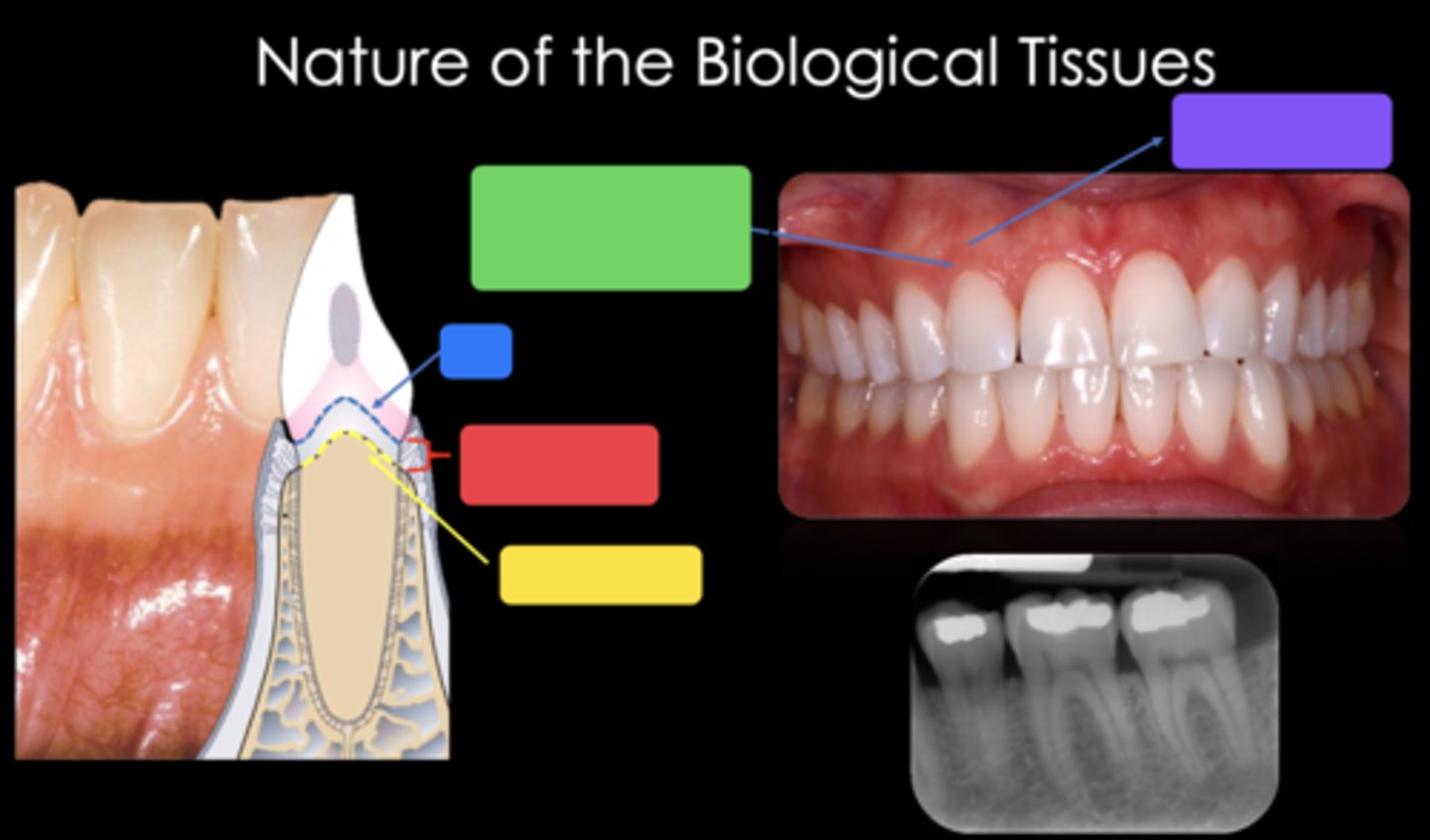
Biological width (2mm)
Identify the structure in the red box
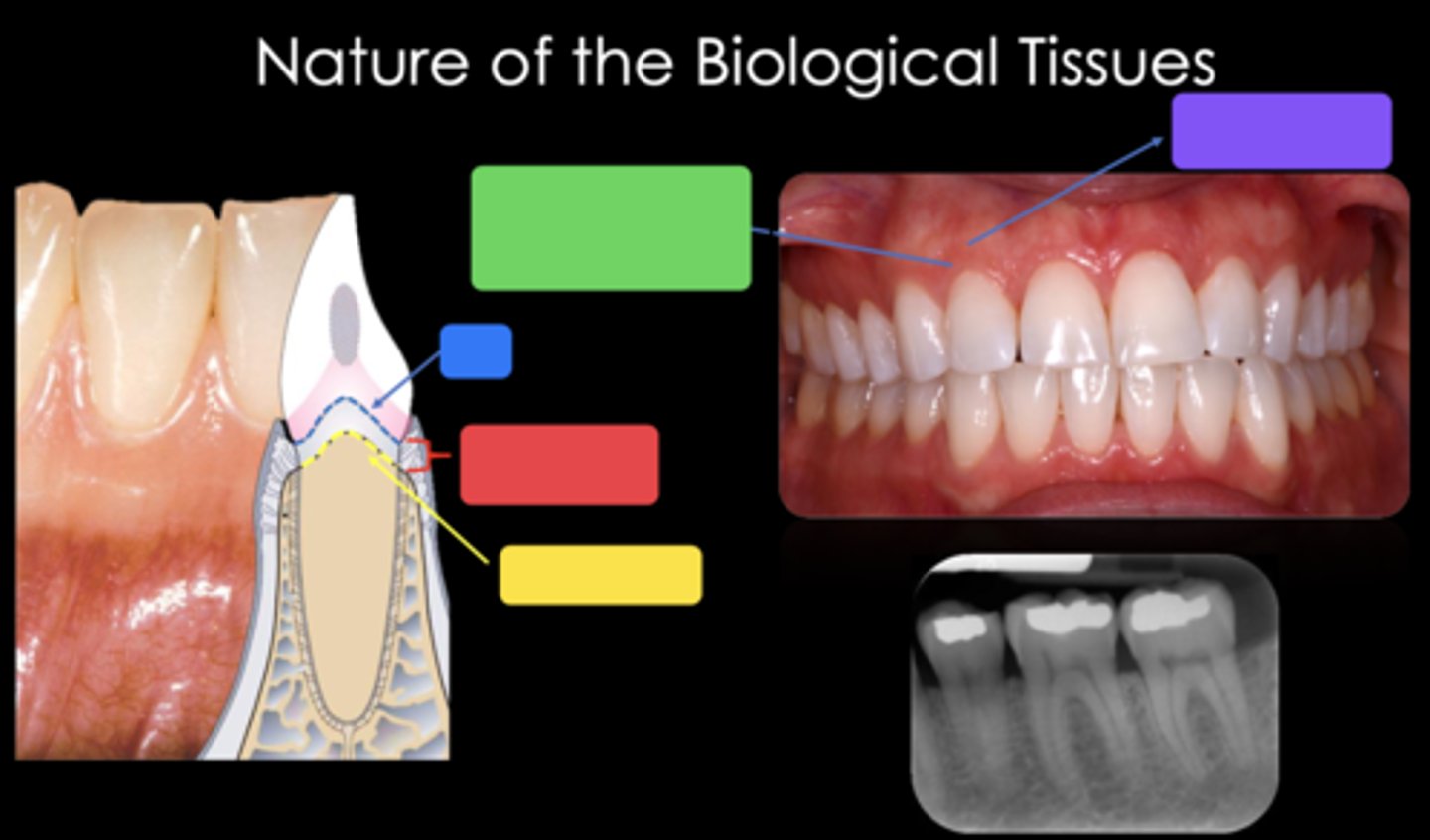
Crest of bone
Identify the structure in the yellow box
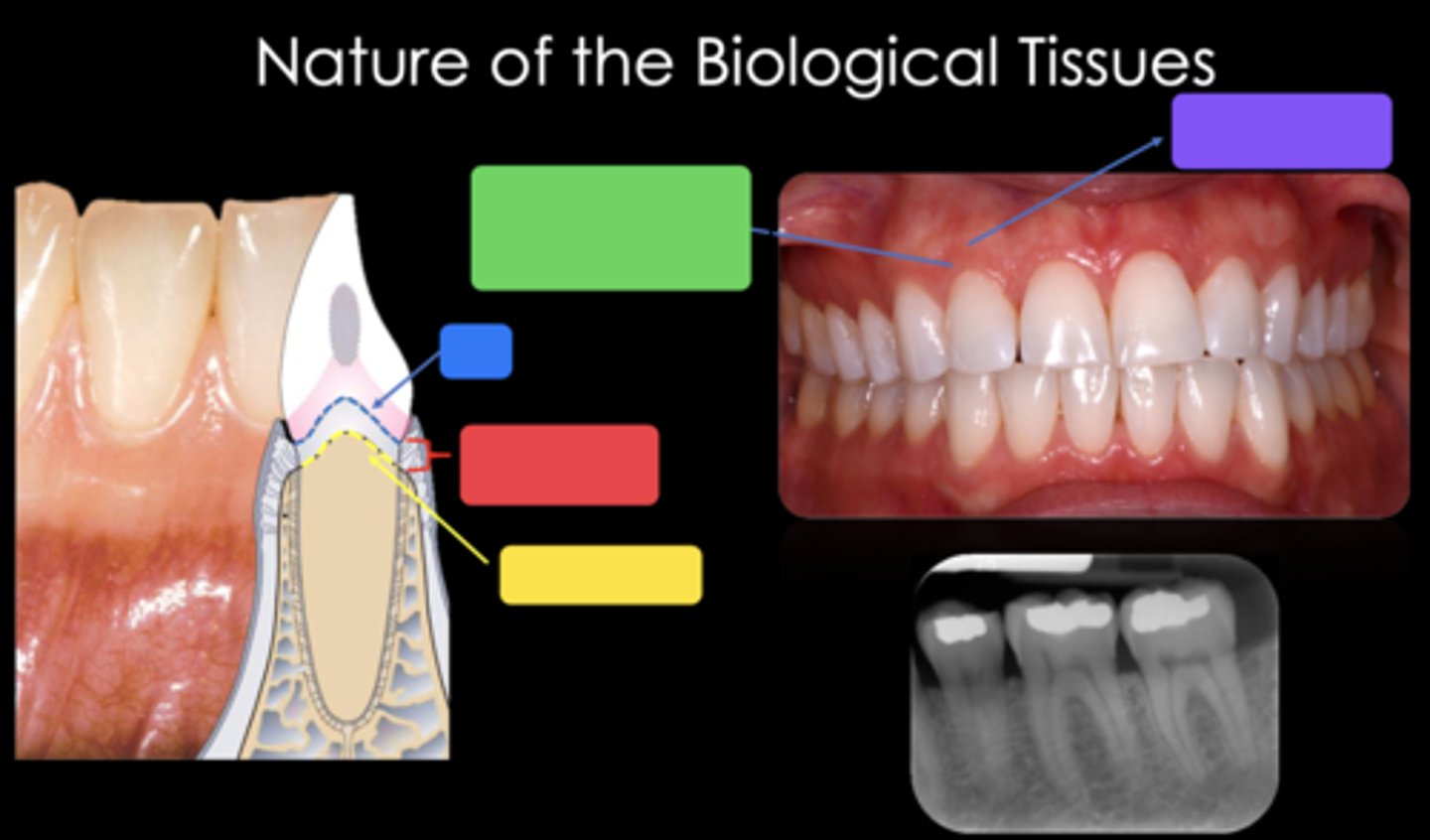
Free gingival margin (marginal gingiva) - nonkeratinized
Identify the structure in the green box
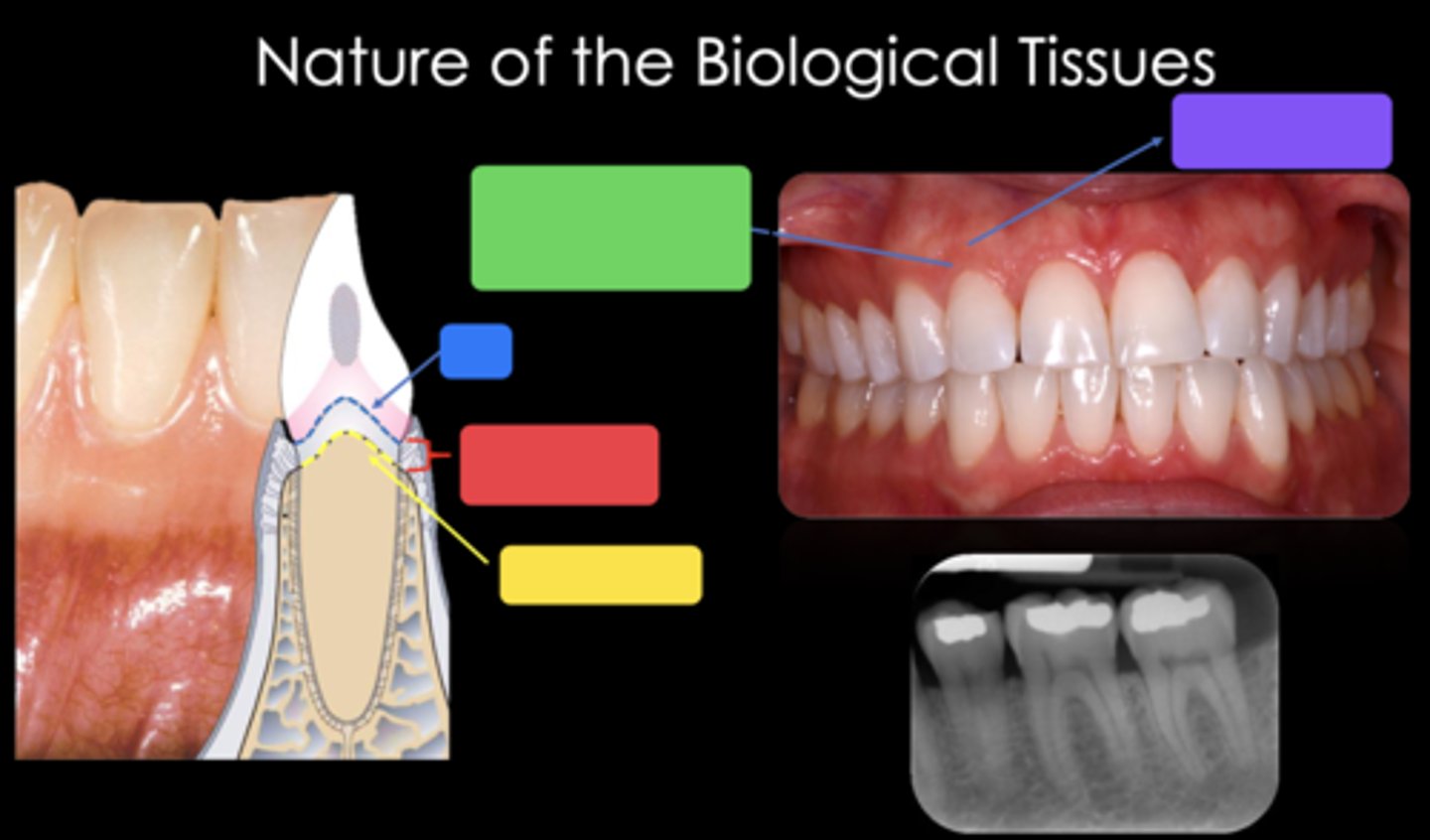
Attached gingiva - keratinized
Identify the structure in the purple box
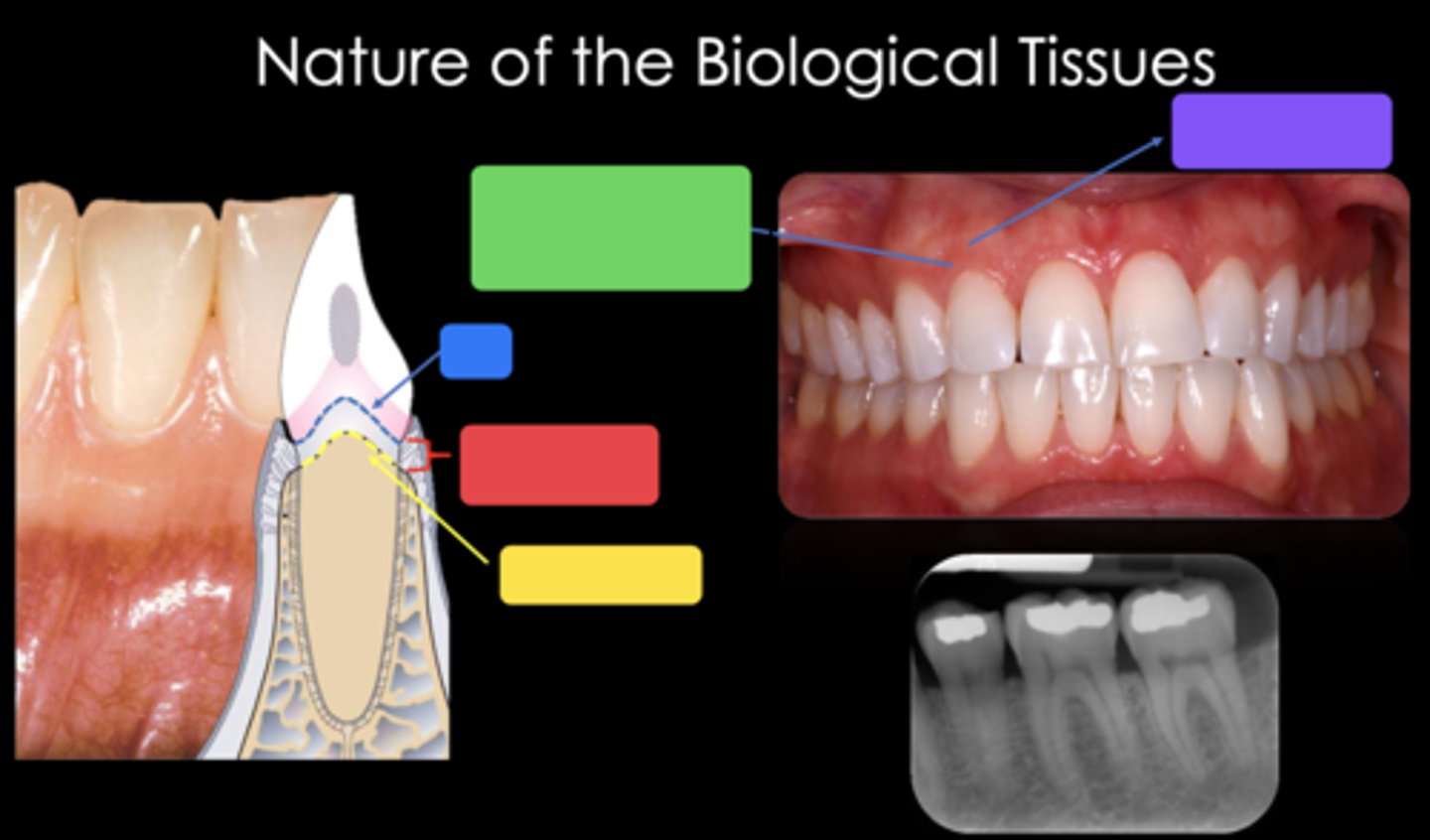
Trapezoidal (the long side is towards the occlusal or incisal and the short side of the trapezoid is towards the gingiva)
All crowns in the permanent dentition have a ___________ shape from a buccal or lingual view
B) They promote healthy interdental papillae
What is one function of properly formed proximal contacts?
A) They increase tooth enamel strength.
B) They promote healthy interdental papillae.
C) They reduce tooth sensitivity to hot and cold.
D) They increase the size of the interproximal spaces.
They prevent food from packing between teeth
Why are proximal contact areas important for oral health?
They stabilize the teeth in the arches
What role do proximal contacts play in dental arches?
interproximal contact area
The area of contact between two adjacent teeth where proximal surfaces meet.
interproximal contact area
serve to prevent food from lodging between the teeth
Proximal contact areas
Allows protection of the gingival tissue:
Proximal contact areas
Prevents build up of excessive bacteria, plaque, calculus:
Proximal contact areas
Offers support to adjacent and opposing teeth in the arches
Anterior teeth are more incisal versus posterior teeth are more cervical
How does the proximal contact area differ in anterior versus posterior teeth?
More centered
Slightly more buccal
Anterior teeth have contact areas that are normally ____________ in the faciolingual dimension versus posterior teeth have proximal contacts that are normally located ____________ in the faciolingual dimension.
Interdental papilla
- A triangle is formed on its base by the crestal bone of the alveolar bone and the sides by the interproximal surfaces of the adjacent teeth.
The interproximal space is a triangle space filled with the...
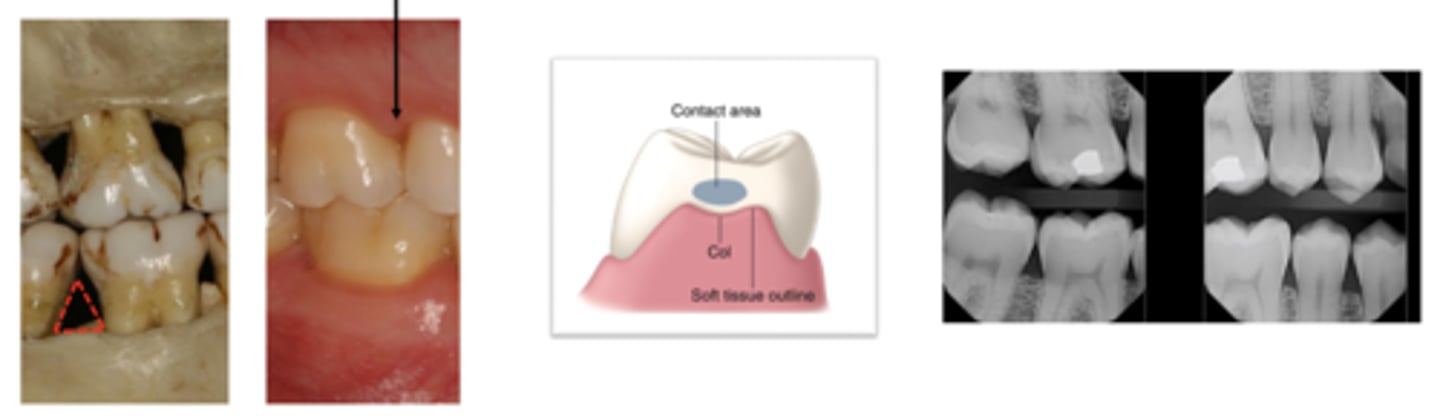
• Food impaction between teeth.
• Potentially increasing the risk of periodontal disease.
• Caries
• Tooth movement
• Halitosis due to retention of food that results from food decomposition
Improper contacts and interproximal spaces may result in:
embrasure
The V-shaped space around the contact area of two adjacent teeth
embrasure
serve as spillways for masticated food
embrasure
Integral part of the self cleansing process for teeth:
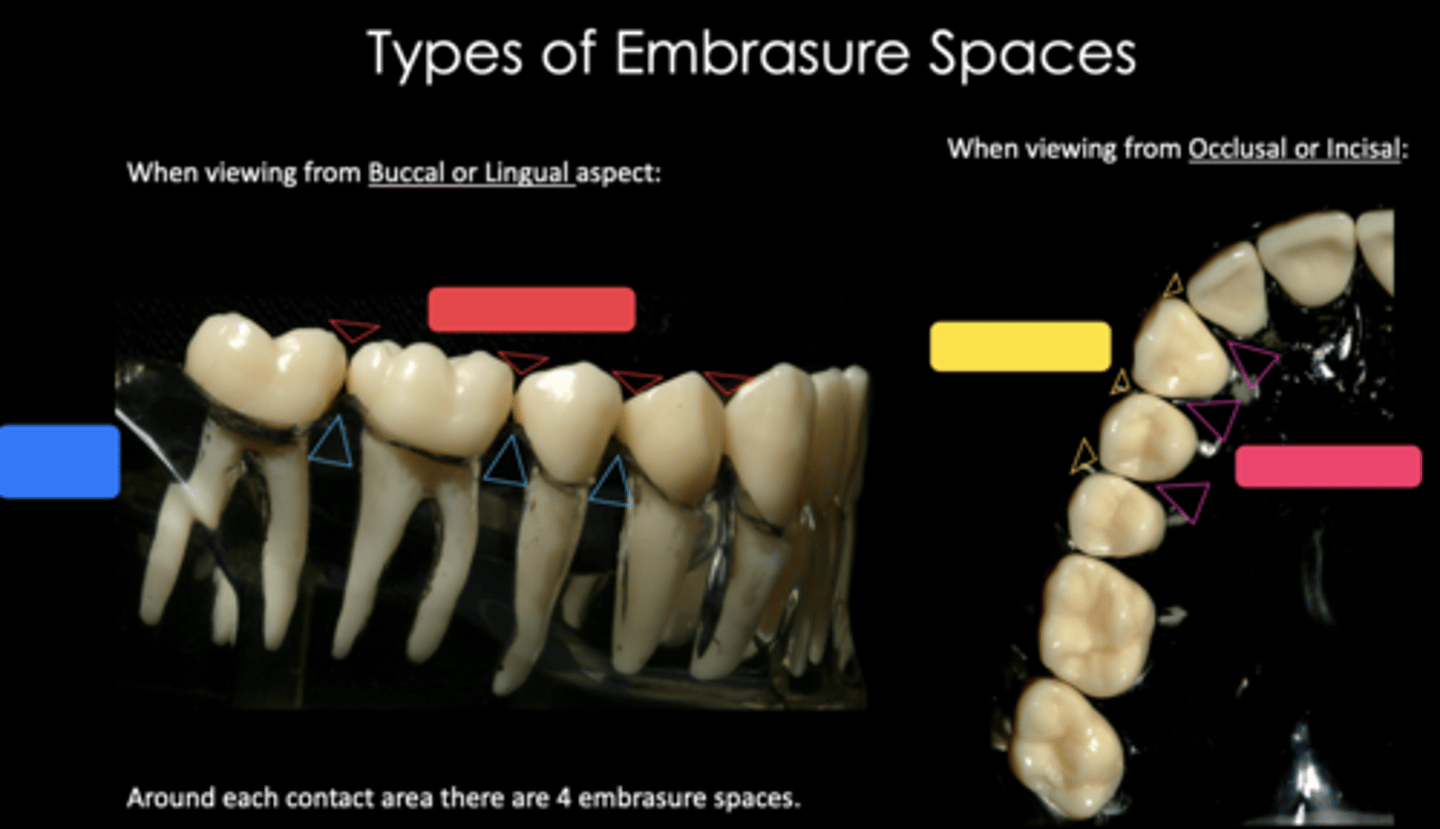
Four:
1. Incisal or Occlusal
2. Facial (Labial or Buccal)
3. Lingual
4. Gingival or Cervical (interproximal)
How many embrasures does each contact area have?
facial and lingual HOC
believed to protect and stimulate the gingival tissues during the mastication of food
Gingival/cervical
Identify the embrasure space in blue
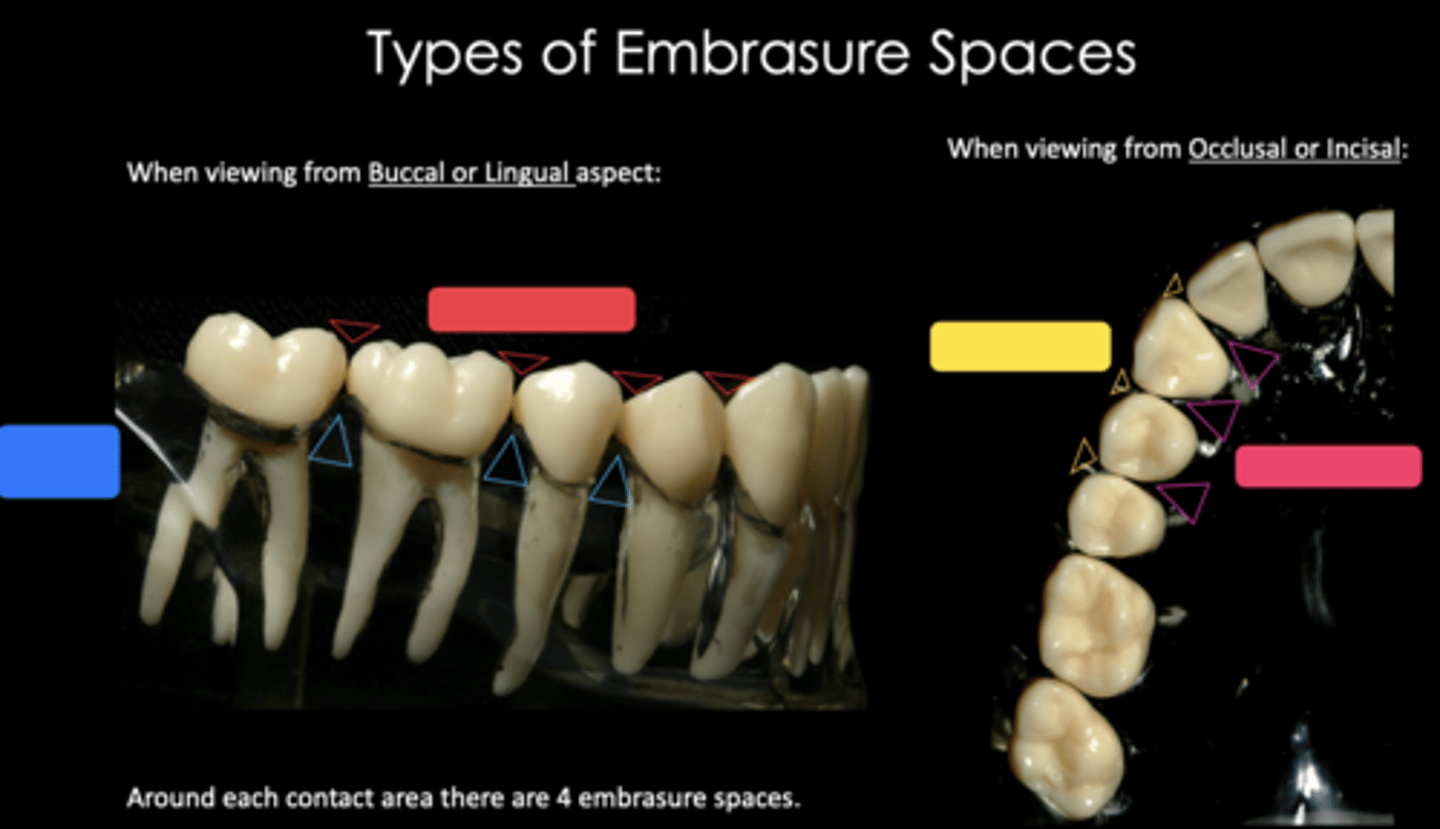
Occlusal/incisal
Identify the embrasure space in red
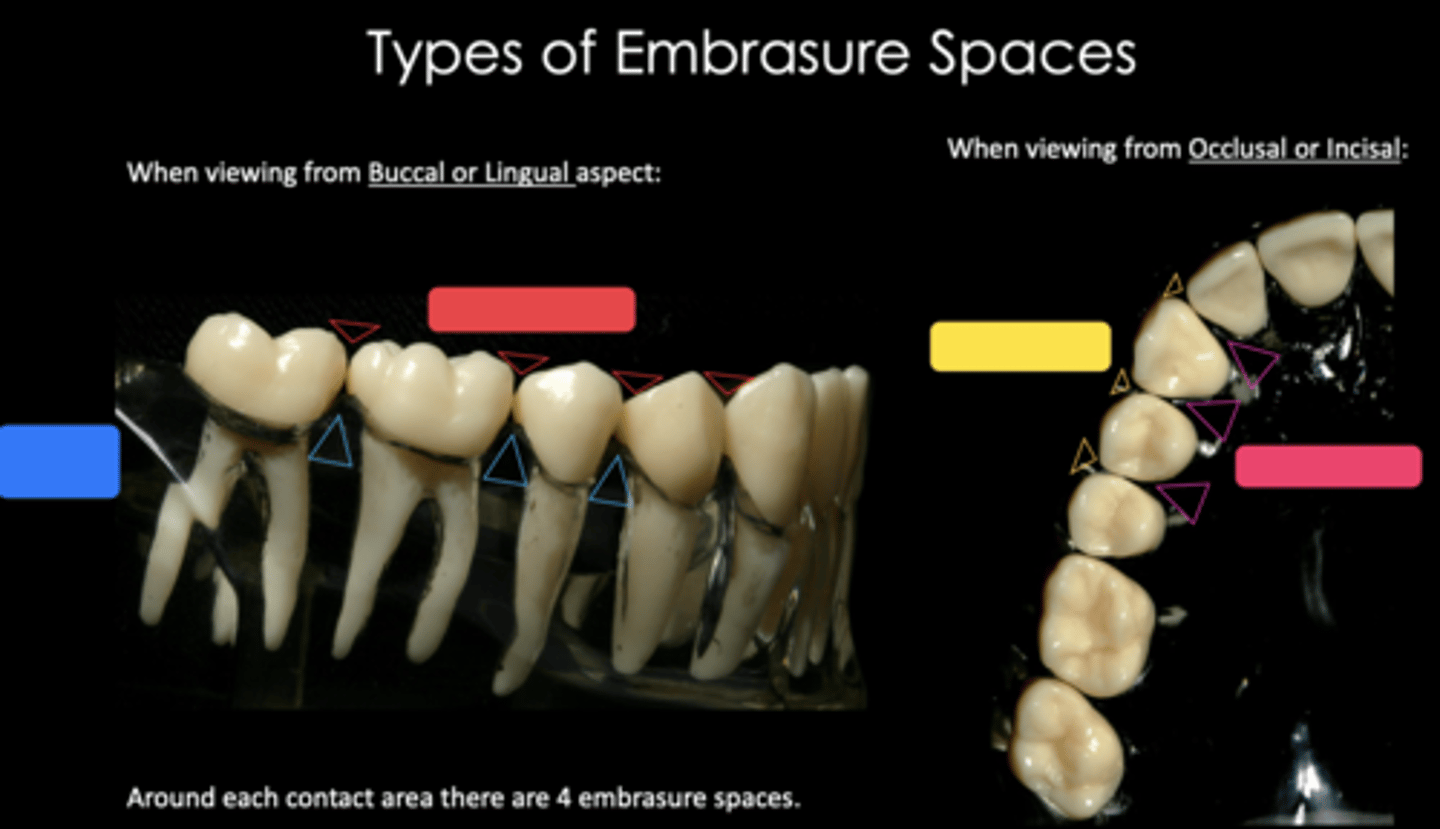
Buccal/labial
Identify the embrasure space in yellow
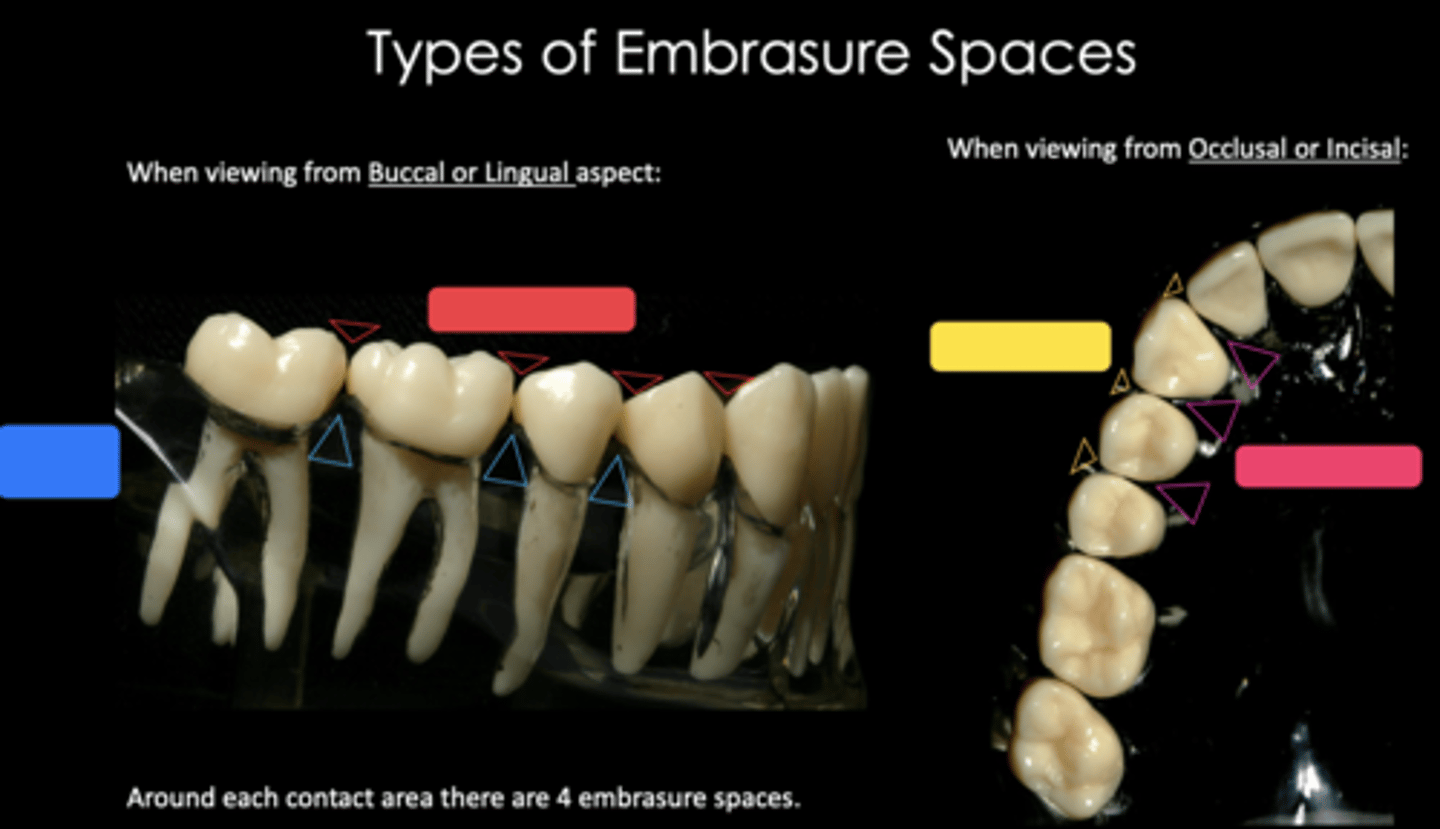
Lingual/palatal
Identify the embrasure space in pink
The facial embrasure between the First and Second Maxillary Molars (1st molar converges buccally instead of lingually)
Lingual embrasures are larger than the facial embrasures because of lingual convergence of the crown, except for...
These facial embrasures are larger on the mesial and distal sides of the Maxillary First Molar
In the permanent maxillary first molars, where are the facial embrasures larger?
The embrasures are approximately the same size due to the symmetrical nature of this tooth
How do the Permanent Mandibular Central Incisors facial and lingual embrasures compare?
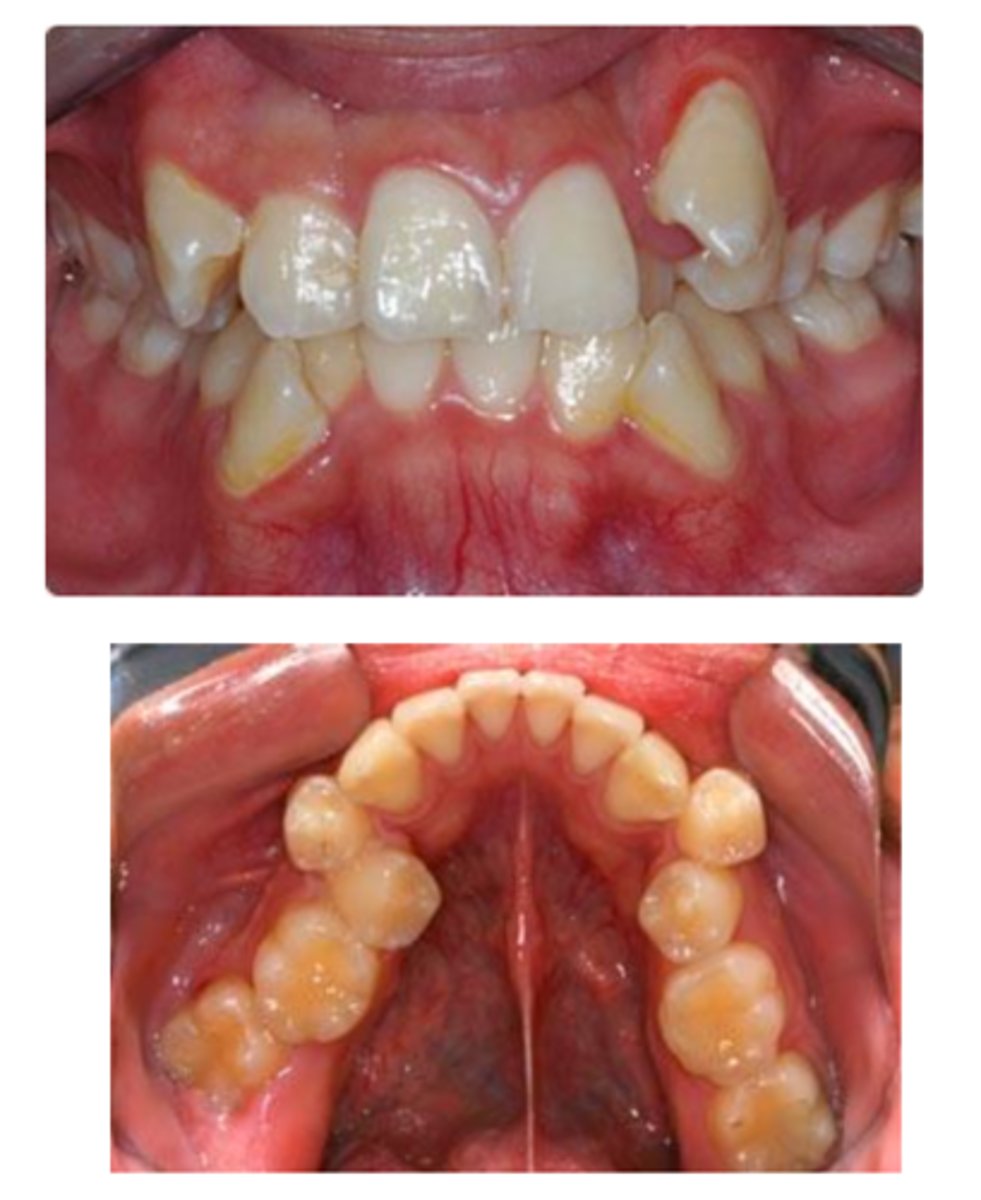
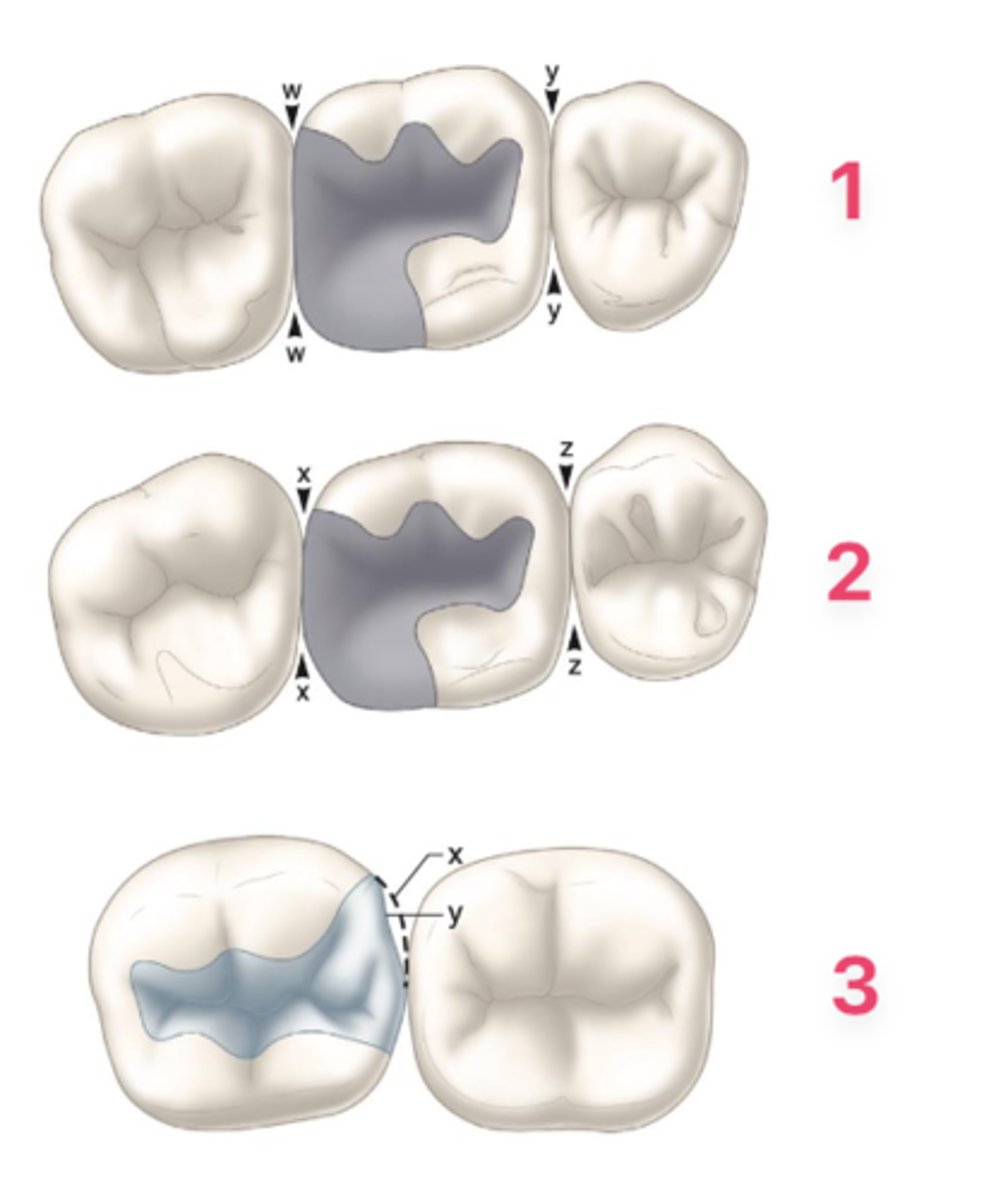
1 - Too closed (can cause food impaction)
2 - Perfect!
3 - Too open (can cause food impaction)
How do these three restorations compare?
Height of contour (Crest of curvature)
Greatest convexity or bulge on the crown of a tooth:
- Protect and stimulate gingival tissues during mastication of food.
- Prevents trauma to the gingiva by moving food away from the gingival collar.
- Prevention of food being forced into the gingival sulcus.
- Subtle enough to prevent food accumulation at the CEJ.
- Aids in the self-cleansing process.
Importance of Proper Contours:
under- stimulation of supporting tissues and will cause food stagnation- can lead to tooth decay
Over-contoured tooth deflects food
from gingiva and results in...
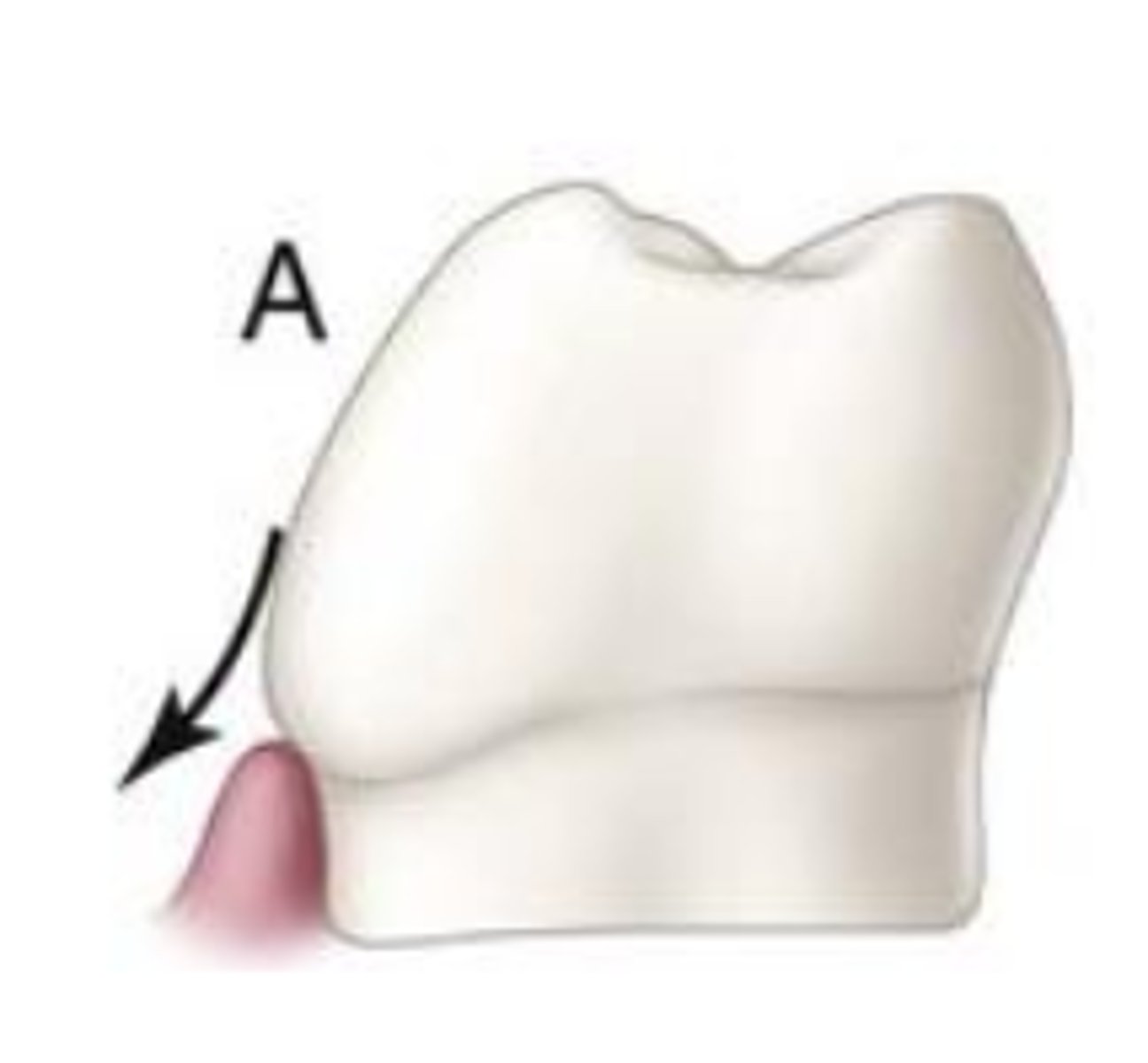
Soft tissue irritation and food impaction
Under-contour of tooth may result in...
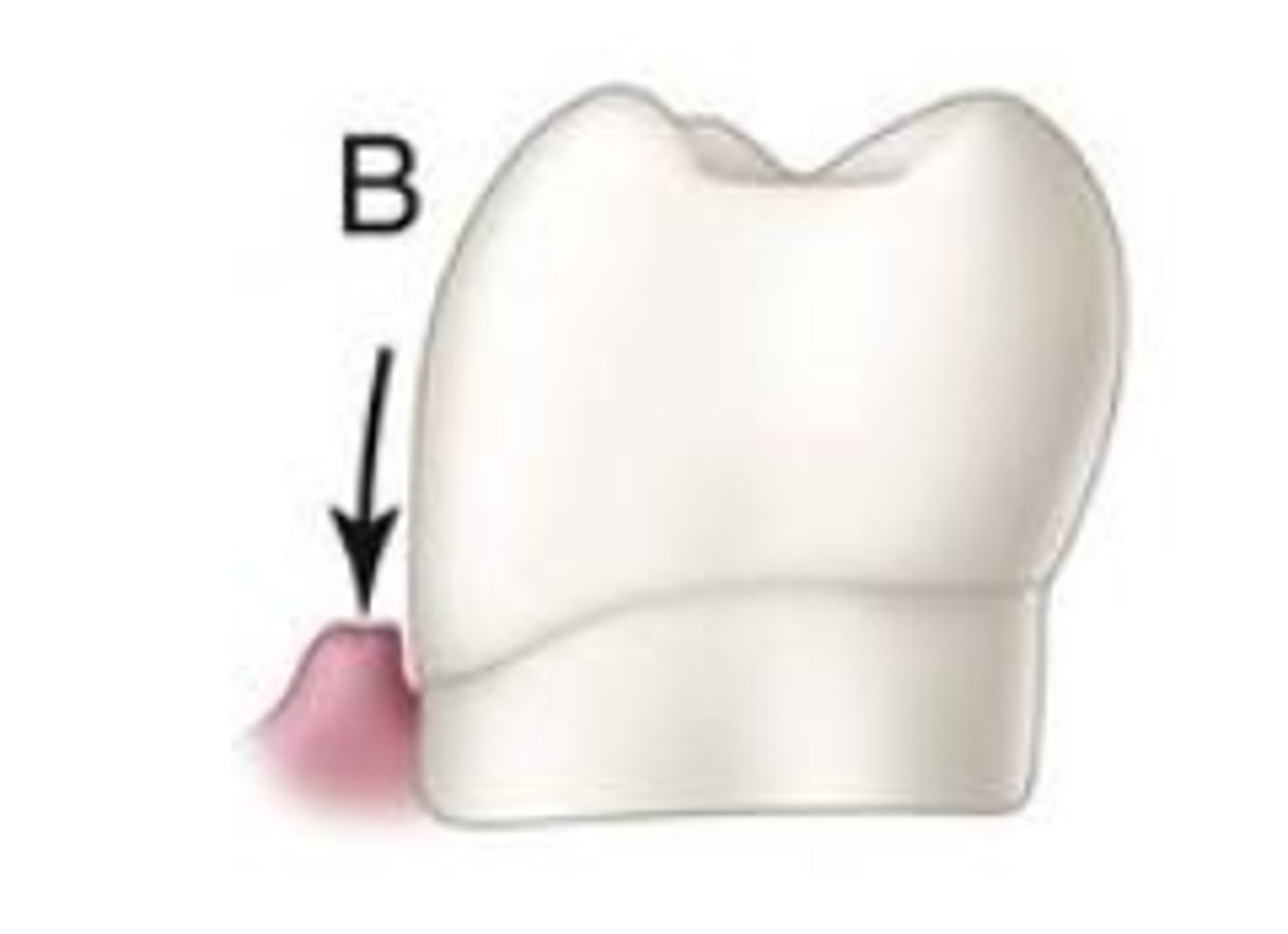
adequate stimulation of supporting tissue, preserving healthy gingival tissue
Correct contours of a tooth permits...
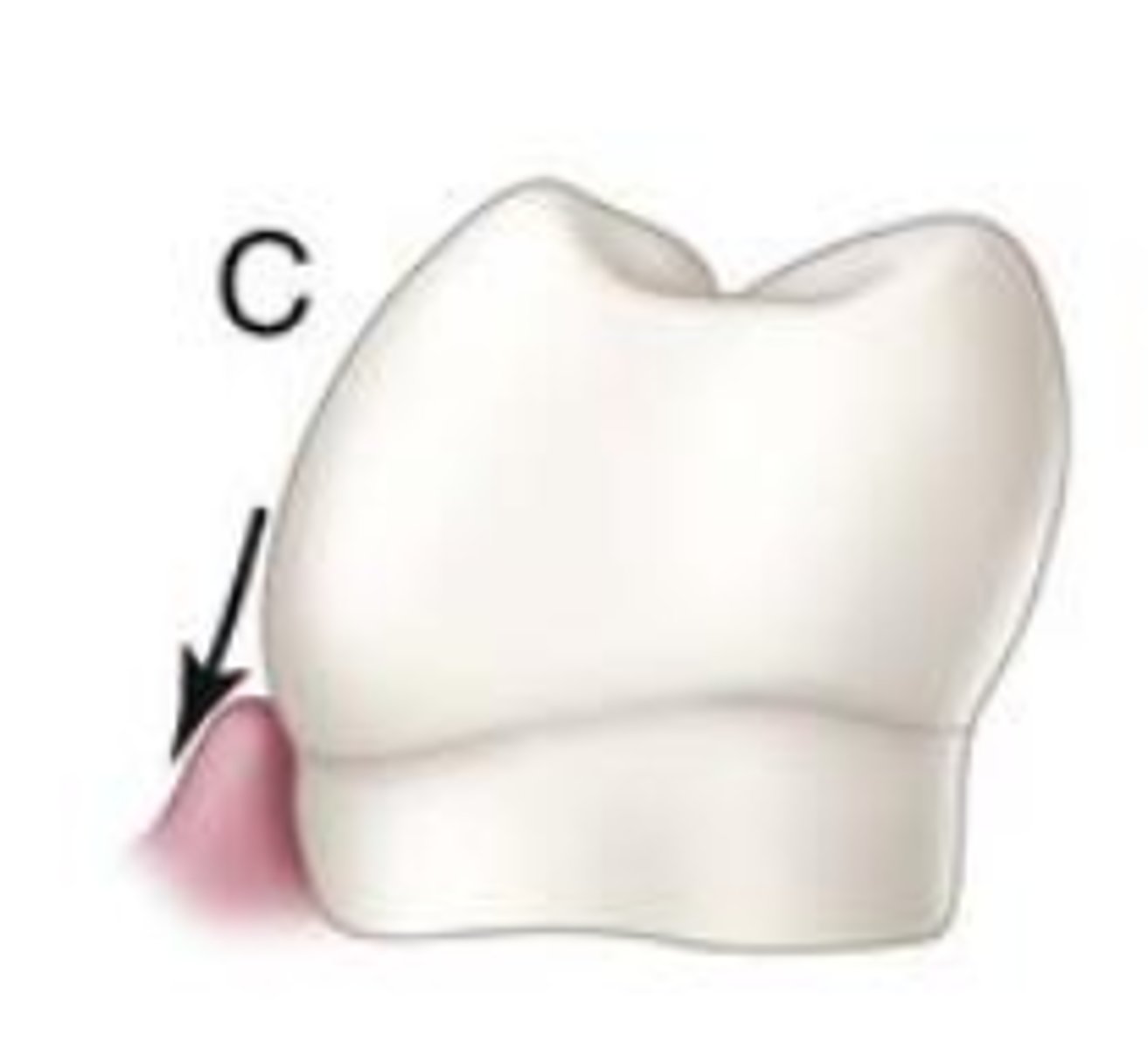
Cervical third
The facial and lingual HOC of all permanent anterior teeth is in the...
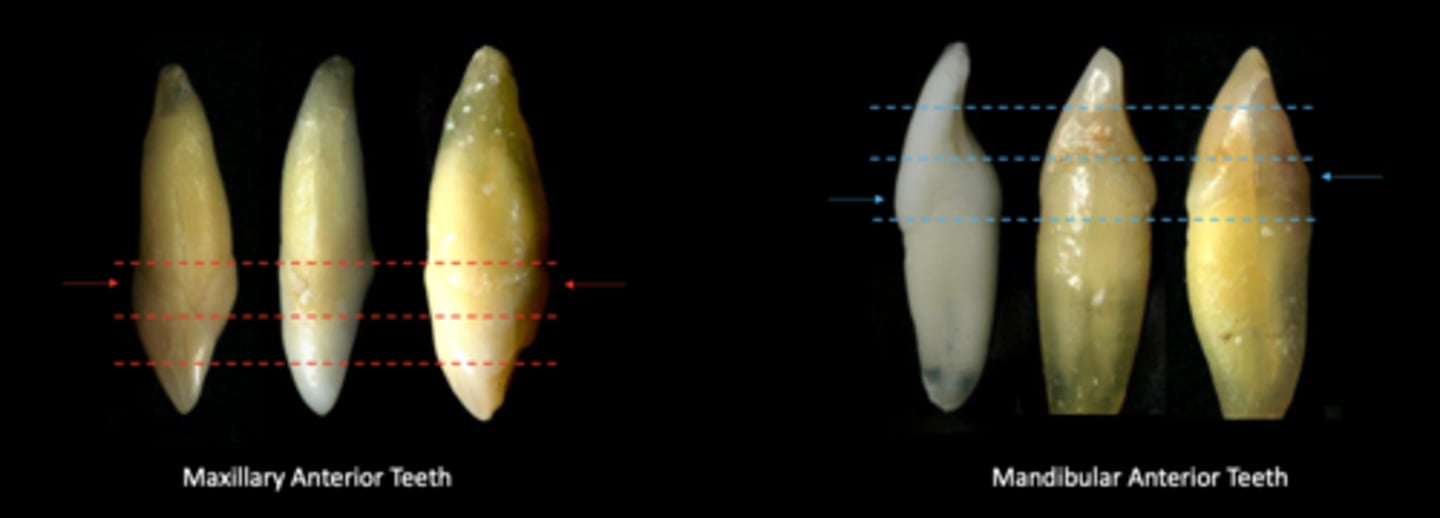
Cervical third
The Facial HOC for all posterior teeth is in the...
incisal third
mesial contact area for maxillary central incisors:
junction of incisal and middle third
distal contact area for maxillary central incisors:
junction of incisal and middle third
mesial contact area for maxillary lateral incisors:
middle third
distal contact area for maxillary lateral incisors:
junction of incisal and middle third
mesial contact area for maxillary canine:
middle third
distal contact area for maxillary canine:
maxillary lateral incisor &
maxillary canine
the largest incisal embrasure is between:
mandibular lateral incisor &
mandibular canine
the second largest incisal embrasure is between:
maxillary central incisor &
maxillary lateral incisor
the third largest incisal embrasure is between:
mandibular central incisors
the smallest incisal embrasure is between:
mandibular central incisor &
mandibular lateral incisor
the second smallest incisal embrasure is between:
maxillary central incisors
the third smallest incisal embrasure is between:
Maxillary canine & maxillary premolar
Largest occlusal embrasure between
middle third
From an incisive view, the facio-lingual locations of interproximal contacts for all anterior teeth are in the _______ of the crown
mesial surface of maxillary and mandibular 1st molars
the occluso-gingival location of interproximal contacts for all posterior teeth are located in the middle third of the crown EXCEPT:
junction of middle and occlusal third
location of mesial interproximal contacts for maxillary and mandibular 1st molars is located :
lingual
generally, which embrasures are larger: lingual or facial?
mesial and distal embrasures of maxillary first molars &
mandibular central incisors and the mesial of the mandibular lateral incisors
lingual embrasures are larger than facial embrasures for all teeth EXCEPT:
mandibular central incisors &
mesial of the mandibular lateral incisors
which teeth have a lingual and facial embrasures that are approximately equal in size.
cervical third
The buccal HOC for maxillary posterior teeth is in the...
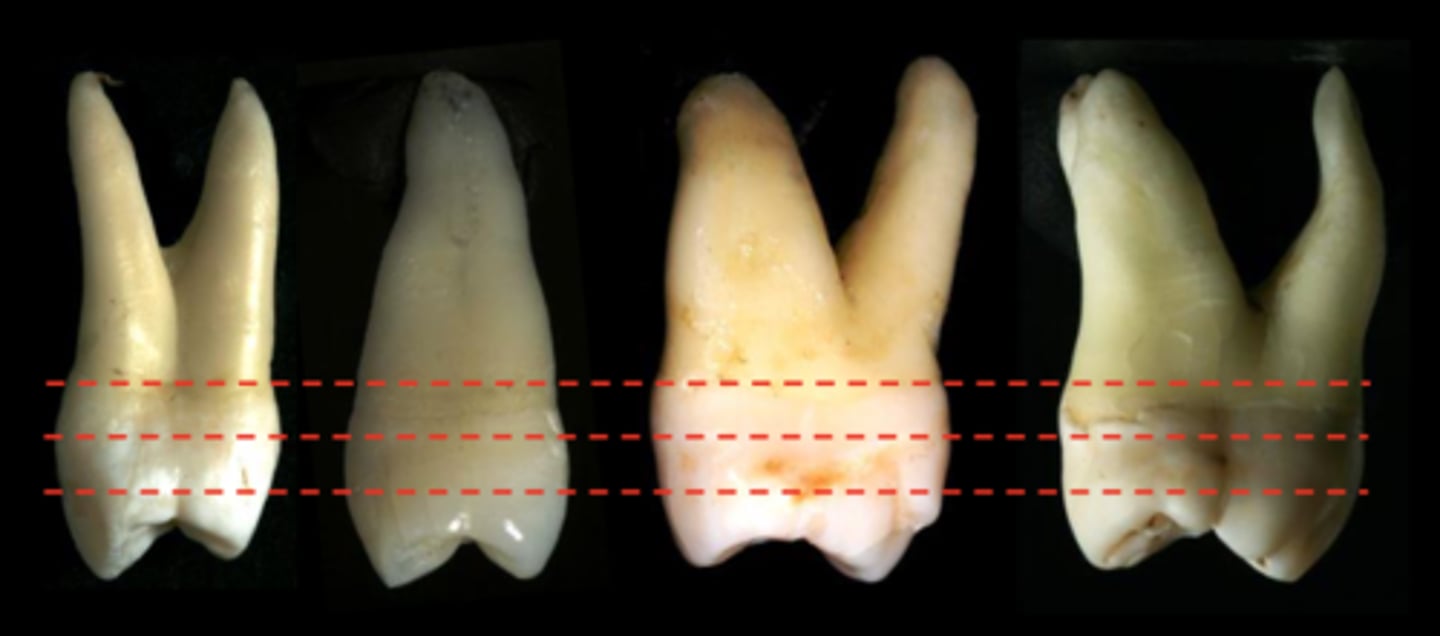
Middle third
The lingual HOC for maxillary posterior teeth is in the...
Cervical third
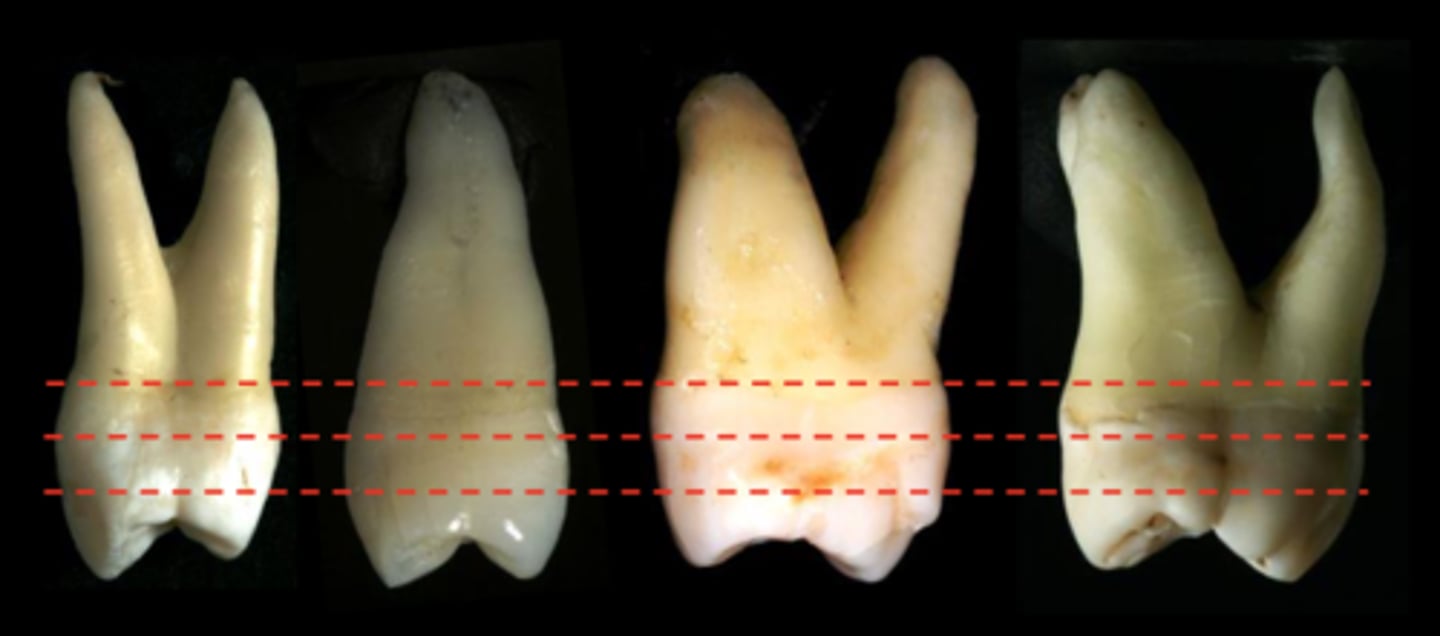
Buccal HOC for mandibular posterior teeth
Middle third
Lingual HOC for mandibular posterior teeth except for mandibular 1st premolar and mandibular 2nd premolar
Middle third but approaches occlusal third
Lingual HOC for mandibular 1st premolar
Occlusal third
Lingual HOC for mandibular 2nd premolar
Mandibular Anterior teeth, which can be as little as 0.5mm
Teeth with the least degree of Facial/Lingual HOC
Mandibular molars, which can be as great as 1mm
Teeth with the greatest degree of facial/lingual HOC
Contact areas
The mesial and distal HOC are normally located at the...
A little more facially
Mesial surfaces of First Molars have their Facio-lingual contacts located
Junction of middle and occlusal thirds of crowns
Mesial surface of First molars have their occlusal gingival contacted located at the
True
T/F: Mesial and Distal embrasures of Permanent Maxillary First possess larger Facial/Buccal embrasures, due to the unique morphology of this tooth
True
T/F: The Permanent Mandibular Centrals and the Mesial of the Mandibular Lateral Incisors possess Facial and Lingual embrasures that are approximately the same size or are equal in size
True, except for Maxillary first molars and Mandibular Central/Lateral Inscisors
T/F: generally, lingual embrasures are larger than facial embrasures for all teeth
middle third
generally, the lingual heights of contour of maxillary and mandibular posterior teeth are in the ______ of the crowns, but there are exceptions.
mandibular second premolar
what tooth's lingual height of contour is in the occlusal third of the crown (this is the only posterior tooth with this characteristic)
mandibular molars
The teeth with the greatest degree of facial/buccal or lingual heights of contour are the:
mandibular anterior teeth
The teeth with the least degree of facial/buccal or lingual height of contour are the:
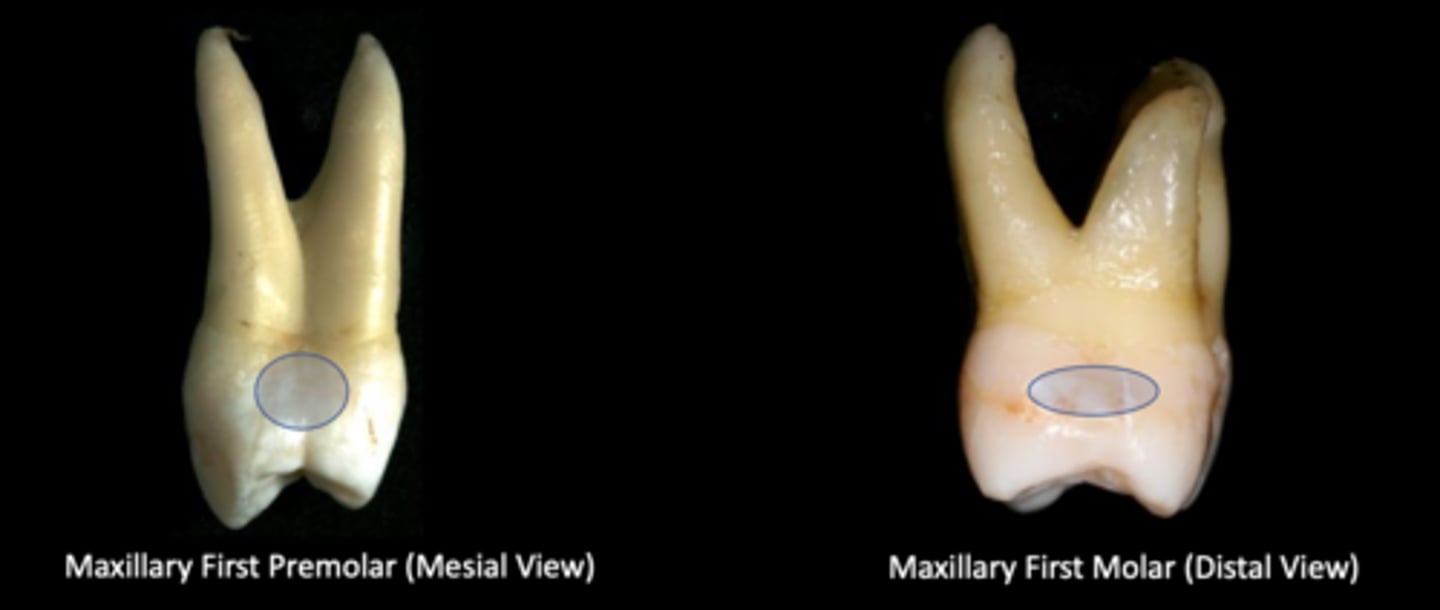
mesial surface of maxillary 1st premolar (deep) and distal surface of maxillary 1st molar which have concavities
Mesial and distal contours of the crowns of all permanent teeth are either flat or convex, except for what two teeth that have concavities?
Their contours are concave
What is unique about the mesial surface of maxillary 1st premolar and distal surface of maxillary 1st molar?
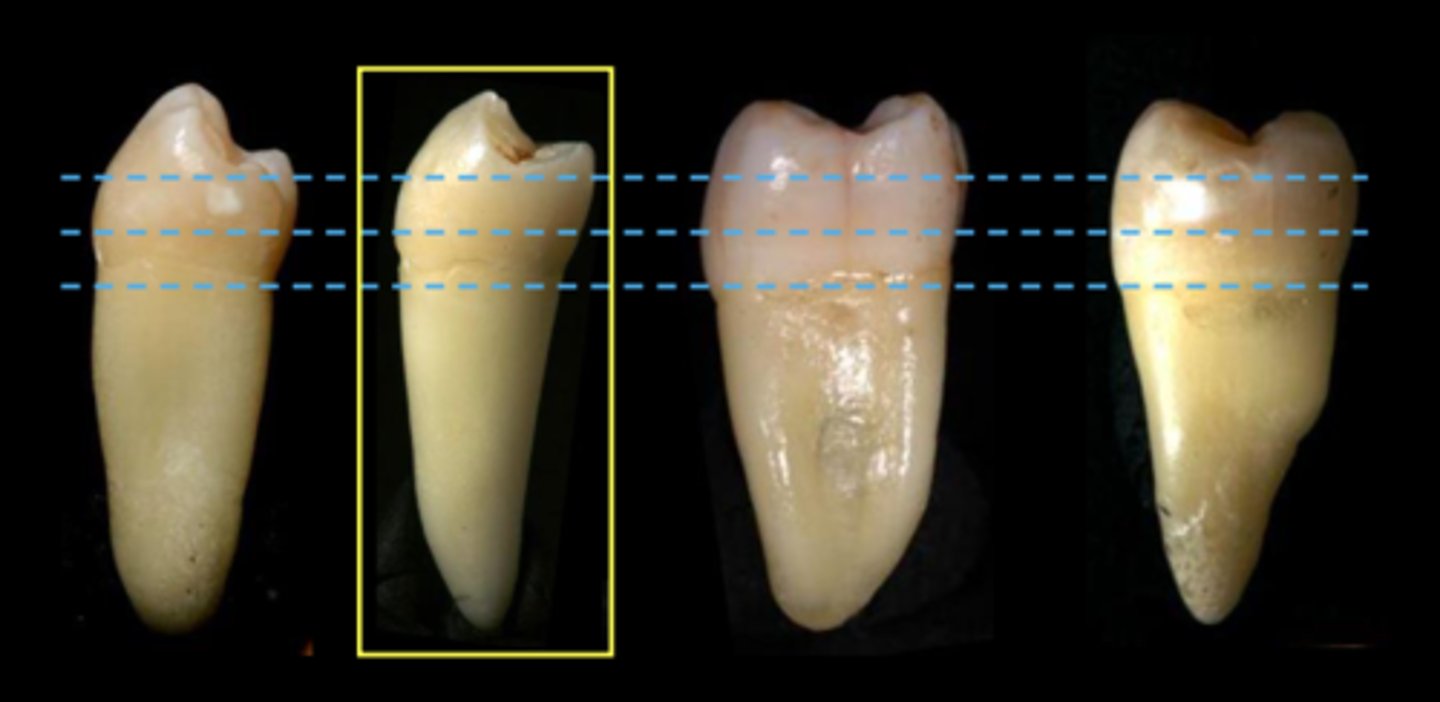
greater
The more anterior the tooth, the ______ is the curve of the cervical line.
less
The more posterior the tooth, the ________ the curve of the cervical line.
greater
Generally, the mesial surface of a tooth has a ________ curvature than the distal
greater
The curvature of the cervical line for any tooth type (e.g., Central Incisors) is _______ on the Maxillary tooth when compared to the same surface of the same tooth type of the Mandibular arch
trapezoidal
All permanent tooth crowns, when viewed from the facial or lingual, are_________ in shape
wedge (or triangular)
All permanent anterior crowns, when viewed from the interproximal, are ______ in shape
trapezoidal
All maxillary posterior permanent tooth crowns, when viewed interproximally, are _______ in shape
rhomboidal
All Mandibular Posterior Permanent tooth crowns, when viewed from the interproximal, are ________ in shape
triangular
from an incisal view, maxillary and mandibular anterior teeth are ______ in shape
hexagonal
from an occlusal view, maxillary premolars are ______ in shape
rhomboidal
from an occlusal view, maxillary molars are ______ in shape
diamond
from an occlusal view, mandibular 1st premolars are ______ in shape
round (2-cusp type) or square (3-cusp type)
from an occlusal view, mandibular 2nd premolars are ______ in shape
hexagonal
from an occlusal view, mandibular 1st molars are ______ in shape
rectangular
from an occlusal view, mandibular 2nd molars are ______ in shape
Anterior teeth
Do anterior or posterior teeth have a greater CEJ curvature?
Maxillary
Do mandibular or maxillary teeth have a greater CEJ curvature?
Permanent
Do permanent or primary teeth have a greater CEJ curvature?
Mesial
Generally, does the mesial side of a tooth or distal side have a greater CEJ curvature?