Don't hate the player
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
A 70-year-old woman presents with a 1-hour history of crushing substernal chest pain. Shortly after admission, the patient expires. An autopsy reveals calcium deposits in the intima of coronary arteries affected by atherosclerosis. Which of the following terms describes this autopsy finding?
a. Dystrophic calcification
b. Hyperplastic calcification
c. Hypertrophic calcification
d. Metastatic calcification
e. Physiological calcification
a. Dystrophic calcification
Activated oxygen (oxygen radicals) can be produced by all of the following except...
a. Ionizing radiation
b. Biological aging
c. Reperfusion injury after ischemia
d. excessive studying
d. excessive studying
Granulation tissue contains type 3 collagen, ...
a. Neutrophils
b. Baso-phils
c. Type 4 collagen- basement membrane
d. Newly formed capillaries
d. Newly formed capillaries
A 32-year-old woman has an abnormal cervical Pap-smear. A cervical biopsy is obtained. This cross section of endocervix shows normal columnar epithelium at both margins and a focus of squamous epithelium in the center. which of the following terms best describes the adaptions to chronic injury?
a. Atrophy
b. Dysplasia
c. Hyperplasia
d. Hypertrophy
e. Metaplasia
e. Metaplasia
Enlargement of myocardial cells as a result of longstanding hypertension is an example of
a. Hypertrophy
b. Hyperplasia
c. Metaplasia
d. Dysplasia
a. Hypertrophy
an indigestible foreign body is likely to produce
a. an abscess
b. acute inflammation with resolution
c. acute inflammation leading to chronic inflammation
d. glanulomatous inflammation
d. glanulomatous inflammation
the following statement about polymorphonuclear neutrophils is true:
a. They perform phagocytosis
b. They are antigen presenting cells
c. They secrete histamines
d. They are usually seen in chronic inflammation
a. They perform phagocytosis
the following inflammatory mediator is derived from plasma
a. bradykinin
b. thromboxane
c. histamine
d. prostagladins
a. bradykinin
the following statement about macrophages is true:
a. they are derived from megakaryocytes
b. they express CD4 surface antigens
c. they secrete antibodies
d. they are antigen-presenting cells
d. they are antigen-presenting cells
Leukocyte rolling is mediated by
a. Selectins
b. Integrins-adhesion
c. Adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily
d. Complement- cell signaling and tagging
a. Selectins
Basement membrane contains
a. Type I collagen- final phase of repair tissue
b. Type II collagen
c. Type III collagen- intermediate phase of repair tissue
d. Type IV collagen
d. Type IV collagen
The following cell type secretes antibodies
a. T helper cells- does not have antibodies
b. T suppressor cells- does not have antibodies
c. B cells- antibodies on cell membrane
d. Plasma cells
d. Plasma cells
The following cellular change is a characteristic of irreversible cell injury
a. Hydropic swelling of the endoplasmic reticulum
b. Swelling of the mitochondria
c. Nuclear pyknosis- nucleus decreases in size during NECROSIS
d. Plasma membrane blebs
c. Nuclear pyknosis- nucleus decreases in size during NECROSIS
14. The following is a characteristic of necrosis
a. DNA fragmentation by endonucleases
b. Intense inflammatory response
c. Cytoplasmic buds
d. Rapid shrinking in size of cell
b. Intense inflammatory response
A 48-year-old man from Nigeria complains of persistent cough, night sweats, and fever. A sputum culture grows acid-fast bacilli. The patient is diagnosed with miliary tuberculosis. He subsequently dies of respiratory failure. Examination of the lungs at autopsy reveals numerous scattered granulomas composed of amorphous granular material surrounded by chronic inflammatory cells. Which of the following terms best describes these pathological findings?
a. Caseous necrosis
b. Coagulative necrosis
c. Dystrophic calcification
d. Liquefactive necrosis
e. Metastatic calcification
a. Caseous necrosis
A 25-year-old carpenter punctures his thumb with a rusty nail. Within 24 hours, the wound becomes a 1-cm red sore that drains a thick, yellow fluid. Which of the following biologic processes accounts for tissue swelling at the site of injury in this patient
a. Complement fixation
b. Endothelial cell separation
c. Neutrophil chemotaxis
d. Platelet aggregatio
c. Neutrophil chemotaxis
A 58-year-old woman with autoimmune hemolytic anemia was transfused with 24 units of blood over a period of 3 years. She subsequently dies of pneumonia. At autopsy, the liver shows accumulation of brown material, primarily within Kupffer cells, which stains blue with a Prussian blue stain. What is the term for this pigment?
a. Anthracosis
b. Melanin
c. Hemosiderin
d. Lipofuscin
e. Transferrin
c. Hemosiderin
A keloid is
a. Cytokine
b. An inflammatory cell
c. A hypertrophic scar
d. A byproduct of the complement cascade
c. A hypertrophic scar
The following is important in opsonization
a. C3a
b. C3b
c. C5a
d. C5b
b. C3b
the following are characteristics of inflammation except
a. Tumor
b. Dolor
c. Horror
d. rubor
c. horror
A 10-year-old girl is brought into the physician's office in mild respiratory distress. She has a history of allergies to cats and wool and her parents state that she has recurrent episodes of respiratory tract infections. Physical examination shows expiratory wheezes and use of accessory respiratory muscles. Which of the following mediators of inflammation is most likely responsible for mast cells degranulation in the lungs of this patient with bronchial asthma?
a. Bradykinin
b. C3a and C5a
c. Interleukin 1
d. Kallikrein
e. Tumor necrosis factor alpha
b. C3a and C5a- anaphylatoxins
A 30-year-old man presents with fever and headache. His blood pressure is 190/130. His serum creatinine is 6.0. A kidney biopsy is obtained. By microscopy, you observe an artery that is inflamed and exhibit amorphous pink substance in the wall. Which of the following best accounts for the pink material in this patient with polyarteritis nodosa?
a. Coagulative necrosis
b. Dystrophic calcification
c. Fat necrosis
d. Fibrinoid necrosis
e. Liquefactive necrosis
d. Fibrinoid necrosis- injured blood vessels
edema with a low protein count is known as a
a. transudate
b. serosanguinous exudate
c. fibrinous exudate
d. purulent exudate
a. transudate
serotonin is released by
a. mast cells
b. basophils
c. platelets
d. neutrophils
c. platelets
activation of Hageman Factor (Factor XII) leads to
a. Activation of arachidonic acid metabolism
b. Production of oxygen free radicals
c. Activation of complement cascade
d. Synthesis of angiotensin II
c. Activation of complement cascade
a female neonate is born after a 38-week gestation. Physical examination reveals syndactyly affecting the third and hour toes of the left foot. This developmental birth defect is most likely associated with failure to activate which of the following families of enzymes?
a. Caspase
b. Elastase
c. Phospholipase
d. Sphingomyelinase
a. Caspase
Aspirin inhibits
a. The cyclooxygenase pathway
b. The lipoxygenase pathway
c. Kallikrein
d. Phospholipases
a. The cyclooxygenase pathway
A 68-year-old coal miner is admitted for evaluation of shortness of breath. The patient was a heavy smoker of cigarettes over the past 50 years. His face is puffy and red, and the physical examination reveals edema of the lower extremities. The patient subsequently dies of respiratory insufficiency. A section of a mediastinal lymph node is examined at autopsy. The blurred material observed in this specimen most likely represents which of the following intracellular storage materials?
a. Carbon
b. Hemosiderin
c. Lipofuscin
d. Silica
a. Carbon
Secretion of a cytokine by a macrophage that acts on a local neutrophil is an example of
a. Autocrine function
b. Paracrine function
c. Endocrine function
d. Mixed function
b. Paracrine function
Nitric Oxide is produced by
a. Platelets
b. Neutrophils
c. Endothelial cells
d. Fibroblasts
c. Endothelial cells
During the process of inflammatory cells exiting the intravascular space and migrating to the site of injury firm adhesion is accomplished by
a. Selectins
b. Addressins
c. Integrins
d. Cellular glue
c. Integrins
a granuloma contains
a. Epithelioid histiocytes
b. Neutrophils
c. Mast cells
d. Eosinophils
a. Epithelioid histiocytes
An 88-year-old woman with diabetes and ischemic heart disease dies in her sleep. At autopsy, many hepatocytes contain brown cytoplasmic granules that do not stain with Prussian blue. What is the proper name for this "wear and tear" pigment associated with aging?
a. Amyloid
b. Councilman bodies
c. hemosiderin
d. Hyaline
e. lipofuscin
e. lipofuscin
Which statement about T cells is true?
a. They home to the bone marrow during embryonic development
b. They produce antibodies
c. They recognize antigens in association with MHC molecules
d. They have a granular cytoplasm
c. They recognize antigens in association with MHC molecules
the following statement about Class I MHC molecules correct?
a. They are only expressed on macrophages
b. They are expressed on all cells
c. They play an important role in type I hypersensitivity reactions- IgE
d. They play an important role in antigen presentation- only class II
b. They are expressed on all cells
The antigen presenting cell forms a complex with antigen in association with
a. MHC Class I
b. MHC Class II
c. Cytokines
d. B7 costimulators
b. MHC Class II
A 65-year-old woman presents with a 2-day history of productive cough and fever. Her temperature is high. An x-ray film of the chest shows consolidating ... and sputum cultures are positive for S. pneumoniae. Which of the following terms best describes the primary function of inflammatory cells in this patients...?
a. Antibody productions
b. Cell mediated immunity
c. Fibrinolysis
d. Histamine release
e. Phagocytosis (no option e in guide?)
d. Histamine release
In type I hypersensitivity mast cells are activated by cross- linking of
a. IgA Fc receptors
b. IgD Fc receptors
c. IgE Fc receptors
d. IgG Fc receptors
c. IgE Fc receptors
in apoptosis, ligand binding to the "death receptor" leads to the activation of
a. Caspase 6
b. Caspase 7
c. Caspase 8
d. Caspase 9
c. Caspase 8
A sailor on a nuclear-powered submarine is seen by a physician after a breach in the reactor containment system. Physical examination is unremarkable, but the patient subsequently develops profound pancytopenia. His hemoglobin is 7.8. WBC count is 900, and platelet count is 20,000. It is estimated that the sailor received total body radiation. What substance, formed through the radiolysis of water, killed cells in this patient's bone marrow by interacting with proteins, lipids, and DNA?
a. Free fatty acids
b. Hydrogen peroxide
c. Hydroxyl radicals
d. Nitric oxide
c. Hydroxyl radicals
in apoptosis, release of mitochondrial cytochrome C leads to the activation of Apaf-1 and
a. Caspase 6
b. Caspase 7
c. Caspase 8
d. Caspase 9
d. Caspase 9
The following is considered preneoplastic
a. Hypertrophy
b. Hyperplasia
c. Metaplasia
d. Dysplasia
d. Dysplasia
An 80-year-old man suddenly develops crushing substernal chest pain. Analysis of serum troponin and an ECG confirms an acute myocardial infarction. The patient subsequently develops an arrhythmia and expires. What type of necrosis is featured in this photomicrograph of the left ventricle?
a. Caseous necrosis
b. Coagulative necrosis
c. Dystrophic calcification
d. Fat necrosis
e. Liquefactive necrosis
b. Coagulative necrosis
The following statement about tattoos are true
a. The produce granulomas and eventually lead to the development of caseous necrosis
b. They trigger autoimmune disease
c. They consist of metallic and vegetable pigments engulfed by dermal macrophages
d. They trigger type I hypersensitivity reactions
c. They consist of metallic and vegetable pigments engulfed by dermal macrophages
A abscess cavity filled with neutrophils shows
a. Coagulative necrosis
b. Liquefactive necrosis
c. Fat necrosis
d. Caseous necrosis
b. Liquefactive necrosis
The following is characteristic of tuberculosis
a. Coagulative necrosis
b. Liquefactive necrosis
c. Fat necrosis
d. Caseous necrosis
d. Caseous necrosis
hydrogen peroxide is converted to water by
a. superoxide dismutase
b. glutathione peroxidase
c. caspase
d. ceramide
b. glutathione peroxidase
Pancreatitis and trauma are associated with
a. Coagulative necrosis
b. Liquefactive necrosis
c. Fat necrosis
d. Caseous necrosis
c. Fat necrosis
The following is true about bradykinin
a. It is converted to kininogen
b. It is synthesized by kallikrein
c. It is a cell-derived inflammatory mediator
d. It is a potent vasoconstrictor
b. It is synthesized by kallikrein
Apoptosis is
a. Programmed cell death
b. Characterized by nuclear karyolysis
c. Never physiological
d. The only thing on this exam I really know
a. Programmed cell death
Which of the following is involved in cell adhesion?
a. Selectins
b. Addresins
c. Integrins
d. Cellular glue
c. Integrins
Histamines are released by
a. Mast cells
b. Lymphocytes
c. Platelets
d. Neutrophils
a. Mast cells
A 62-year-old alcoholic presents to the emergency room with 8 hours of severe abdominal pain and vomiting. Physical examination discloses exquisite abdominal tenderness. Serum levels of amylase and piase are elevated. In this patient with acute pancreatitis, fatty acids are precipitated as soaps in complex with which of the following?
a. Calcium
b. Chloride
c. Magnesium
d. Potassium
e. Sodium
a. Calcium
A 5-month-old female infant is brought to the physician after a 3 day period of severe coughing, wheezing, and respiratory distress. Physics examination shows rhinorrhea, mild cyanosis, and fever. Despite respiratory treatment, the infant dies of respiratory insufficiency and complications of viral pneumonia. Histologic examination of the lung at autopsy shows a bronchiole with an intense inflammatory cell infiltrate. The infiltrate is primarily composed of which of the following inflammatory cells?
a. Eosinophils
b. Lymphocytes
c. Macrophages
d. Mast cells
e. Neutrophils
e. Neutrophils
A 12-year-old girl presents with a 6 day history of hypertension, oluguria, and hematuria. She was seen 6 months earlier for a severe throat infection with group A streptococci. Physical examination shows puffiness around the eyes and putting edema of the lower extremities. Which of the following best characterizes the patient's peripheral edema?
a. Effusion
b. Fibrinous exudate
c. Purulent exudate
d. Serosanguinois exudate
e. Transudate
e. Transudate
A 15-year-old boy receives a deep laceration in his right leg during a hockey game. The wound is cleaned and sutured. Compared to healing by secondary intention, healing by primary intention in this patient is characterized by an increased rate of which of the following biological processes?
a. Angiogenesis
b. Collagen deposition
c. Neutrophil chemotaxis
d. Re-epithelialization
e. Smooth muscle hyperplasia
d. Re-epithelialization
A 10-year-old girl lacerated her thumb picking up broken glass in the kitsch. Four hours later, the wound appears red and swollen. Compared to granulation tissue, the scar tissue that forms in this patient's hand will contain more of which of the following components?
a. Blood vessels
b. Cross-linked collagen
c. Edema fluid
d. Macrophages
e. proteoglycans
b. Cross-linked collagen
An 18-year-old woman present with a 6 month history of malaise, joint pain, weight loss, and sporadic fever. Her is high. Other physical findings include malar rash, erythematous pink plaques with telangiectatic vessels, and unbalancing purpuric papules on her legs. Laboratory studies show elevated levels of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine. Antibody to double stranded DNA is positive. Which of the following best explains the pathogenesis of glomerulonephropathy in this patient?
a. Antibody- dependent cellular cytotoxicity
b. Antibody-mediated complement fixation
c. Cell-mediated hypersensitivity
d. Immediate hypersensitivity
e. Immune complex disease
e. Immune complex disease
A 20-year-old woman presents with a runny nose. In addition to a viral infection, which of the following is a possible mechanism of acute rhinitis in this patient?
a. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
b. Antibody-dependent complement-mediated cytolysis
c. Delayed type hypersensitivity reaction
d. IgE mediated mast cell granulation
e. Immune complex deposition in arterioles and capillaries
d. IgE mediated mast cell granulation
A 20-year-old man presents to his family physician for treatment of itching after exposure to poison ivy. The patient's hands and arms appears red and are covered with oozing blisters and crusts. Which of the following cells plays the most important role in the pathogenesis of this patient's hypersensitivity reaction?
a. B lymphocytes
b. Basophils- type I hypersensitivity
c. Eosinophils
d. PMNs
e. T cells- type IV delayed type hypersensitivity
e. T cells- type IV delayed type hypersensitivity
A 10-year-old girl is rushed to the emergency room after suffering a tonic clonic seizure 3 weeks after visiting a cave. The child appears irritable and agitated. Laboratory studies establish a diagnosis of rabies and encephalitis. What glycoprotein in the surface of target cells is required for lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity of virally infected cells in this patient?
a. CD4
b. CD8
c. HLA class I
d. HLA Class II
e. IgM
c. HLA class I
A 40-year-old man complains of having yellow skin and sclerae. Physical examination reveals jaundice and hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies demonstrate elevated serum bilirubin, decreased serum albumin, and prolonged prothrombin time. Serologic tests reveal antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen. The serum is also positive fir HBsAg and HBeAg. Which of the following glycoproteins serves as a specific cell surface marker for cytotoxic lymphocytes in this patient with viral hepatitis?
a. CD4
b. CD8 - 8
c. HLA CLASS I
d. HLA CLASS II
e. Membrane immunoglobulin
b. CD8 – 8
In an COVID-19 Antibody Test, the presence of which immunoglobulin suggests an active virus?
IgM
In an COVID-19 Antibody Test, the presence of which immunoglobulin suggests acquired immunity?
IgG
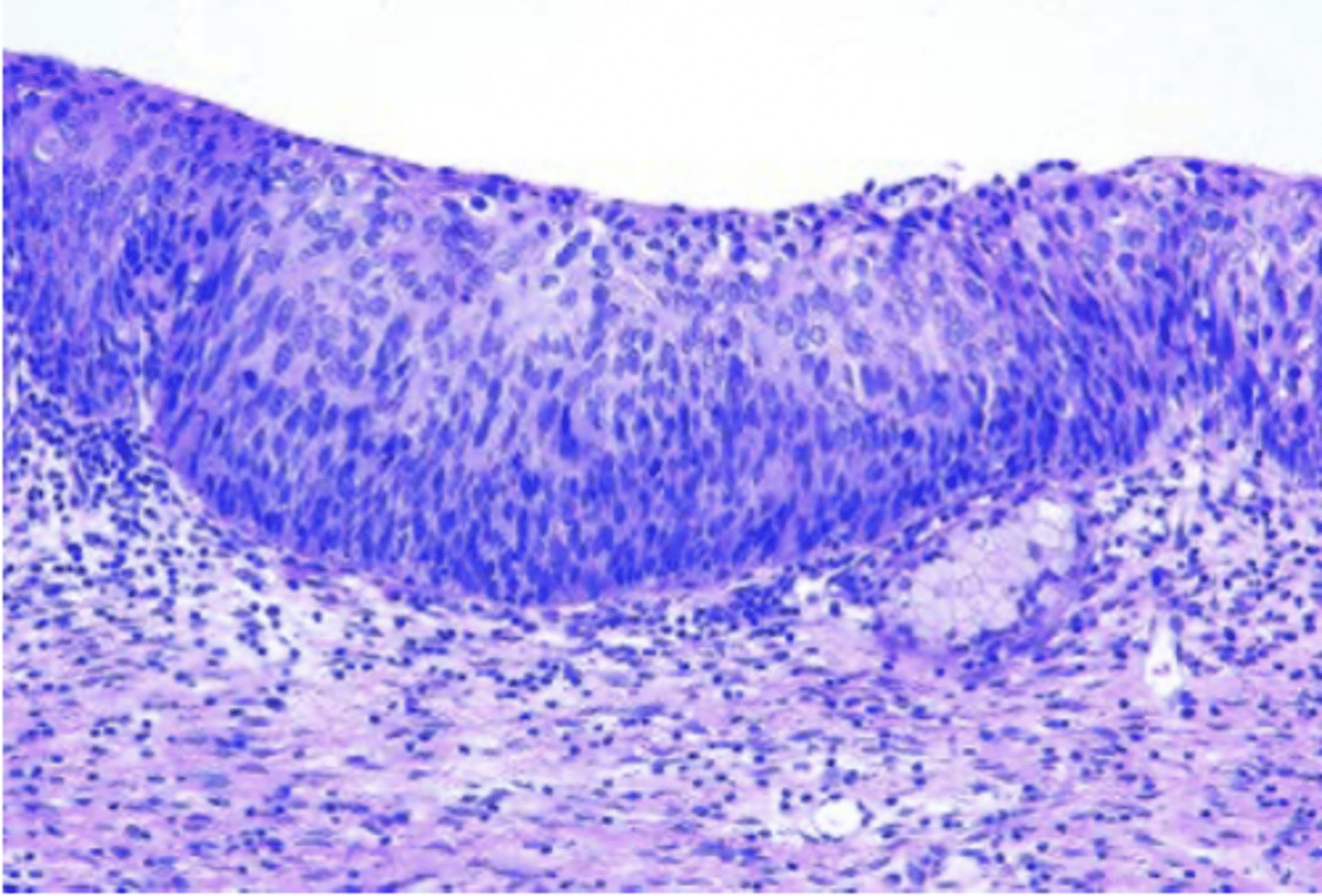
A 32-year-old woman has an abnormal cervical Pap smear. A cervical biopsy is obtained.This section of endocervix shows normal columnar epithelium at both margins and a focus of squamous epithelium in the center (biopsy shown). Which of the following terms best describes this adaptation to chronic injury?
A) Atrophy
B) Dysplasia
C) Hyperplasia
D) Hypertrophy
E) Metaplasia
E) Metaplasia
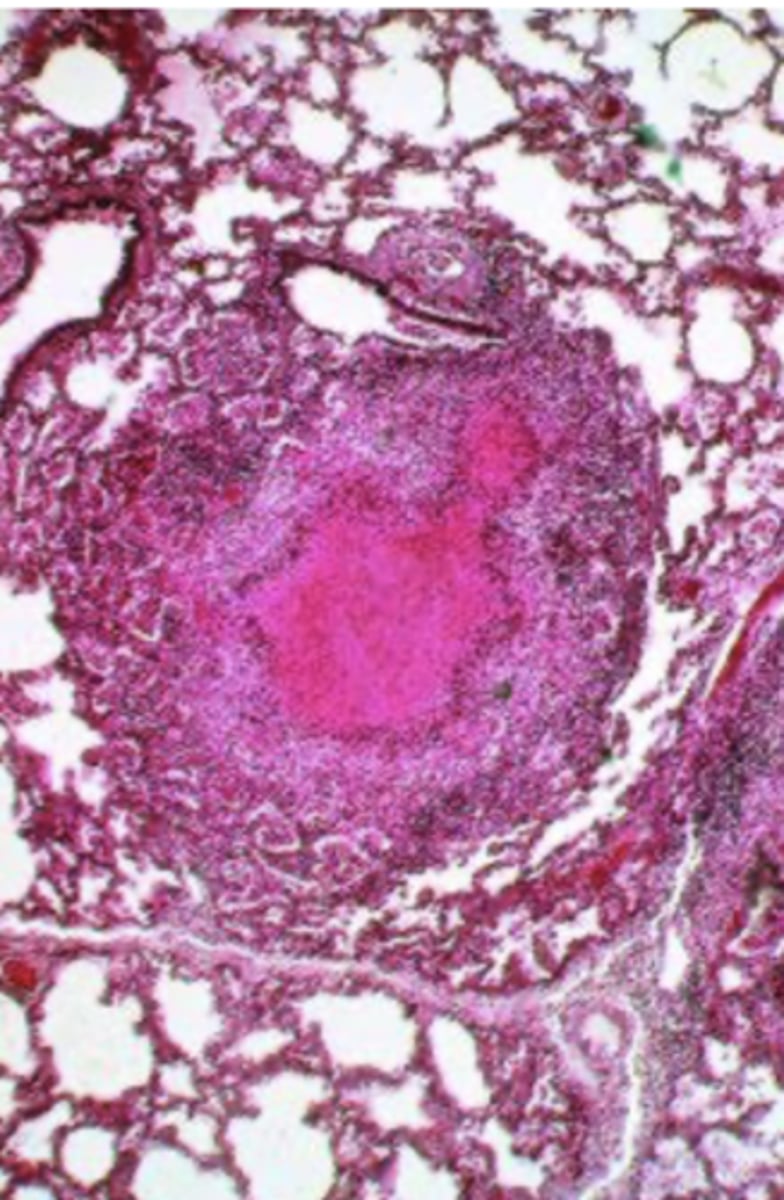
A 48-year-old man from Nigeria complains of persistent cough, night sweats, and fever. A sputum culture grows acid-fast bacilli. The patient is diagnosed with miliary tuberculosis. He subsequently dies of respiratory failure. Examination of the lungs at autopsy reveals numerous scattered granulomas composed of amorphous granular material surrounded by chronic inflammatory cells (shown). Which of the following terms best describes these pathologic findings?
a. caseous necrosis
b. coagulative necrosis
c. dystrophic calcification
d. liquefactive necrosis
e. metastatic calcification
a. caseous necrosis
A 56-year-old woman with a history of hyperlipidemia and hypertension develops progressive, right renal artery stenosis. Over time, this patient's right kidney is likely to demonstrate which of the following morphologic adaptations to partial ischemia?
a. atrophy
b. dysplasia
c. hyperplasia
d. hypertrophy
e. neoplasia
a. atrophy
A 59-year-old man suffers a massive heart attack and expires 24 hours later due to ventricular arrhythmia. Histologic examination of the affected heart muscle at autopsy would show an abundance of which of the following inflammatory cells?
a. fibroblasts
b. lymphocytes
c. macrophages
d. neutrophils
e. plasma cells
d. neutrophils
A 36-year-old woman with pneumococcal pneumonia develops a right pleural effusion. The pleural fluid displays a high specific gravity and contains large numbers of polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes. Which of the following best characterizes this pleural effusion?
a. fibrinous exudate
b. lymphedema
c. purulent exudate
d. serosanguieous exudate
e. transudate
c. purulent exudate
Aspirin is effective in relieving symptoms of acute inflammation because it inhibits which of the following enzymes?
a. cyclooxygenase
b. myeloperoxidase
c. phospholipase A2
d. protein kinase C
e. superoxide dismutase
a. cyclooxygenase
A 74-year-old woman presents with acute chest pain and shortness of breath. Cardiac catheterization demonstrates occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Laboratory studies and ECG are consistent with acute myocardial infarction. Which of the following is the most likely pathologic finding in the affected heart muscle 4 weeks later?
a. Capillary-rich granulation tissue
b. Collagen-rich scar tissue
c. Granulomatous inflammation
d. Neutrophils and necrotic debris
e. Vascular congestion and edema
b. Collagen-rich scar tissue
A 4-year-old boy falls on a rusty nail and punctures his skin. The wound is cleaned and covered with sterile gauze. Which of the following is the initial event in the healing process?
a. Accumulation of acute inflammatory cells
b. Deposition of proteoglycans and collagen
c. Differentiation and migration of myofibroblasts
d. Formation of a fibrin clot
e. Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of cellular debris
d. Formation of a fibrin clot
A 41-year-old woman complains of pelvic pain of 4 months. Endometrial biopsy reveals an excess of plasma cells and macrophages within the stroma. The presence of these cells within the endometrial stroma is evidence of which of the following conditions?
a. acute inflammation
b. chronic inflammation
c. granulation tissue
d. granulomatous inflammation
e. menstruation
b. chronic inflammation
An 82-year-old man dies 4 years after developing congestive heart failure. He had a history of multiple myocardial infarcts over the past 10 years. A trichrome stain of heart muscle at autopsy is shows areas with bright blue staining. What is the predominant type of collagen found in this mature scar tissue?
a. type I
b. type II
c. type IV
d. type V
e. type VI
a. type I
A 58-year-old woman undergoes lumpectomy for breast cancer. One month following surgery, she notices a fi rm 0.3-cm nodule along one edge of the surgical incision. Biopsy of this nodule reveals chronic inflammatory cells, multinucleated giant cells, and extensive fibrosis. The multinucleated cells in this nodule most likely formed in response to which of the following pathogenic stimuli?
a. bacteria infection
b. foreign material
c. lymphatic obstruction
d. neoplastic cells
e. viral infection
b. foreign material
A CT scan of a 43-year-old woman with a parathyroid adenoma and hyperparathyroidism reveals extensive calcium deposits in the lungs and kidney parenchyma. These radiologic findings are best explained by which of the following mechanisms of disease?
a. arteriosclerosis
b. dystrophic calcification
c. granulomatous inflammation
d. metastatic calcification
e. tumor embolism
d. metastatic calcification