ecology chapter 20
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
primary production
the rate at which chemical energy in an ecosystem is generated by autotrophs, derived from the fixation of carbon during photosynthesis and chemosynthesis
majority of energy on earth comes from photosynthesis. True or False?
True
Gross primary production
the amount of energy that autotrophs capture by photosynthesis and chemosynthesis per unit of time.
The GPP in most terrestrial ecosystems is equivalent to the total of all plant photosynthesis. True or False?
True
The GPP of an ecosystem is controlled by…
climate through it’s influence on rates of photosynthesis
Leaf area index
the area of leaves per unit ground area
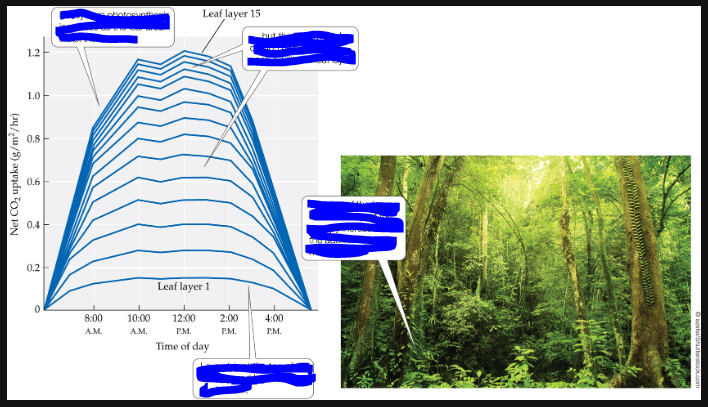
what is labeled?
ecosystem photosynthesis increases as the leaf area index increases
but the incremental carbon gain is less for each additonal leaf layer
shading of the leaves below the top of the canopy increases with the addition of each new leaf layer
Layer 1 is at the top of the canopy and layer 15 is at the bottom
A plant uses all of the carbon it fixes by photosynthesis. True or False?
False, A plant uses approximately half of the carbon it fixes by photosynthesis in cellular respiration to support biosynthesis and cellular maintenance.
All living plant tissues lose carbon via….
respiration
plant that have a large proportion of nonphotosynthetic stem tissue tend to…
have higher overall respiratory carbon losses than herbaceous plants.
plant respiration rates increase with increasing temperatures and as a result…
respiratory carbon losses are higher in tropical forests than in temperate and boreal forests
net primary production
the amount of energy per unit of time that producers capture by photosynthesis and chemosynthesis, minus the amount they use in cellular respiration.
The equation of net primary production
NPP = GPP - respiration
NPP of a terrestrial ecosystem is the amount of energy captured by autotrophs that results in….
an increase in living plant matter, or biomass
the energy left over for plant growth, plant reproduction, defense, and consumption by herbivores and detritivores
NPP
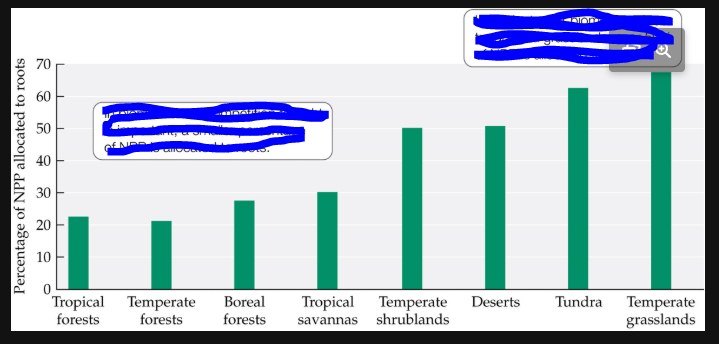
what is labeled?
in nutrient-poor biomass, such as tundra and grasslands, over 50% of NPP is allocated to roots
in biomes where competition for light is important, a smaller percentage of npp is allocated to roots.