B2.1 Membranes and membrane transport
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Structure of phospholipids
Hydrophobic tails made of a glycerol and a phosphate molecule
Hydrophilic tails made of fatty acid chains
Molecular size affects
Membrane permeability
Diffusion
Net movement of particles from a higher to a lower concentration
When can simple diffusion only happen
If phospholipid bilayer is permeable to particles
State and define the two membrane proteins
Integral proteins: Penetrate the phospholipid bilayer to remain permanently attached to the membrane
Peripheral proteins: Only appear on one side of protein
Examples of integral proteins
Glycoproteins
Ion channels
Carrier proteins
Protein pumps
Examples of peripheral proteins
G proteins
Any other protein that are receptor complexes involved in cell signalling
Membrane protein functions (JETRAT)
Junctions – Connect + join two cells together
Enzymes – Fixing to membranes localises metabolic pathways
Transport – Responsible for facilitated diffusion + active transport
Recognition – Markers for cellular identification
Anchorage – Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
Transduction – Function as receptors for peptide hormones
Aquaporins
Water channels in some cells
Channel proteins
Transmembrane proteins that connects the cytoplasm to the aqueous solution inside the cell
3 different ways of pump protein in membranes
Using energy (active transport)
Only move particles across membrane (one direction)
Usually moves particles against concentration gradient
Semi-permeable membrane
Allows passage of certain small solutes and is freely permeable to the solvent
Glycoproteins
Conjugated proteins with carbohydrates as the non-polypeptide component
Formation of carbohydrate
Single monosaccharide between 2 and 4 sugar units
Functions of carbohydrate chains
Cell recognition
Attachement points for other cells
Glycocalyx
Carbohydrate-rich layer on the outer face of the plasma membrane of an animal cells
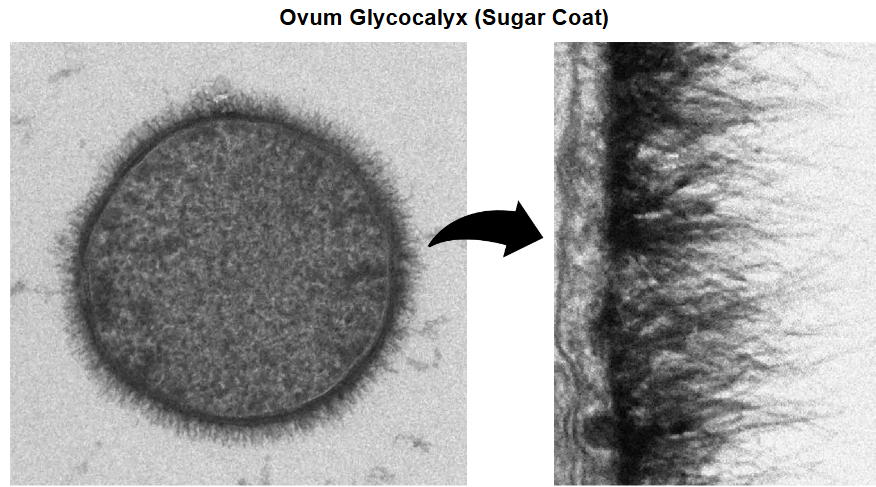
Extracellular matrix
Network for external molecules that provide structure and biochemical support to surrounding cells
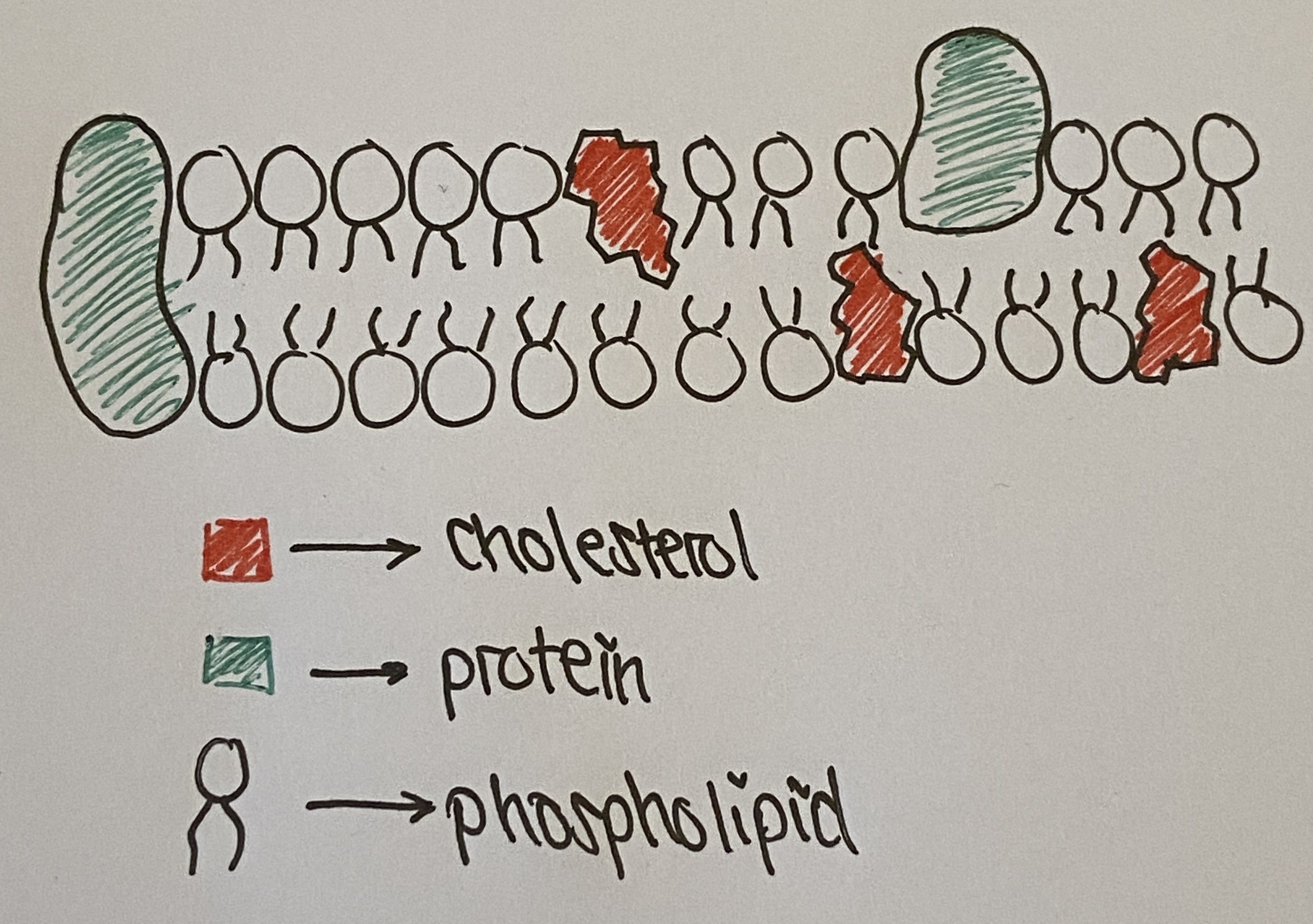
Draw the fluid mosaic model and include:
peripheral and integral proteins, glycoproteins, phospholipids and cholesterol
(draw and label)
Outline the factor of what the fluidity of a membrane is affected by
The composition of fatty acids within the phospholipid bilayer
Distinguish between unsaturated and saturated fats
Unsaturated | Saturated |
high viscosity | low viscosity |
kinky hydrocarbon tail | straight hydrocarbon tail |
low melting point | high melting point |
has double bonds | has no double bonds |
packed together | loosely packed together |
high fluidity | low fluidity |
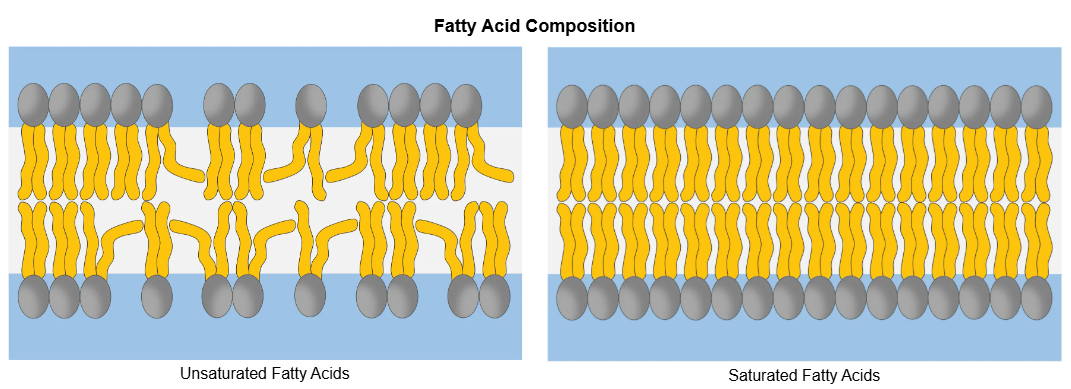
Example(s) of adaptations in membrane composition in relation to habitat
Increasing USFAs at lower temperatures
Increasing SFAs at higher temperatures
Cholesterol
An amphipathic sterol in charge of membrane fluidity
Explain the role of cholesterol in the plasma membrane
At high temps, it stabilises membrane, increases MPs, decreases fluidity
At low temps, it inserts itself between P.L.B.L and prevents stiffness and crystallisation, increases fluidity
Vesicle
Small sac of membrane with a droplet of fluid inside
Facilitated diffusion
Specific ions passing across a membrane in either direction
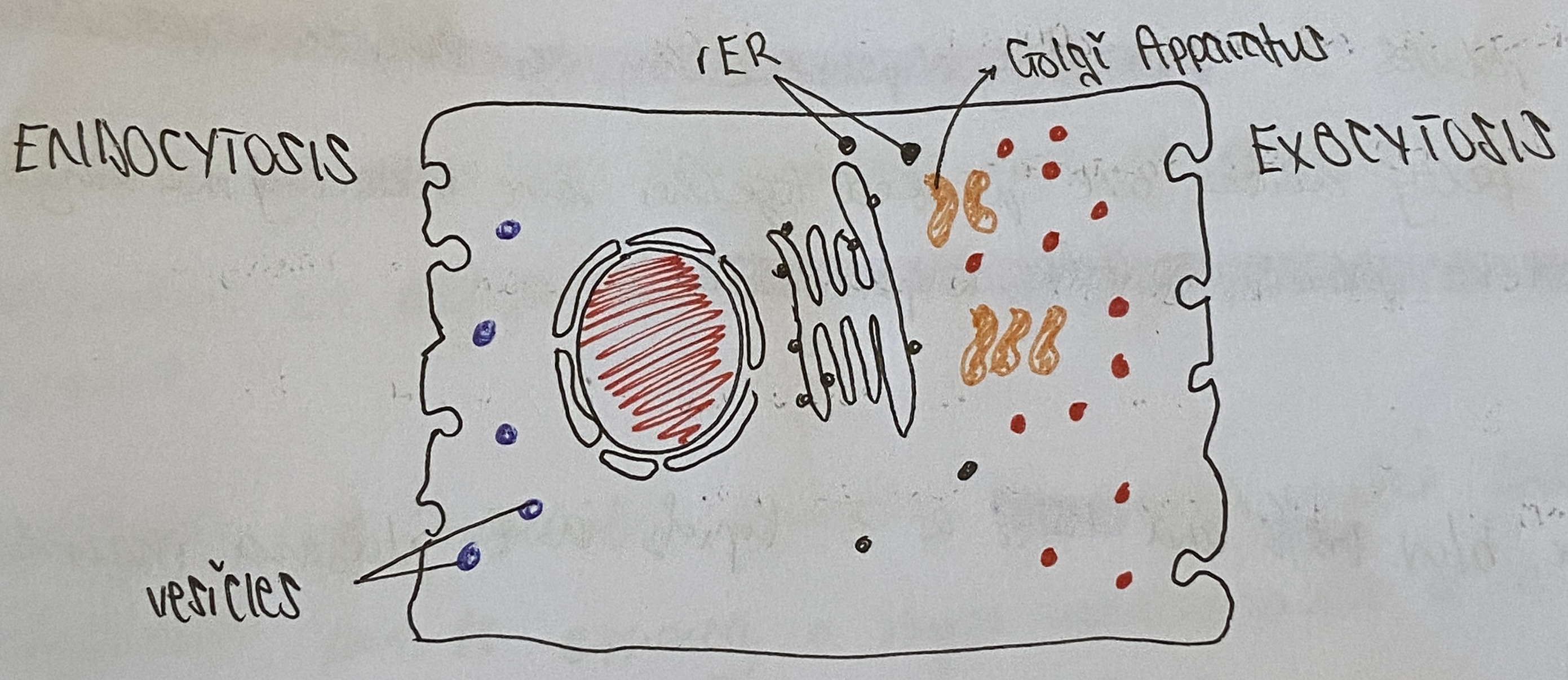
Endocytosis
Large substances enter a cell without passing through the membrane
Invagination of membrane envelopes the molecule
Invagination is sealed off to form an intracellular vesicle
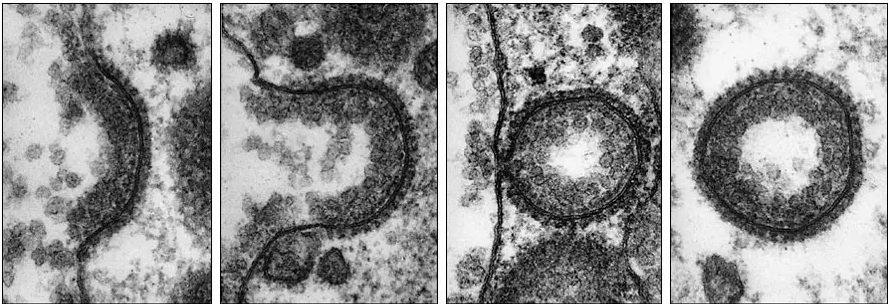
Phagocytosis
Solid substances are ingested
Pinocytosis
Liquids/dissolved substances are ingested
Exocytosis
Large substances leave the cell without crossing the membrane
Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane
This process adds vesicular phospholipids to cell membrane
Ion channels
Integral membrane protein that has a hydrophilic inner pore which ions pass
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter released from the nerve cells to stimulate adjacent cells
Binding causes a:
Conformational change
Binding of acetylcholine is
Reversible
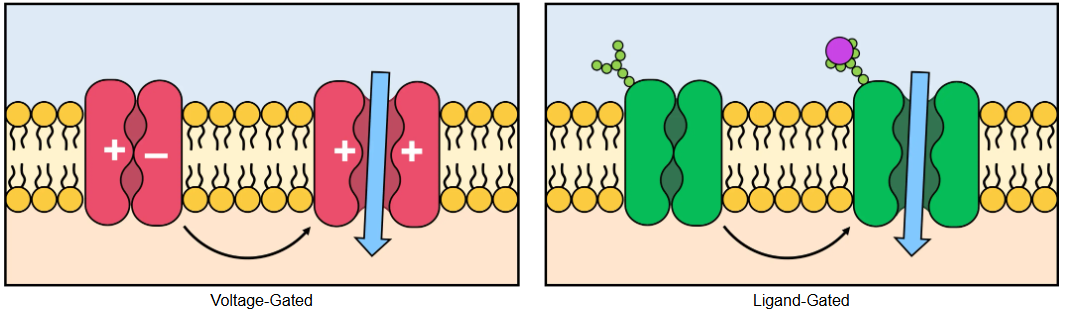
Voltage-gated ion channels + example
Cycle between an open and closed conformation according to the transmembrane voltage
E.g., Sodium-potassium channels
Sodium channels: IN to the neuron (depolarisation)
Potassium channels: OUT of the neuron (repolarisation)
Ligand-gated channels
Change their conformation in response to the binding of a specific chemical (ligand)
Muscles contain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors that will trigger the opening of an ion channel when activated
Draw and distiguish voltage-gated and ligand-gated ion channels
(draw and label)
VOLTAGE
One (+ -) side, one (+ +) side
LIGAND
No + or - sides
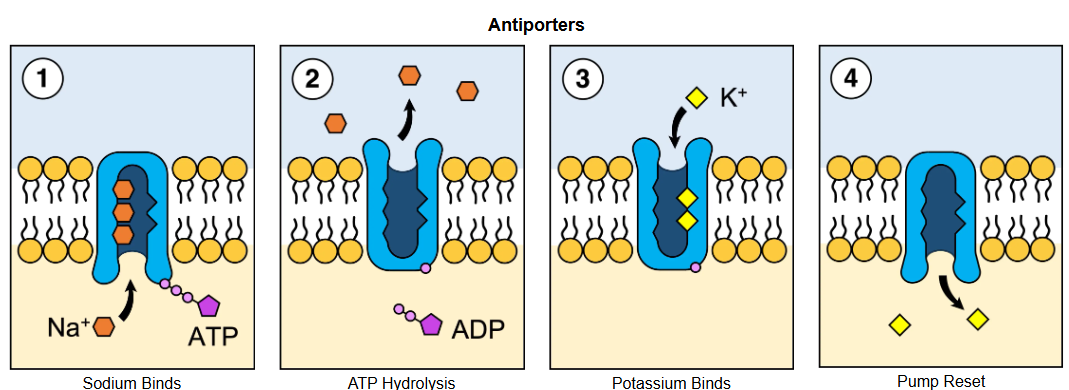
Antitransporters
Move two molecules in opposite directions across the membrane
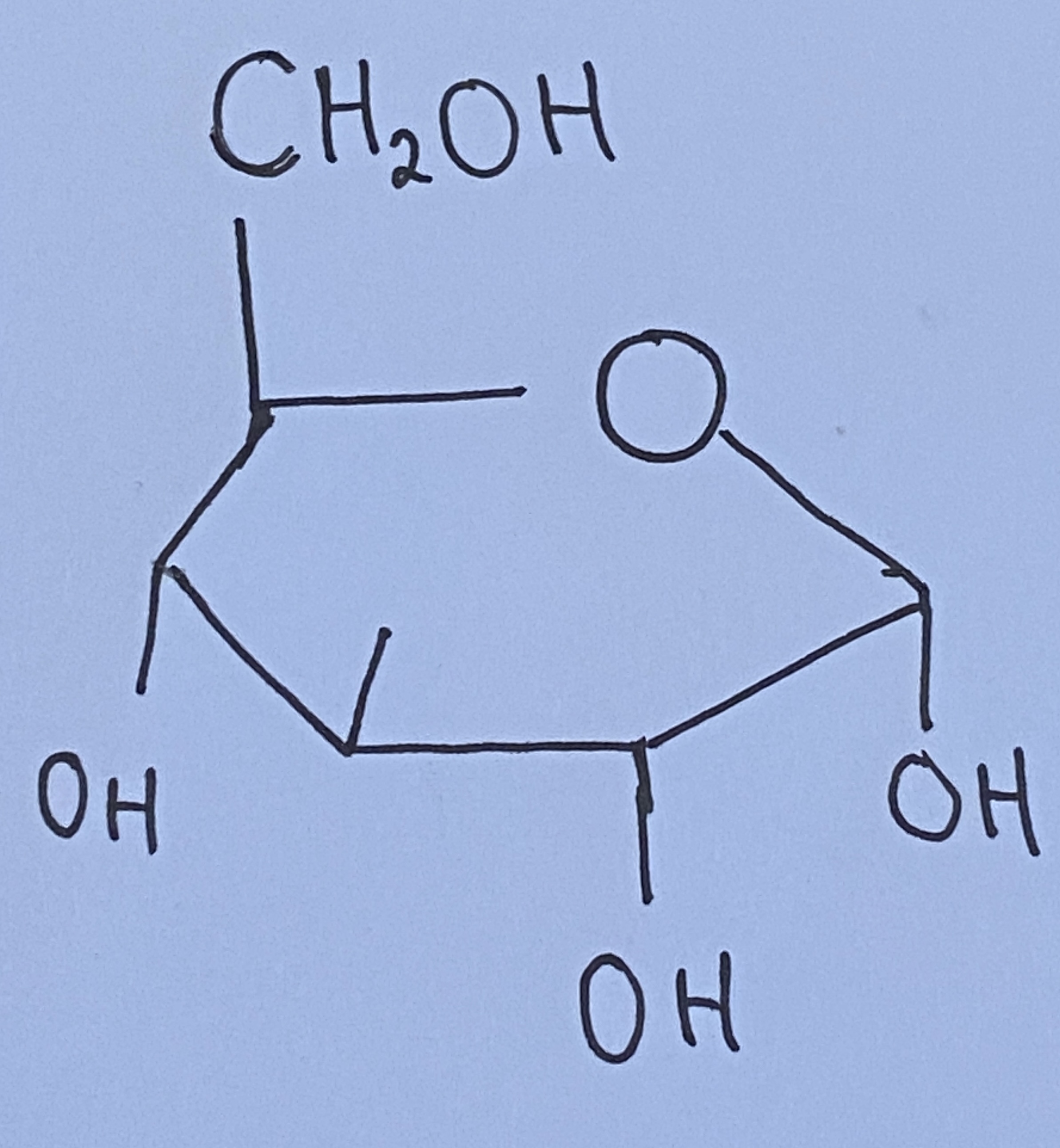
Glucose molecule
(draw and label)
Cotransporters
Link the movement of an ion along its concentration gradient to the movement of a solute against its concentration gradient
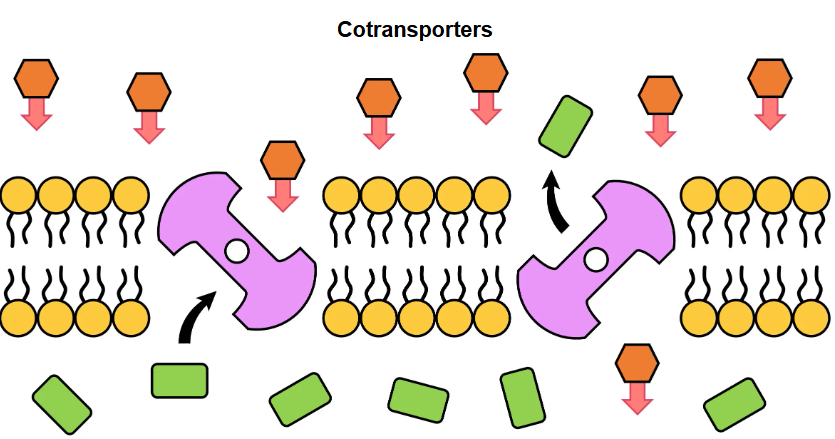
Example of cotransport
The absorption of glucose in the kidneys and small intestine (contransported with sodium ions)
CAMs
Cell-adhesion molecules
Metastasis
Movement of spread of cancer cells
Outlien 4 processes with examples that allow substances to pass through the plasma membrane
Osmosis Diffusion of water from an area of high water potential
Simple diffusion Diffusion from a high concentration to low concentration (e.g. steroid hormones)
Exocytosis Diffusion of vesicles with membranes to release a large molecule (e.g. nuerotransmitters)
Endocyosis The infolding of membranes to form a vesicle and take in a large molecule; (e.g. macrophages engulfing pathogens)
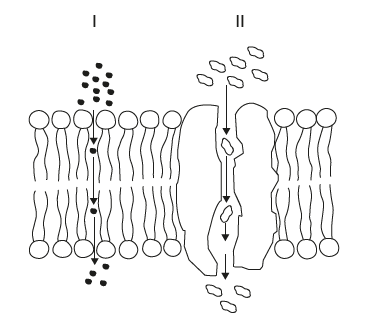
What is happening in I and II?
I: Simple diffusion
II: Facilitated diffusion
Locations of lipid bilayers in cells.
Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts
Function of cell membrane
Acts as a barrier and has ability to control what substances are able to move in and out of it
Anchoring junctions
Holds cells together to strengthen contact within tissues
Tight (occluding) junctions
Create tight seals that result in an impermeable barrier to diffusion
Gap junctions
Links cells together to allow the movement of material between them
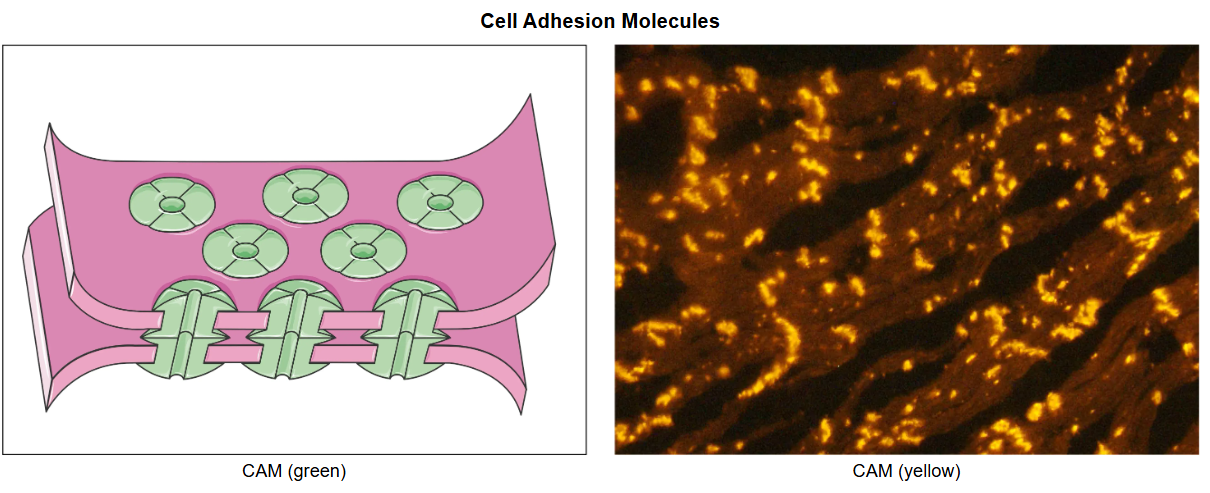
CAMs are typically..
proteins with phospholipid bilayer domains