European Middle Ages, Again
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Middle Ages
the era in European history that followed the fall of the Roman Empire, lasting from about 500 to 1500 A.D.

Franks
a Germanic people who settled in the Roman province of Gaul (present day France) and established a great empire during the Middle Ages.
monastery
a religious community of men (called monks) who have given up their possessions to devote themselves to a life of prayer and worship.

secular
concerned with worldly rather than spiritual matters.

Carolingian Dynasty
A dynasty of Frankish rulers, lasting from 751 A.D. to 987 A.D.

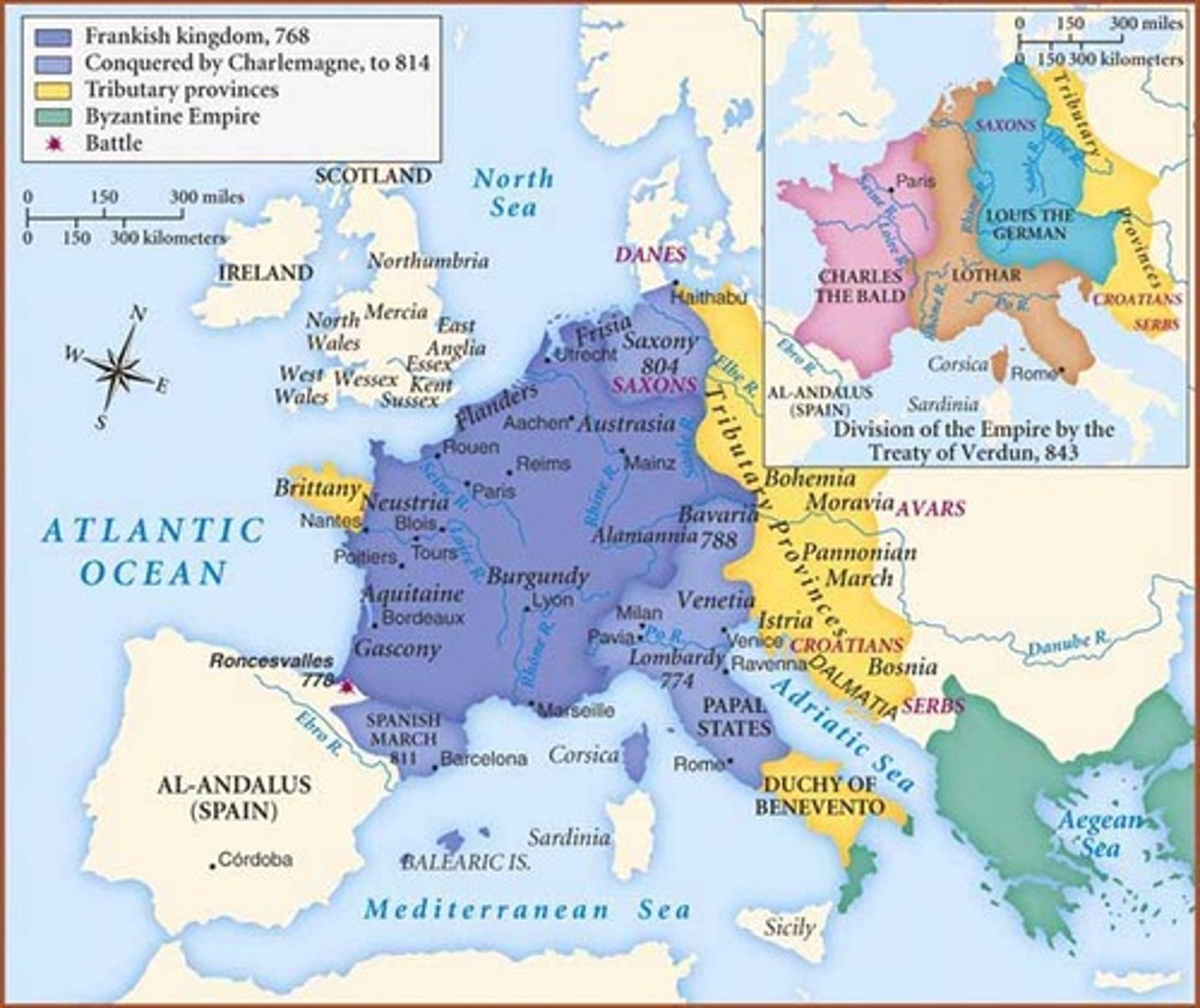
Charlemagne
His name means "Charles the Great." He was king in the late eighth and early ninth centuries and extended his empire by conquests. He was crowned emperor of "The Roman Empire" in 800 by the Pope.

lord
in feudal Europe, a person who controlled land and could therefore grant estates to vassals.

fief
an estate granted to a vassal by a lord under the feudal system in medieval Europe.
vassal
In Feudal Europe, a person who received a grant of land from a lord in exchange for a pledge of loyalty and services.

knight
In medieval Europe, an armored warrior who fought on horseback.

serf
a medieval peasant legally bound to live and work the land on a lord's estate.

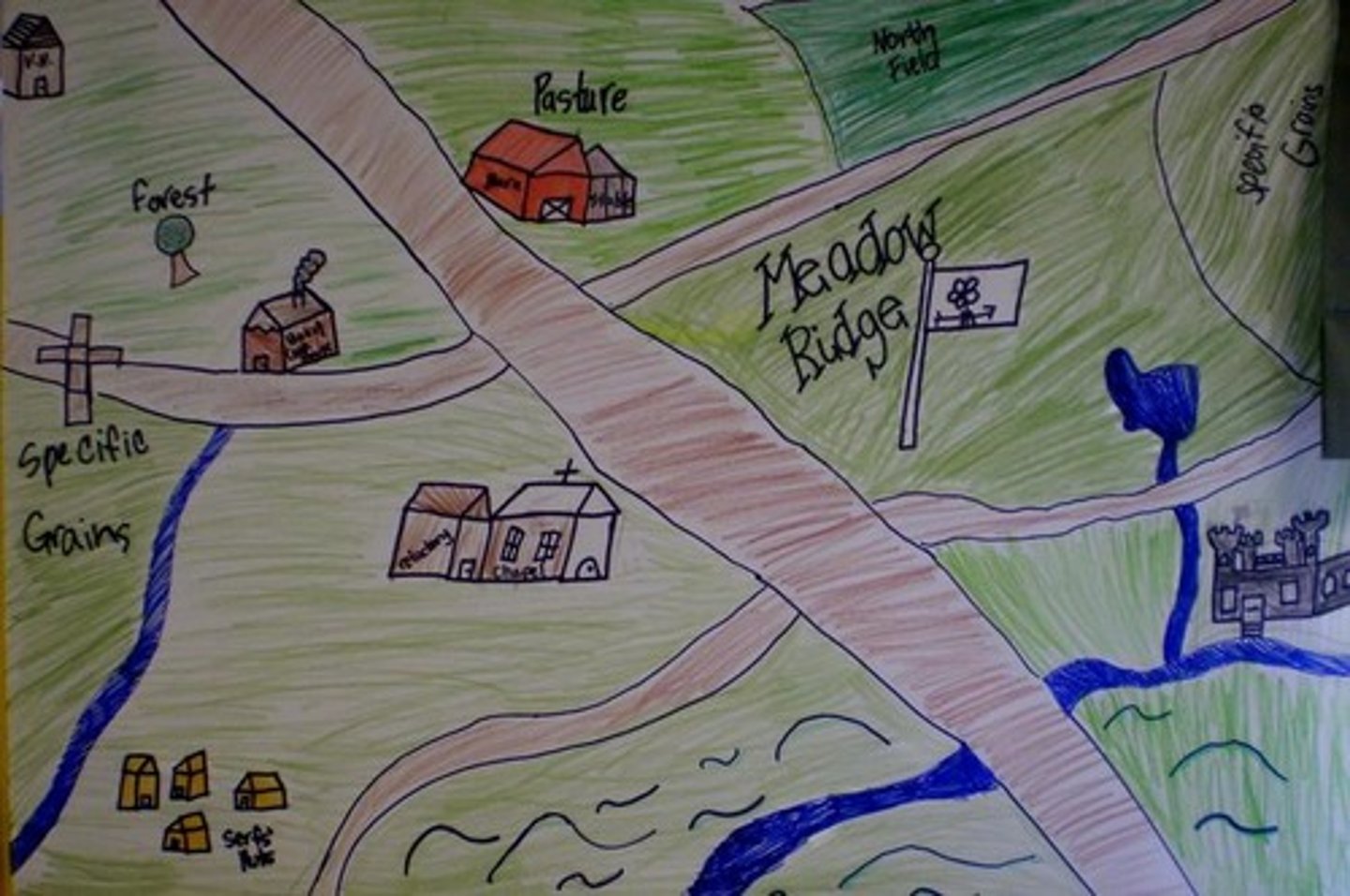
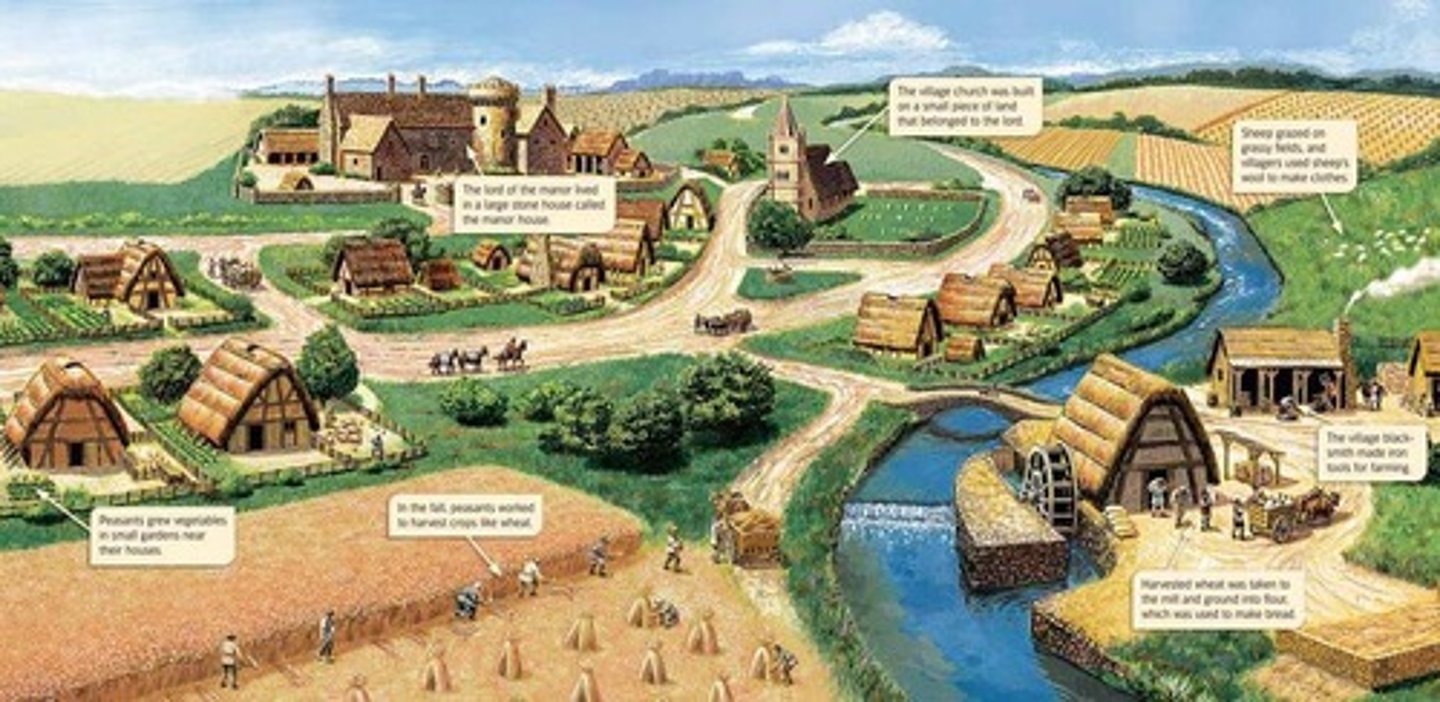
manor
a lord's estate in feudal Europe
tithe
a family's payment of 10% of its income to a church.

chivalry
a code of behavior for knights in medieval Europe, stressing ideals such as courage, loyalty, and devotion.

tournament
a mock battle between groups of knights

troubadour
a medieval poet or musician who traveled from place to place entertaining people with songs of courtly love.

clergy
a body of church officials who perform religious services- such as a priest, minister or rabbi

sacrament
one of the Christian ceremonies in which God's grace is transmitted to people (ex. baptism, communion)

canon law
the body of laws governing the religious practices of a Christian Church.

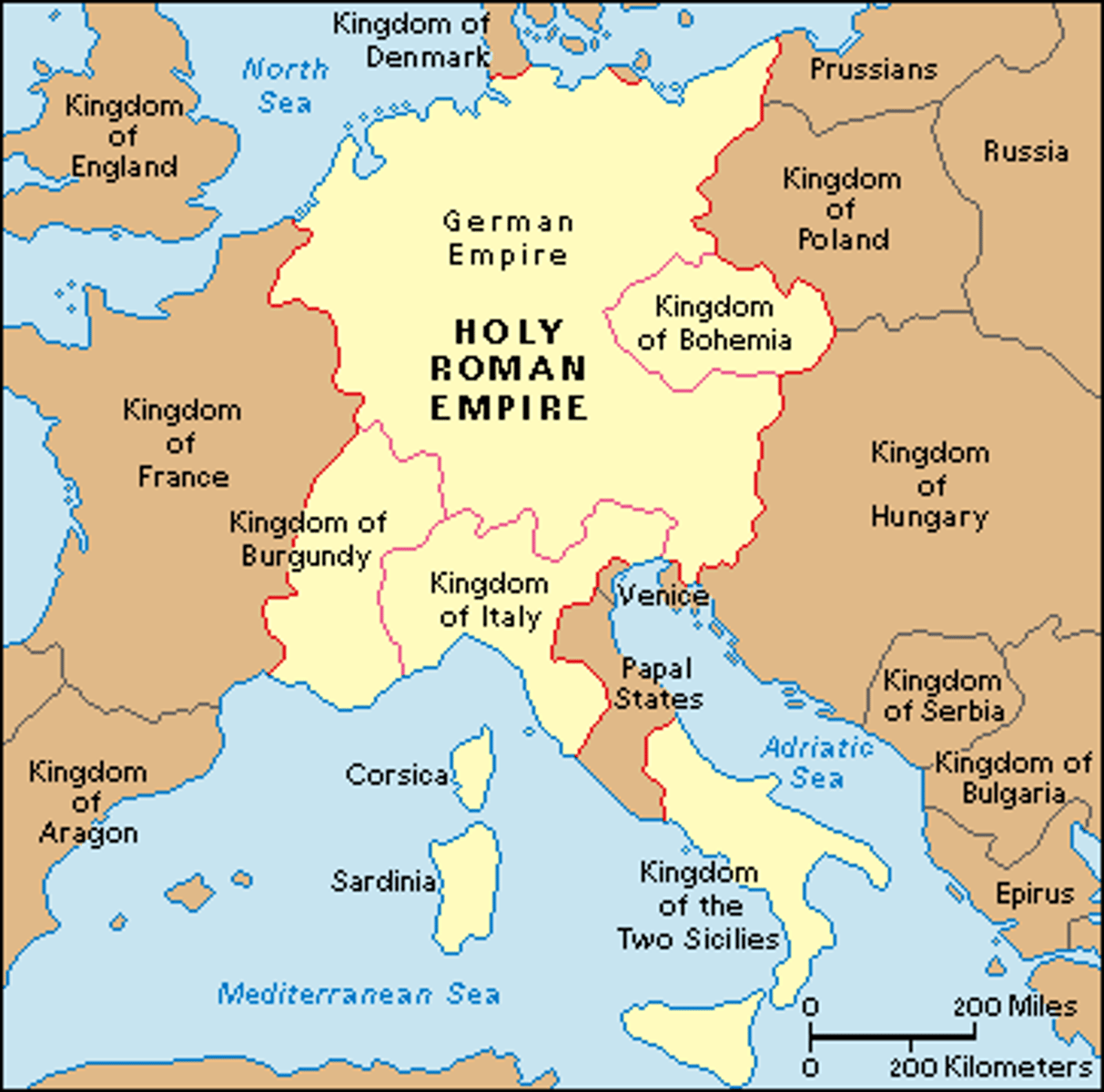
Holy Roman Empire
an empire established in Europe in the 10th century A.D., originally consisting mainly of lands in what is now Germany and Italy.
lay investiture
the appointments of religious officials by kings or nobles.

What caused the Hundred Years' War?
France and England fought over control of France.
The Hundred Years' War was a fight between England and France caused by English kings' claim that they were the rightful kings of France.
Which pope ordered priests to give up their wives and children or face dismissal?
Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII (pontificate 1073-1085) vigorously championed reform and the expansion of papal power.
What did the Crusaders do to the inhabitants of Jerusalem when they conquered the city in 1099?
Slaughtered most of them, including women and children
According to the chronicle of Fulcher of Chartres, who was on the First Crusade, the streets of Jerusalem were ankle deep with blood.
Where did universities first develop?
Italy and France
In the eleventh century in Bologna and other Italian cities, wealthy businessmen established municipal schools, which developed in the twelfth century into much larger universities; universities also developed at that time in France.
What was the relationship between rats and the spread of the bubonic plague?
Rats carried the fleas that carried the bacteria that caused the disease.
Although fourteenth-century people were not aware of it, the bacteria that causes bubonic plague was carried by fleas that lived on rats. Rats lived near people, where they could find food. The fleas jumped from the rats to people, biting and infecting them.
One of the negative consequences of the Crusades was the targeting of what group in Europe with legal restraints and violence?
Jews
Inspired by the ideology of holy war, Christian armies on their way to Jerusalem on the First Crusade joined with local mobs to attack Jewish communities; later Crusades continued to attack Jews, who were falsely blamed for the ritual murders of Christian children.
What was chivalry in the context of the European Middle Ages?
Code of conduct for knights that prescribed loyalty and other behaviors
Chivalry was a code of conduct originally devised by the clergy to transform the typically crude and brutal behavior of the knightly class; chivalrous values included loyalty, bravery, generosity, honor, graciousness, mercy, and gallantry toward women.
What was the primary field of study in the university at Salerno, Italy?
Medicine
Medicine was primarily studied in Salerno, where Greek and Muslim physicians studied the use of herbs as cures and experimented with surgery.
Who did Joan of Arc claim spoke to her and encouraged her to fight for Charles VII?
Saints Michael, Catherine, and Margaret
Joan of Arc claimed that she heard the voices of three saints—Michael, Catherine, and Margaret—tell her to support Charles VII and help him be crowned king of France by defeating the English.
Under Pope Gregory VII's reform, what punishment was merited by a ruler who appointed a church official after the church had banned the practice?
Excommunication
If a secular ruler appointed a church official in violation of the church's ban on that act, he would ultimately be excommunicated by the church.
On what basis was the First Crusade (1095-1099) considered successful?
Jerusalem was captured, and several "Crusader states" were established.
The First Crusade had proclaimed Jerusalem as its goal, and in 1099 Jerusalem was captured and four "Crusader states" were established.
What were the summae produced by Scholastics of thirteenth-century Europe?
Texts that collected and organized knowledge
Thirteenth-century Scholastics collected and organized knowledge on all topics; these collections were called summae.
Byzantine Empire
(~330-1453 C.E.) Formerly known as the Eastern Roman Empire, this Greek-inspired empire followed the ways of the Eastern Orthodox Church. With a capital city in Constantinople (formerly Byzantium), this empire was richer than its western counterpart.
Western Roman Empire
(284-476 C.E.) The term for the Roman Empire after Diocletian divided it into two parts. Fell due to barbarian invasions, high taxes, and corrupt rulers.
Constantine
An early emperor of the Byzantines who issued the Edict of Milan, allowing for Christianity within the Empire.
Emperor of the Roman Empire who moved the capital to Constantinople. He eventually converted to Christianity as well.
Justinian I
Famous Byzantine emperor who codified laws under "____" Code, built the Hagia Sophia, and married Theodora. He was Macedonian.
Theodora
Justinian's wife, who helped stage a revolt to lower taxes and increased women's rights in the Byzantine Empire by allowing women to own land equal to the value of their dowries.
Constantinople
Capital of the Byzantine Empire
monasteries
Where monks live and worship, important to the Byzantine Empire's reputation for scholarship, science, and religion
missionaries
Religious people who travel to spread their religion. Byzantines who did this traveled among the Slavs.
icons
Religious images used for worship; a matter of debate between the Catholic and Orthodox Churches
Patriarch
Byzantine version of the pope
Diocletian
Emperor of Rome responsible for dividing Rome into Eastern and Western Empires
The Great Schism
In 1054, the church split into two branches: Orthodox and Catholic. They disagreed about liturgical practices (like using icons in worship) and the primacy (or supreme power) of the pope in Rome.
The First Crusade
Began in 1095 by Urban II, this mission had two goals. The Western churches wanted to take the Holy Land from Muslims, while the Byzantines wanted to protect Constantinople from invasions. At the end of this crusade, Christians captured Jerusalem and Antioch.
The Fourth Crusade
In 1204, Roman Catholics fought against Orthodox Christians to capture the Byzantine capital of Constantinople.
Positive Effect of the Crusades
Increased trade, Europeans borrowed Greco-Roman culture from Byzantines, kings left their feudal manors alone and they became "towns" that ruled themselves, literature from Arabia was brought west (Sinbad, Ali Baba and the Forty Theives, Aladdin)
Negative Effects of the Crusades
Hatred of Jews, loss of lives, destruction of Muslim communities, disagreement between eastern and western churches, kings increased taxes to fund them
pilgrimage
A religious voyage
Feudalism
Social and political system in which lords rule over vassals, who work for them. In turn, lords protect their vassals.
Dark Ages
Term describing the Early Middle Ages or Medieval period in Europe, from the fall of the Roman empire to roughly 1000 C.E.
Lord
In Feudalism, the baron or noble who ruled over an area, owned the land, and protected his vassals.
Vassal
In Feudalism, the person who was loyal to a lord and farmed his land in return for protection.
Fief
The piece of land given by a lord to a vassal
City-State
A city and its surrounding areas, ruled independently by nobles. Examples include Venice and Florence.
Urban II
Pope who called for the first Crusade in 1095
Hundred Years' War
Between 1337 and 1453, England and France engaged in a series of conflicts with this name.
Magna Carta
Document written by lords or nobles in England in 1215 to increase the power of Parliament and lower taxes, signed by King John.
Manorialism
an essential element of feudal society, was the organizing principle of rural economy. The economic power belonged to the lord of the manor, who was supported economically from his land and from contributions from the peasant population under his authority.
Heresy
opinion profoundly at odds with what is generally accepted.
Reconquista
the name given to a long series of wars and battles between the Christian Kingdoms and the Muslim Moors for control of the Iberian Peninsula. Spain discriminating against Muslim and Jewish living under Christian rule. Proof of purity of blood was necessary.

Crusades
were a series of intermittent Papal sanctioned military campaigns beginning in the late 11th-century. They commenced with a call to arms by Pope Urban II who was responding to a request for military support for the Byzantine Empire.

Craft Guilds
an association of workers of the same trade for mutual benefit.
Commercial Revolution
was a period of European economic expansion, colonialism, and mercantilism
Scholasastics
a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics ("scholastics," or "schoolmen") of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100-1700, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending dogma
Gothic
of or in the style of architecture prevalent in western Europe in the 12th-16th centuries, characterized by pointed arches, rib vaults, and flying buttresses, together with large windows and elaborate tracery.

Vernacular Literature
literature written in the vernacular—the speech of the "common people". It gradually transformed local dialects into literary languages such as French, German, Italian, and English.......
Black Death
Bubonic Plague. In the early 1330s an outbreak of deadly bubonic plague occurred in China. The bubonic plague mainly affects rodents, but fleas can transmit the disease to people.
What time period is considered the Early Middle Ages or Dark Ages?
476 AD to 1000 AD
What time period is considered the High Middle Ages?
1000 AD to 1250ish AD
What time period is considered the Late Middle Ages?
1250ish/1300 to the Renaissance