6.3.1 Ecosystems
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
define ecosystem
an area where biotic organisms and abiotic environmental factors interact forming a relatively self-sustaining system driven by energy flows and nutrient cycles
define niche
the role of an organism within an ecosystem, only one species can occupy a specific niche
what is the name for the role of an organism in an ecosystem
niche
what are the types of nutrition
autotrophic- photoautotrophic and chemoautotrophic, and heterotrophic- holozoic and saprotrophic
define autotrophic nutrition
a process of obtaining carbon from carbon dioxide
define heterotrophic
a process of obtaining carbon from breakdown of organic compounds
what is the name for the process of obtaining carbon from breakdown of organic compounds
heterotrophic nutrition
what is the name for the process of obtaining carbon from carbon dioxide
autotrophic nutrition
define photoautotrophic
a process of obtaining carbon from carbon dioxide using energy from light
what is the name for the process of obtaining carbon from carbon dioxide using energy from light
photoautotrophic nutrition
define chemoautotrophic
a process of obtaining carbon from carbon dioxide using energy from chemical reactions, starts food chains where there is no sunlight
what is the name for the process of obtaining carbon from carbon dioxide using energy from chemical reactions, starts food chains where there is no sunlight
chemoautotrophic nutrition
define holozoic
a process of obtaining carbon by ingestion and internal digestion of organic compounds
what is the name for the process of obtaining carbon by ingestion and internal digestion of organic compounds
holozoic nutrition
define saprotrophic
a process of heterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed organic matter
what is the name for the process of heterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed organic matter
saprotrophic nutrition
define detritivores
organisms that shed detritus, ingest it and digest it internally (holozoic nutrition), they precede decomposers in the process of decomposition
define decomposers
a saprotrophic microorganism that breaks down dead organic matter to simpler organic or inorganic material
what is the difference between detritivores and decomposers
detritivores precede decomposers in the process of decomposition, detritivores use holozoic nutrition and decomposers use saprotrophic nutrition
define hummus
dead organic matter in the soil
what is the name for the dead organic matter in the soil
hummus
define biomass
the total quantity of dry mass in an organism, commonly measured for a trophic level or a population/community inhabiting a certain region
what is the name for the total quantity of dry mass in an organism, commonly measured for a trophic level or a population/community inhabiting a certain region
biomass
define dynamic
a word to describe the change in distribution and abundance of species in an ecosystem over time
what are the features of an ecosystem
different in size
dynamic
biotic factors
abiotic factors
what are the types of change in an ecosystem
cyclic change, directional change, erratic/unpredictable change
what is cyclic change in an ecosystem
repeat in a rhythm e.g. tides, seasons
what is directional change in an ecosystem
gradual change in one direction that lasts longer than the lifetime of organisms e.g. erosion of coastline
examples of different size ecosystems
rock pool, playing field, large tree
what are examples of erratic change in an ecosystem
hurricane, lightening, tsunami, forest fires
what are examples of biotic factors affecting ecosystems
food chains/webs
decomposition
predator-prey relationships
competition
cooperation
providing a habitat
disease- pathogens and parasites
what are the steps of a food chain called
trophic levels
what are the trophic levels
1- producer, 2- primary consumer, 3- secondary consumer, 4- tertiary consumer
what are the types of food chain
grazing food chains, detrital/decomposer food chain
what are decomposer food chains
involve decomposition, allows nutrient cycling
what is the role of producers
all organisms depend on producers for energy and biomass, energy enters the ecosystem through producers
what do producers depend on
the activity of decomposing microorganisms for most of their supply of inorganic ions e.g. nitrates, phosphates, magnesium
what are decomposers
microorganisms e.g. bacteria, fungi, that digest dead organic matter by external secretion of enzymes to then absorb the productions- saprotrophic nutrition
what does the saprotrophic nutrition of decomposers allow for
this type of nutrition releases all nutrients into the soil including minerals, taken up by producers, mineral recycling is dependent on decomposer activity
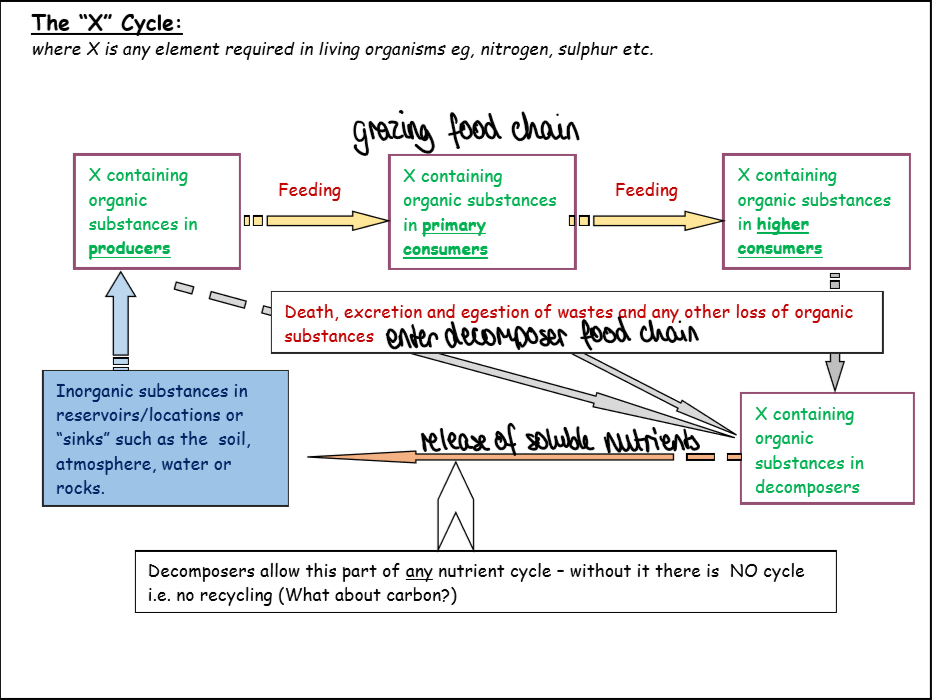
what is the nutrient cycle
organic substances containing element taken up by producers
primary consumers take in organic substances containing element
higher consumers take in organic substances containing element (grazing food chain)
death excretion and egestion of wastes and other loss of organic substances enters decomposer food chain
decomposers break down organic substances containing element
release of soluble nutrients so inorganic substances in reservoirs or sinks e.g. soil, water or rocks contain element
what are predator-prey relationships
part of a food chain, numbers of each, affect the other cyclically
what are the types of competition
intraspecific- between members of the same species, interspecific- between members of different species
what are the types of cooperation in an ecosystem
intraspecific- between members of the same species e.g. social insects, interspecific- between members of different species
what are the types of interspecific cooperation
mutualism e.g. coral and algae, commensalism- when one species gains and the other is neutral e.g. barnacles on whales
what are the abiotic factors that affect ecosystems
climatic factors, topographic factors, edaphic factors
what are climatic factors
wind speed, precipitation, temperature, wave action, light intensity
what are topographic factors
altitude, gradient, shape of land, aspect (direction land is facing)
what are edaphic factors
soil nutrients- features of the soil, river bed
what does an abiotic factor need to be
measurable
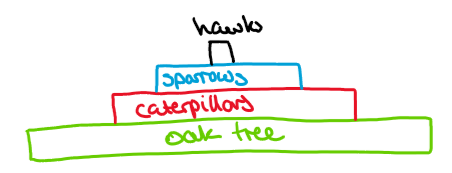
what are the types of measurement between trophic levels in an ecosystem
pyramid of numbers, pyramid of biomass, energy transfer in ecosystems
what is a pyramid of numbers as a way of measuring trophic levels
to show the relative numbers of individuals at each trophic level

what is a pyramid of biomass as a way of measuring trophic levels
to show the relative amount of biomass at each trophic level
how is biomass measured
dry in an oven at 80’C, weigh sample until it remains at a constant mass to know all the water is removed
how to calculate the efficiency of biomass transfer between trophic levels
=quantity of biomass transferred/total quantity of biomass available *100
what does the equation quantity of biomass transferred/total quantity of biomass available *100 represent
efficiency of biomass transfer
what does productivity mean
the rate at which energy transfers between trophic levels in an ecosystem
what is the word for the rate at which energy transfers between trophic levels in an ecosystem
productivity
what is productivity measured in
kJ m^-2 yr^-1 for land or kJ m^-3yr^-1 for an aquatic food chain (using years allows seasons to be taken into account)
what is the rate at which energy enters the food chain through producers called
primary productivity
what is primary productivity
the rate at which energy enters the food chain through producers
what are the levels of primary productivity
gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP)
what is gross primary productivity
the rate at which the solar energy absorbed by the plant is converted to chemical energy through photosynthesis
what is the name for the rate at which the solar energy absorbed by the plant is converted to chemical energy through photosynthesis
gross primary productivity
what is the normal GPP value and why
around 2%, a lot of the light energy, mainly green light, is reflected so not absorbed, doesn’t hit chloroplasts, of the energy absorbed, much is lost through respiration and evaporation of water
what is net primary productivity
the energy stored in the biomass of producers, different to GPP as energy is lost in respiration
what is the name for the energy stored in the biomass of producers
net primary productivity
how to calculate NPP
GPP-respiration
what is secondary productivity
when herbivores and carnivores consume food, energy and biomass is transferred along the food chain
how is energy and energy in biomass lost at each trophic level
respiration, death, excreta (urine), egesta (faeces)
what are the types of energy lost that are available to decomposers
death, excreta (urine) and egesta (faeces)
what is the name for the energy that is incorporated into the biomass of the animal
secondary production
what is secondary production
the energy that is incorporated into the biomass of the animal
what limits the length of food chains
at each step energy-containing materials are transferred, but not all the energy from one trophic level transfers to the next
what is the impact of not all the energy from one trophic level transferring to the next
limits the length of food chains
why is a lot of food consumed by herbivores lost as faeces
the cellulose in plant cell walls is hard to digest
what are the ways farmers can maximise energy flow in primary or secondary production
maximise energy input
maximise growth
control disease
control grazing/predation
reduce interspecific competition
reduce energy loss
how can you maximise energy input in producers and primary consumers
producers: optimum planting distances between crops, provide light on overcast days, seed early in the season, primary consumers: provide good quality feed
how can you maximise growth in producers and primary consumers
producers: provide water (irrigation) or fertilisers containing NPKS, carbon dioxide enriched greenhouses, selective breeding for fast growth, crop rotation with legumes, primary consumers: selective breeding for fast growth, kill just before adulthood, provide food supplements e.g. vitamins and minerals
how can you control disease with producers and primary consumers
producers: sow disease-resistant GM crops, spray fungicides/herbicides, primary consumers: antibiotics and vaccines
how can you control grazing/predation in producers and primary consumers
producers: pest-resistant GM crops, fencing to exclude grazers, use pesticides, primary consumers: control predators such as foxes and wolves, keep animals in shed protected from predators
how can you reduce interspecific competition in producers and primary consumers
producers: ploughing and herbicides kill weeds, primary consumers: control competitors
how can you reduce energy loss in producers and primary consumers
producers: breed plants that maximise energy storage in edible products e.g. seeds, tubers, primary consumers: keep animals in warm environments, restrict movement to reduce energy lost to respiration
what is the carbon cycle
carbon containing compounds in plants → carbon containing compounds in herbivores → carbon containing compounds in carnivores → carbon containing compounds in dead remains and excretory products → carbon containing compounds in decomposers → carbon atoms in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from respiration
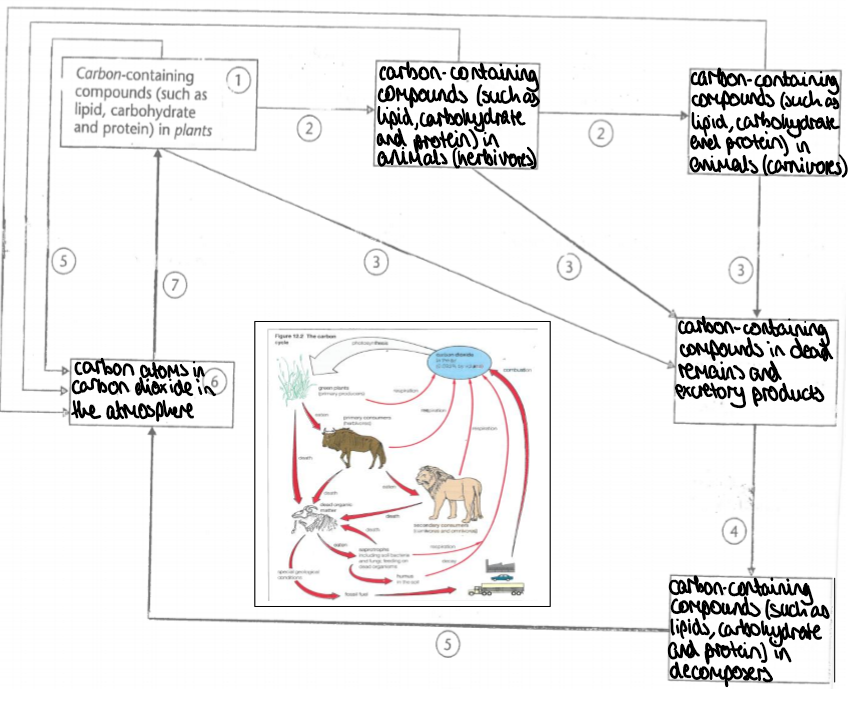
why do carbon levels have peaks and troughs
different seasons- in summer more plants so more photosynthesis, in winter increased fuel combustion
what is the general nitrogen cycle
plant biomass → animal biomass → NH4+ → nitrite ions NO2- → nitrate ions NO3- → plant biomass/ N2 gas in atmosphere → plant biomass/ NH4+
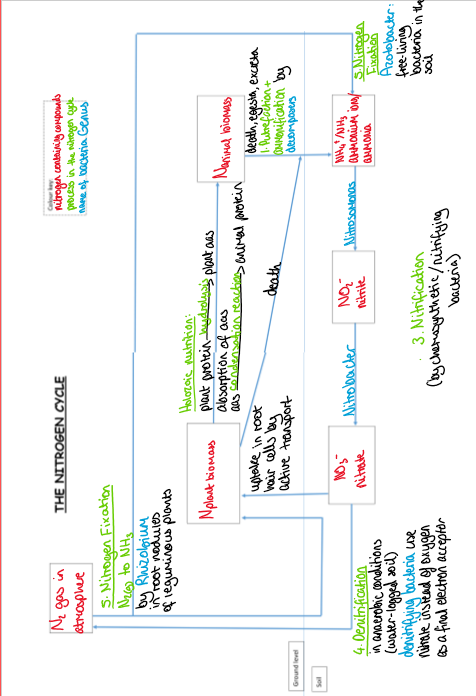
what happens in the transfer of nitrogen between plant biomass and animal biomass
holozoic nutrition, plant protein hydrolysed to plant amino acids, absorption of amino acids by animals, amino acids go through a condensation reaction to form animal protein
what connects plants to ammonium ions in the nitrogen cycle
death
what happens in the transfer of nitrogen between animal biomass and ammonium ions
ammonification by decomposers, death, egesta or excreta
what is ammonification
decomposers convert nitrogen-containing molecules in dead organisms, faeces and urine into ammonium compounds
what is nitrification
where ammonium compounds in the soil are converted to nitrogen-containing molecules that can be used by plants by nitrifying/chemosynthetic bacteria
what are the stages of nitrification
NH4+ → nitrite ions NO^-2 → nitrate ions NO^-3
what bacteria converts ammonium ions into nitrite ions in nitrification
nitrosomonas
what does nitrosomonas do
converts ammonium ions into nitrite ions in nitrification
what converts nitrite ions to nitrate ions in nitrification
nitrobacter
what does nitrobacter do
converts nitrite ions to nitrate ions in nitrification
what is the name for the process of converting ammonium ions to nitrite and then nitrate ions
nitrification
what is denitrification
denitrifying bacteria convert nitrate ions back into nitrogen gas
in what form does nitrogen enter plants and why
nitrate ions as they are highly soluble
how are nitrate ions converted back into nitrogen gas in the atmosphere
by denitrifying bacteria in anaerobic conditions e.g. water-logged soil, use nitrate instead of oxygen as a source of energy for respiration
when does denitrification take place
in anaerobic conditions e.g. water-logged soil