2-3. Fairness
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
How can a threshold be determined if the distributions of 2 groups are very different?
2 group-specific thresholds.
m is a metric of interest, e.g., FPR, acceptance rate
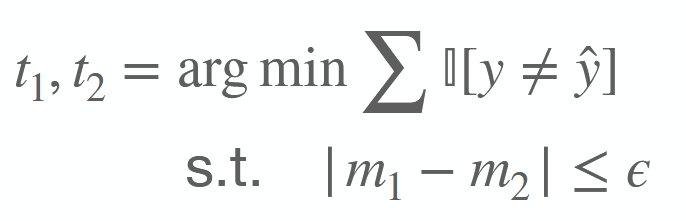
What are 3 approaches to ensure fair classification?
Pre-processing: Change training data.
In-processing: Change model training procedure.
Post-processing: Change model decisions.
→ In-processing is most flexible.
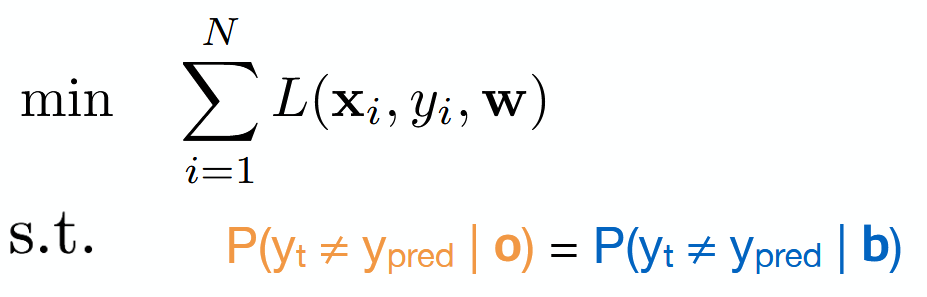
What is a problem in training models under fairness constraints?
Non-convex for many well-known classifiers (logistc, SVM).
→ Hard to compute efficiently.
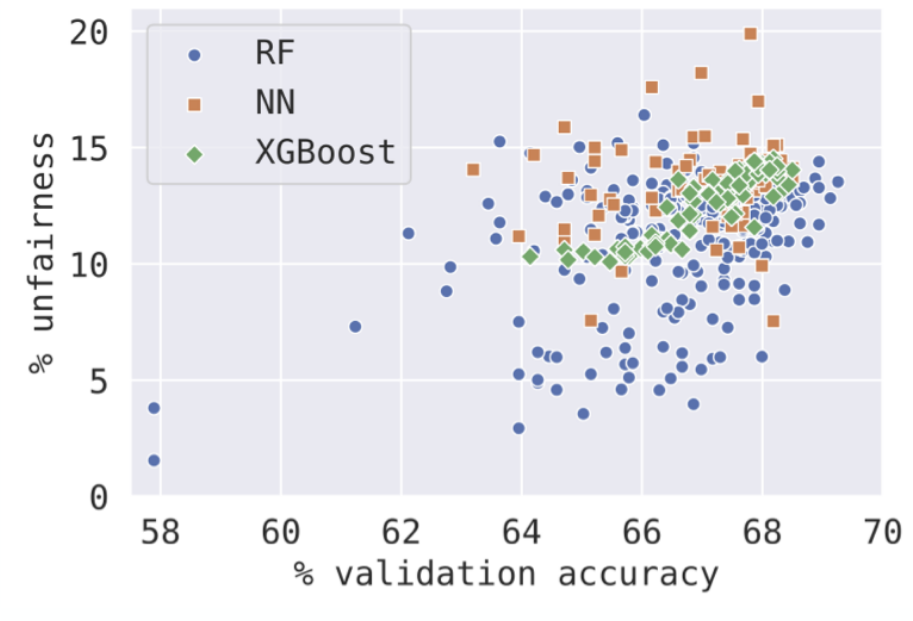
How can Hyperparameter Optimization be used for fairness?
Hyperparameters have massive impact on performance.
Train model under different hyperparameters and observe trade-off between accuracy and unfairness.
What is a common misconception about the goal of a ML model?
The goal is not to train the most accurate classifier on your data.
Instead, we want to optimise some real-world criteria under given constraints.
Example: Maximize community safety without putting more than 1000 people in jail.
What is the True Positive Rate (TPR)?
P(y^ = 1 | y = 1)
Calculated by TPR = TP / (TP + FN)
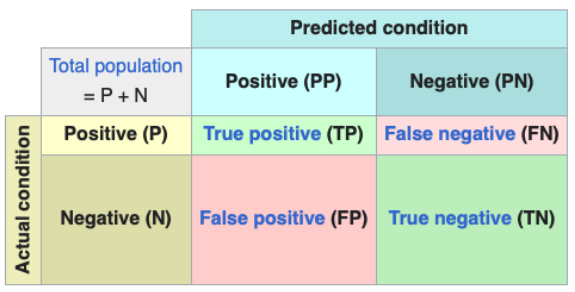
What is the True Negative Rate (TNR)?
P(y^ = 0 | y = 0)
Calculated by TNR = TN / (TN + FP)
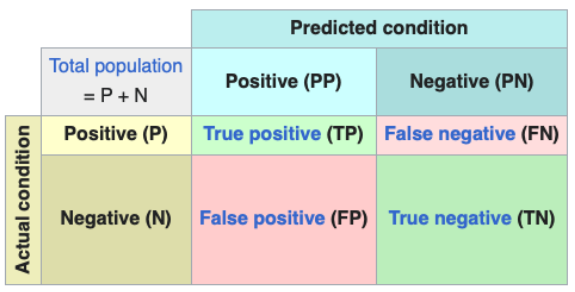
What is the Positive Predictive Value (PPV)?
P(y = 1 | y^ = 1)
Calculated by PPV = TP / (TP + FP)
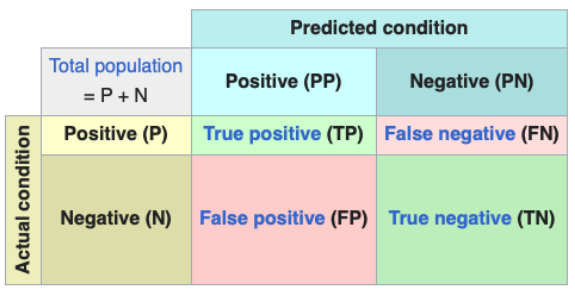
What is the Negative Predicive Value (NPV)?
P(y = 0 | y^ = 0)
Calculated by NPV = TN / (TN + FN)
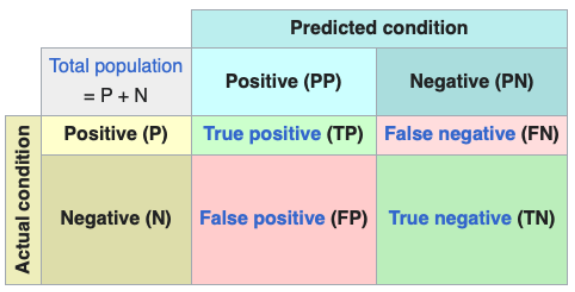
What is the Positive Prediction Rate (PPR)?
P(y^ = 1)
Calculated by PPR = (TP + FP) / (TP + FP + FN + TN)
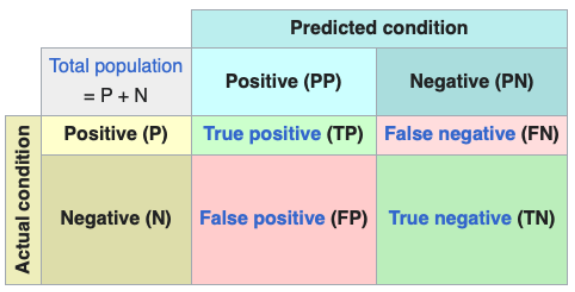
What is Direct Discrimination in ML?
Sensitive features z (race, gender, age) are used to make predictions → z ∩ x ≠ ∅
Can also be hidden by using features that correlate with sensitive features (f.e. location with race).
How can Indirect Discriminiation be measured in ML?
Statistical Parity (aka disparate impact)
Equality of opportunity (aka disparate mistreatment)
How is Statistical Parity (Disparate Impact) defined?
P(y^ = 1 | z = 0) = P(y^ = 1 | z = 1)
→ Same outcome probability for both groups.
How is Equality of Opportunity (Disparate Mistreatment) defined?
P(y^ = 0 | y = 0, z = 0) = P(y^ = 0 | y = 0, z = 1)
→ Probability of correct outcome should be equal among groups.
When is it impossible to have equal values across all measures of the confusion matrix for 2 groups?
When the underlying risk score distribution of the groups is different.
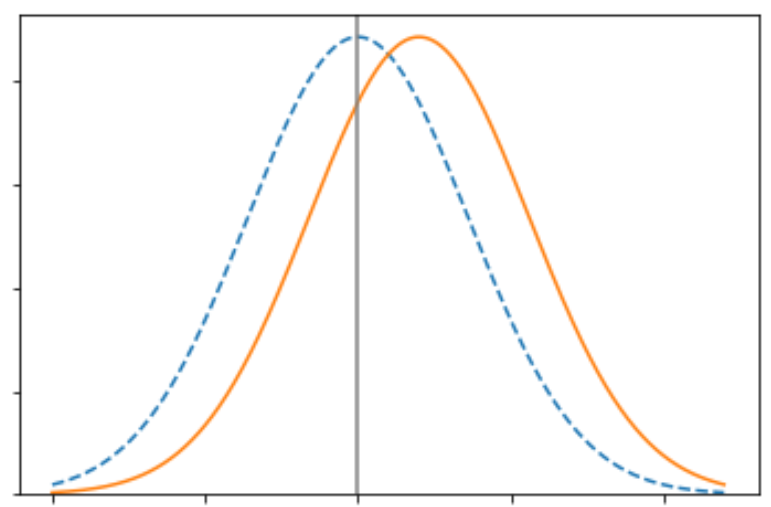
What is the narrow view of fairness?
Similar people should get similar treatment.
Groups do not rely matter / sensitive groups should be disregarded.
What is the broad view of fairness?
Society should be structured to grant people equal opportunities.
Most broad / substantial interventions required.
What is the middle view of fairness?
Decision makers should consider past injustices that are causes of current differences in qualifications.
Scope is individual risk prediction scenarios.