Evolutionary Concepts: Selection and Speciation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Population
Group of individuals of the same species.
Genotypic Frequency
Proportion of different genotypes in a population.
Allele Frequency
Proportion of a specific allele in a population.
Disruptive Selection
Favors extreme phenotypes over intermediate ones.
Stabilizing Selection
Favors average phenotypes, reducing variation.
Directional Selection
Favors one extreme phenotype over others.
Microevolution
Small-scale evolutionary changes within a species.
Macroevolution
Large-scale evolutionary changes over long periods.
Species
Group capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
Reproductive Isolation
Barriers preventing species from interbreeding.
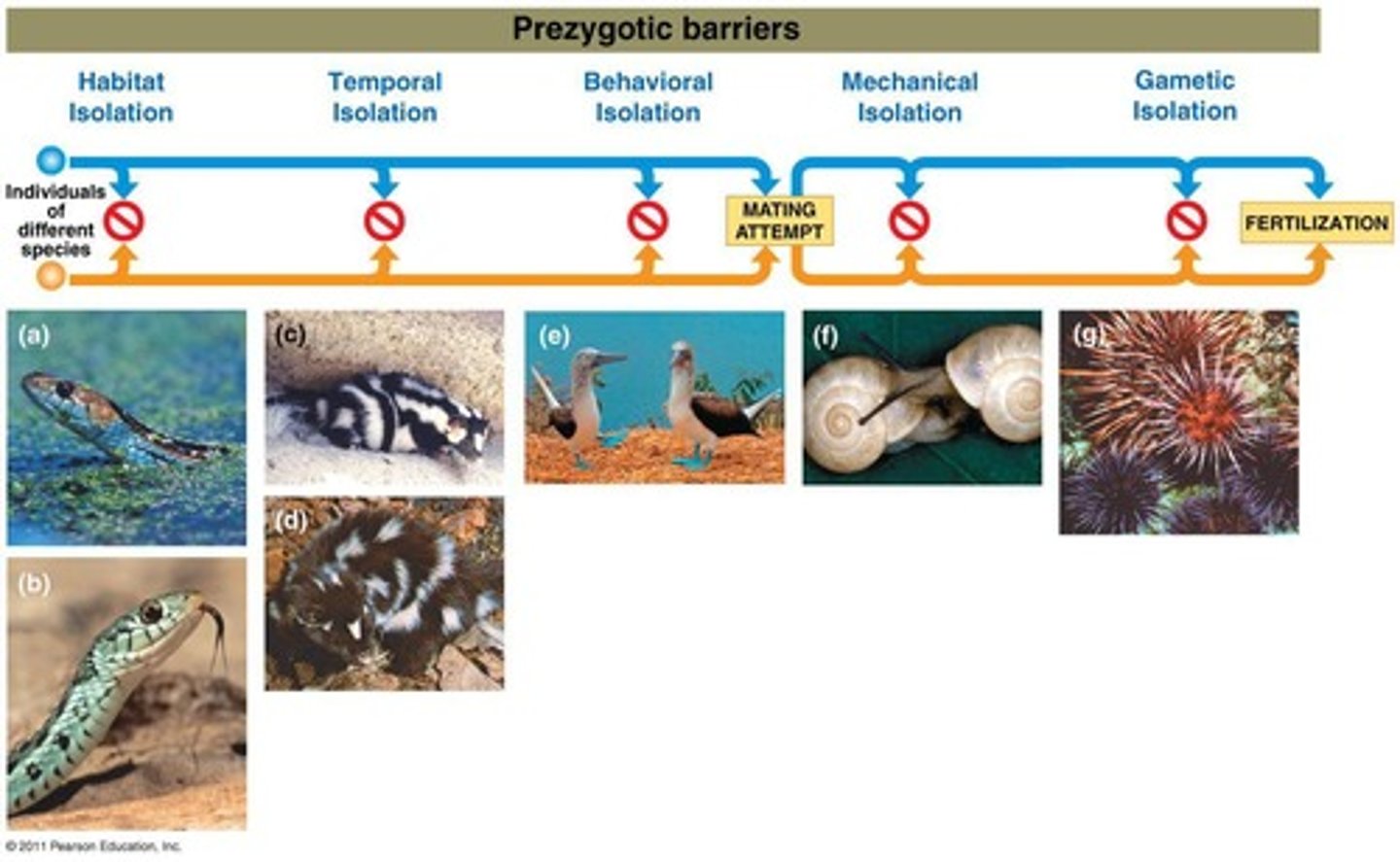
Prezygotic Barriers
Prevent mating or fertilization between species.
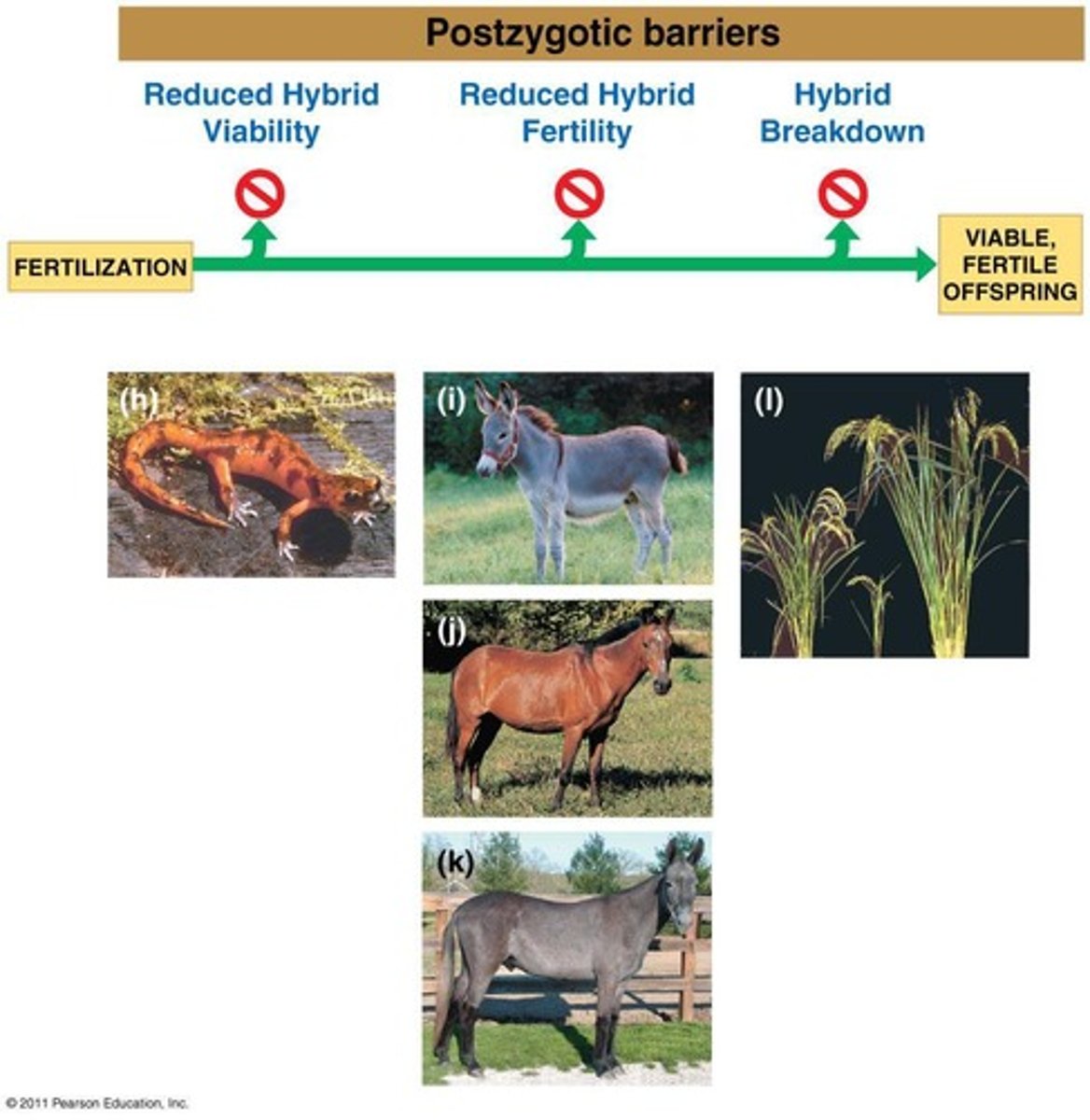
Postzygotic Barriers
Prevent hybrid zygotes from developing into viable adults.
Allopatric Speciation
Speciation due to geographical isolation.
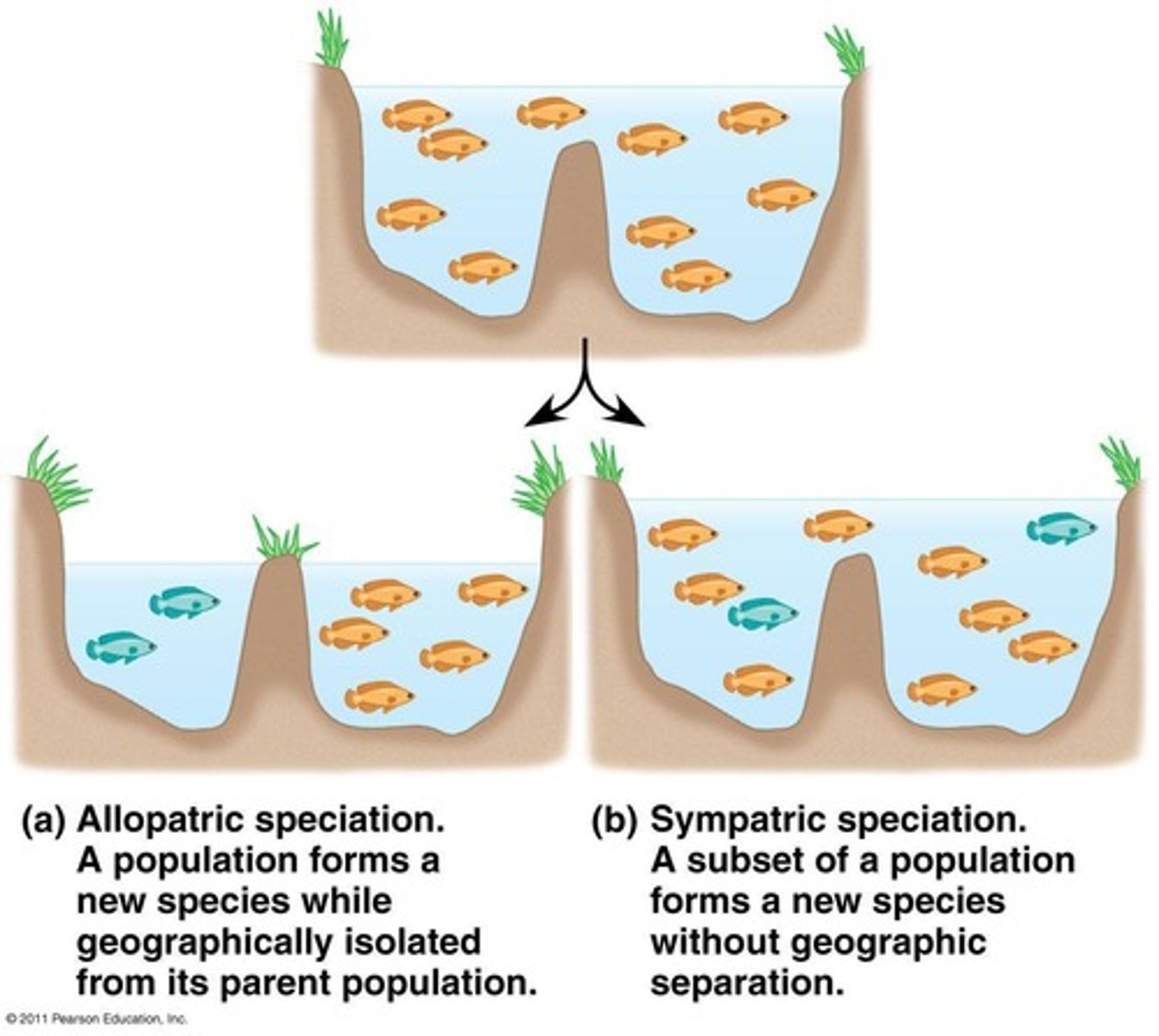
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation occurring within overlapping populations.
Autopolyploidy
Chromosomal duplication within a single species.
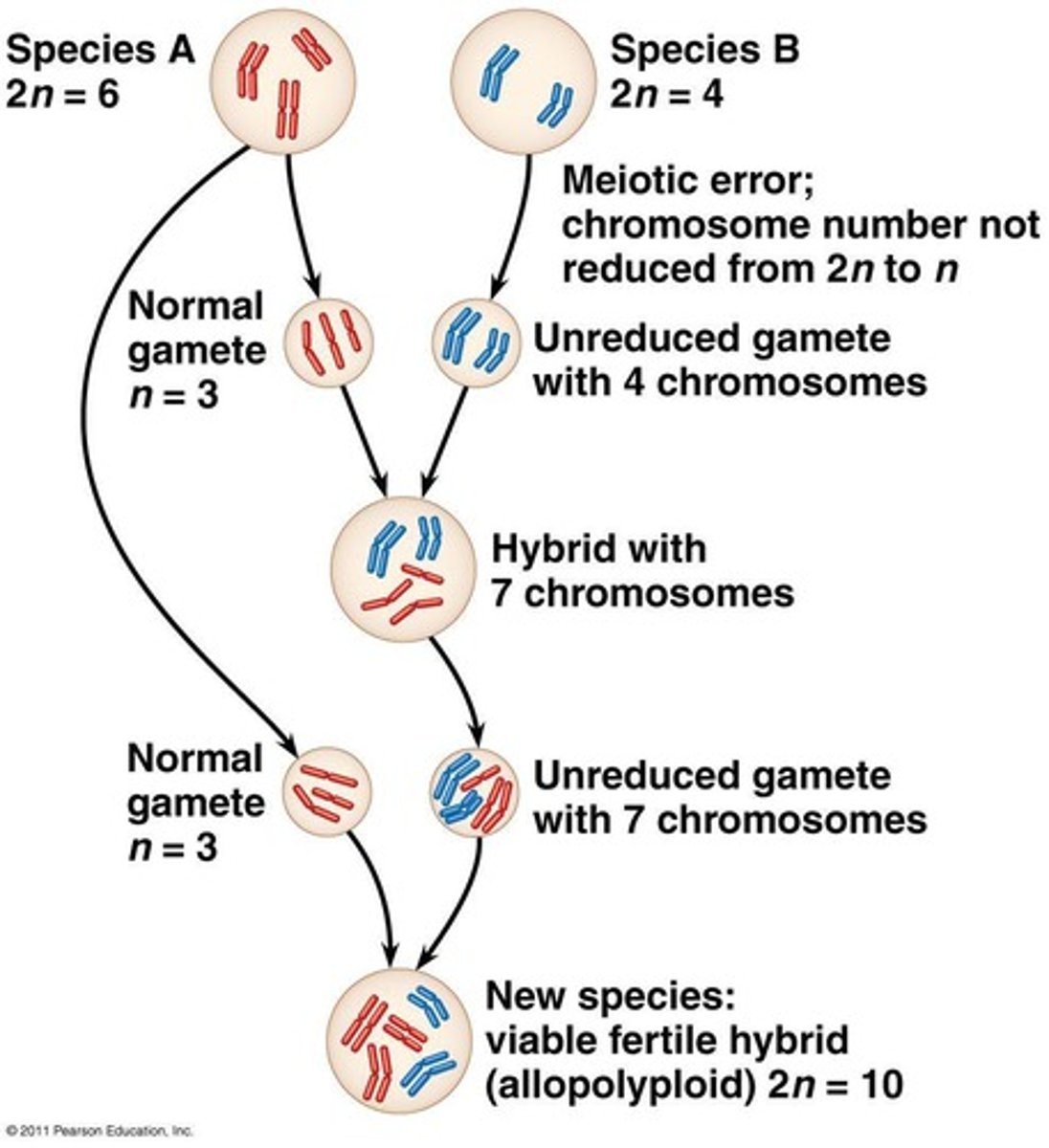
Allopolyploidy
Hybridization between two species leading to polyploidy.
Adaptive Radiation
Rapid evolution of diversely adapted species from a common ancestor.

Founder Effect
Genetic drift occurring when a few individuals establish a new population.
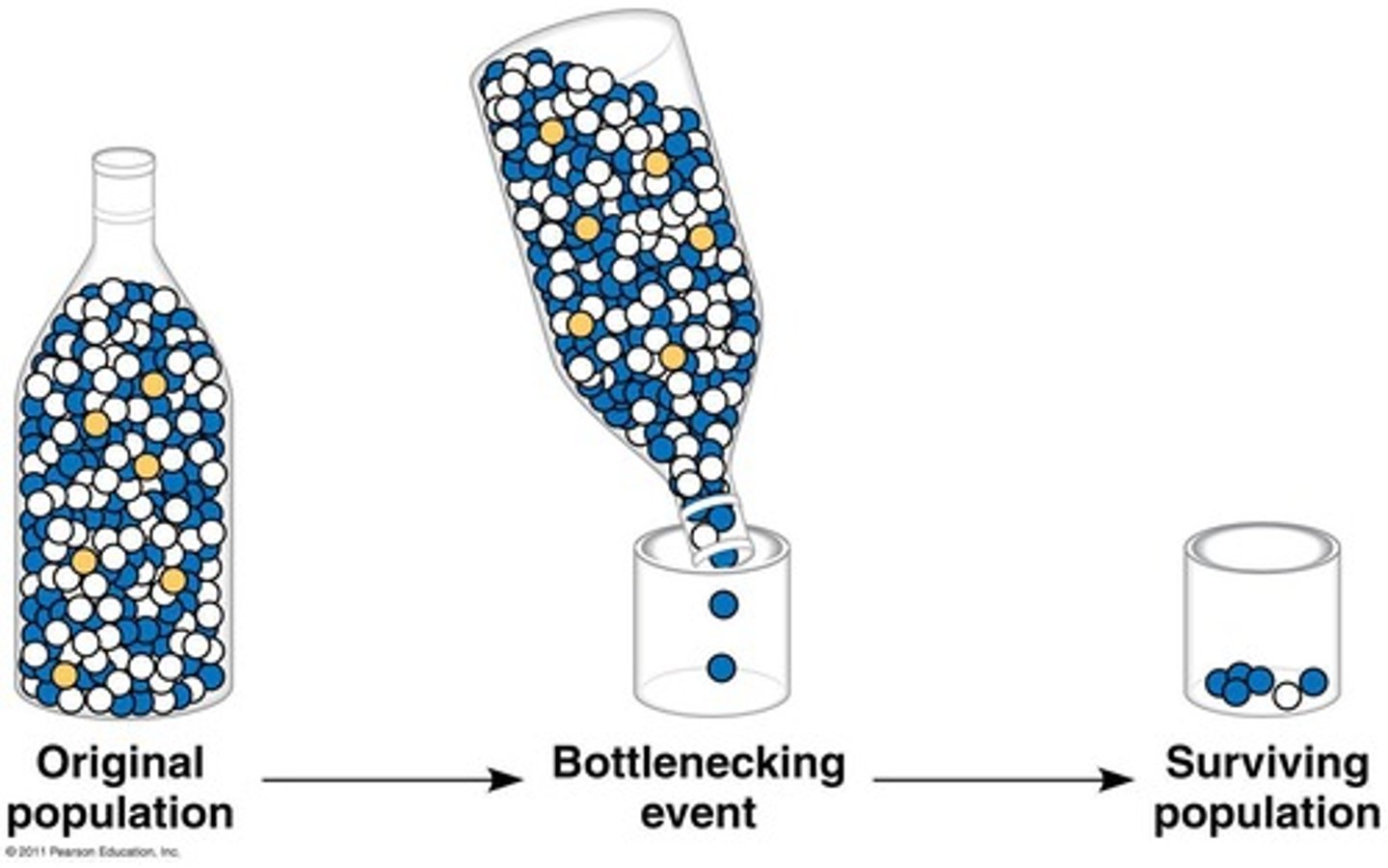
Bottleneck Effect
Loss of genetic diversity due to a drastic reduction in population size.
Gene Flow
Movement of alleles between populations through migration.
Natural Selection
Process where individuals with advantageous traits reproduce more.
Sexual Selection
Natural selection based on mate choice and competition.
Sexual Dimorphism
Differences in appearance between males and females.
Heterozygote Advantage
Higher fitness of heterozygous individuals compared to homozygotes.
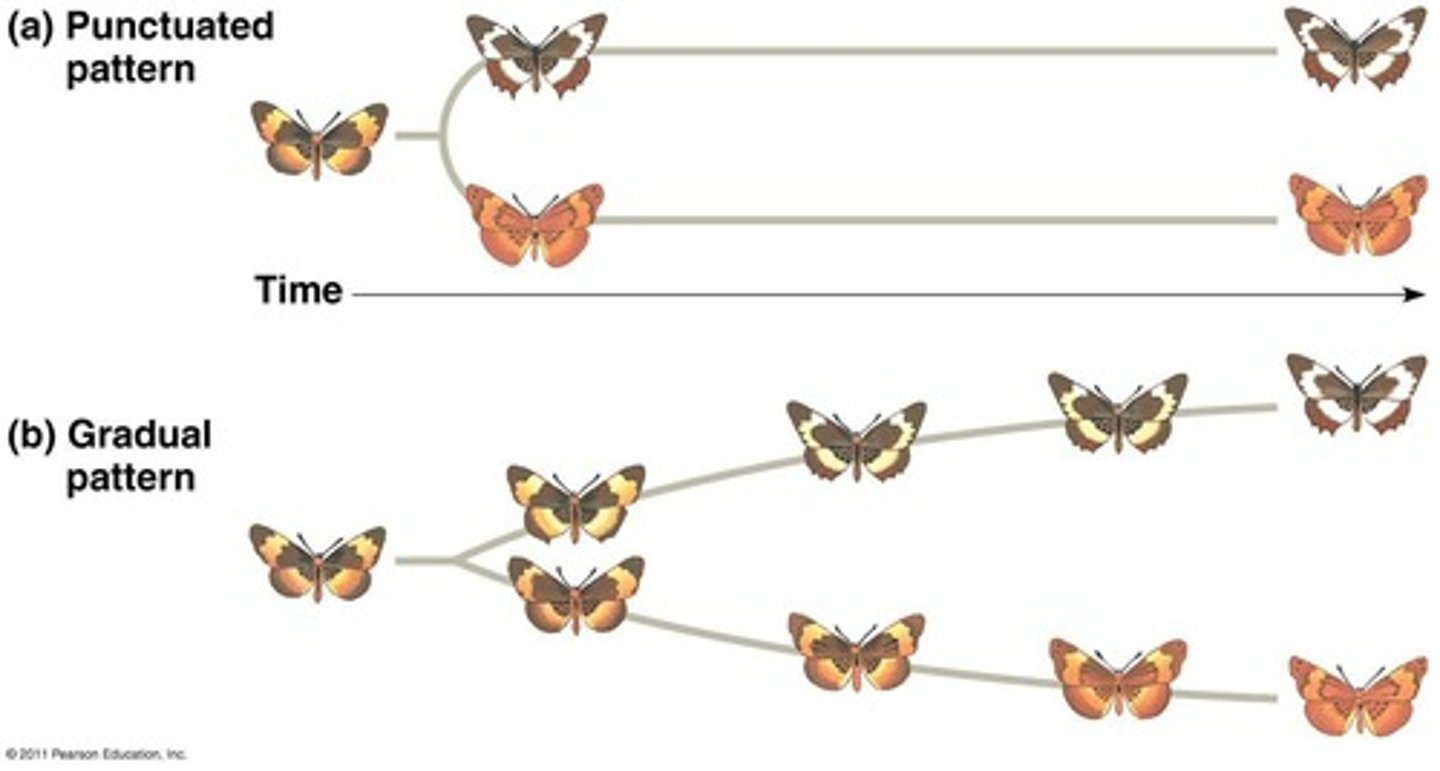
Punctuated Equilibrium
Evolution characterized by long periods of stasis interrupted by rapid change.
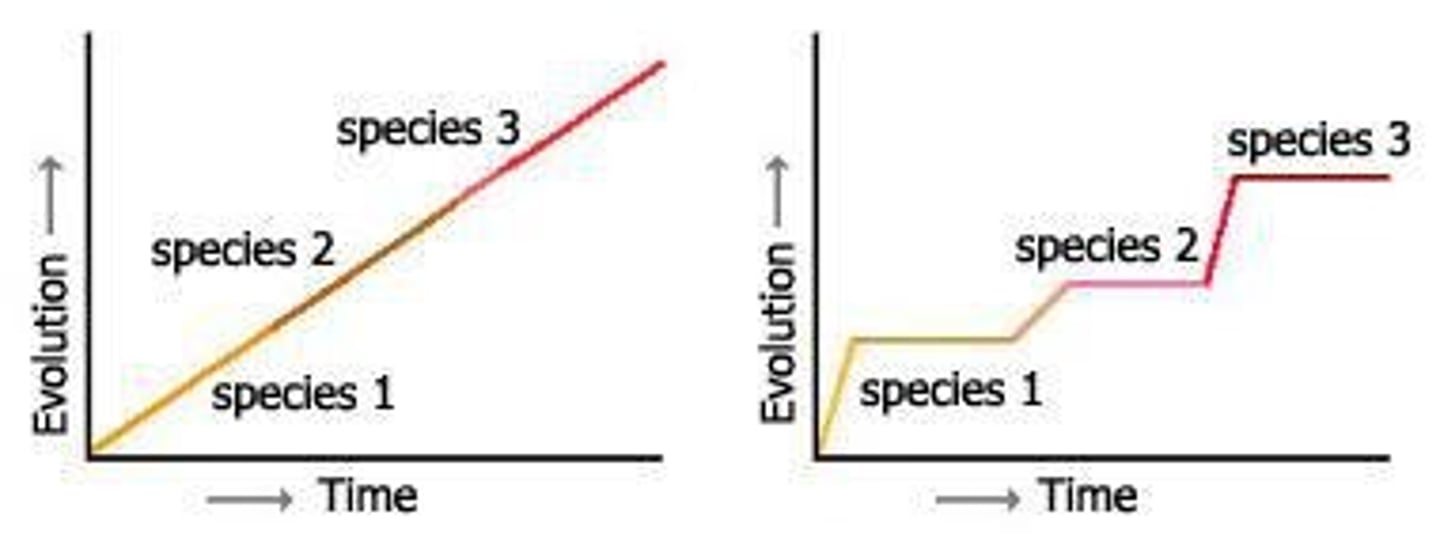
Gradualism
Slow, continuous evolution over long periods.
Hybrid Breakdown
Reduced fitness of subsequent generations of hybrids.