Star Formation and Interstellar Medium: Gas, Dust, and Protostars
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What are the dark clouds where stars form called?
Giant molecular clouds
What is the typical temperature of star-forming clouds?
About 10 K
What triggers the gravitational collapse of star-forming clouds?
Cloud collisions, shock waves from nearby stars, or passage of a galactic spiral arm
What happens during the gravitational collapse of a star-forming cloud?
It fragments into star-sized globules, releasing gravitational energy.
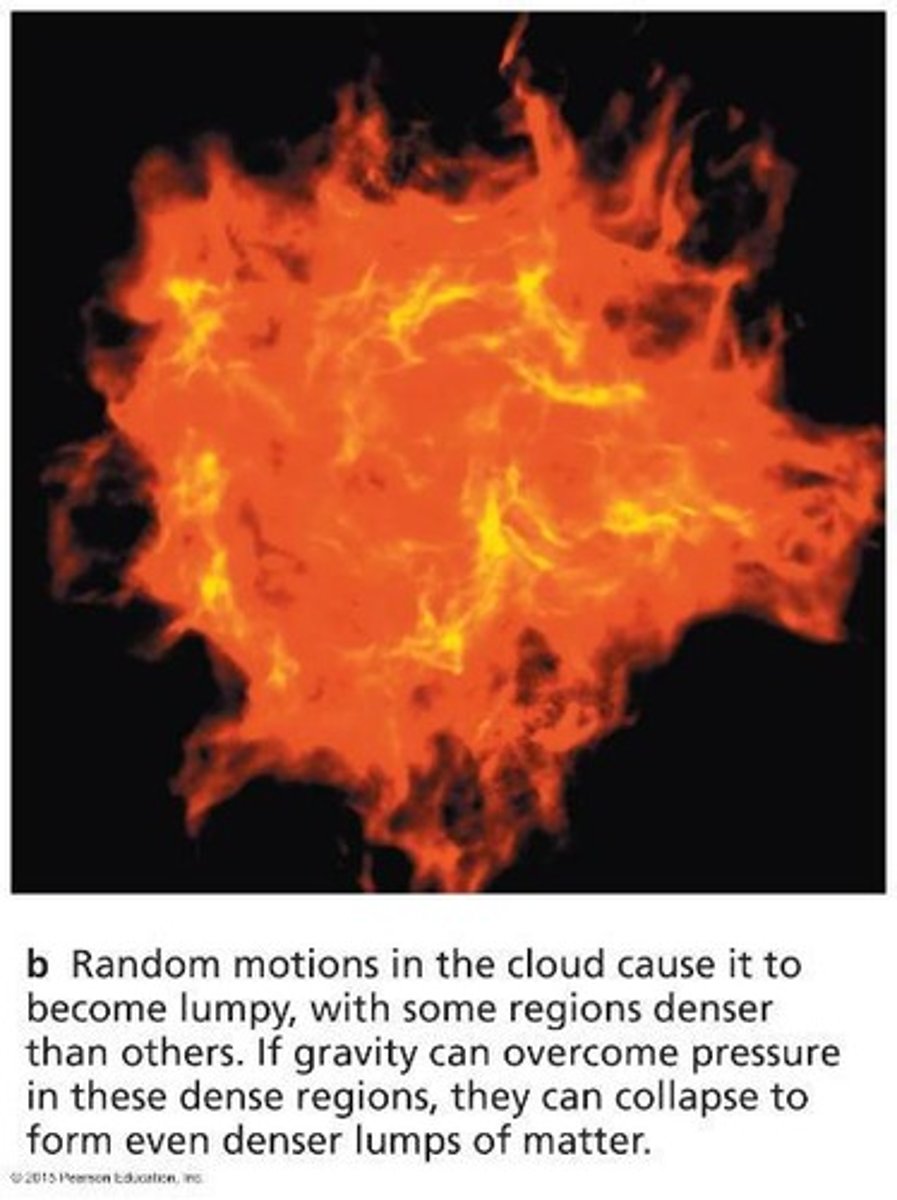
What percentage of gravitational energy is retained as heat during collapse?
50% is retained to heat the gas.
What occurs to the temperature and density during the gravitational collapse of a cloud?
They rise, leading to higher pressures.
What are the lumps in a cloud that can become stars called?
Cores
What is formed when the center of a cloud fragment becomes dense enough?
A protostar
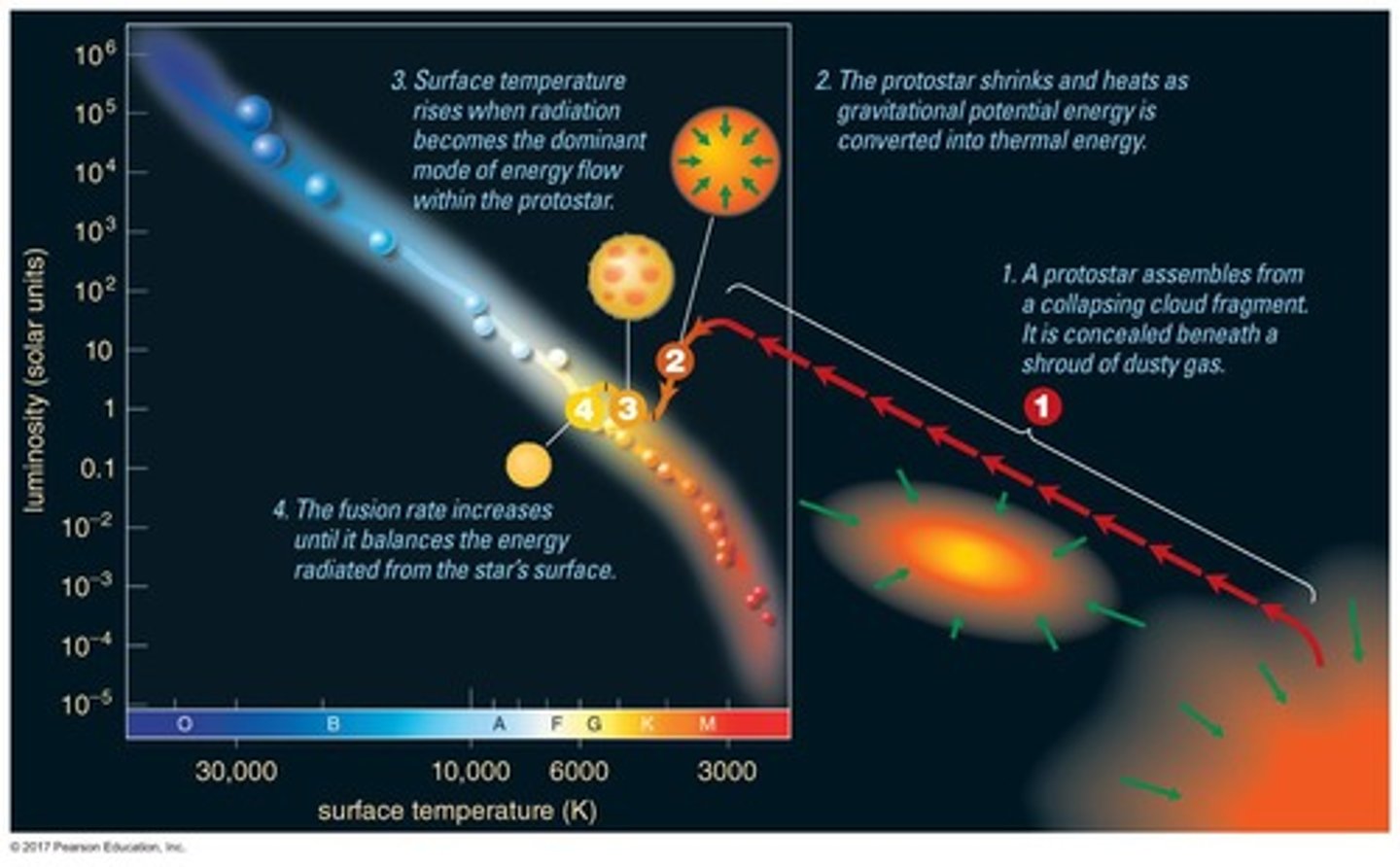
What is the process by which thermal energy builds up in a contracting cloud fragment?
Trapping of thermal energy
What causes a contracting cloud to spin faster?
Conservation of angular momentum
What happens to a cloud as it contracts and spins?
It flattens into a disk.
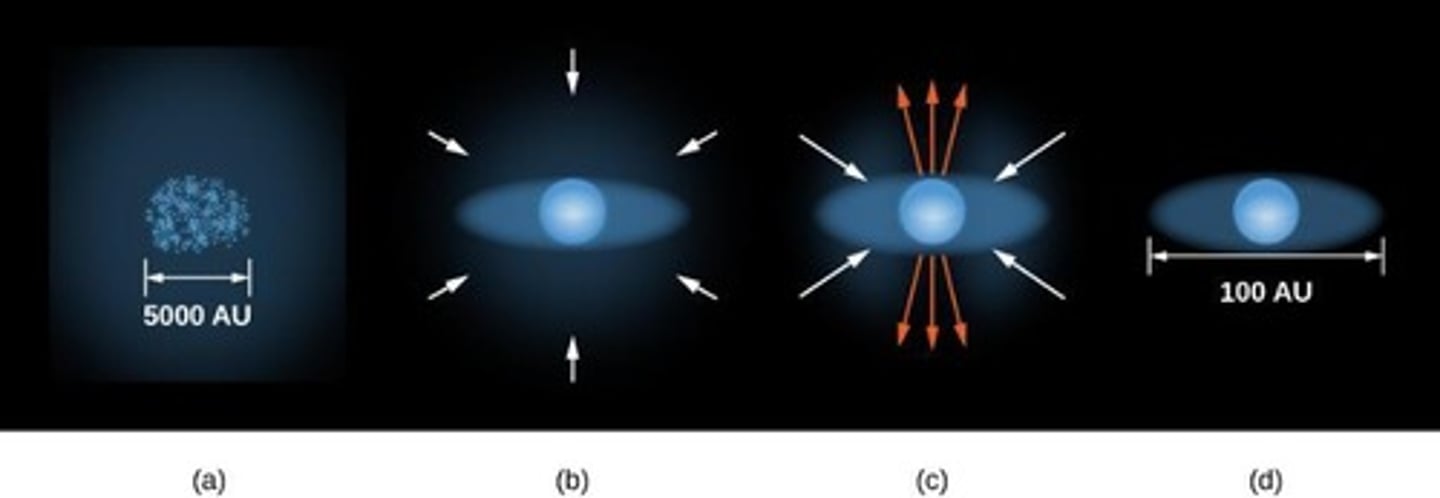
What is the role of collisions between gas particles in a contracting cloud?
They reduce random motions and help the cloud flatten.
What is the significance of gas jets in the context of protostars?
They flow outward from protostars, indicating energy and material ejection.
What do the disks around protostars indicate?
They are regions where matter is accumulating around a young star.
What are protoplanetary disks?
Disks of gas and dust surrounding young stars where planets may form.
What is the age of the star HD 141943 as observed in protoplanetary disks?
About 17 million years
What is the age of the star HD 191089 as observed in protoplanetary disks?
About 12 million years
What happens to the surrounding gas when a protostar grows?
It may be blown away by the protostar or a neighboring star.
What is the effect of gravity on a cloud during contraction?
It causes the cloud to become smaller and increases internal pressure.
What is the role of CO in the contraction of star-forming clouds?
It helps in radiating thermal energy away, allowing contraction to continue.
What instrument is used to block the light of a central star while imaging its protoplanetary disk?
A coronograph
What age is the star HD 141943?
About 17 million years
What age is the star HD 191089?
About 12 million years
What do the dark, dusty disks around young stars in the Orion Nebula represent?
Protoplanetary disks
How large are the protoplanetary disks observed in the Orion Nebula?
Ranging from two to eight times the orbit of Pluto
What does the red glow at the center of each protoplanetary disk indicate?
A young star, no more than a million years old
What does the ALMA image of the young star HL Tau reveal about its protoplanetary disk?
Multiple rings and gaps indicating the presence of emerging planets
What happens at a core temperature of 10^7 K in a star's lifecycle?
Hydrogen fusion ignites
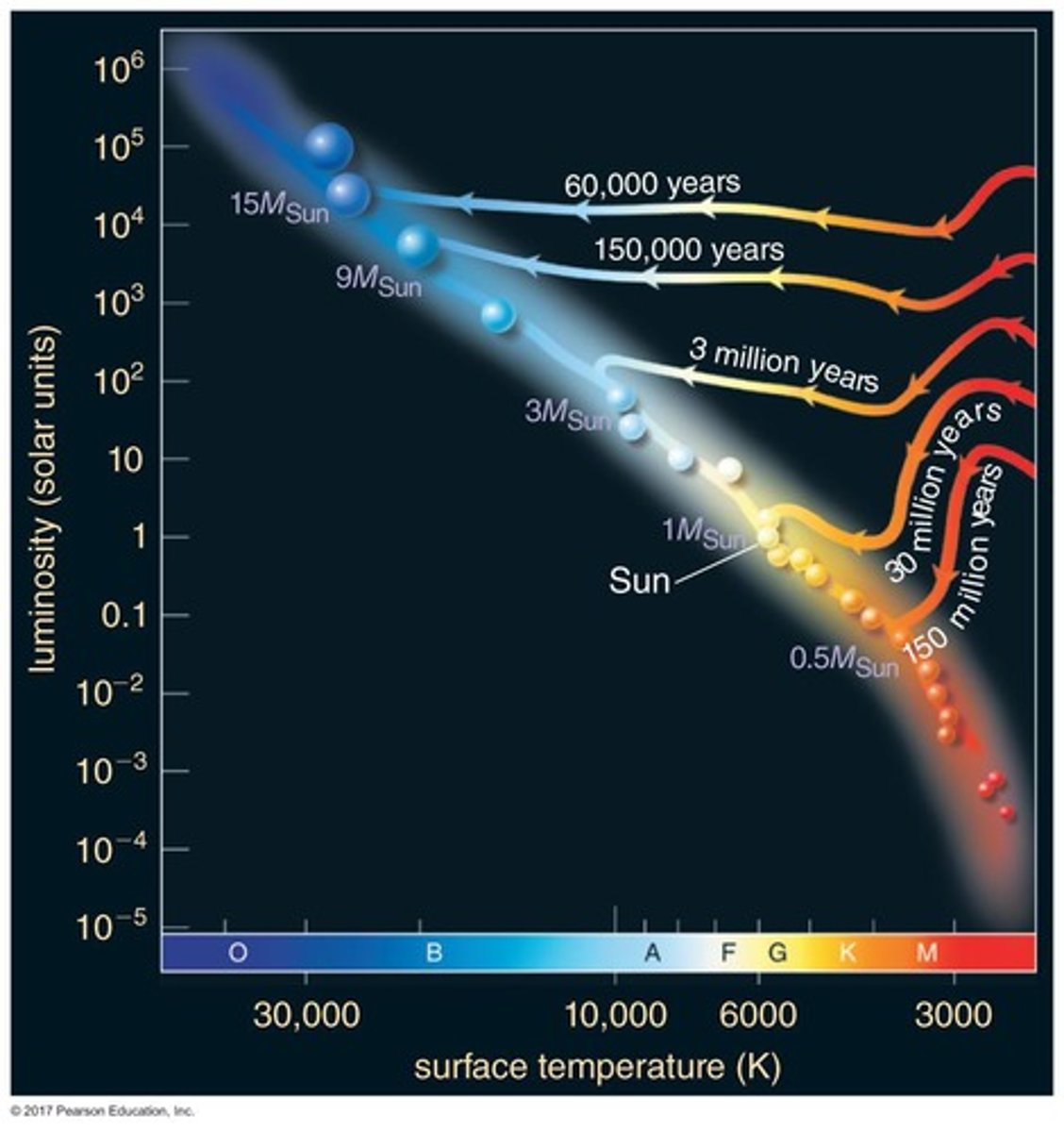
How long does it take for a solar mass star to reach the main sequence?
About 30 million years
What is the Zero-Age Main Sequence (ZAMS)?
The point at which a star begins hydrogen fusion and becomes a main-sequence star
How does the mass of a star affect its evolution towards the main sequence?
More massive stars reach the main sequence more quickly
What do evolutionary tracks on the H-R diagram show?
How stars of different masses change during the early parts of their lives
What is the significance of the Eagle Nebula's pillars of dust?
They are regions of higher density that may harbor embryonic stars
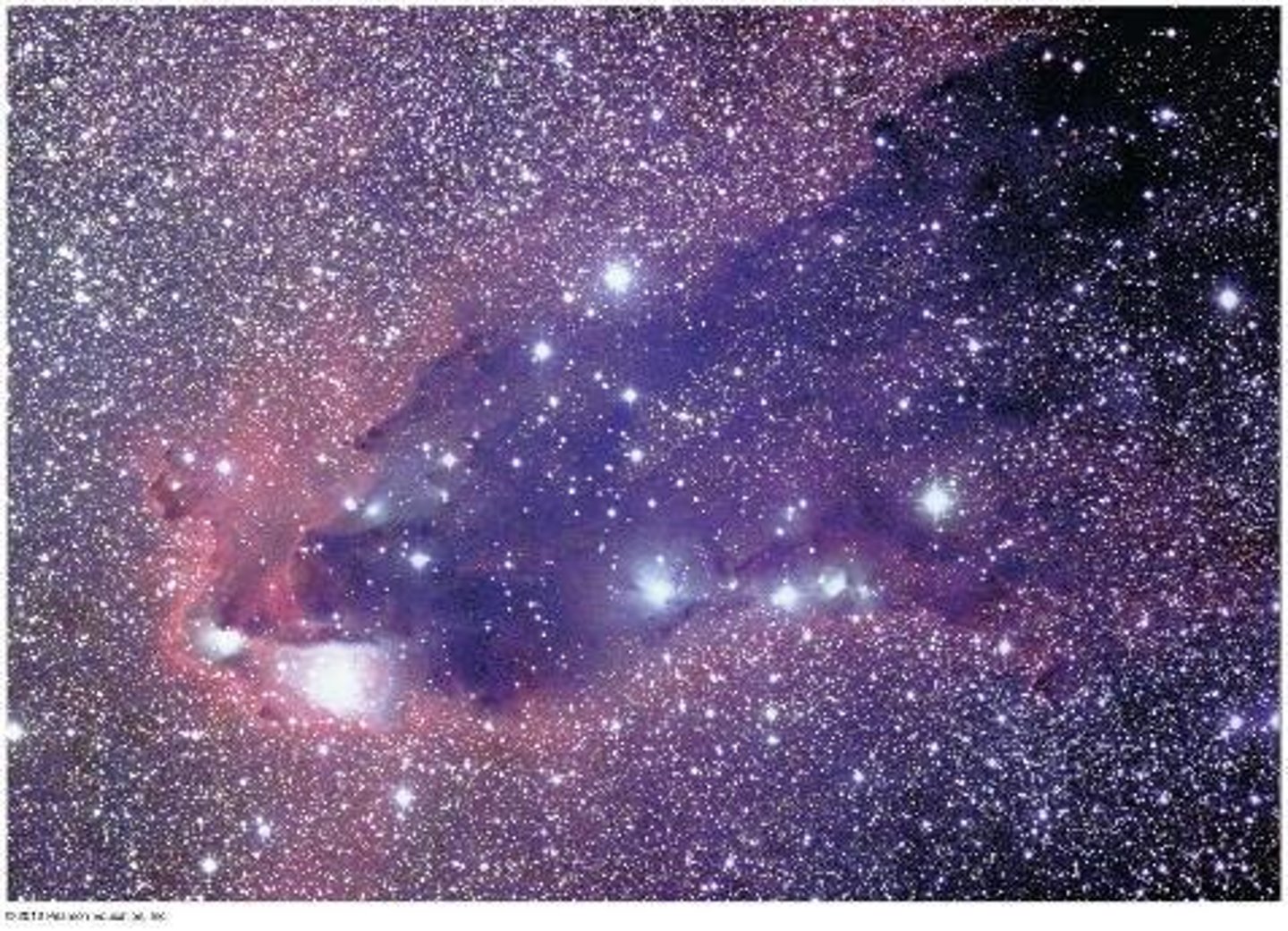

What is the distance of the Eagle Nebula from Earth?
About 7000 light-years
What does the Orion Nebula contain that is significant for star formation?
Some of the youngest stars in the solar neighborhood
What is the Trapezium cluster in the Orion Nebula?
A cluster of four very bright stars that energize the nebula
How does infrared radiation help in studying the Orion Nebula?
It penetrates dust more easily than visible light, revealing more detail
What are evaporating gas globules (EGGs)?
Dense globules in the Eagle Nebula that may harbor embryonic stars
What are the Trapezium stars?
A group of four bright stars located at the center of the visible-light image of the nebula.
What is the Carina Nebula known for?
It is a star-forming region where jets powered by newly forming stars are embedded in a cloud of gas and dust.
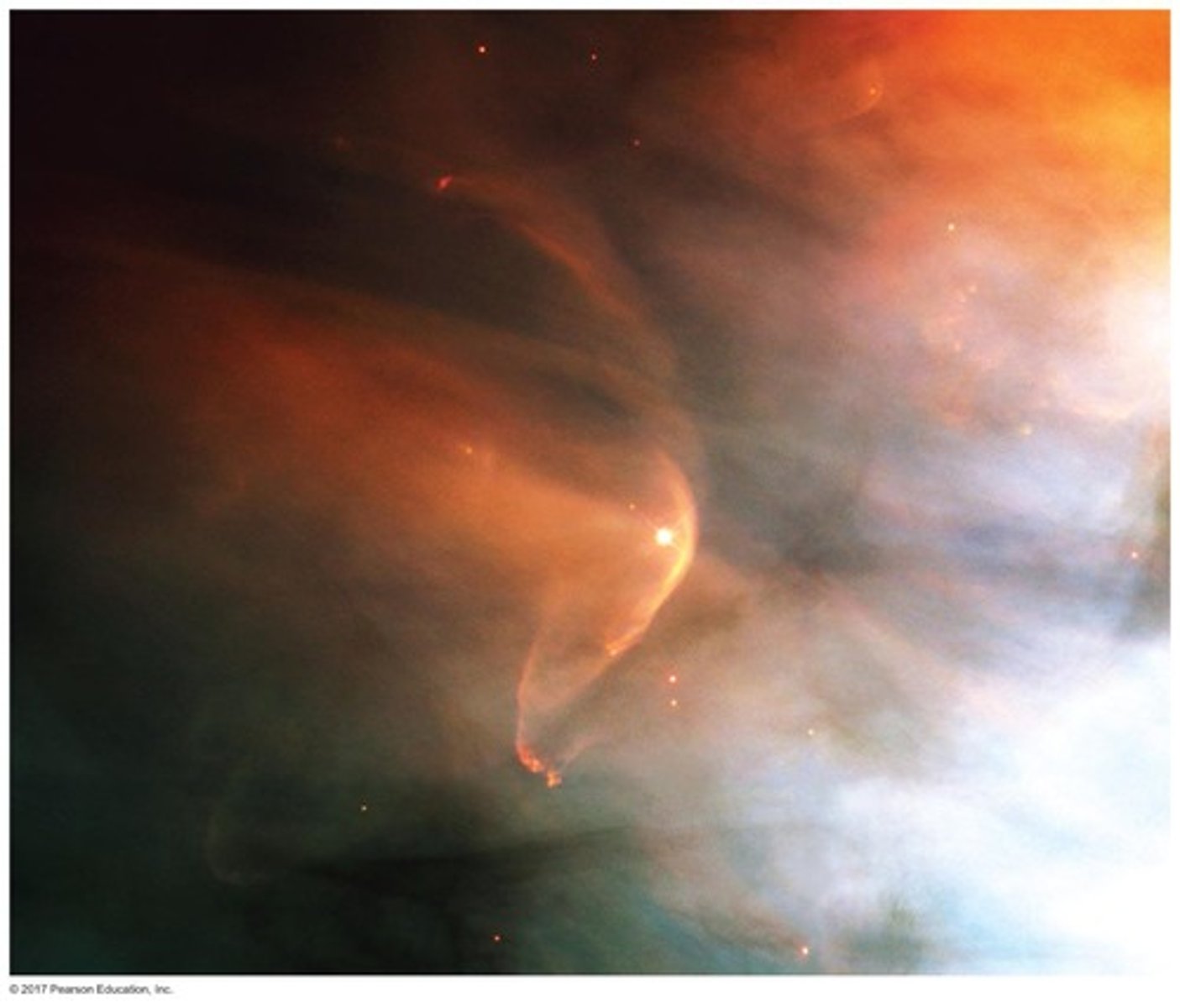

How old is the star cluster Westerlund 2?
Westerlund 2 formed within the Carina star-forming region about 2 million years ago.
What is the significance of stellar winds in star formation?
Stellar winds and radiation pressure from hot stars sculpt the surrounding gas and dust in star-forming regions.
What is a protostar?
A protostar is a dense core within a molecular cloud where a star is forming, surrounded by a disk of material.
What happens when a stellar wind breaks out from a protostar?
The wind is confined by the disk to flow out along the two poles of the star, eventually sweeping away surrounding cloud material.
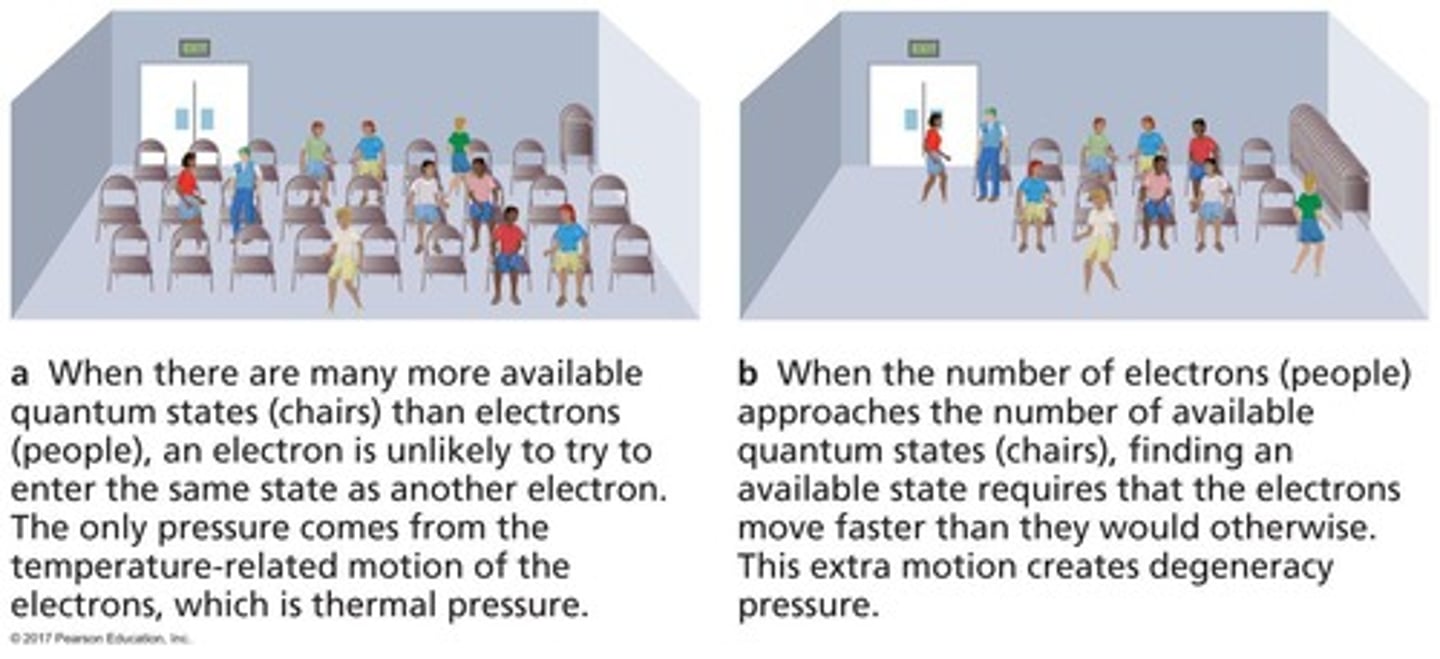
What is degeneracy pressure?
A quantum mechanical effect that prevents two electrons from occupying the same state in the same place, halting contraction in objects less than 0.08 MSun.
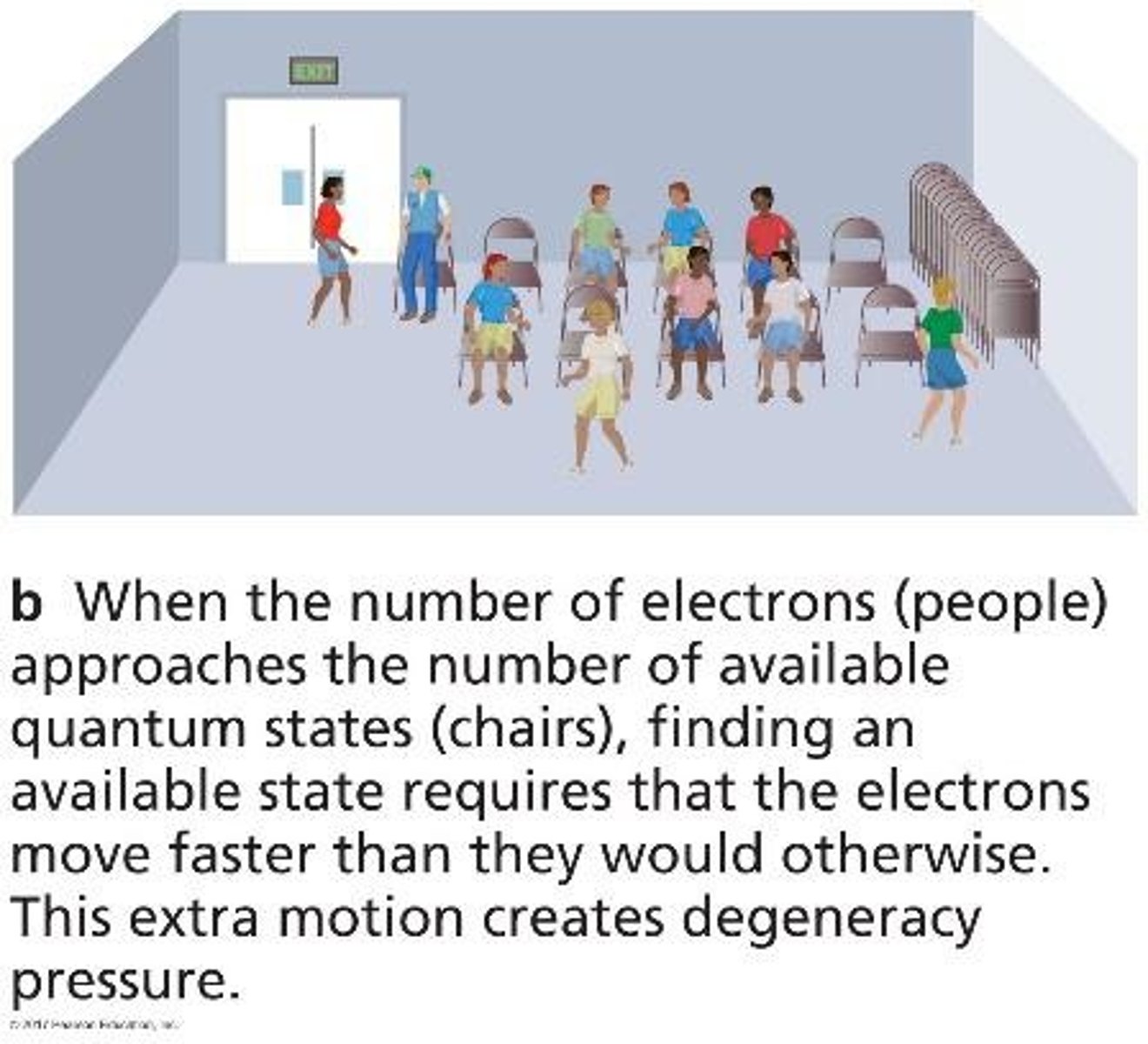
What are brown dwarfs?
Starlike objects that are not massive enough to start fusion, typically having a mass less than 0.08 MSun.

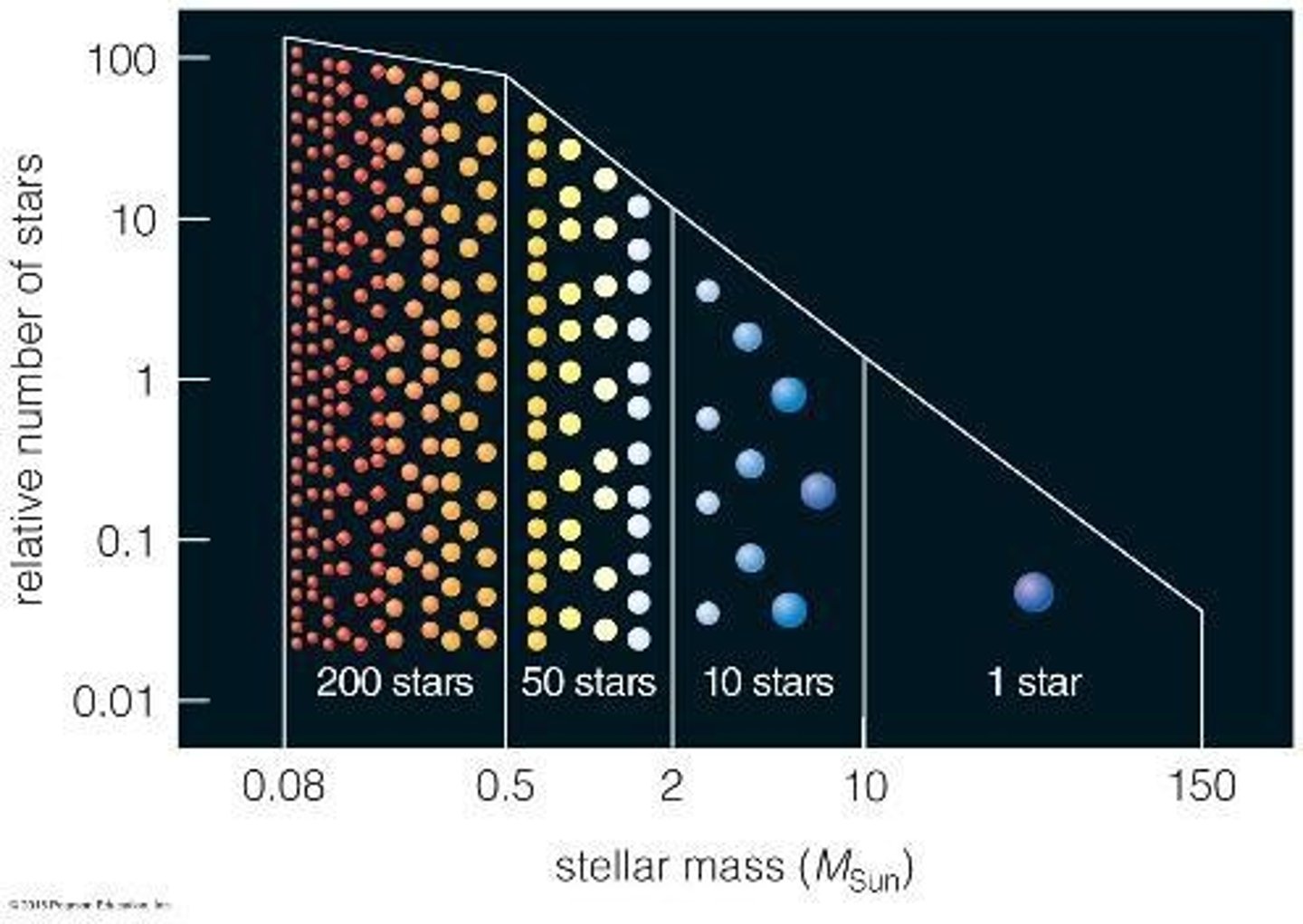
What is the upper mass limit for newborn stars?
The upper limit is about 150 MSun, although some observations suggest stars may exceed this limit.
What is the significance of radiation pressure in massive stars?
Radiation pressure from photons can drive the matter of very massive stars into space, limiting their maximum mass.
What is the estimated mass of the Pistol Star?
Originally thought to be 200 solar masses, it is now believed to be over 100 solar masses.
How do we measure the age of star clusters?
By observing the H-R diagram, which shows the relationship between the luminosity and temperature of stars.
What are the characteristics of young star clusters?
They are loose, open clusters found in the galactic plane, containing O and B stars on the main sequence.

What is the typical mass range for newborn stars?
Newborn stars can range from about 0.08 MSun to an upper limit of around 100 MSun, with some rare cases observed up to 300 MSun.
What is the role of thermal pressure in star formation?
Thermal pressure, dependent on heat content, is the main form of pressure in most stars but cannot stop contraction alone.
What is the relationship between star clusters and their formation?
Stars within a cluster share a common age, chemical composition, and distance but can have different masses and ages.
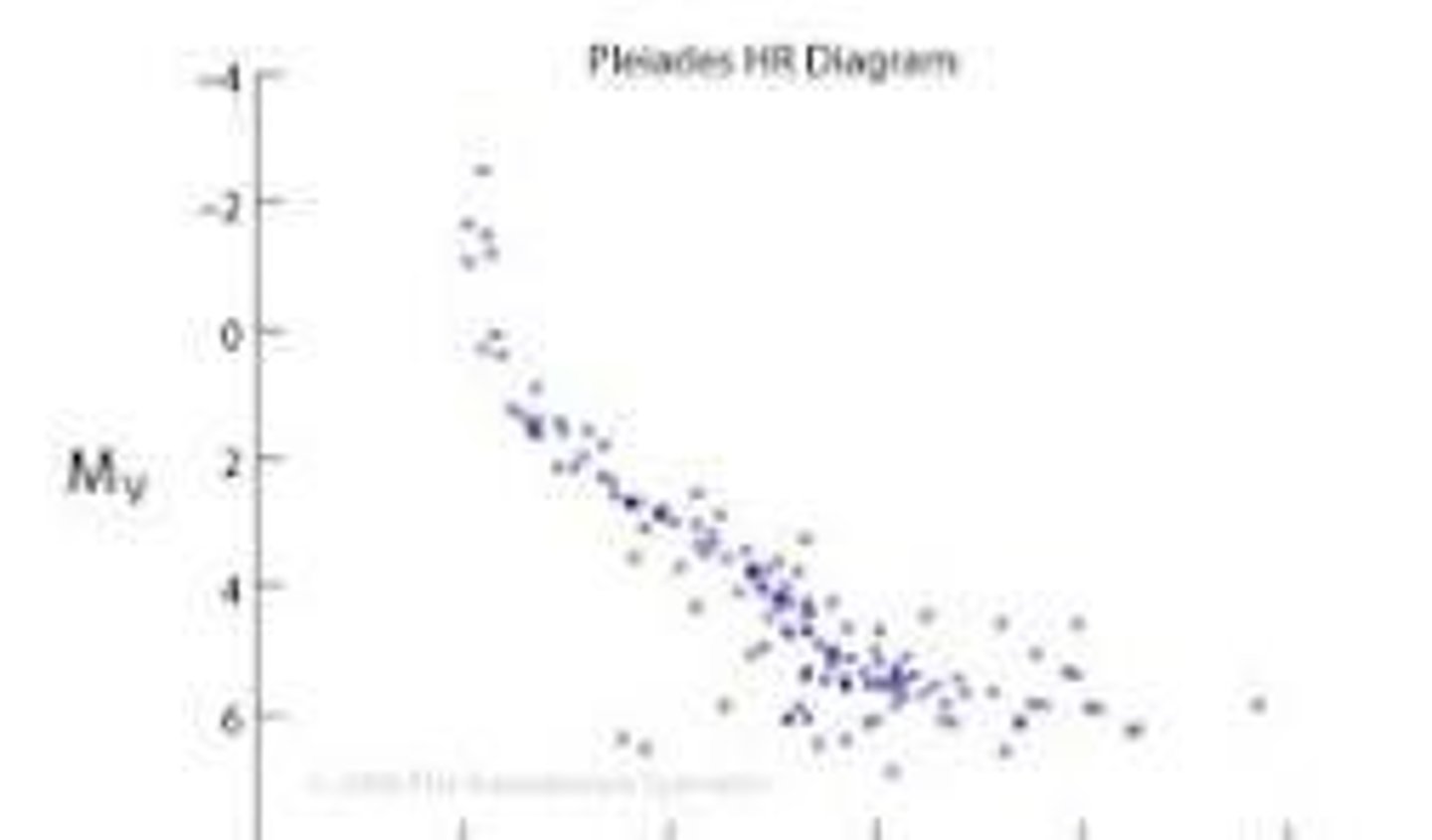
What happens to stars in a cluster over time?
As stars age, they may disperse and no longer be recognizable as a cluster due to their individual motions.
What is the significance of the H-R Diagram?
The H-R Diagram plots stars based on their luminosity and temperature, helping to determine their age and evolutionary stage.
What is the impact of ionized gas surrounding young stars?
The pressure from hot, ionized gas compresses nearby material in molecular clouds, initiating gravitational collapse for new star formation.
What is the interstellar medium primarily composed of?
Gas (99%) and dust (1%)

What are the main components of the gas in the interstellar medium?
98% hydrogen and helium, 2% heavier elements
What is the typical size range of interstellar dust grains?
10-8 to 10-7 meters (1/100 to 1/10 of a micron)
What elements are commonly found in interstellar dust?
Carbon (C), oxygen (O), silicon (Si), and iron (Fe)
How can we determine the composition of interstellar gas?
By analyzing absorption lines in the spectra of stars
What is the significance of the Orion Nebula in studying interstellar gas?
It emits red glow from ionized hydrogen, indicating hot young stars nearby
What phenomenon produces the 21-centimeter line in hydrogen atoms?
The spin flip of the electron in the hydrogen atom
Who were Harold Ewen and Edward Purcell?
They were physicists who made the first detection of interstellar 21-cm radiation
What is a supernova remnant and its significance in the interstellar medium?
The remains of a dying star that can heat surrounding gas to millions of K
What is the role of interstellar dust in blocking light from stars?
It obscures the view of stars located behind dust clouds
What is a dark nebula, and how is it identified?
A dark interstellar cloud that obscures light from stars behind it
What is the relationship between NGC 3603 and its parent gas cloud?
NGC 3603 is a young star cluster formed from the surrounding gas cloud
What is the appearance of Barnard 68, and why is it significant?
A dark interstellar cloud that obscures light due to its proximity to Earth
What happens to the gas and dust in the interstellar medium as stars form and die?
They cycle through stages of formation, life, and return to interstellar space
What is the effect of massive stars on their surrounding gas clouds?
They blow bubbles in the gas clouds and can trigger new star formation
How does the light from hot stars affect the appearance of interstellar dust?
It can cause the dust to glow or scatter light, creating visual phenomena
What is the significance of the Balmer series in relation to interstellar gas?
It indicates the presence of hot young stars that ionize surrounding gas
What is fullerene C60, and why is it notable in interstellar studies?
A molecule with a cage-like structure, significant for its presence in interstellar dust
What is Barnard 68 and how is it represented in infrared?
Barnard 68 is a dark cloud of interstellar dust that appears in infrared images as it emits radiation at a wavelength of 2.2 microns, revealing stars behind it that are obscured in visible light.
Who was Edward Emerson Barnard and what was his contribution to astronomy?
Edward Emerson Barnard (1857-1923) made significant observations that advanced astronomical explorations.
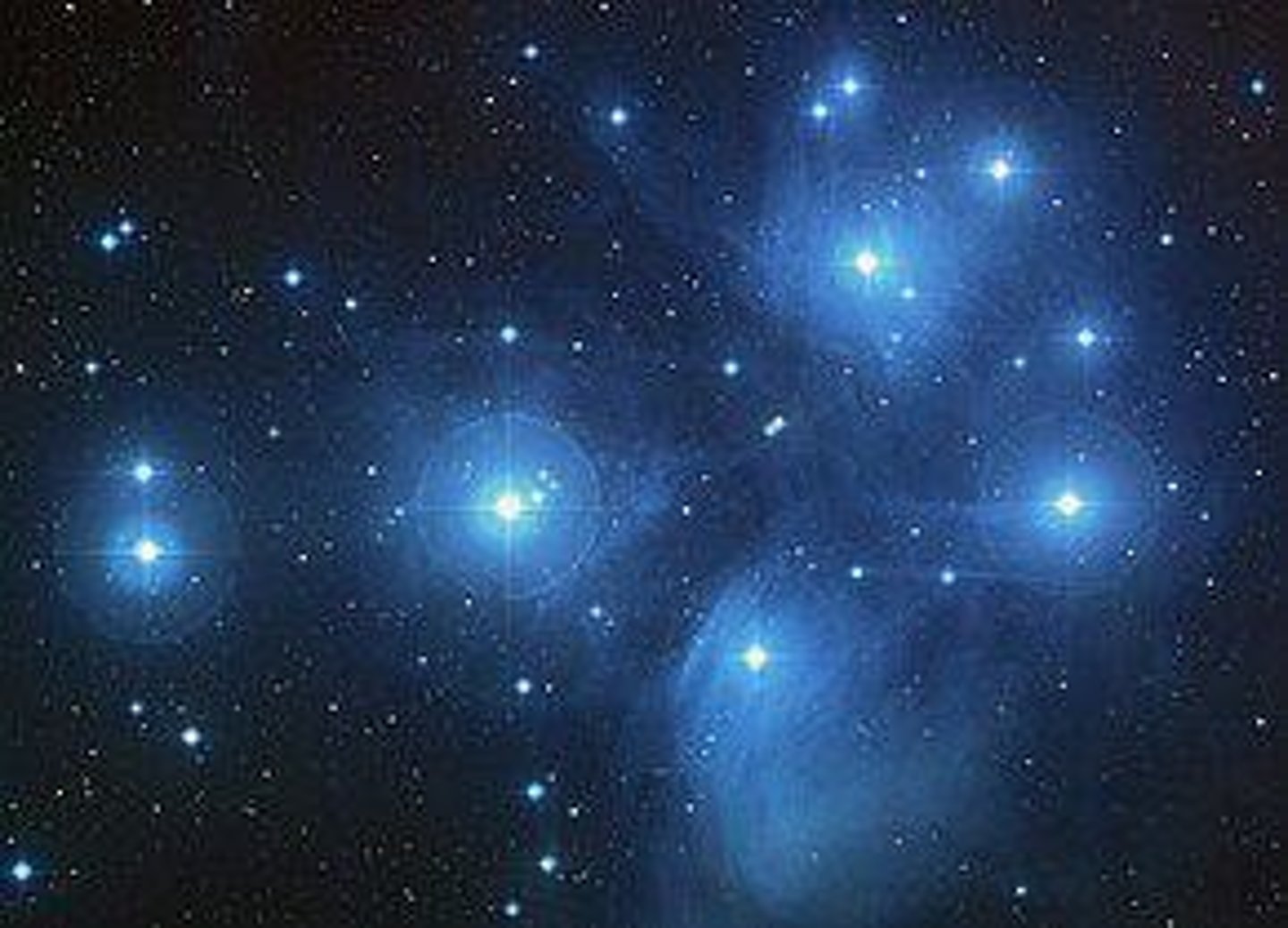
What is a reflection nebula and how does it relate to the Pleiades Star Cluster?
A reflection nebula, like the one surrounding the Pleiades Star Cluster, shines by scattering light from nearby bright stars, making the dust appear bluish.
How does interstellar dust affect the appearance of distant stars?
Interstellar dust scatters blue light more efficiently than red light, making distant stars appear redder.
What is the Horsehead Nebula and how does it appear in visible versus infrared light?
The Horsehead Nebula is a dark cloud of dust that appears prominently in visible light against a bright background, while in infrared light, it shows bright regions where dust is heated by nearby stars.
What does the infrared emission from the plane of the Milky Way indicate?
Infrared emission from the Milky Way, captured by the Spitzer Space Telescope, shows regions of dust emitting at various wavelengths, indicating areas where dust is warmed by young stars.
Who was Victor Hess and what did he discover?
Victor Hess (1883-1964) discovered cosmic rays during balloon flights that reached high altitudes.
What does the X-ray image of the sky reveal about cosmic sources?
The X-ray image made by the ROSAT satellite shows different X-ray energies, indicating a source of X-rays surrounding the Sun.
What does the computer simulation of the Milky Way's interstellar medium show?
The simulation illustrates the distribution of neutral hydrogen gas, giant molecular clouds in spiral arms, and low-density holes created by supernova explosions.
What is the Local Interstellar Cloud, also known as Local Fluff?
The Local Interstellar Cloud is a low-density region of interstellar matter that the solar system is currently moving through, with a density of about 0.3 atoms per cm³.
What is the temperature of the Local Interstellar Cloud?
The temperature of the Local Interstellar Cloud is approximately 7,000 K.
How long ago did the solar system enter the Local Interstellar Cloud?
The solar system is thought to have entered the Local Interstellar Cloud between 44,000 and 150,000 years ago.
What is the expected duration for the solar system to remain within the Local Interstellar Cloud?
The solar system is expected to remain within the Local Interstellar Cloud for another 10,000 to 20,000 years.