IGCSE Business (copy)
1/295
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
296 Terms
Business
An organisation which produces goods and services.
Need
A need is a good or service essential for living.
Want
A want is a good or service which people would like to have, but which is not essential for living. People's wants are unlimited.
Economic problem
There exist unlimited wants but limited resources to produce the goods and services to satisfy those wants, this creates scarcity.
Scarcity
Scarcity is the lack of sufficient products to fulfill the total wants of the population.
Factors of production
Factors of production are those resources needed to produce goods or services. There are four factors of production and they are in limited supply.
(factor of production) Land
Land is the term used to cover all of the natural resources provided by nature and includes fields, forests, oil, gas, metals and other resources.
(factor of production) Labour
Labour is the term used to describe the number of people available to make products.
(factor of production) Capital
Capital is the finance, machinery and equipment needed for the manufacture of goods.
(factor of production) Enterprise
Enterprise is the skill, and risk-taking ability of the person who brings the factors of production together to produce a good or a service. For example, the owner of a business. These people are called entrepreneurs.
Opportunity cost
Opportunity cost is the next best alternative given up by choosing another item.
Specialisation
Specialisation occurs when people and businesses concentrate on what they are best at.
Why specialisation is common
•Specialized machinery and technology are widely available
•Increasing competition means businesses have to have low cost
•Higher living standards can result from being specialized
Division of labour
Division of labour is when the production process is split up into different tasks and each worker performs one of these tasks. It is a form of specialisation.
Advantages of division of labour and job specialization
•Workers are trained in one task and specialize in this-Increases efficiency
•Less time is wasted moving from one workbench to another
•Employment increases
•Lower costs
•Increased production
Disadvantages of division of labour and job specialization
•Workers can become bored doing just one job-efficiency might fall
•If a worker is absent no one else can do the job- production might be stopped
•Products become standardized
•Small businesses can't compete
Added value
Added value is the difference between the selling price of a product and the cost of bought in materials and components.
How to increase added value
-Increase selling price but keep the costs the same, to do this you need to have a good image of your product
-Reduce cost but keep selling price the same, this might decrease the quality
Primary sector
The primary sector of industry extracts and uses the natural resources of the earth to produce raw materials used by other businesses
Secondary sector
The secondary sector of industry manufactures goods using raw materials provided by the primary sector.
Tertiary sector
The tertiary sector of industry provides services to consumers and the other sectors of industry.
Industrialization
The growing importance of the secondary sector in developing countries
Advantages of industrialization
•National output increases which increases average living standard
•Increasing output can result in lower imports and higher exports
•Employment increases
•Tax money increases
•Value is added to the country's raw materials
Disadvantages of industrialization
•More people move to the city which causes housing and social problems
•Expansion on manufacturing may make it difficult for businesses to recruit and maintain staff
•Business import costs will increase
•Pollution from factories add to the countries environmental problems
•multinational companies will comparative with the small businesses
De-industrialisation
De-industrialisation occurs when there is a decline in the importance of the secondary, manufacturing sector of industry in a country.
Disadvantages of de-industrialization
•Increase in competition for businesses
•Structural unemployment- some people don't have the skills to work in the tertiary sector so the become unemployed
Advantages of de-industrialization
•Income and living standards of the citizens increase
Why does de-industrialization happen
-Sources of primary products become depleted
-Most developed countries can't compete in manufacturing against newly industrialized countries
-As the country's total wealth increases and living standards rise, more people spend more money on travel and restaurants than on manufactured products
Mixed economy
A mixed economy has both a private sector and a public sector.
Private sector
Businesses not owned by the government. Services are charged and paid for by the customer
Public sector
Government owned and controlled businesses and organisations. Services provided are free and are paid for by taxes.
Privatisation
When governments sell public sector businesses to private sector businesses
Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is a person who organises, operates and takes the risk for a new business venture.
Benefits of being an entrepreneur
-Independence- able to choose how to use time and money
-Able to put ideas into practice
-May become famous and successful if business grows
-May be profitable and the income might be higher than working as an employee for another business
-Able to make use of personal interests and skills
Disadvantages of being an entrepreneur
-Risk-the business might fail
-Capital- have to put own money into business and might have to find other sources of money
-Lack of knowledge and experience in starting and operating a business
-Opportunity cost- lost income from not being employed in another business
Qualities of an entrepreneur
-Hard working- Have to work long hours and have few vacation days
-Risk taker- Making decisions to produce goods or services that people might buy is potentially risky
-Creative- A new business needs new ideas about products , services and ways to attract customers, in order to make it different from other companies
-Optimistic- Looking forward to the future is essential, if you think you will fail you will fail
-Self-confident- Necessary to convince to convince banks, other lenders and customers that your business will be successful
-Innovative- Being able to put new ideas into practice in interesting and different ways is important
- Independent- Will often have to work on their own before they can hire other people, have to be able to be motivated and be able to work by their self
-Effective communicator- Talking clearly and confidently to banks, other lenders, customers and government agencies about the new business will raise the profile of the new business
Why do governments support business startups
-Reduce unemployment- New businesses will often create jobs
-Increase competition- New businesses give customers more choice and compete with already established businesses
-Increase output- The economy benefits from being increased output of goods and products
-Benefit society-Entrepreneurs may create social enterprises
-Can grow further- May help some small firms grow to become very large and important in the future
How do governments help business
-Business idea and help- Governments organize advice and support sessions offered by experienced people
-Finance- Loan money to businesses at small interest rates
-Labour- Gives businesses money to train employees
Research- Encourage universities to make their research facilities available to new businesses
Business plan
A business plan is a document containing the business objectives and important details about the operations, finance and owners of the new business.
How does a business plan help an entrepreneur
-Help them stay on strategy
-Objectives will be clear
- Helps have a good idea about cost and revenue
-Helps with keeping track of what customers they are aiming at
-Helps with hiring people and buying machinery
-Encourages banks to give them loans
Ways to measure business size
-# of employees
-Value of output
-Value of sales
-Value of capital employed
Business size: #of employees
This method is easy to calculate and compare with other businesses.
Limitations:
-Some firms use productions methods which use very little labour and give a high output, this is true for capital intensive companies which use a lot of machinery.
-Also should 2 part-time employees be considered one employee or two
Value of output
Common way to compare business in the same industry(especially secondary sector)
Limitations:
-A high value of output does not mean that a business is large when using other methods, e.g a business employing very few people might produce very few very expensive products each year might have a higher value of output then a business which produces cheap products but has a large amount of employees
-Also the value of output might be different than value of sales of some products aren't sold
Value of sales
Common way to compare the size of retailers, usually selling the similar kind of product
Limitations:
- It could be misleading to use this to measure when comparing the size of businesses who sell different products
Value of capital employed
The total capital invested into the business.
Limitations:
-Some companies might employ a very little amount of capital but might have a large number of employees.
Value
How much something is worth.
Capital employed
Capital employed is the total value of capital used in the business.
Why do owners want their business to grow
-Possibility of higher profit for owner
-Higher status and prestige given to owners and managers, managers of bigger firms are usually paid more
-Lower average cost( Economies of sale)
-Larger market share- this gives the business more influence when dealing with suppliers and distributors
Internal growth
Internal growth occurs when a business expands its existing operations, e.g creating a new product or expanding to another market(location)
External growth
External growth is when a business takes over or merges with another business.
Integration
Integration is when one firm is integrated into another one.
Merger
A merger is when the owners of two businesses agree to join their firms together to make one businesses.
Takeover
A takeover is when one business buys out the owners of another business.
Horizontal integration
Horizontal integration is when one firm merges with or takes over another one in the same industry at the same stage of production.
Benefits of horizontal integration
-Internal economies of scale
-Cost savings from rationalisation
-Potential to secure revenue "synergies"
-Wider range of products - (diversification)
-Reduces competition by removing rivals
-Increases market share and pricing power
-Can make the entry barriers higher for new rivals
Benefits of vertical integration
-Control of the supply chain - this helps to reduce
costs and improve the quality of inputs into the
production process
-Improved access to key raw materials perhaps at
the expense of rival businesses
-Better control over retail distribution channels
-Removing suppliers, information and retailers from competitors which helps to make a market less contestable
Vertical integration
Vertical integration is when one firm merges with or takes over another one in the same industry but at a different stage of production, it can be forward (higher stage of production) or backward (lower stage of production).
Conglomerate integration
Conglomerate integration is when one firm merges with or takes over a firm in a completely different industry, this is also known as diversification.
Benefits of conglomerate integration
-Diversification spreading the risk taken by the
business
-Transfer of ideas between the different
sections of the business
Problems of business growth and how to overcome them
-Larger business is harder to control- Operate business in small units
-Poor communication- Operate business in small units or use newest IT technology
-Expansion is expensive so business will be short in finance- Expand slowly and ensure sufficient long-term finance is available
-Integrating with a business is hard- Introducing different styles of management requires good communication with the workforce, they need to understand why it is happening
Why do some businesses stay small
-The type of industry the business operates in- Firms in industries that offer specialised products or personal services. It would be difficult for them to do this if they expanded
-Market size- if the market size is small than a business which operates in that market is likely to remain small
-The owner's preference- Owner might want to avoid the stress and worry of running a large company
Why some businesses fail
-Poor management
-Failure to plan for change
-Poor financial management
-Over-expansion
-Risks of new business startups
Sole trader
Sole trader is a business owned by one person.
Liability
The state of being responsible for something, especially by law.
Limited liability
Limited liability means that the liability of shareholders in a company is only limited to the amount they invested.
Unlimited liability
Unlimited liability means that the owners of a business can be held responsible for the debts of the business they own. Their liability is not limited to the investment they made in the business.
Partnership
Partnership is a form of business in which two or more people agree to jointly own a business.
Partnership agreement
A partnership agreement is the written and legal agreement between business partners. Not essential to have it but always recommended.
Unincorporated business
An unincorporated business is one that does not have a separate legal identity. Sole traders and partnerships are unincorporated businesses.
Incorporated business
Incorporated businesses are companies that have separate legal status from their owners.
Shareholders
Shareholders are the owners of a limited company. They buy shares which represent part ownership of a company.
Annual general meeting (agm)
An 'agm' is a legal requirement for all companies. Shareholders may attend and vote on who they want to be on the Board of Directors for the coming year.
Dividends
Dividends are payments made to shareholders from the profits (after tax) of a company. They are the return to shareholders for investing in the company.
Joint venture
A joint venture is when two or more businesses agree to start a new project together, sharing the capital, the risks and the profits.
Franchise
A franchise is a business based upon the use of the brand names, promotional logos and trading methods of an existing successful business. The franchisee buys the license to operate this business from the franchisor.
Public corporations
These are businesses that are fully owned by the government. But they are managed by a board of directors who are made clear what the purpose of the business is.
Business objectives
Business objectives are the aims or targets that a business works towards. SMART- specific, measurable, agreed upon, realistic, time oriented.
Benefits of business objectives
-They give workers and managers a clear target to work towards
-Making decisions will be easier since they will focus on "will it help us achieve our objectives"
-Helps unite entire business under one goal
-Can compare how business has performed compared to its objectives
Different types of objectives
-Survival
-Profit
-Growth
-Returns to shareholders
-Market share
-Service to the community
Objectives of social enterprises
Social: to provide jobs and support for the disadvantaged groups in society
Environmental: to protect the environment
Financial: to make a profit to reinvest back into the business.
Market share
Market share is the proportion of total market sales achieved by one business.
Stakeholder
A stakeholder is any person or group with a direct interest in the performance and activities of a business.
Stakeholder groups
-Owners
-Consumers
-Workers
-Government
-Managers
-Banks
-The entire community
Objectives for owner
-Growth of the business so their investment is worth more
-Want a share of the profit made by company
Objectives for workers
-Regular payment
-Contract of employment
-Job security
-Job that gives satisfaction and provides motivation
Objective for consumers
-Safe and reliable products
-Value for money
-Well-designed product of good quality
-Reliability of service and maintenance
Objective for managers
- High salaries for their important work
- Job security
-Growth of business so they can have more status and power
Objective for Government
-Business to be successful, will pay taxes, employ workers and increase country output
-Business to follow laws
Objective of the whole community
-Jobs for working population
-Product that does not damage the environment
-Safe products that are socially responsible
Objective for banks
-Business to pay back money lent with interest
Motivation
Motivation is the reason why employees want to work hard and work effectively for the business.
Why people work
-Money: to pay for necessities and some luxuries
-Security: A sense of security I.e. knowing that your job and pay are safe - you are not likely to lose your job
-Social needs: feeling part of a group or organization, meeting people, making friends at work
-Esteem needs (self-importance): feeling important, feeling that the job you do is important
-Job satisfaction: enjoyment is derived from feeling that you have done a good job
F.W. Taylor (content theories)
-People worked for only one reason; money
-Managers role was to maximize efficiency
-Motivation was either incentive or threat
-Devise equipment and methods to improve
productivity
-Pay scheme to reward workers that achieved
targets, and penalties for those that did not, e.g.
differential piece-rate.
-It was all about control
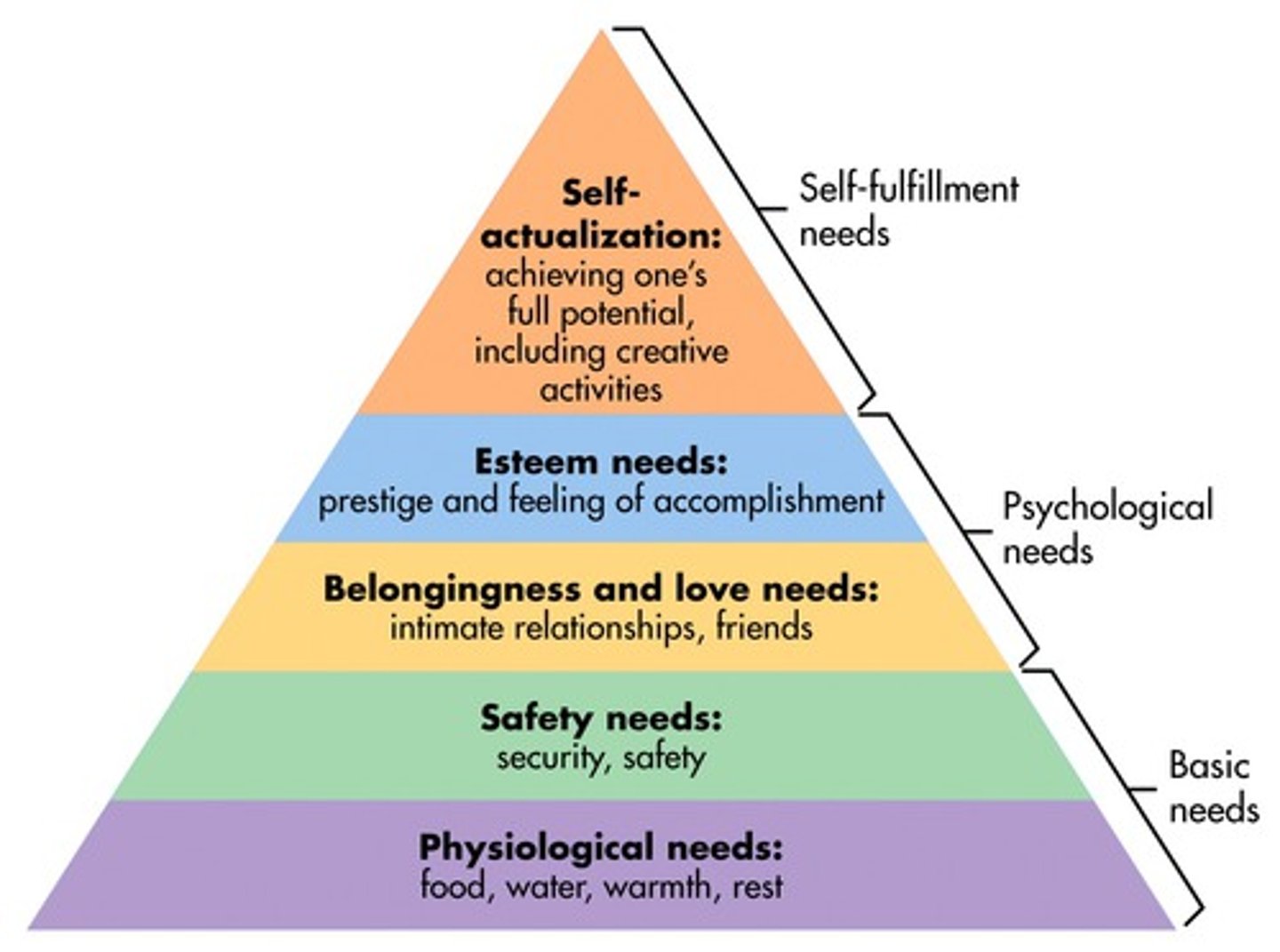
Maslow (content theories)
-There is a hierarchy of needs
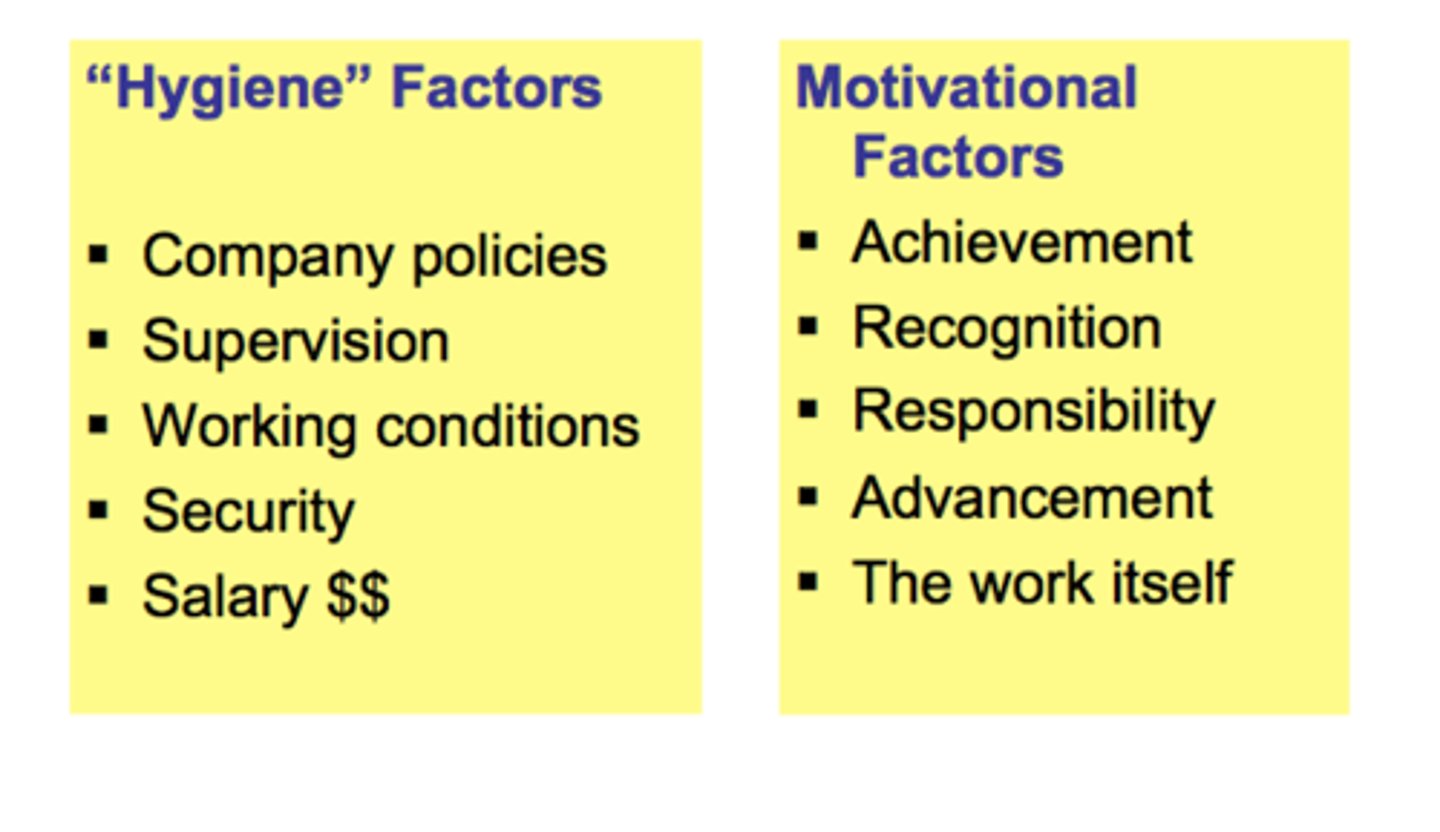
Herzberg (content theories)
-His focus was job satisfaction
-Hygiene factors were identified as factors that can lead to workers being dissatisfied.
-Motivators are factors, which help employees to gain job satisfaction, such as recognition of the job they are doing.
Wage
A wage is payment for work, usually paid weekly.
Salary
A salary is payment for work, usually paid monthly.
Commission
Commission is payment relating to the number of sales made .
Profit sharing
Profit sharing is a system whereby a proportion of the company's profits is paid out to employees.
Bonus
A bonus is an additional amount of payment above basic pay as a reward for good work.