Module 7 - Evolution of Genes and Genomes
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
included on exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
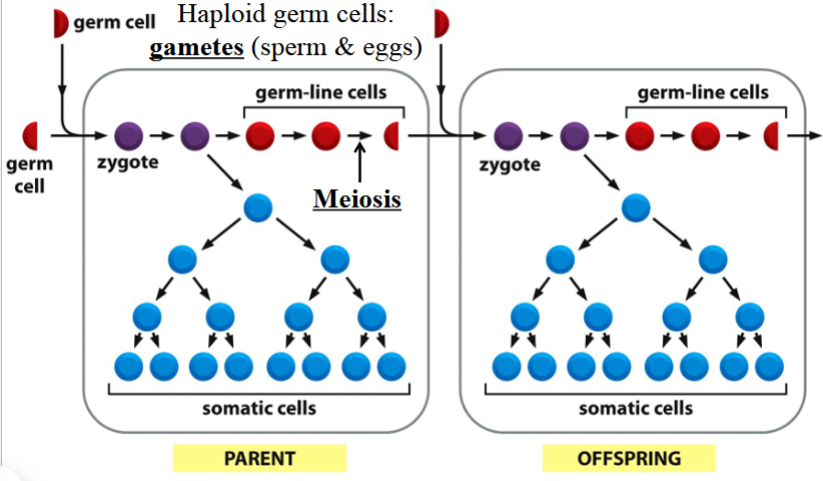
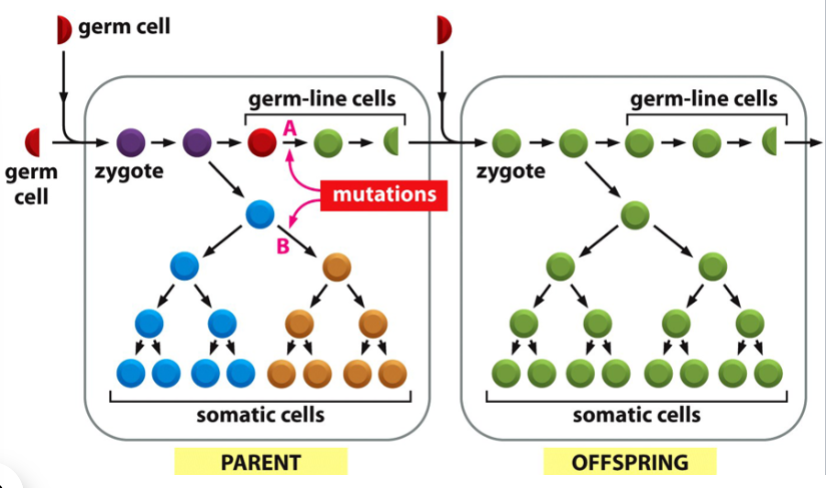
germ line
the cell lineage in a multicellular organism that contributes to the formation of the next generation by producing gametes (sperm or eggs)
(germ and gametes start with g, children (the result of sperm and eggs) are germs)
cells in this lineage are haploid (gametes)
gets aside early during development
(depicted in red in the picture)
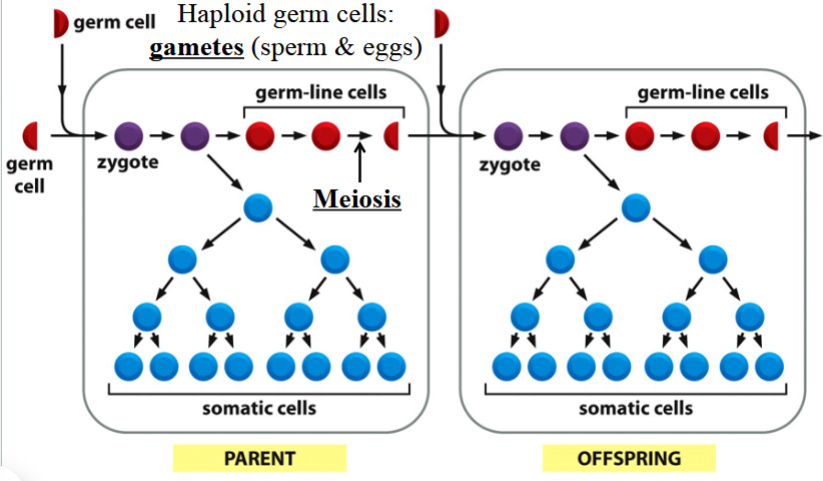
somatic cell
body cell
any cell in a multicellular organism that is not a germ line cell
cells in this lineage are diploid
(depicted in blue in the picture)
if a mutation occurs in a germ line cell:
after the lineage is set aside, the mutation will not affect the individual but may be passed to the next generation; may result in a heritable trait
(mutation is indicated in green)
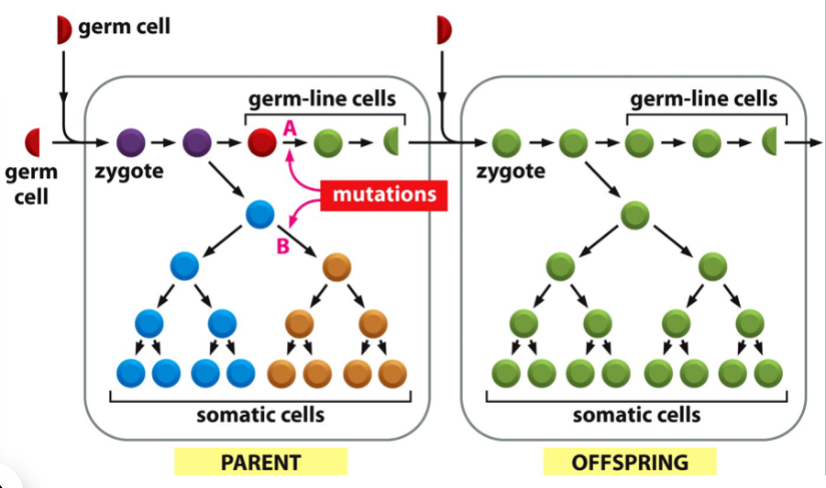
if a mutation occurs in a somatic cell:
the mutation may affect the individual in which the mutation occurred
(mutation is indicated in green)
genetic changes that contribute to gene alteration and genome evolution (4 of them)
mutation within a gene
mutation in a regulatory region
gene duplication
horizontal transfer
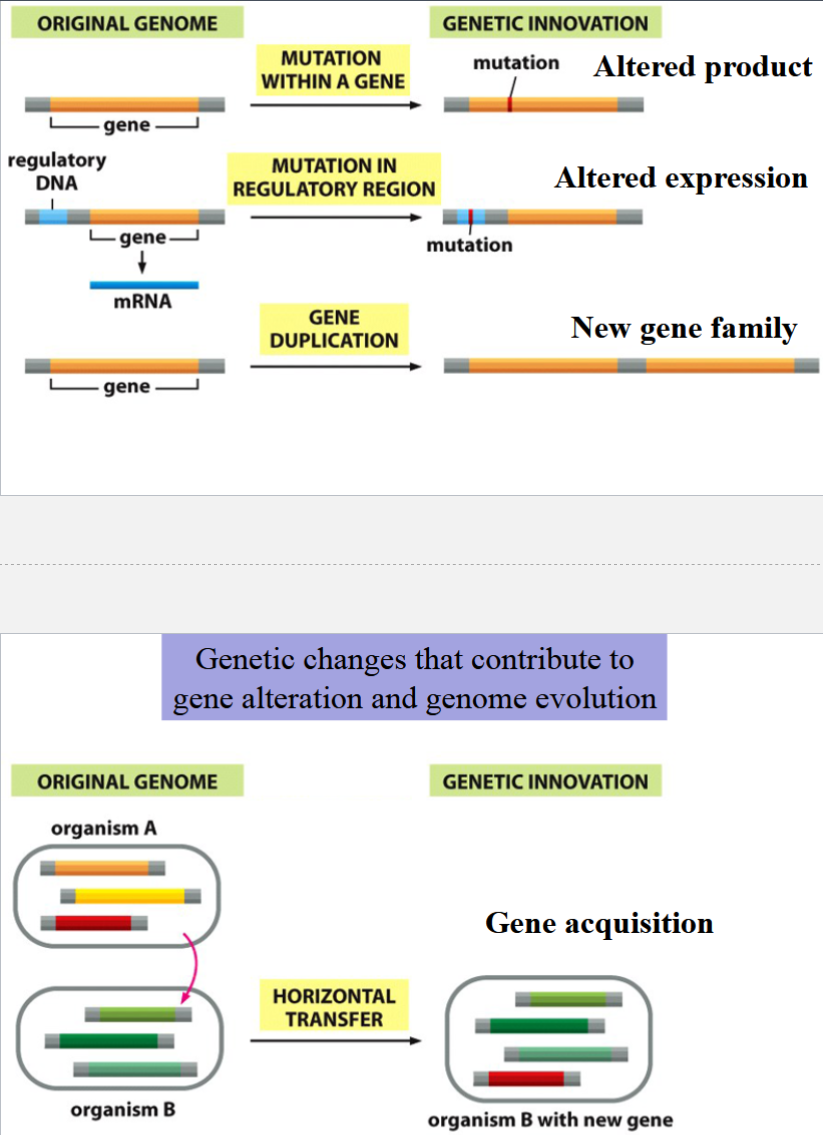
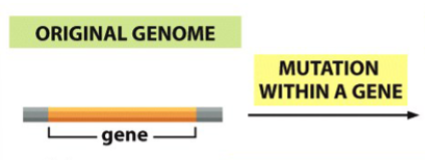
genetic innovation (result) of mutation within a gene
altered gene product

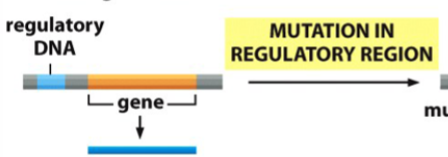
genetic innovation (result) of mutation in a regulatory region
altered gene expression

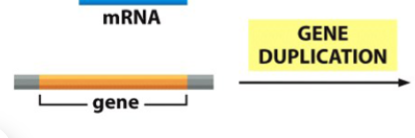
genetic innovation (result) of gene duplication
new gene family

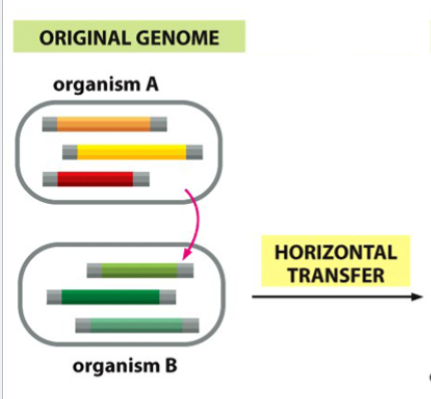
genetic innovation (result) of horizontal transfer
gene acquisition


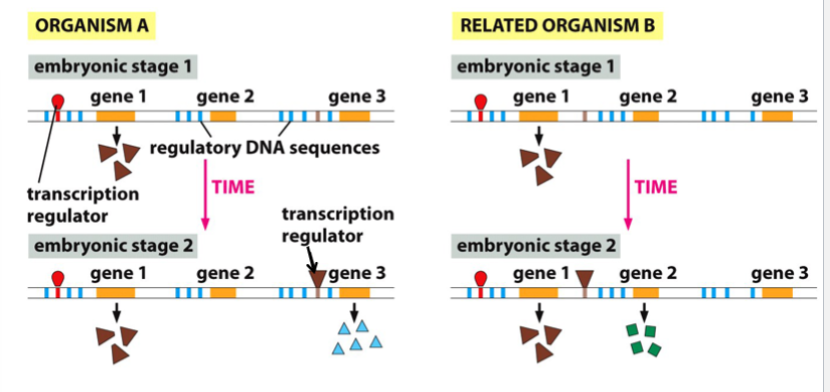
effect of regulatory regions on gene expression
differences in regulatory DNA may result in different developmental pathways, even in closely related species with the same sets of development-related genes
e.g. two species have (and express) gene 1 early on (gene 1 codes for a transcription regulator, which is active at a later embryonic stage)
in organism A, the regulator binds to regulatory DNA in front of gene 3
in organism B, the regulator binds to regulatory DNA in front of gene 2
as a result, different genes (gene 3 vs gene 2) are expressed despite the same genes, because of differences in the regulatory DNA

example: mutation in regulatory DNA in Drosophila
a mutation in regulatory DNA occurs
the antennapedia gene is ectopically expressed in the head
result: leg or leg-like structures form on the fly’s head

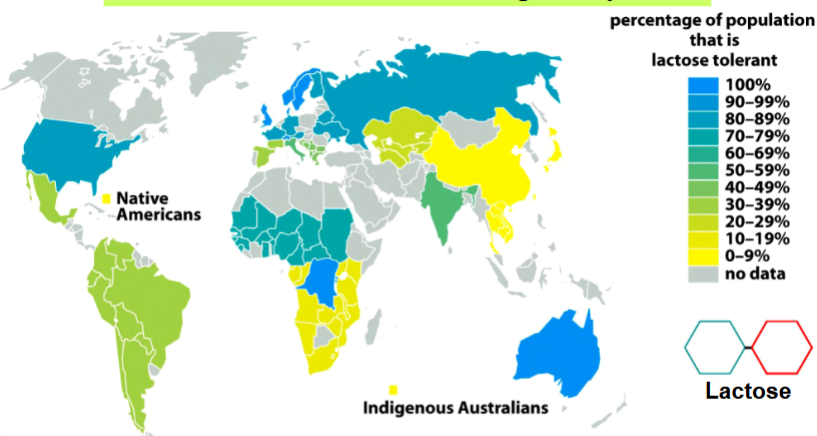
example: mutation in regulatory DNA of the lactase gene
a mutation occurs in the regulatory DNA of the lactase gene
mutation allows for lactase (an enzyme) to be made beyond infancy
result: the ability to digest lactose
the mutation was selected for in populations where humans first domesticated cattle (Northern Europe and Central Africa)
gene families
groups of genes that originate from a common ancestral gene
grouped by similarities in structure and/or function
originate by gene duplications
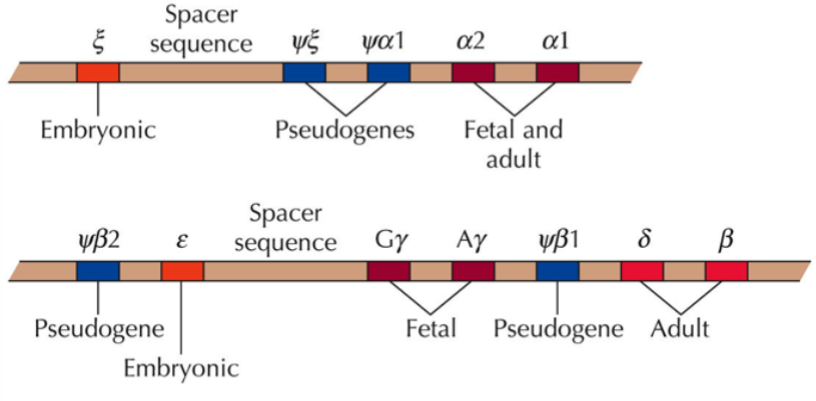
e.g. the globin gene family
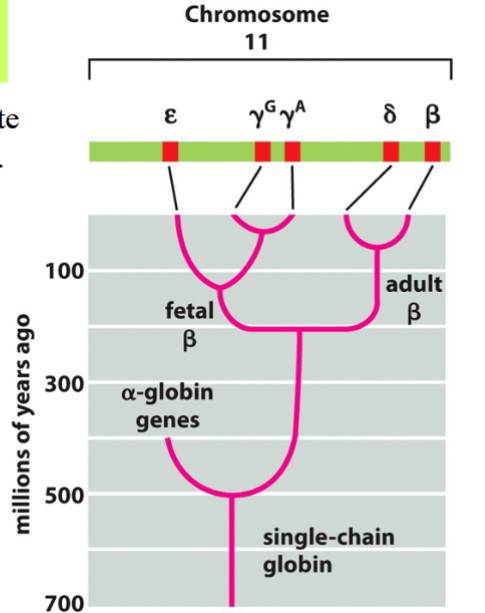
the globin gene family
example of a gene family
genes code for subunits of hemoglobin
all the genes have the same structure: 3 exons and 2 introns
different versions are expressed during fetal, embryonic, and adult stages (embryonic and fetal globins have higher affinities for oxygen than adult globins)
some members of the family are pseudogenes
adult version contains 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits
the alpha-globin cluster (top in picture) is on chromosome 16
the beta-globin cluster (bottom in picture) is on chromosome 11
hemoglobin
the protein that transports O2 in the circulatory system
subunits are coded for by genes in the globin gene family
pseudogenes
non-functional genes
e.g. some members in the globin gene family
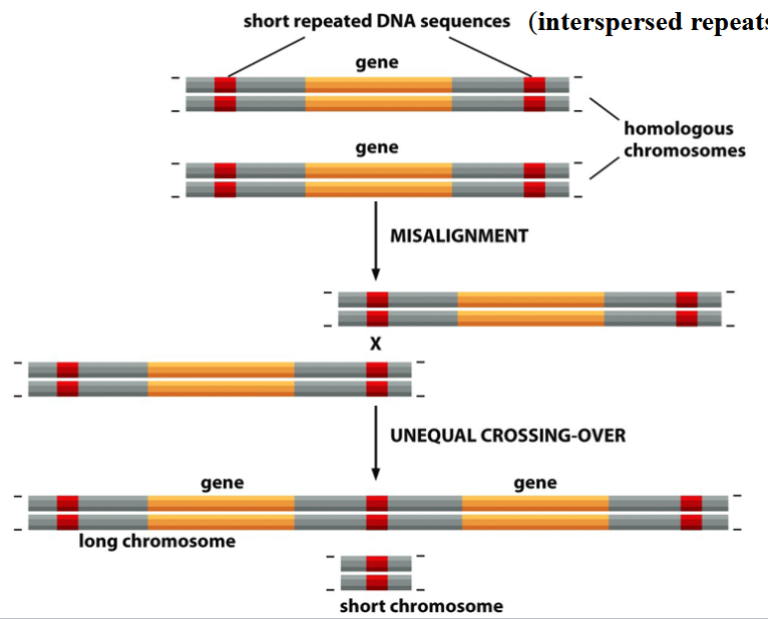
gene duplication by unequal crossing over
short repeated sequences within homologous chromosomes mauy cause misalignments and unequal crossing over
these interspersed repeats are non-coding, scattered throughout the genome
unequal crossing over → chromosomes with altered sizes and genetic contents
genetic rearrangement by mobile genetic elements
transposition of mobile genetic elements can mediate recombination of genes or regulatory sequences (in eukaryotes)
if two similar mobile genetic elements are inserted near each other in a chromosome, transposition may occur using the ends of the 2 different elements
result: movement of the entire segment of the chromosome between them
(if the ends of only 1 element were used, then just that element would be transposed, not the larger piece of chromosome)
transposition of regulatory sequences can alter the tissue-specific patterns of gene expression
exon transposition by mobile genetic elements
like normal genetic rearrangement by mobile genetic elements, but with a little extra
if the transposed segment includes an exon, then its insertion into a second gene alters and creates a new version of that second gene
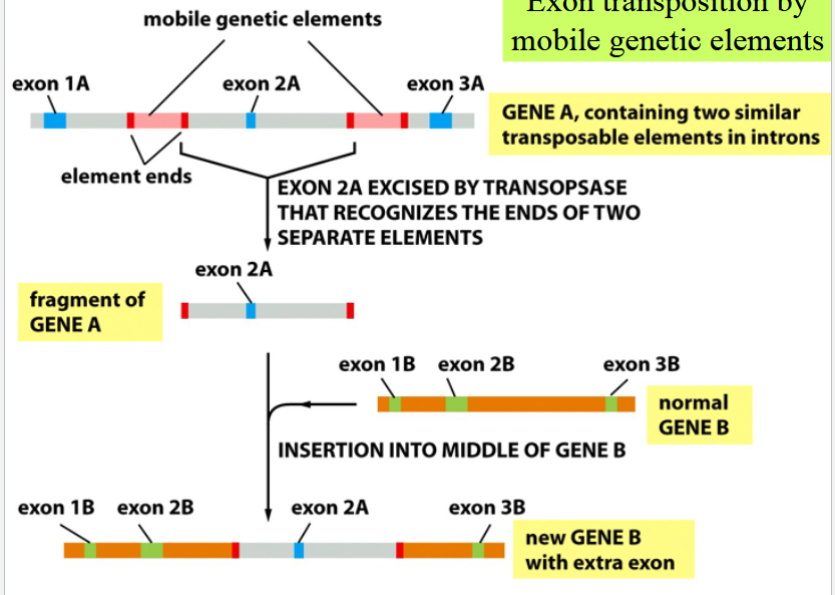
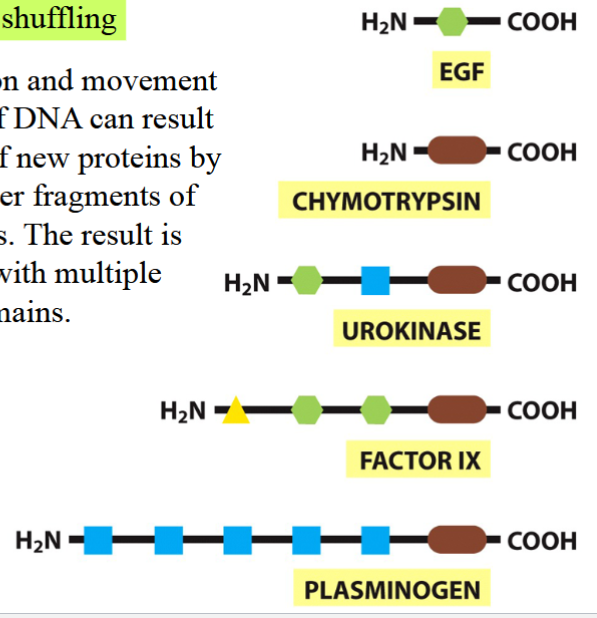
exon shuffling
duplication and movement of DNA segments can result in the origin of new proteins
new proteins result by piecing together fragments of different genes
result: new proteins with multiple functional domains
genetic changes that contribute to gene alteration and genome evolution
vertical transfer
horizontal transfer
vertical transfer
genetic change from parent to progeny through gametes (normal genetic change)
contributes to gene alteration and genome evolution
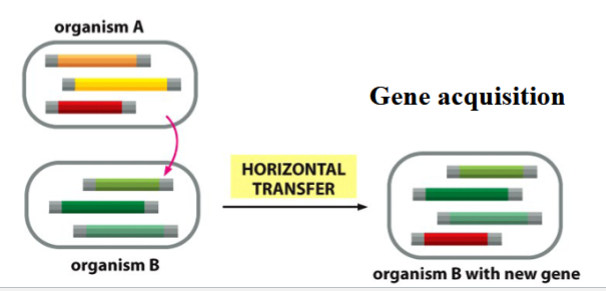
horizontal gene transfer
genetic change from one organism to another (not progeny, and not through gametes)
contributes to gene alteration and genome evolution
e.g. viral infections, conjugation
conjugation
transfer of genetic information from one bacterium to another through a sex pilus
sex between bacteria, essentially
result: genetic recombination without reproduction
an example of horizontal gene transfer
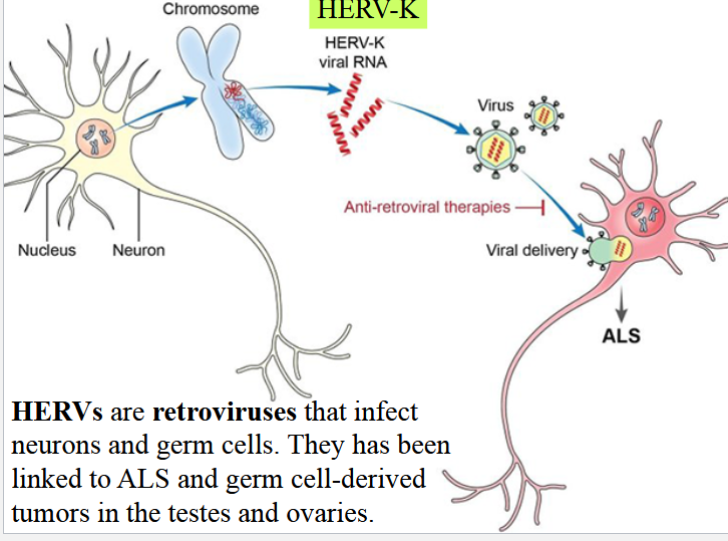
human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs)
retroviruses that infect neurons and germ cells
linked to ALS and germ cell-derived tumors in testes and ovaries
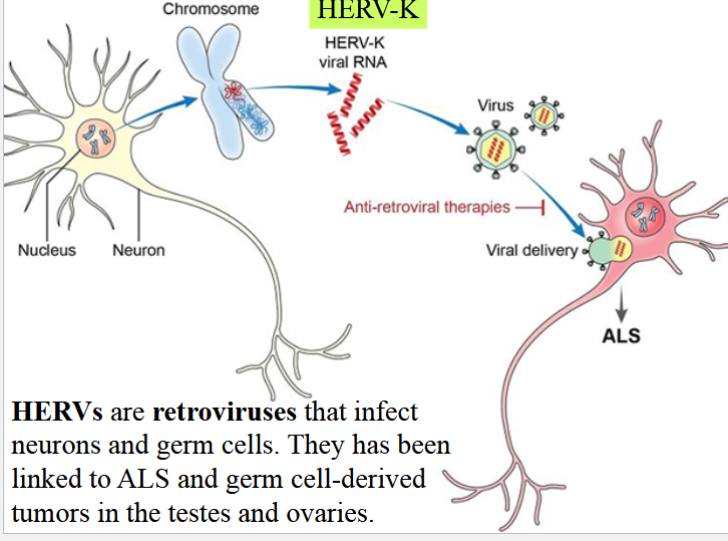
ALS
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, aka Lou Gehrig’s disease
a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects neurons in the brain and spinal cord
believed to be caused by HERV-K
HERV-K: an ancient virus that was incorporated into human DNA 2-5 million years ago
in some examined patients of this disease, HERV-K was elevated, and the entire virus had come to life