1.02 Parasternal Long Axis View (LAX)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
What position should a patient be in for this view?
LLD (with sponge on their back to held support them).
2
New cards
How is an EKG performed?
3 EKG electrodes are placed on the patient to display a single EKG lead. One is placed on the right arm, one on the left arm, and the other on the left chest (left lower belly).
3
New cards
What are the four different selections for transducers?
* 3-3.5 MHz for averaged-sized adults
* 2-2.4 MHz for large adults
* 5-7.5 MHz for children
* 7.5-10 MHz for neonatals
* 2-2.4 MHz for large adults
* 5-7.5 MHz for children
* 7.5-10 MHz for neonatals
4
New cards
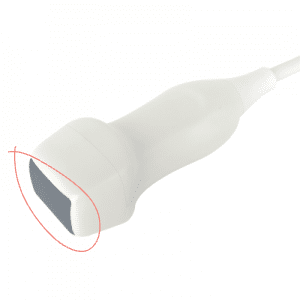
What is the footprint?
The contact area of the ultrasound transducer with the skin surface.
5
New cards
What is the image marker?
Describes the orientation index image marker on all ultrasound transducers.

6
New cards
What does movement of the transducer imply?
The actual movement of the footprint of the transducer on the chest wall along the scan plane. This is done without changing the rotation or tilt of the transducer.
7
New cards
What does tilting a transducer mean?
The up and down movement of the transducer from a fixed point on the chest wall. Th footprint does not move, it is just rocked up and down, thus tilting.
8
New cards
What is angulation of a transducer?
Refers to the side to side movement of the transducer from a fixed point on the chest wall. The footprint does not move, but is angled side to side (to midline or laterally).
9
New cards
What is rotation?
Refers to pivoting or twisting of the transducer from a fixed position on the chest wall. You can rotate clockwise or anti-clockwise.
10
New cards
What is depth?
A control that adjusts the vertical field of view of the image.
11
New cards
The depth of an image affects what?
The frame rate.
12
New cards
The deeper the field of view, the (greater/less) time required for the signal to return to the transducer and the (faster/slower) the frame rate.
Greater; slower
13
New cards
The closer the field of view, the (greater/less) time required for the signal to return to the transducer and the (faster/slower) the frame rate.
Less; slower
14
New cards
In order to maintain the frame rate, the smallest view of view should be employed while doing what?
Maintaining all of the anatomy within the image sector.
15
New cards
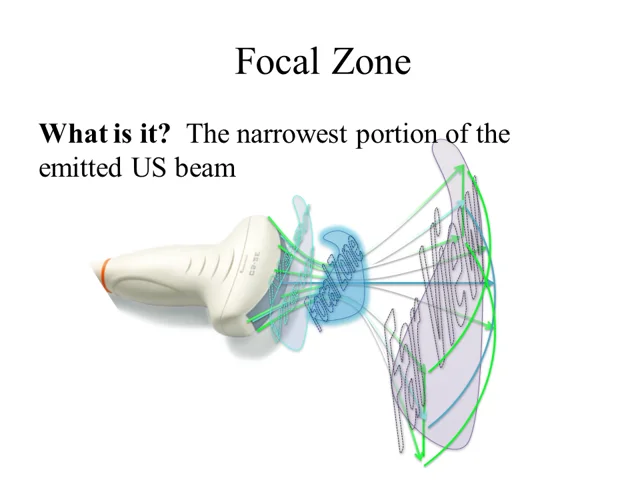
What is the focal zone?
The region of the image at which the ultrasound beam is the narrowest (where lateral resolution is the best).
16
New cards
Where should the focal zone be set at?
Slightly behind what you are looking at.
17
New cards
What is gain?
A control that amplifies the ultrasound signal.
18
New cards
What does gain do?
It adjusts the displayed amplitude of all received signals and affects the brightness of signals on the display.
19
New cards
Optimal gain settings should NOT do what?
Show lots of echos in fluid, like blood, unless a pathology is present.
20
New cards
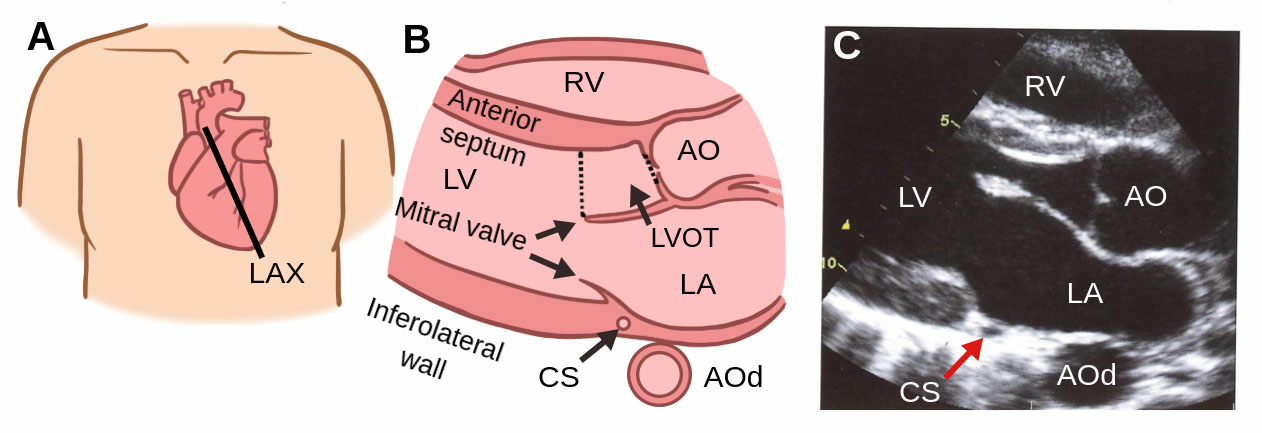
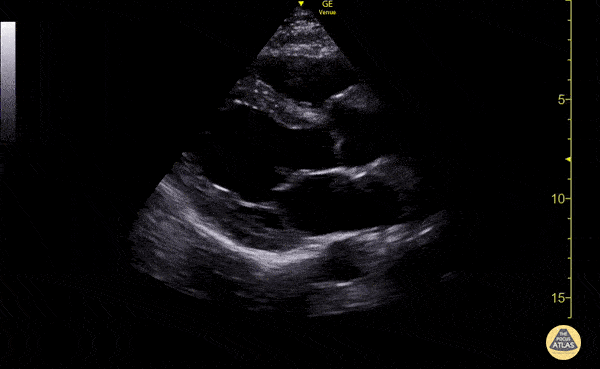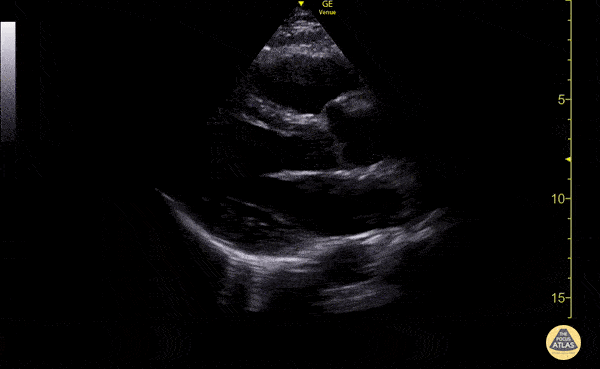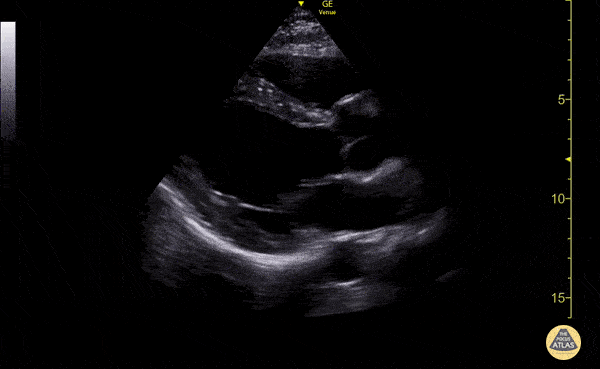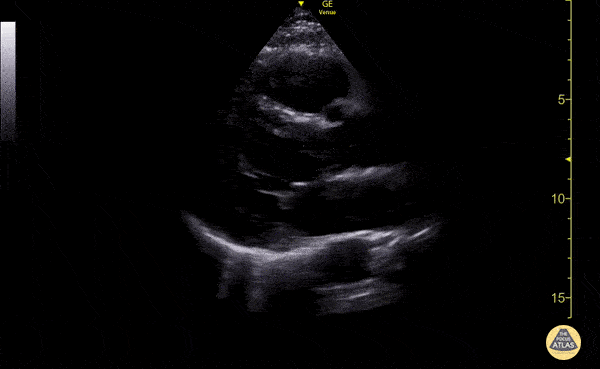
What is the parasternal LAX?
Parasternal long axis view, this is where the heart is sliced vertically.
21
New cards
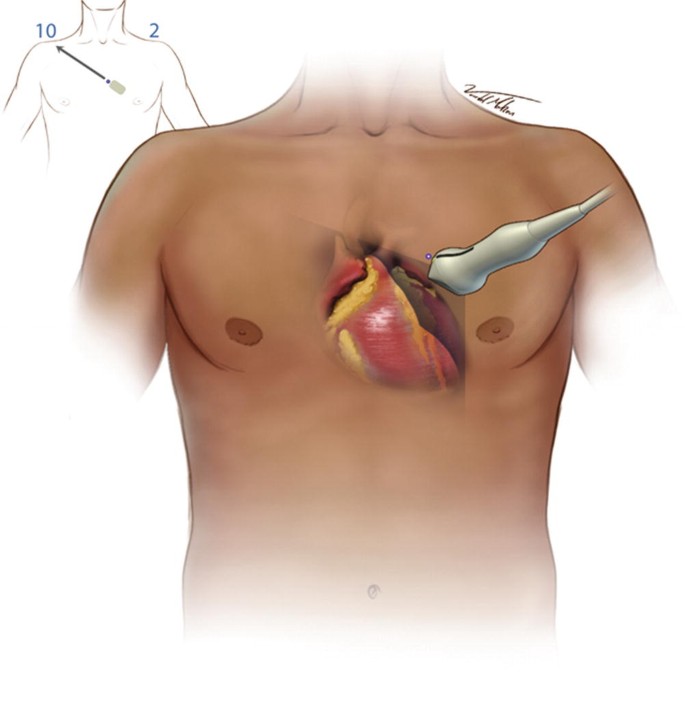
Where on the body is the LAX view performed?
Between the 3rd-5th intercostal space, where the transducer is close to the sternum, specifically the left sternal border.
22
New cards
In parasternal LAX, is the transducer close to the sternum or far?
Close.
23
New cards
Where should the orientation marker be pointing towards to obtain a parasternal LAX?
Towards the patient’s right shoulder. Image the heart inside the body.
24
New cards
When looking at an ultrasound image, how deep should your depth be?
Where there is about a thumb size of myocardium from the bottom of the screen to the back of the heart.
25
New cards
For optimal images, the transducer should be angled in what way to the structure of interest?
Perpendicular to the structure in interest (90°).
26
New cards
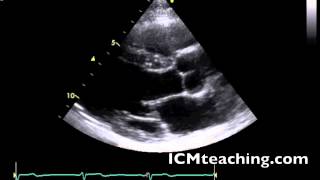
Where is the anterior wall of the RV in a parasternal LAX view?
At the top of the view.
27
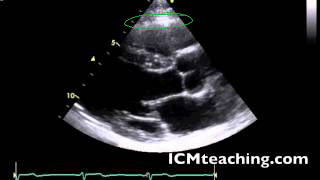
New cards
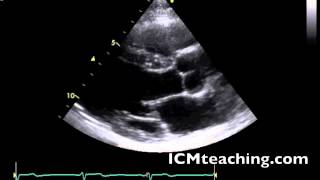
Where is the RV chamber in an parasternal LAX view?
At the top, below the anterior wall of the RV.
28
New cards
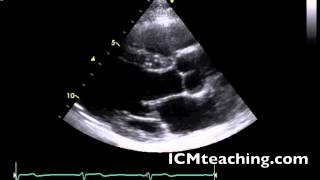
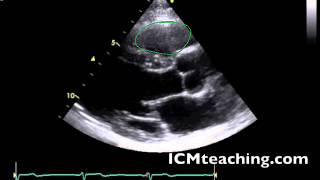
Where is the interventricular septum in a parasternal LAX view?
The tissue below the RV and above of the LV.
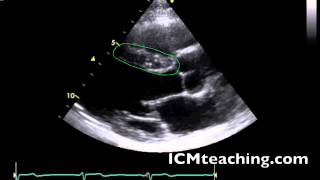
29
New cards
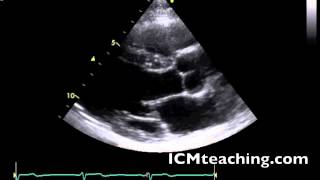
Where is the aortic root in a parasternal LAX view?
On the mid right part of the screen; to the right of the aortic valve.
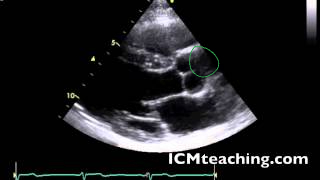
30
New cards
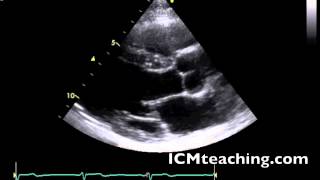
Where is the aortic valve in a parasternal LAX view?
To the left of the aortic root.
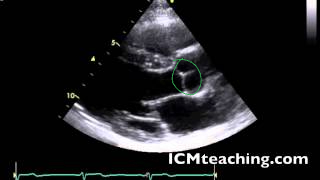
31
New cards
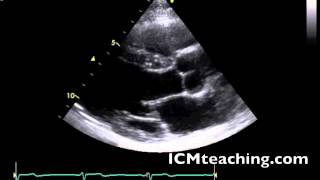
Where is the right coronary cusp of the aortic valve in a parasternal LAX view?
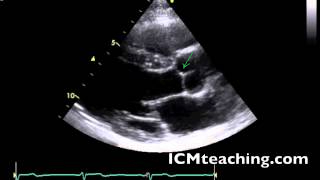
32
New cards
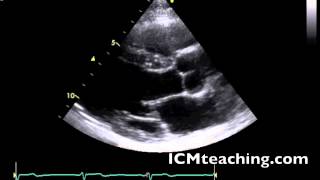
Where is the non coronary cusp of the aortic valve in a parasternal LAX view?
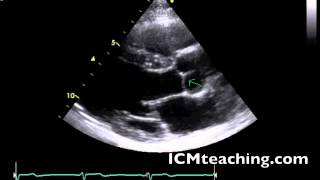
33
New cards
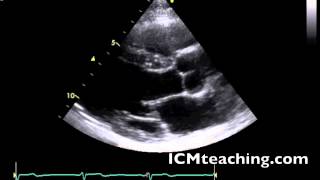
Where is the LV outflow tract in a parasternal LAX view?
To the left of the aortic valve.
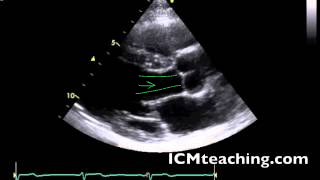
34
New cards
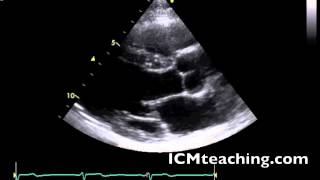
Where is the LV in a parasternal LAX view?
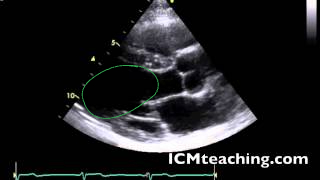
35
New cards
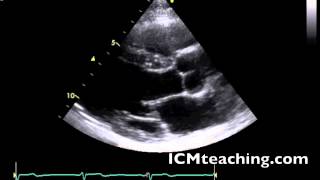
Where is the LA in a parasternal LAX view?
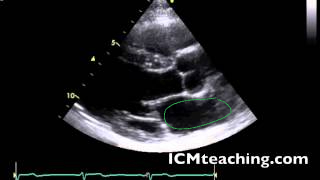
36
New cards
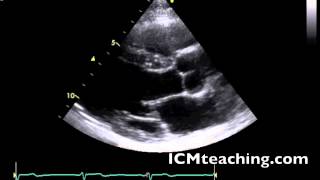
Where is the mitral valve in a parasternal LAX view?
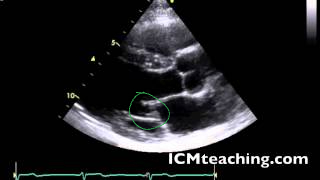
37
New cards
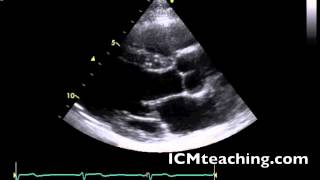
Where is the anterior mitral valve leaflet in a parasternal LAX view?
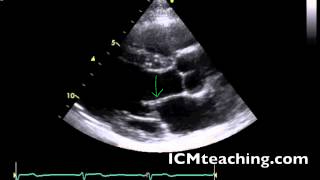
38
New cards
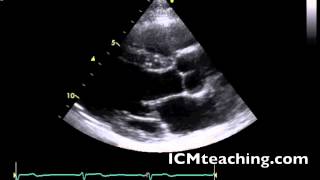
Where is the posterior mitral valve leaflet in a parasternal LAX view?
39
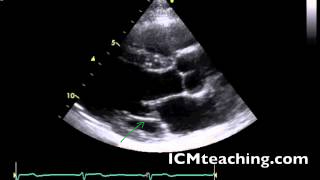
New cards
Where is the coronary sinus in a parasternal LAX view?
(hard to see in this picture)
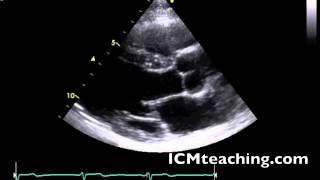
40
New cards
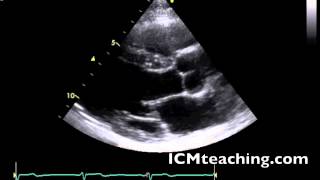
Where is the descending aorta in this picture?
(not visible in this picture but it is circled where it would be)
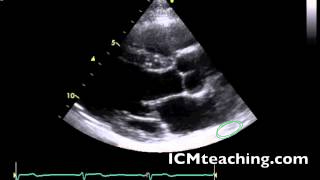
41
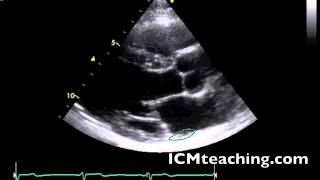
New cards
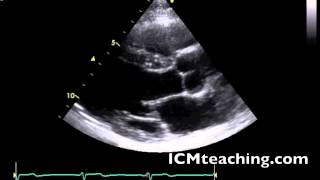
Where is the LV posterior wall (LVPW or inferolateral wall)?
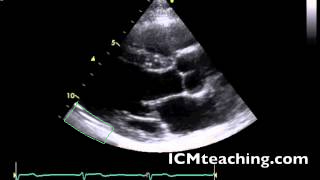
42
New cards
How to you get the the parasternal long axis right ventricle inflow tract (LAX RVIT) from the parasternal LAX?
By angling the transducer towards the patient’s right hip.
43
New cards
What structures can be seen in a parasternal LAX RVIT?
* RA
* RV
* Tricuspid valve
* Coronary sinus
* IVC
* Eustachian valve
* RV
* Tricuspid valve
* Coronary sinus
* IVC
* Eustachian valve
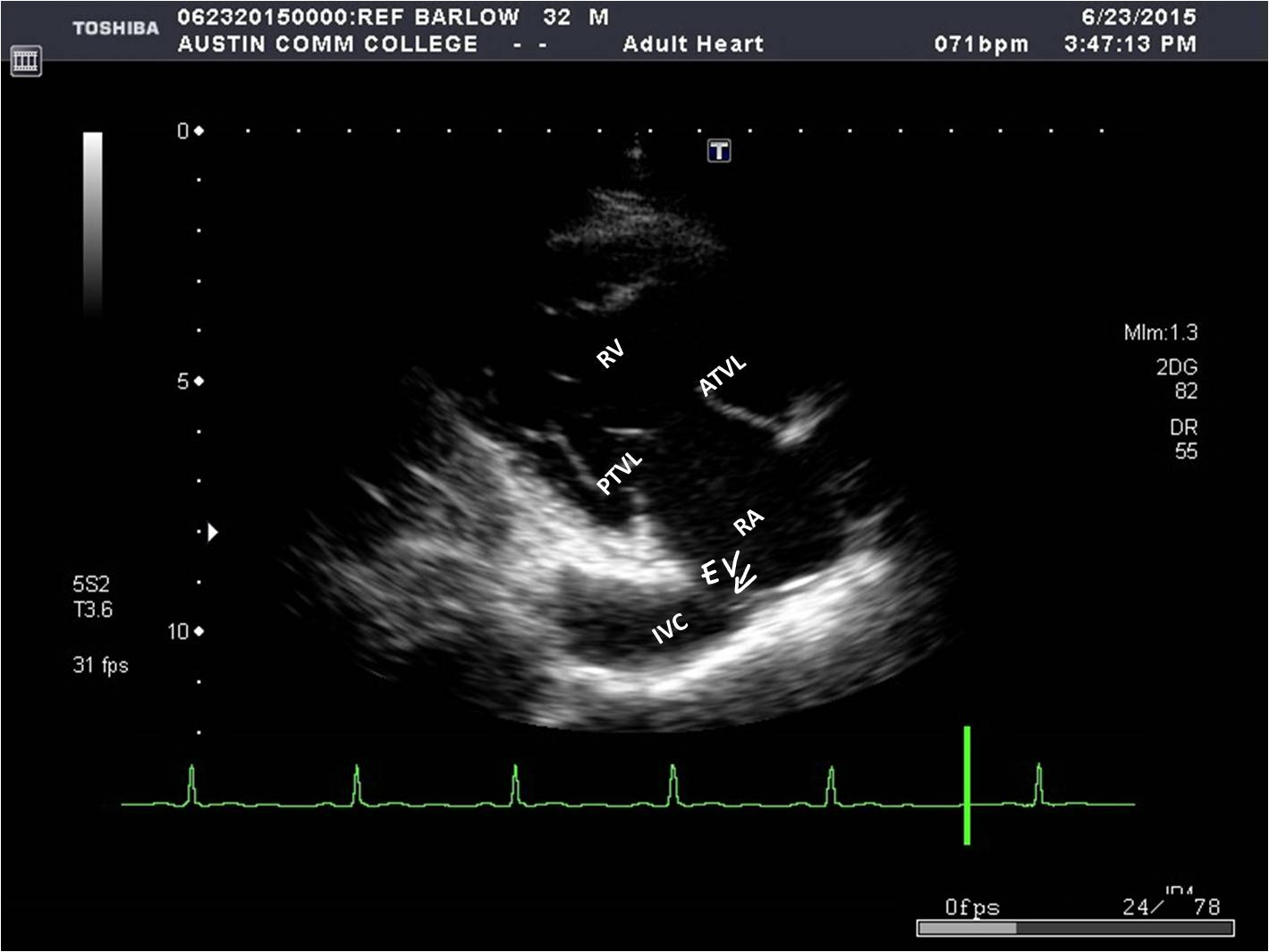
44
New cards
How do you get to a parasternal long axis right ventricle outflow tract (LAX RVOT) from parasternal LAX view?
By angling the transducer towards the patient’s left shoulder.
45
New cards
What structures can be seen in a parasternal LAX RVOT?
* RVOT
* PV
* Main pulmonary artery (MPA)
* Right pulmonary artery (RPA)
* PV
* Main pulmonary artery (MPA)
* Right pulmonary artery (RPA)
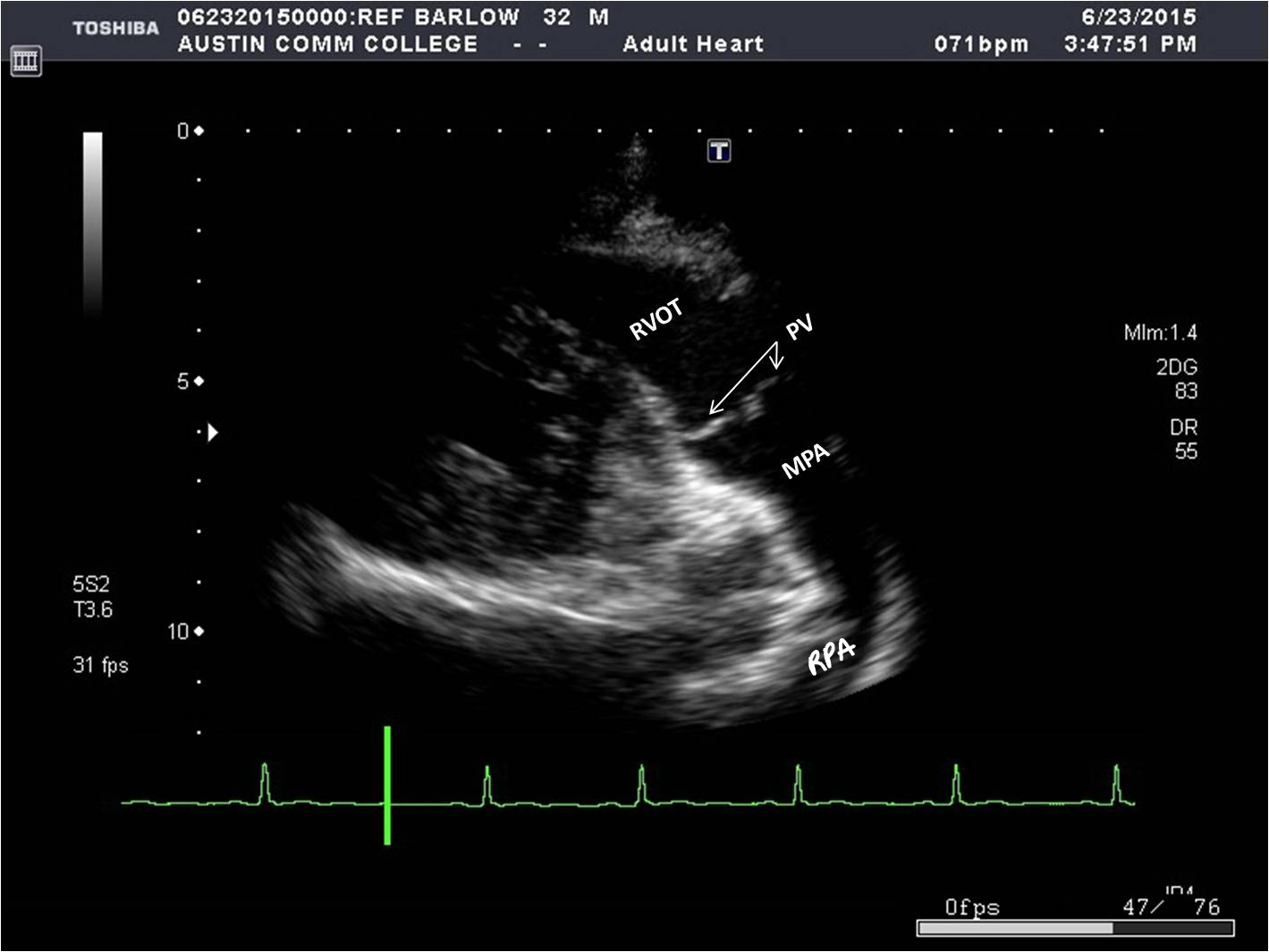
46
New cards
What is a good way of remembering whether or not you are looking at parasternal LAX RVIT or RVOT?
If you are IN, you’re HIP, but if you’re OUT, you get the shoulder.