Oil, Quartering head/tailwinds, Wing terminology
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Aerodynamics of Flight
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
The primary flight controls
Ailerons, rudder, elevator (stabilizer)
What temperatures would carburetor ice most likely occur?
20-70F
How to purge water from fuel system
drain fuel from the tanks and the fuel strainer
Fuel pump systems
use vents to avoid fuel starvation, fuel leaving tank is replaced by incoming air or fuel will stop flowing
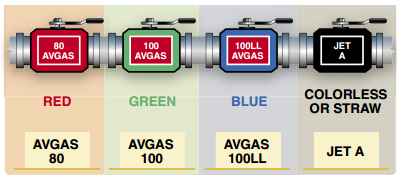
Higher the grade of fuel the better it can withstand
higher temperatures and pressure
What can you do if your grade of fuel is not available?
Use next highest grade of fuel, but can never use Jet A colorless or straw fuel
How to avoid moisture in fuel tanks at night
Moisture condense at night so make sure to fill fuel to minimize condensation from cooling
Detonation
Uncontrolled or explosive ignition (rather than combustion) during power stroke
If a pilot suspects detonation during climb out they should
increase airflow over engine by lowering the nose
Dual ignition system is used for
improved engine performance and safety
The engine will not fail if there is a _____ failure
electrical system failure
Oil helps the engine cool by
oil being forced over the engine parts by the engine driven oil pump
Engine oil is used for
lubricant and dissipating heat
operating with high engine temperature can lead to
excessive oil consumption, loss of power, detonation, serious damage
If aircraft is becoming too hot
enrich the mixture (more fuel=more cooling) which in turn increases airflow
lower nose during climbs, increasing airspeed
How will you know if your electric system failed
radios, lights, and some gauges will stop working

tricycle gear, nosewheel

convectional gear, tailwheel
If the engine oil temperature and cylinder
head temperature gauges have exceeded
their normal operating range, the pilot may
have been operating with...
Too much power and with the mixture set too lean.
(Too much Air and not enough Fuel... Fuel cools the mixture, Air makes it hotter...)
The operating principle of a float-type
carburetor is based on...
The difference in air pressure at the venturi throat and
the air inlet.
During run-up at a high elevation airport the pilot
notices a slight engine roughness that is not affected
by the magneto check but grow worse during the
carburetor heat check... What should he do?
Check the results obtained with a leaner setting of the
mixture.
While cruising at 9,500 feet MSL, the
fuel/air mixture is properly adjusted. What
will occur if a descent to 4,500 feet MSL is
made without readjusting the mixture?
The fuel/air mixture may become excessively lean.
If an aircraft is equipped with a fixed-pitch
propeller and a float-type carburetor, the
first indication of carburetor icing would
most likely be...
Loss of RPM.
The presence of carburetor icing in an
airplane equipped with a fixed-pitch
propeller can be verified by applying
carburetor heat and noting...
A decrease in RPM and then a gradual increase in RPM.
If the grade of fuel used in an aircraft
engine is lower than specified for the engine,
it will most likely cause...
Detonation.
Detonation may occur at high-power
settings when...
The fuel/air mixture ignites instantaneously instead of
burning progressively and evenly.
If a pilot suspects that the engine (with a
fixed-pitch propeller) is detonating during
climb-out after takeoff, the initial corrective
action to take would be to...
Lower the nose slightly to increase airspeed.
The uncontrolled firing of the fuel/air
charge in advance of normal spark ignition
is known as...
Pre-ignition.
Which would most likely cause the cylinder
head temperature and engine oil
temperature gauges to exceed their normal
operating ranges?
Using fuel that has a lower-than-specified fuel rating.
What type of fuel can be substituted for an
aircraft if the recommended octane is not
available...
The next higher octane aviation gas.
For internal cooling, reciprocating aircraft
engines are especially dependent on...
The circulation of lubricating oil.
An abnormally high engine oil temperature
indication may be caused by...
The oil level being too low.
What action can a pilot take to aid in cooling
an engine that is overheating during a
climb...
Reduce rate of climb and increase the airspeed.
What is an advantage of a constant-speed
propeller...
Permits the pilot to select the blade angle for the most
efficient performance.
What should the first action be after starting
an aircraft engine?
Adjust for proper RPM and check for desired
indications on the engine gauges.
Excessively high engine temperatures, either
in the air or on the ground, will... (excluding dentonation)
Cause loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and
possible permanent internal engine damage.
Where can an aircraft’s Operating Limitations
be found?
In a current FAA approved flight manual, approved manual
material, markings, placards, or any combination thereof.
When taxiing with strong quartering
tailwinds, which aileron positions should be
used?
Ailerons down on the side from which the wind is
blowing.
Which aileron positions should a pilot
generally use when taxiing in strong quartering
headwinds?
Aileron up on the side from which the wind is blowing.
Which wind condition would be most
critical when taxiing a nosewheel equipped
high-wing airplane?
Quartering tailwind - combat by ailerons and elevator in neutral
How should the flight controls be held while
taxiing a tricycle-gear equipped airplane
into a left quartering headwind?
Left aileron up, elevator neutral.
How should the flight controls be held while
taxiing a tailwheel airplane into a left
quartering tailwind?
Left aileron down, elevator down.
What is wake turbulence?
Slow rotations or speed creating very large and dangerous vortex’s and can drift a 1000ft per minute
Dihedral and sideslip
is the upward angle thus formed by the tip wings. Sideslip (gust of wind) will cause one wing to decrease in aoa and lift, dihedral helps to combat sideslip.
keel effect
wings wanting to turn into the wind
Taper ratio
thickness of wing, how the thinness decreases from wing tip to root in regard of the cord
What is limit load and ultimate load?
limit load - aircraft shape that does not return to normal
ultimate load - beyond the limit load at which the airplane experiences structural failure
how do you make sharper circles/turns
Reducing speed helps make sharper turns