Module 2: Components of CPU
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Clock cycle
basic unit of time during which the processor performs operations; heartbeat of the processor
clock speed of CPU
measured in hertz, gigahertz for modern processors; each correponds to one oscillation of CPU’s internal clock
stages of CPU basic process of handling instructions
Fetch: retrieve instruction from memory
Decode: interpret instructions
Execute: perform operation
Memory access: if the instruction involves reading or writing data from memory, this happens
write back: CPU writes resulst of operation back to register file or memory
unit of measurement of clock cycle
hertz
CPU cores
modern have many cores; independent processing units capable of processing things in parallel; each one has its own thread(like task)
multi threaded applications
applications where multiple things have to be processed at the same time
CPU parts
control unit; ALU; registers
Control unit(CU)
directions operations in CPU; gets instructions from memory, decodes them, and then sends signals to other parts of the CPU (like the hypothalamus)
ALU
Performs arithmetic and logic operations; operates based on data stored in registers; produces results that can be sent to other part of CPU or written back to memory
Registers
Small, fast storage locations within the CPU that hold data temporarily during instruction execution; types: program counter(PC), accumulator, instruction register(IR), general purpose registers
Program counter(PC)
Holds address of next instruction to be executed
accumulator
holds immediate results of calculations
Instruction registers
holds the current instruction being executed
general purpose registers
used for storing data during computation
cpu components
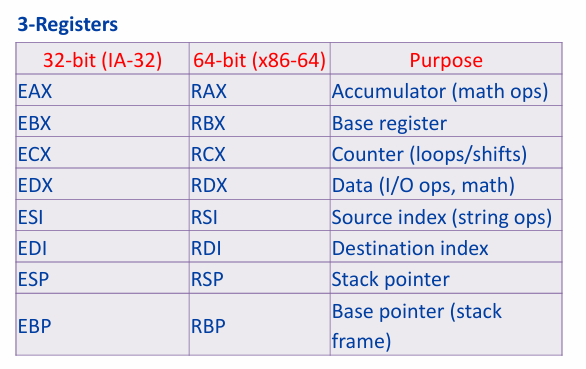
cache memory
sit between CPU and main memory, very fast; helps reduce the time it takes to accomplish certain tasks
L1 cache memory
fastest and smallest; located closest to CPU cores
sometimes integrated into the CPU core
size: 16 KB to 128 KB per core
purpose: stores most frequent instructions and data needed by CPU
speed: fastest cache but limited storage capacity
L2 cache memory
larger and slowly, further from CPU
sometimes shared amongst cores in CPU, other times each core has its own
size: 128 KB to 4 MB per core, depending on CPU design
purpose: store data that is frequently accessed as L1 cache data but still needs to be readily available
L3
even larger and even slower, but still faster than main memory
generally shared across all cores in multi processor
located on same chip as CPU
size: 2 MB to 64 MB (or more) in modern processors
Purpose: stores data that is less frequently used than L1 and L2
speed: slowest of three cache levels but still significantly faster than accessing RAM
CPU example
intel core i9-13900K has:
L1 cache: 32 KM per core(16 KB for data and 16 KB for instructions)
L2 cache: 256 KB per core
L3 cache: 36 mb shared across all cores
cache memory def
memory that allows for faster retrieval of information into the CPU, faster than through RAM/ROM
external cache
used before on-chip cache was common; L2 cache memory, could be physically separate from CPU and placed on separate; chip near the CPU; meant to store data between CPU and RAM; it was faster than accessing data from RAM but slower than the CPU’s internal cache
Buses
communication pathways that connect various components of CPU and the system, allowing data to be transferred between them (like synapses in the brain)
special types:
data bus: transfers data
address bus: carries memory addresses
control bus: carries control signals to manage operations of the CPU and other components\
execution pipeline- piplelining
modern CPUS; breaks down instruction processing into multiple stages that can overlap, allowing multiple instructions to be processed simultaneously in different stages; helps the efficiency of the CPU
data processing pipeline
data collection, cleaning, transformation, analysis, storage, and reporting
example: in machine learning,d ata pipeline can be data extraction, preprocessing, feature engineering, model training, and evalulation
CI/CD pipeline (continuous integration/ continous deplyment)
stages: commit code → code review—> build → test→ deploy
example: developers push code changes to a repository, which triggers the pipeline for automated building, testing, and deployment
task execution pipline
stages: job submission → task assignment→ execution → result collection
example: in distributed computing, large tasks are broken down into smaller sub tasks executed in parallel or sequentially
floating point unit
specialized part of CPU designed to handle calculations involving floating point numbers, scientific calculations, etc.; sometimes integrated into ALU, other times seperate component
execution units (EU)
modern CPUs can have multiple execution units to handle different tasks at the same time
clock
generates regular pulse (or signal) to synchronize operations of components in CPU
Bus Interface Unit (BIU)
existed in older systems; manages communication between CPU and external components like RAM; ensures data is fetched from and written to memory correctly; handless address and control signals
Thermal management
to manage heating and prevent overtemperature; may include thermal sensors too to monitor safe heat levels
integrated graphics
handles graphical tasks, like rendering images, videos, and 3D graphics; reduces the need for seperate graphics card in the system
CPU components diagram
Factors that influence performance of CPU
architecture
number of cores
efficiency of instructions being executed
cpu cores
indepdent procesing units in CPU capable of executing instruction in parallel
CPU components
control unit
arithmetic logic unit
Control unit
responsible for directing operations of CPU
fetches instructions from memory, decodes them to determine what action to take, and then sends signals to other parts of the CPU to carry out the taskA
ALU
performs arithmetic and logic operations
includes basic operations, like addition and subtraction
Register
small, fast storage ocations within the CPU that hold data temporarily during the execution of instructions
Types of registers
program counter
accumulator
instruction register
general purpose register
program counter
holds the address of the next instruction to be executed
accumulator
holds intermediate results of calculations
instruction register
holds the current instruction being executed
general purpose registers
used to store data during computation
Cache memory
memory between CPU and RAM; multiple levels - L1, L2, L3,
L1 cahce
fastest and smallest, typically closest to coreL
L2
bit larger and slightly slower
L3
slower but faster than RAM
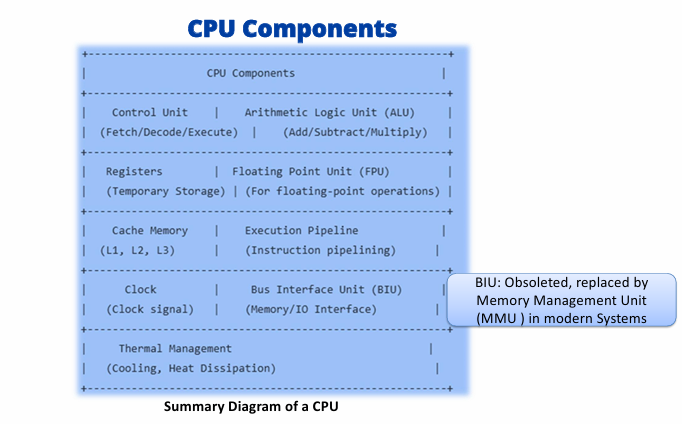
bits vs processors
bits that the processor can support
8 bit processor
process 8 binary digits in a single operation, which is equal to one byte; uses 8 bits to represent integers, chars, and all other data types, so it can handle data values which are represented from 2^8 possible values in a single instruction; used in older or embedded systems; some microcontrollers and small embedded devices use it
16 bit processer
older systems, comon in embeded systems, gaming, consoles, workstations; very specific applications in modern; some very early computers and PCs
32 bit processor
embedded systems, older PCs
64 bit processors
standard for most modern computing, like desktops; can handle larger amounts of memory(more than 4GB), faster data processing, advanced operation systems and applications
128 bit processors
research but not in mainstream commercial devices
computer basic defonition
process to interpret or execute; memory to store data and programs; mechanism to transfer data to and from the outside world