Mass number and isotope (3.1.1.2)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is an atomic number and a mass number?
Atomic number (Z) - the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons as atoms are neutral. All atoms of the same element have the same atomic number.
Mass number (A) - the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It is a measure of mass compared with other types of atoms.
What is an isotope?
An isotope is an atom of an element with the same number of protons (atomic number) but a different number of neutrons (mass number)
What are the properties of isotopes?
Since all isotopes of an element have the same number and arrangement of electrons, they have the same chemical properties.
Since there is a difference in mass they have slightly differing physical properties, like rate of diffusion, and nuclear properties, like radioactivity.
Isotopes which aren’t radioactive are called stable isotopes.
What is relative isotopic mass and relative atomic mass?
Relative isotopic mass - the mass of an isotope compared to 1/12th the mass of a carbon 12 atom.
Relative atomic mass - the weighted mean mass of an atom compared to 1/12th the mass of a carbon 12 atom.
What is relative isotopic abundance and how can this be used to calculate relative atomic mass?
Relative isotopic abundance - the percentage of each isotope that occurs naturally on earth.
Relative atomic mass calculation:
-min,h_400,q_80,w_640.jpg)
What is mass spectrometry and how does it work?
The isotopic abundances used in the calculation of an element’s Ar is measured using a mass spectrometer.
Steps
1) The element being analysed is placed in the mass spectrometer.
2) The sample is vaporized and ionised to form 1+ ions
3) the ions are accelerated through a tube. Heavier ions move more slowly than lighter one, thus separating different ions of different isotopes.
4) The ions reach a detector which records its mass to charge ratio (m/z), which corresponds to its Ar
What are the stages in a time of flight mass spectrometer?
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
This is a common form of mass spectrometry, where all particles of the sample to be analysed are ionised to form 1+ ions
These 1+ ions are then accelerated to high speeds, deflected through the spectrometer and then arrive at the detector
As they hit the detector, the mass spectrum graph is produced
The whole of the apparatus is kept under a high vacuum to prevent any ions that are produced from colliding with molecules in the air

The four key stages of time of flight mass spectrometry are:
Ionisation
Acceleration
Drift region
Detection
What is the first stage of a TOF spectrometer?
Ionisation
i) Electron impact
The sample is vapourised and placed in the mass spectrometer. High-energy electrons are then fired at the the sample, causing the sample to lose an electron.
This technique is quite ‘aggressive’ and the molecule tends to break down due to the energy of the electrons being able to break bonds.
If a sample decomposes and isn’t easily turned into a gas this is of no use.
It tends to be used for elements and molecules with low Mr.
X(g) → x+(g) +e-
ii) Electrospray ionisation
The sample is dissolved in a low boiling solvent and injected into the mass spectrometer via a needle. The needle has a high voltage and causes the droplets of solvent to ‘spray’.
Rather than lose an electron the molecule gains a proton
Electrospray is a ‘gentler’ technique than electron impact. The molecule doesn’t break up, so there are no fragments.
It tends to be with molecules that might decompose under electron impact conditions and large molecule weight.
X + H+ → XH+
What is the second stage of a TOF spectrometer?
Acceleration
The ions are accelerated to the same kinetic energy by an electric field.
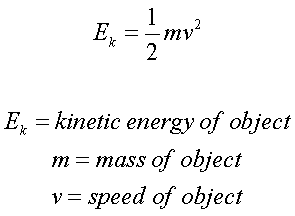
What is the third stage of a TOF spectrometer?
Drift region
All the ions have the same kinetic energy approaching the drift region so how long they take to reach the detector only depends on their velocity.
This is where the name ‘time of flight’ comes from - how long the ions take to cross the region. Thus, the smaller ions cross the region fastest and reach the detector first.
What is the fourth stage of a TOF spectrometer?
Detection
The concentration of each ion arriving at the detector is measure and turned into a current. The machine analysis the current and turns it into a spectrum.
The larger the current generated, the higher the abundance of that ion in the spectrum.
What are the isotopes of chlorine and bromine?
Chlorine - 35Cl , 37Cl
Bromine - 79Br , 81Br