Filariasis & Schstosomiasis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is Nematodes?
It is roundworms and parasites
It has complete digestive tract (moth and anus)
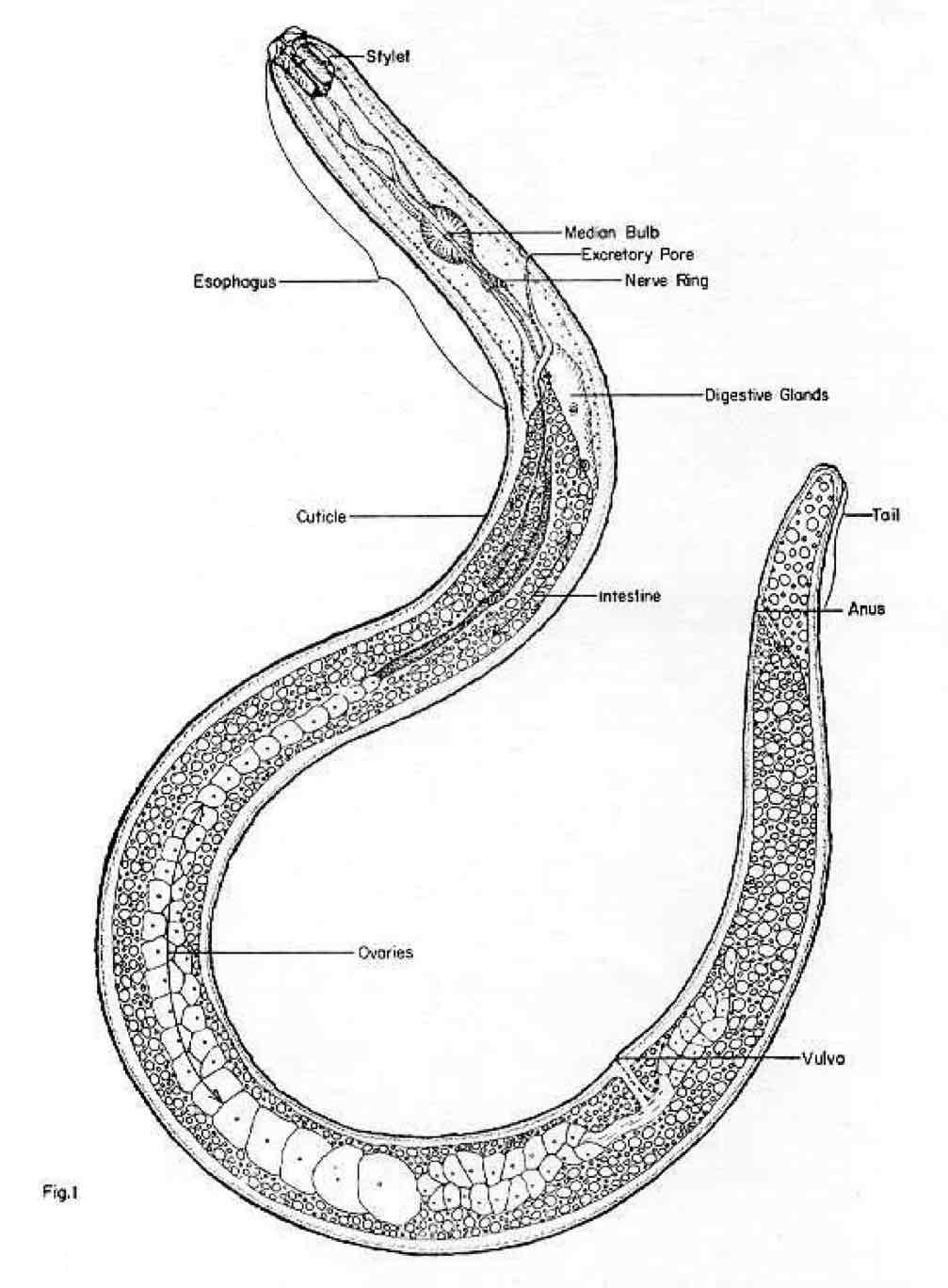
What is Filarial worms?
Tissue-dwelling nematodes
How does Filarial worms are transmitted?
By mosquitoes and other biting flies
What is Lymphatic filariasis?
Adult works live in lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels
What is most important causative agent in Lymphatic filariasis?
Wuchereria bancrofti
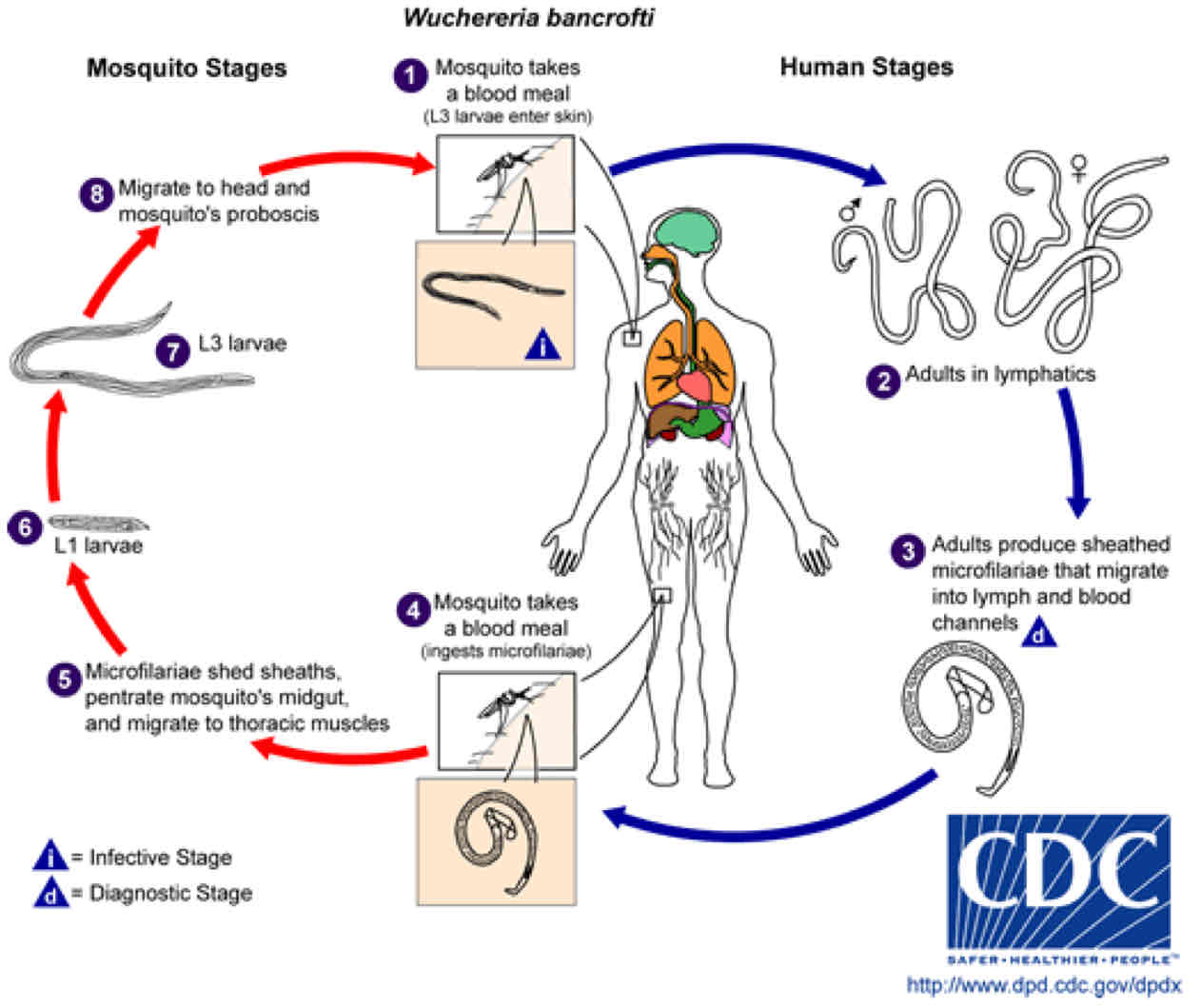
What are the steps of W. Bancrofti life cycle?
1) Infected mosquito transfers Filarial larvae onto skin
2) Larvae penetrate bite wound
3) Larvae enter lymphatic vessels and become adults
4) Adult female release microfilarial larvae
5) Microfilarial larvae enter blood
6) Mosquito ingests microfilarial larvae
What are the s/s of Lymphatic filariasis?
In endemic areas, asymptomatic
Acute
Chronic
Which stage manifestation of Lymphatic filariasis shows lymphedema, elephantiasis?
Chronic
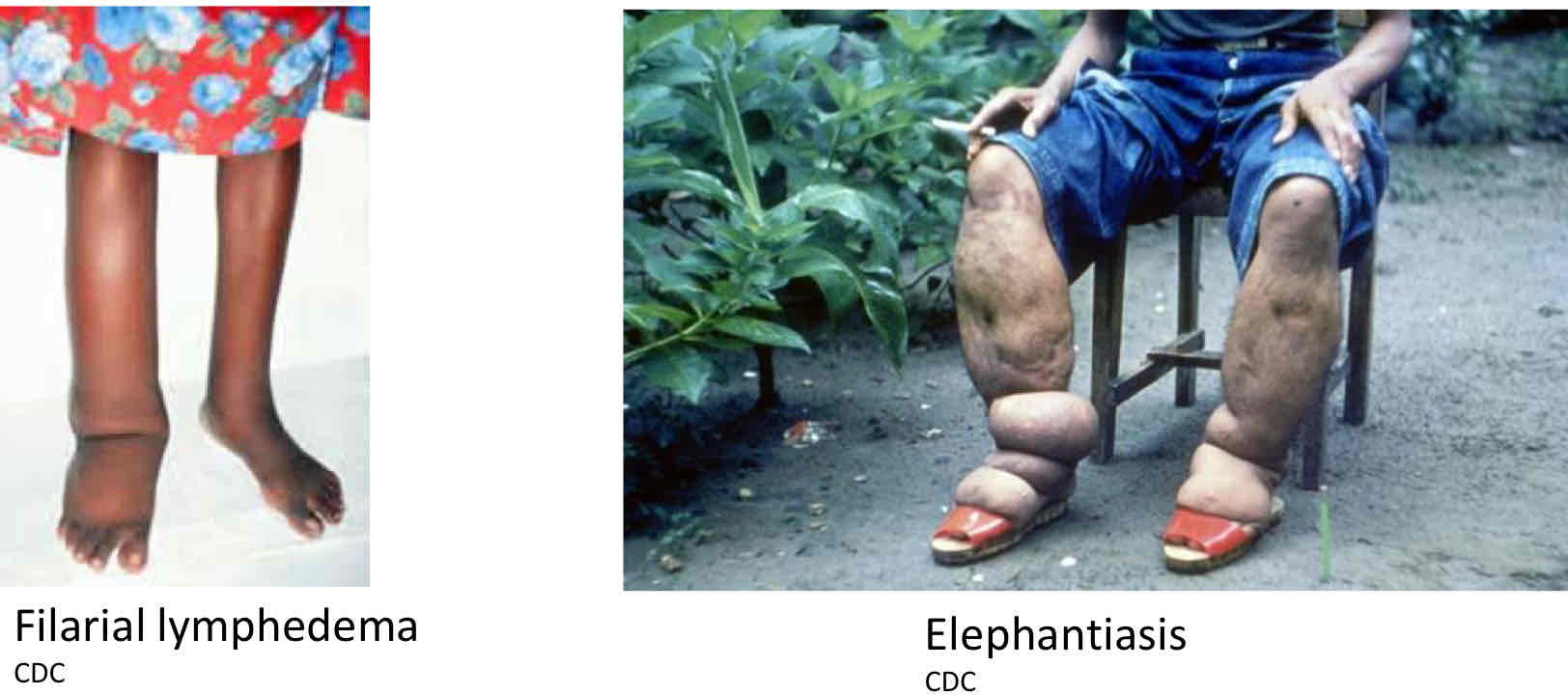
Which manifestation shows chyluria? And what is chyluria?
Chronic
It is lymph passed in urine
Which manifestation of Lymphatic filariasis shows nocturnal wheezing, edematous inflammatory plaque on skin?
Acute
What are the diagnosis of Lymphatic filariasis?
Clinical presentation & patient Hx
Microscopy of blood smears (definitive)
Immunodiagnostics - antigen detection
Ultrasound - imaging of adult worms
What are the treatment of Lymphatic filariasis?
Diethylcarbamazine (DEC)
What are the prevention of Lymphatic filariasis?
Avoid mosquito bites
Mosquito control
Mass administration of DEC
What is Onchocerciasis?
Adult worms live in SQ tissues (Humans are only host)
Also known as River blindness
What is causative agent of Onchocerciasis?
Onchocerca volvulus
Onchocerciasis cause _________ and ________ in endemic area.
Blindness
Skin disease
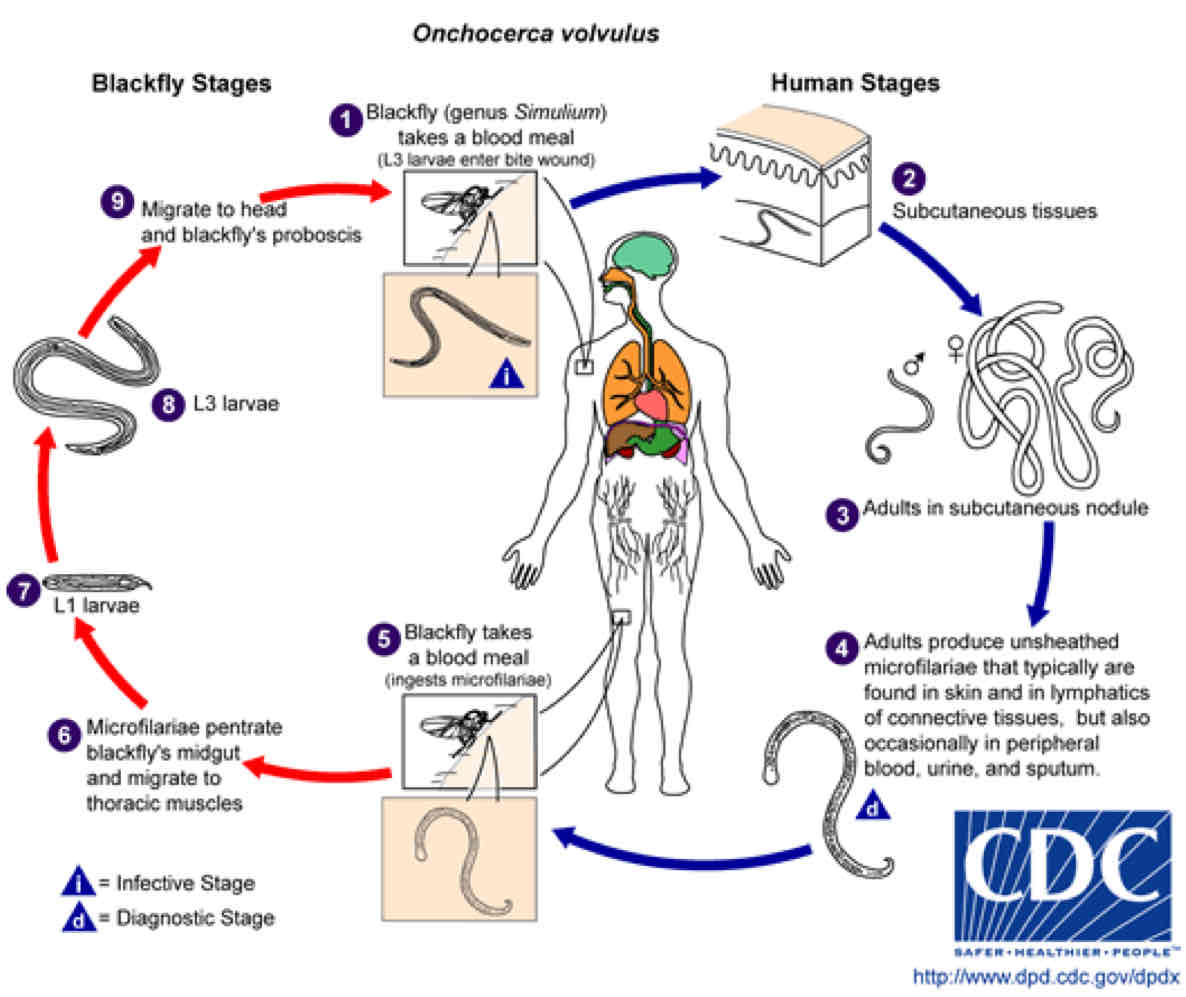
What are the steps of O. Volvulus life cycle?
1) Infected blackfly transfer infective Filarial larvae onto skin
2) Larvae enter bite wound (SQ nodules)
3) Larvae become adults
4) Adult female worms release microfilariae in skin & lymph
5) Blackfly ingests worm
What are the s/s of Onchocerciasis?
SQ nodules - not palpable, no symptoms
Skin disease - rash, itching, cracking, depigmentation, thinning
Eye disease - progressive damage to cornea, retina, optic nerve
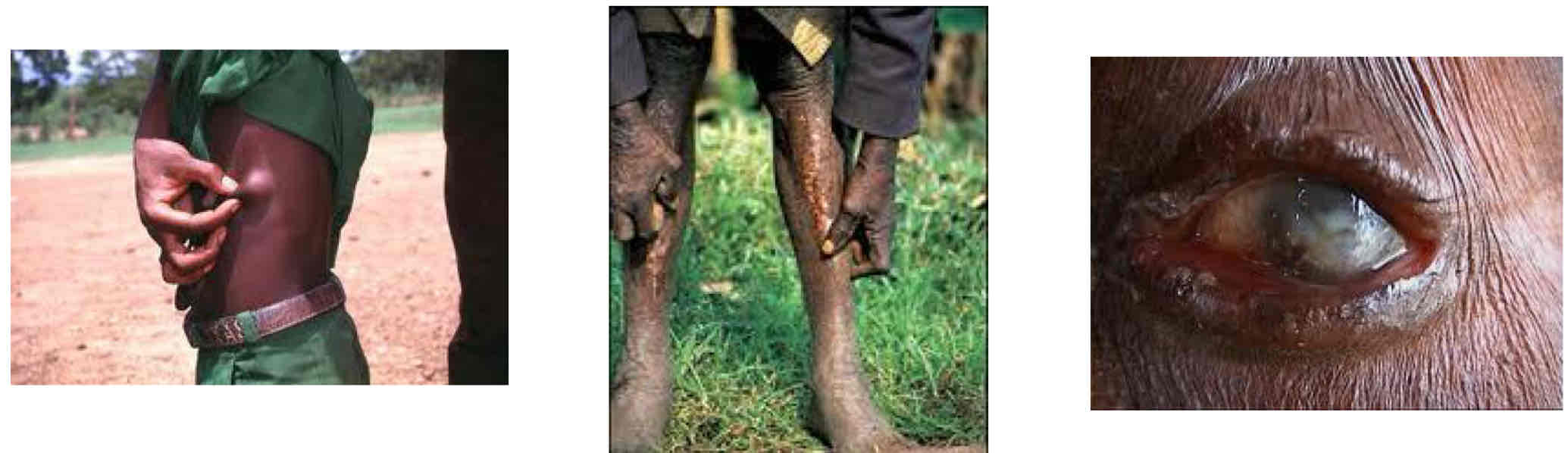
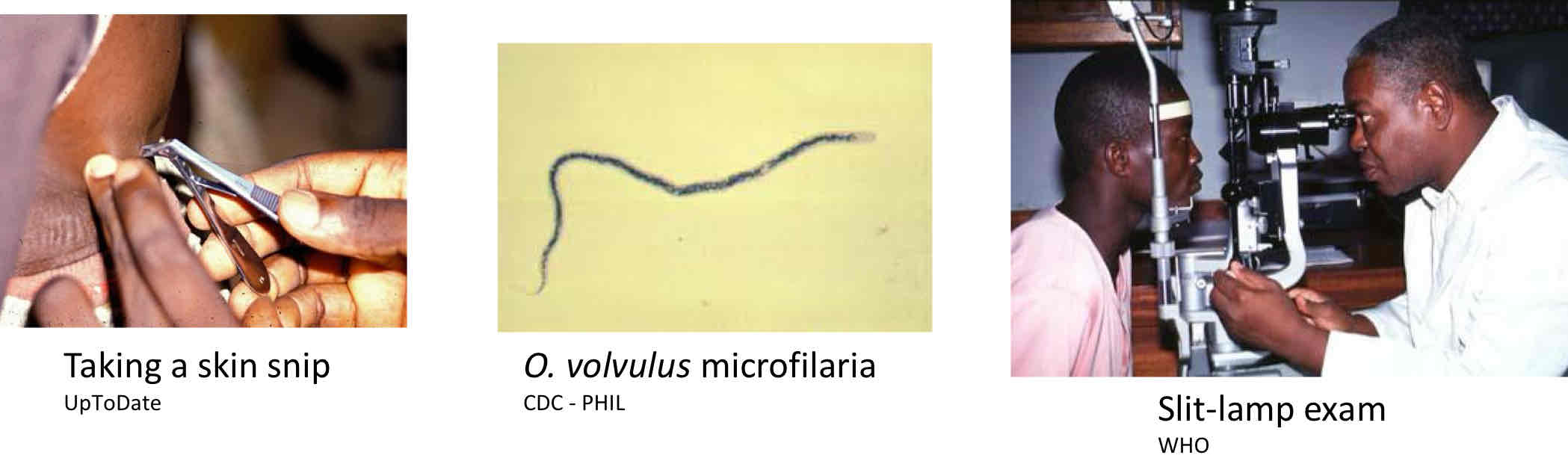
What are the diagnosis of Onchocerciasis?
Clinical presentations & patient Hx
Microscopy - skin snips or nodule biopsy
Slit-lamp eye exam
Ultrasound
What are the treatment of Onchocerciasis?
Ivermectin (Microfilaricide)
Doxycycline (Macrofilaricide)
What is Trematodes?
It is known as Flukes
Parasitic flatworms
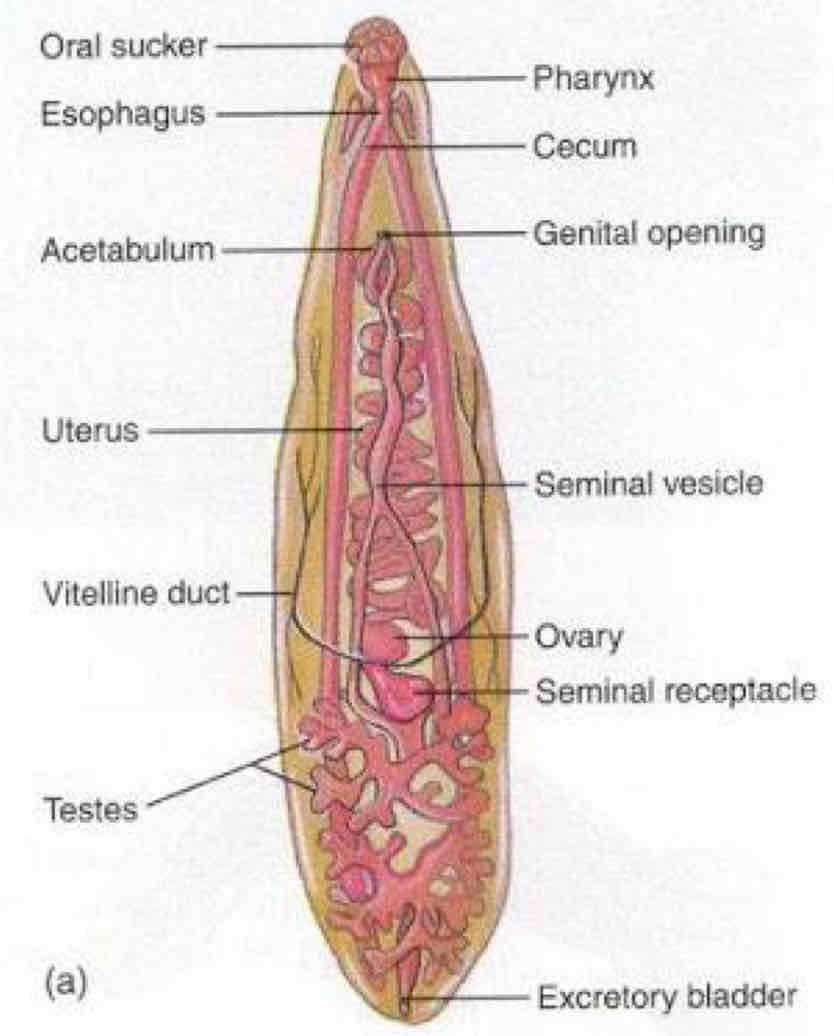
Trematodes has ________ digestive tract
Incomplete - no anus
Trematodes are hermaphroditic, what does it mean?
Male and Female’s reproductive organs are co-existed
(Exception: Schistosome Trematodes)
What is Schistosome Trematodes?
AKA Blood flukes
Live in mesenteric venues/veins of small/large intestine
Live in the venous plexus of urinary bladder
How does Schistosome Trematodes impact host body?
Eggs transverse host tissue, remain in host tissues
Eggs also travels to Liver, CNS, lungs, etc.
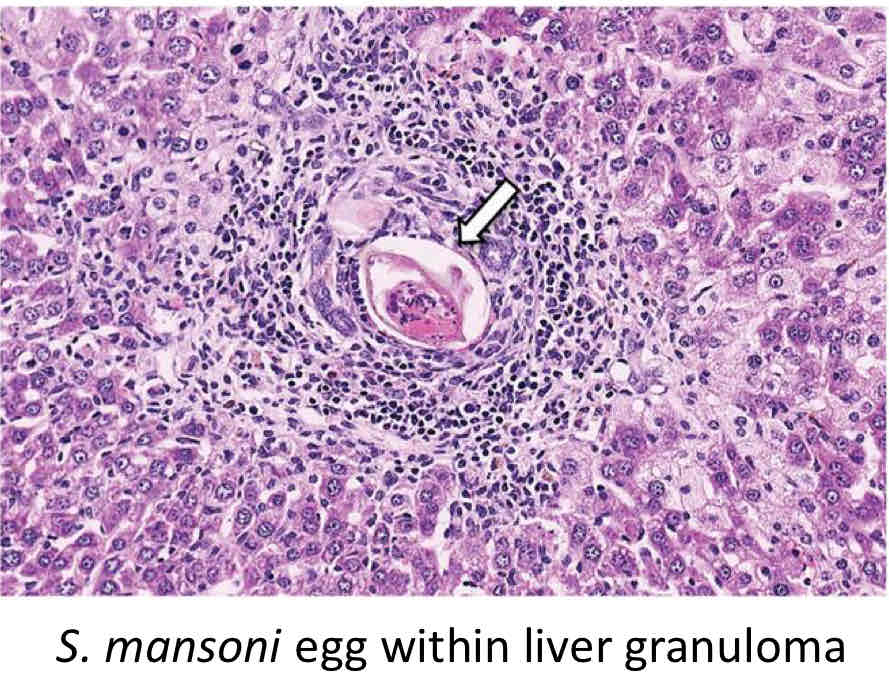
What are 2 subtypes (subspecies) of Schistosomiasis?
1) Haematobium
2) Mansoni
Which subtype of Schistosomiasis is associated with urinary bladder?
Haematobium
Which subtype of Schistosomiasis is associated with Mesenteric blood vessels?
Mansoni
What is intermediate hosts in Schistosomiasis?
Particular snail species
How does human acquire Schistosomiasis?
Contact with freshwater with infectious cercarial larvae (from infected snails)
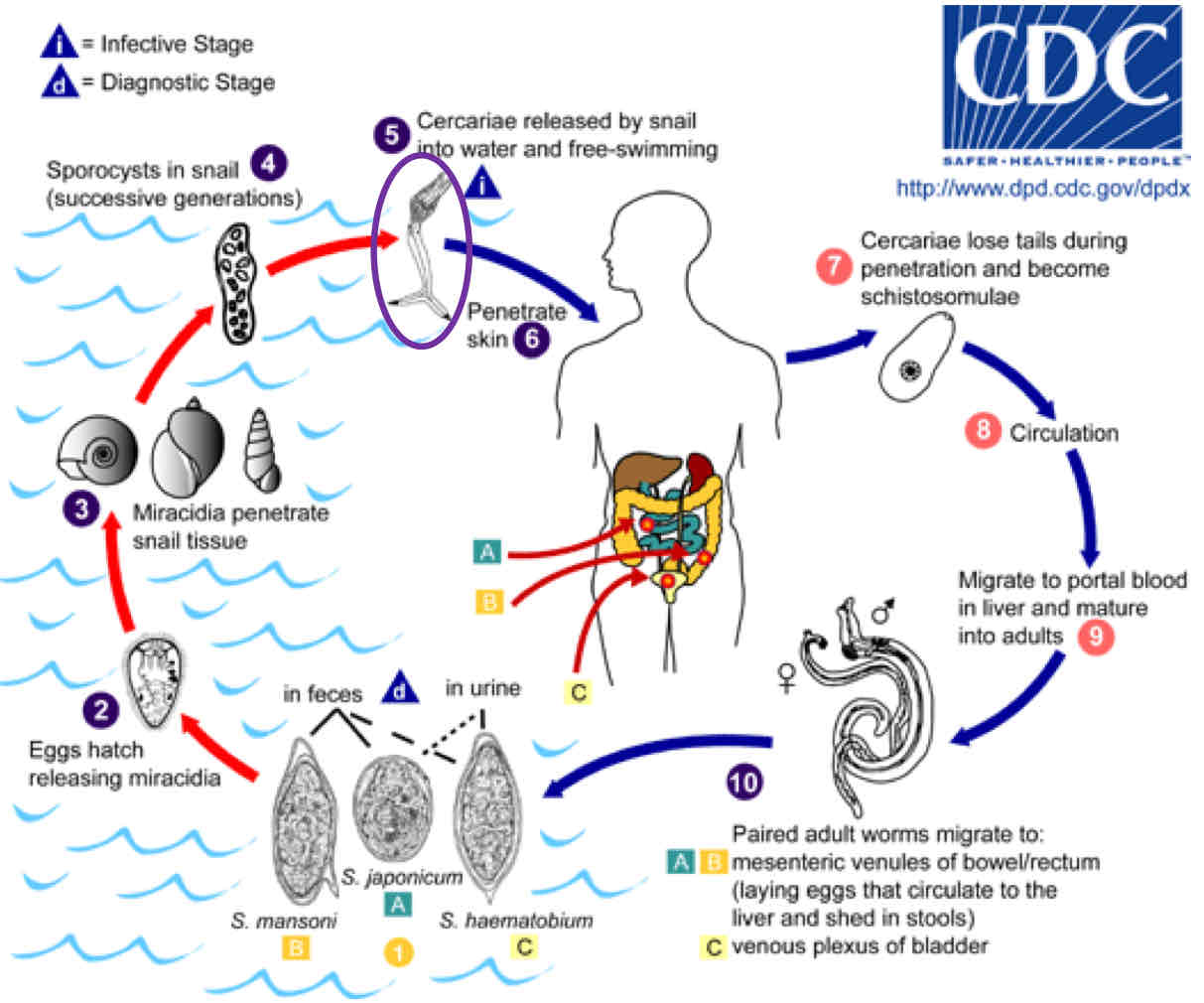
What are the steps of Schistosoma’s life cycle?
1) Egg enter water, hatch, release snail-infecting larvae
2) Parasites develops & asexual reproduced in snail
3) Cercariae - exist from snail
4) Cercariae penetrate skin and into circulation
5) Cercariae migrate and mature in liver
6) Adults form migrate to mesenteric/urinary bladder
What are the s/s of Schistosomiasis?
Most are asymptomatic
Severity depends on worm & host immune
What are 2 infection types of Schistosomiasis?
1) Acute infection
2) Chronic infection
What are significant features of Acute infection of Schistosomiasis?
Cercarial dermatitis - itchy rash at entry site
Katayama fever - fever, chills HA, myalgia, cough, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly
What are 3 types of Chronic infection of Schistosomiasis?
Intestinal schistosomiasis - abd pain, poor appetite, diarrhea, ulcer, anemia, polyps
Hepatic schistosomiasis - hepatosplenomegaly, liver fibrosis, portal hypertension, ascites, esophageal varices
Urogenital schistosomiasis - dysuria, hematuria, bladder fibrosis, kidney damage
What is the treatment of Schistosomiasis?
praziquantel
What is prevention and control of Schistosomiasis?
Avoid freshwater where schistosomiasis occurs
Education
Improved sanitation
Mass drug treatment
Snail control