A&P - Chapter 7: Axial Skeleton Study Flashcards
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Division of the 80 bones of the axial skeleton
8 cranial
14 facial
6 auditory
Hyoid bone
Sternum
24 ribs
24 vertebrae
Sacrum
Coccyx
Functions of the axial skeleton
- supports and protects organs in body cavities
- provides points of attachment for muscles (adjust position of head, neck, and truck, perform breathing movements, stabilize part of appendicular skeleton)
Facial bones
9 superficial - muscle attachment
5 deeper - separate oral and nasal cavities, increase surface area of nasal cavities, help form the nasal septum
Lamboid suture
Separates occiptal from parietal bones + suture bones
Coronal suture
attaches frontal bone to parietal bones
Sagittal suture
between parietal bones
Squamous sutures
between parietal and temporal bones on each side of skull
Sinuses
Air-filled chambers in the skull. Functions to decrease the weight of the skull, lined with mucous membrane that produce mucous that moisten and cleans the air, and serve as resonating chambers in speech
Occiptal bones
Forms much of posterior and inferior surfaces of cranium
External occipital crest
Attaches the ligamentum nuchae
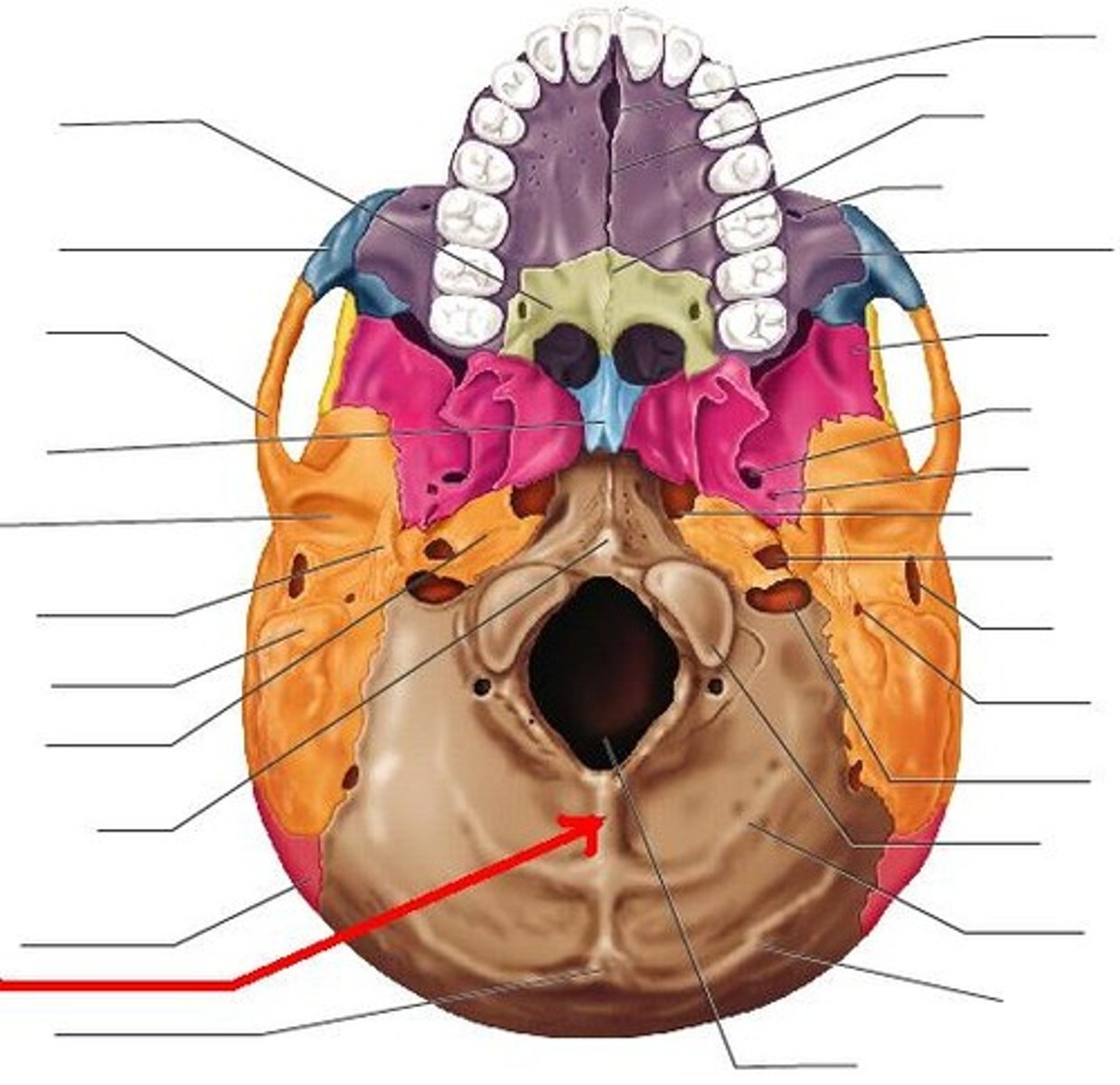
Occipital condyles
articulate with first cervical vertebra
Foramen magnum
Connects cranial cavity with vertebral canal
Jugular foramen
internal jugular vein
Hypoglossal canals
hypoglossal nerve (XII)
Parietal bones (functions)
form part of the superior and lateral surfaces of the cranium
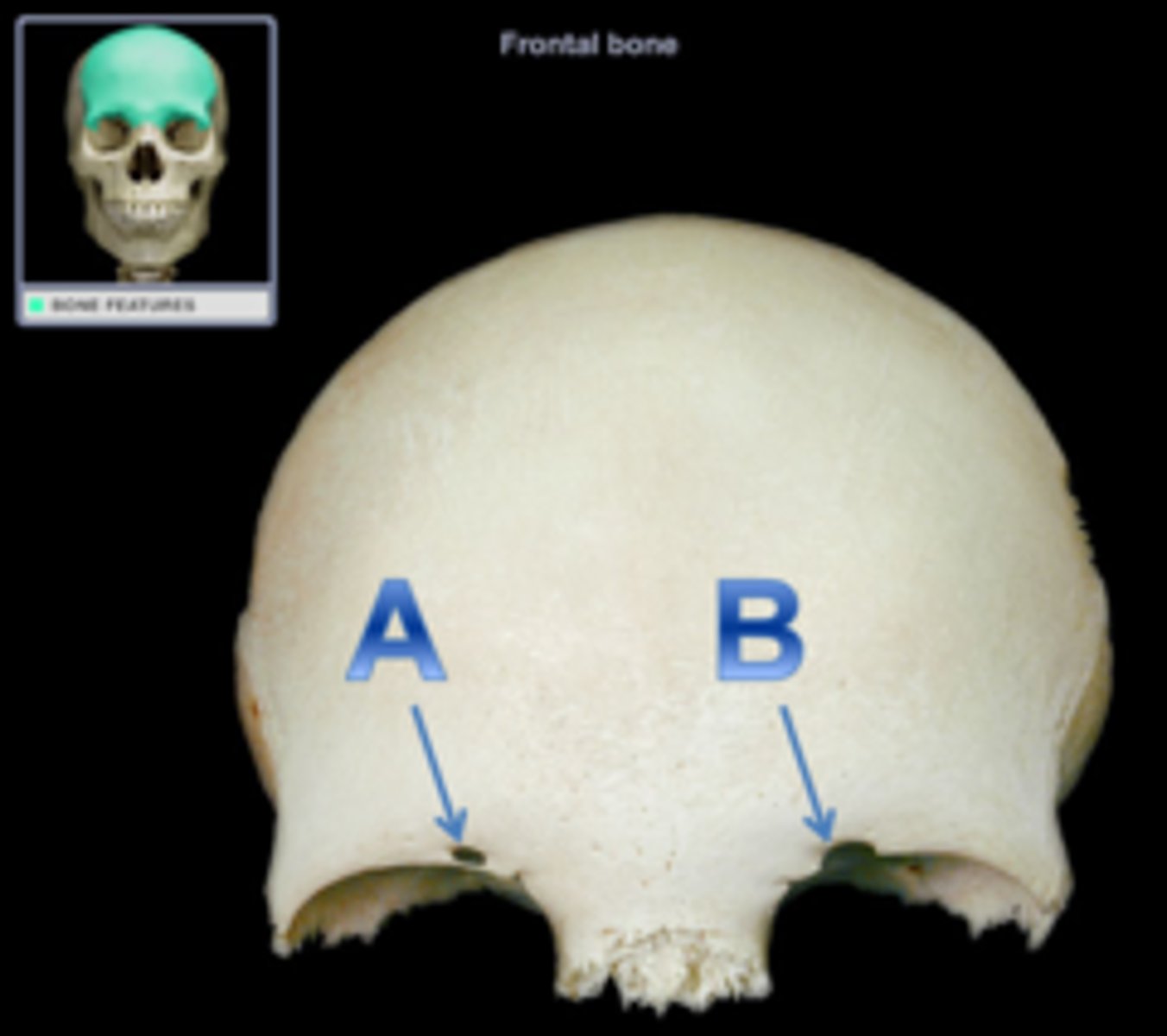
Frontal bone (functions)
Forms the anterior cranium and upper eye sockets
Contains frontal sinuses + frontal sinuses
supra-orbital margin
protects the eye
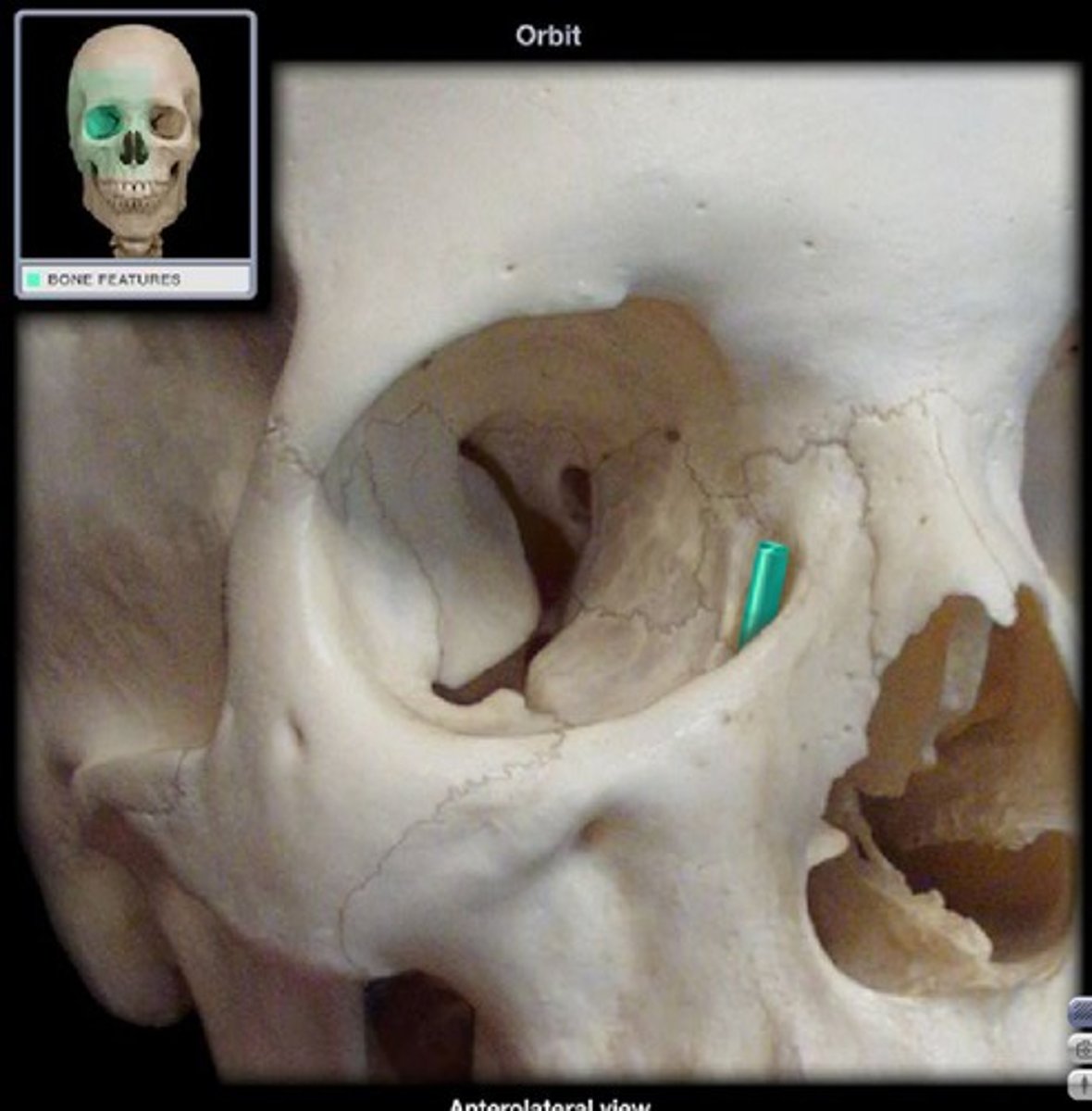
Lacrimal fossa
Depression for the lacrimal gland
Supra-orbital foramen
Blood vessels of eyebrows, eyelids, and frontal sinuses
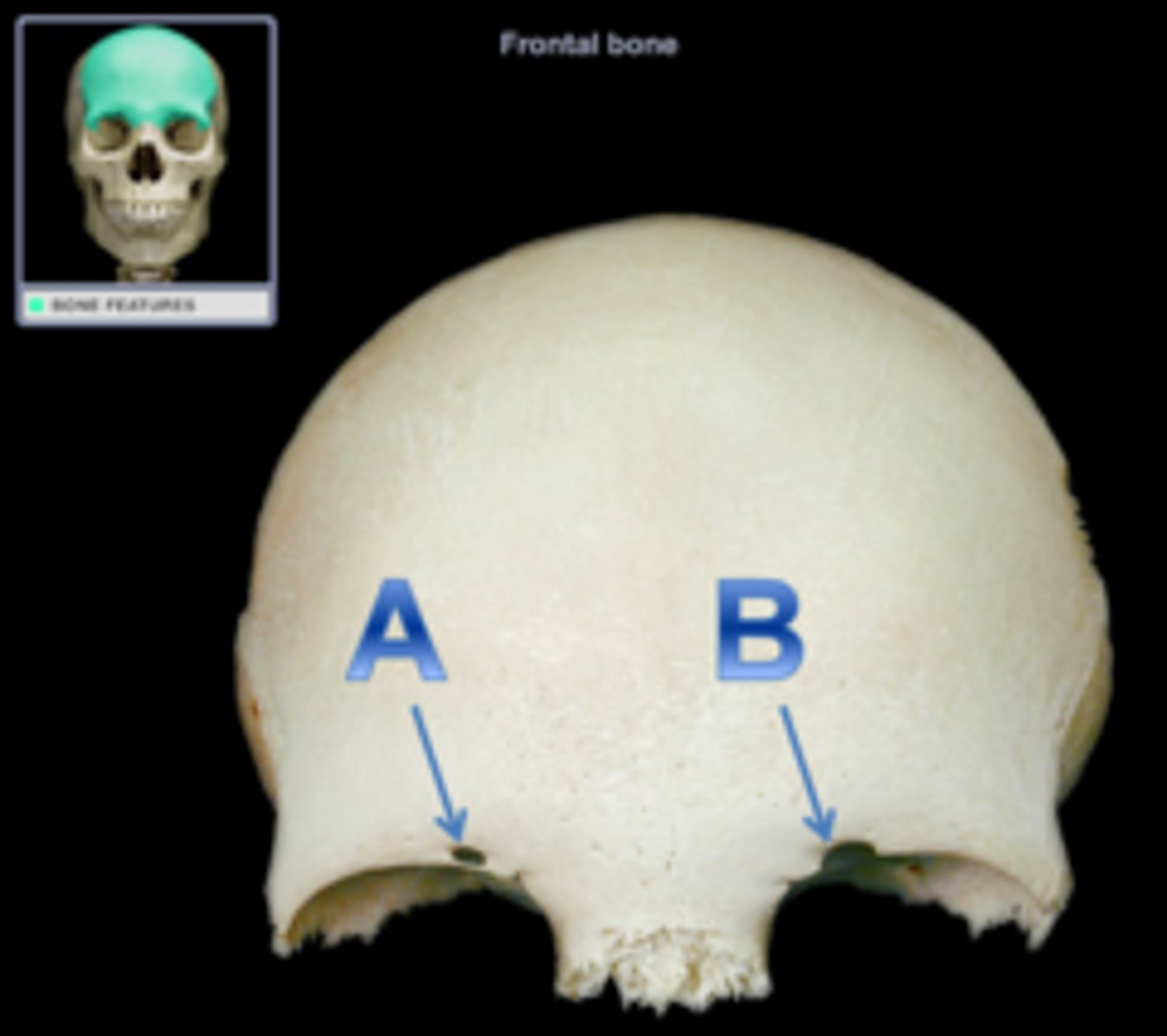
Supra-orbital notch
an incomplete supra-orbital foramen
Temporal bones (functions)
1. Lateral wall of cranium and zygomatic arches
2. Articulates with mandible
3. Surround and protect internal ear
4. Attach muscles of jaw and head
Squamous part
borders the squamous suture
Mastoid process
For muscle attachment and contains mastoid cells that connect to middle ear cavity
Petrous part
Encloses sutures of internal ear
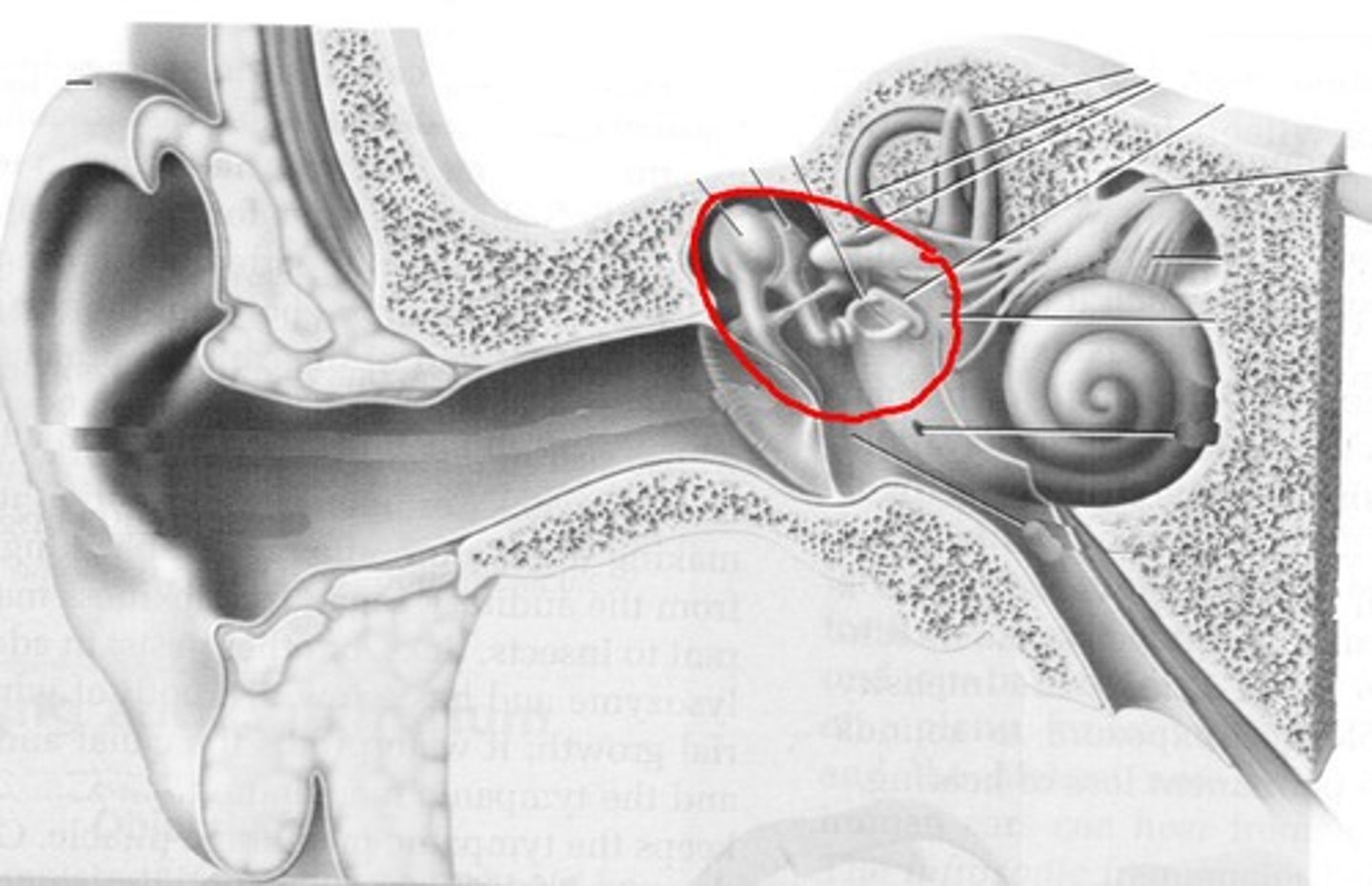
Auditory ossicles
Three tiny bones in tympanic cavity and transfer sound vibrations from tympanic membrane to internal ear
corotid canal
internal carotid artery
foramen lacerum contains
hyaline cartilage, small arteries, and auditory tube
external acoustic meatus of temporal bone
leads and ends at the tympanic membrane
stylomastoid foramen of temporal bone
facial nerve
internal acoustic meatus of temporal bone contains
blood vessels, nerves of the internal ear, and facial nerves
sphenoid bones functions
forms part of the floor of the cranium
unites the cranial and facial bones
strengthens the sides of the skull
body of the sphenoid
forms central axis of the sphenoid
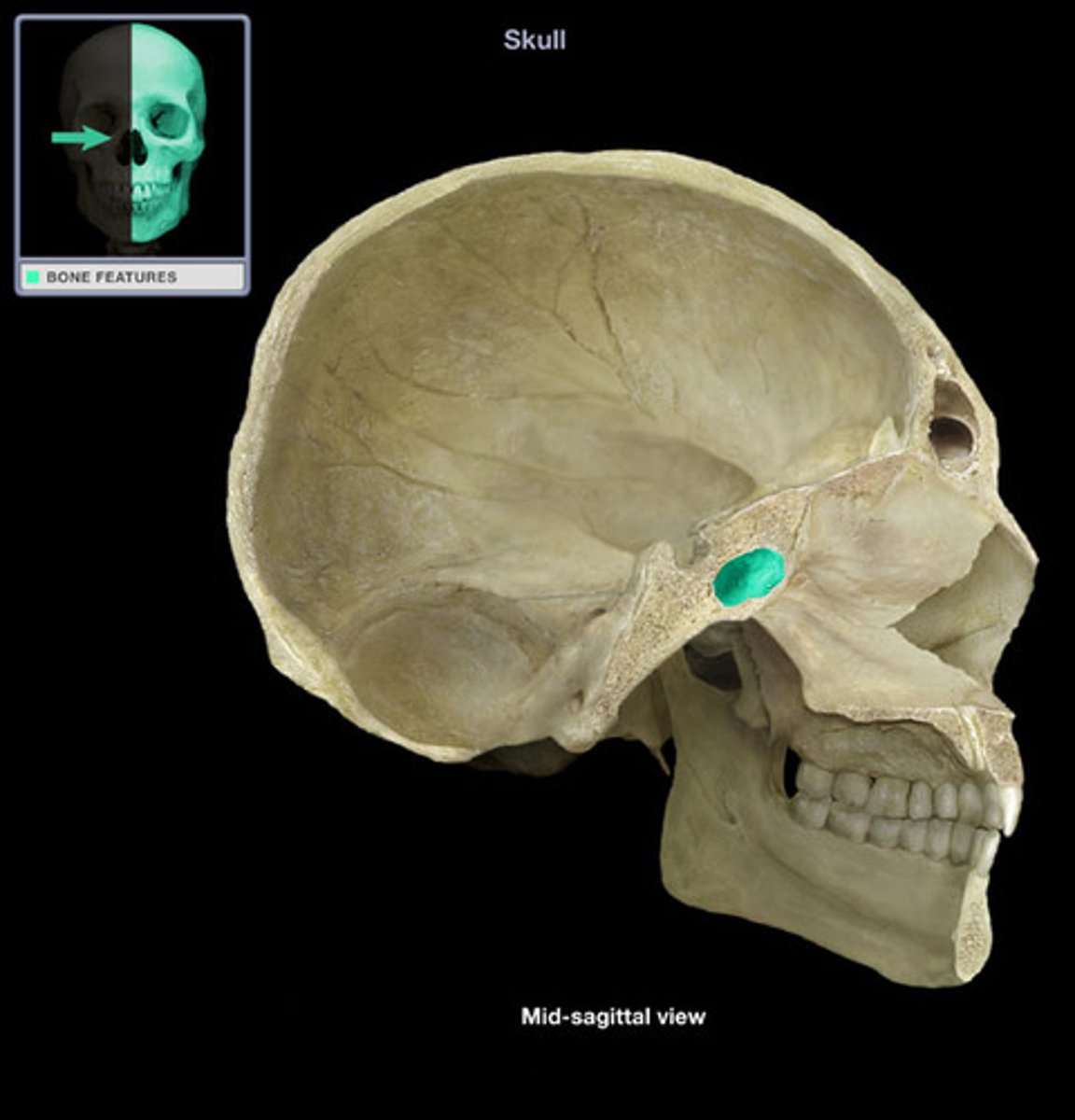
sella turcica of sphenoid bone
saddle-shaped enclosure on the superior surface of the body of the sphenoid that houses the pituitary gland
hypophyseal fossa of sphenoid bone
depression within the sella turcica that holds the pituitary gland
sphenoidal sinuses of the sphenoid
either sides inferior to the sella turcica
lesser wings of the sphenoid
inferior to the sella turcica
greater wings of the sphenoid
form part of the cranial flor + sphenoidal spine lies at corner of each wing
pterygoid process of the sphenoid
forms the pterygoid plates to attach muscles of the lower jaw and soft palate
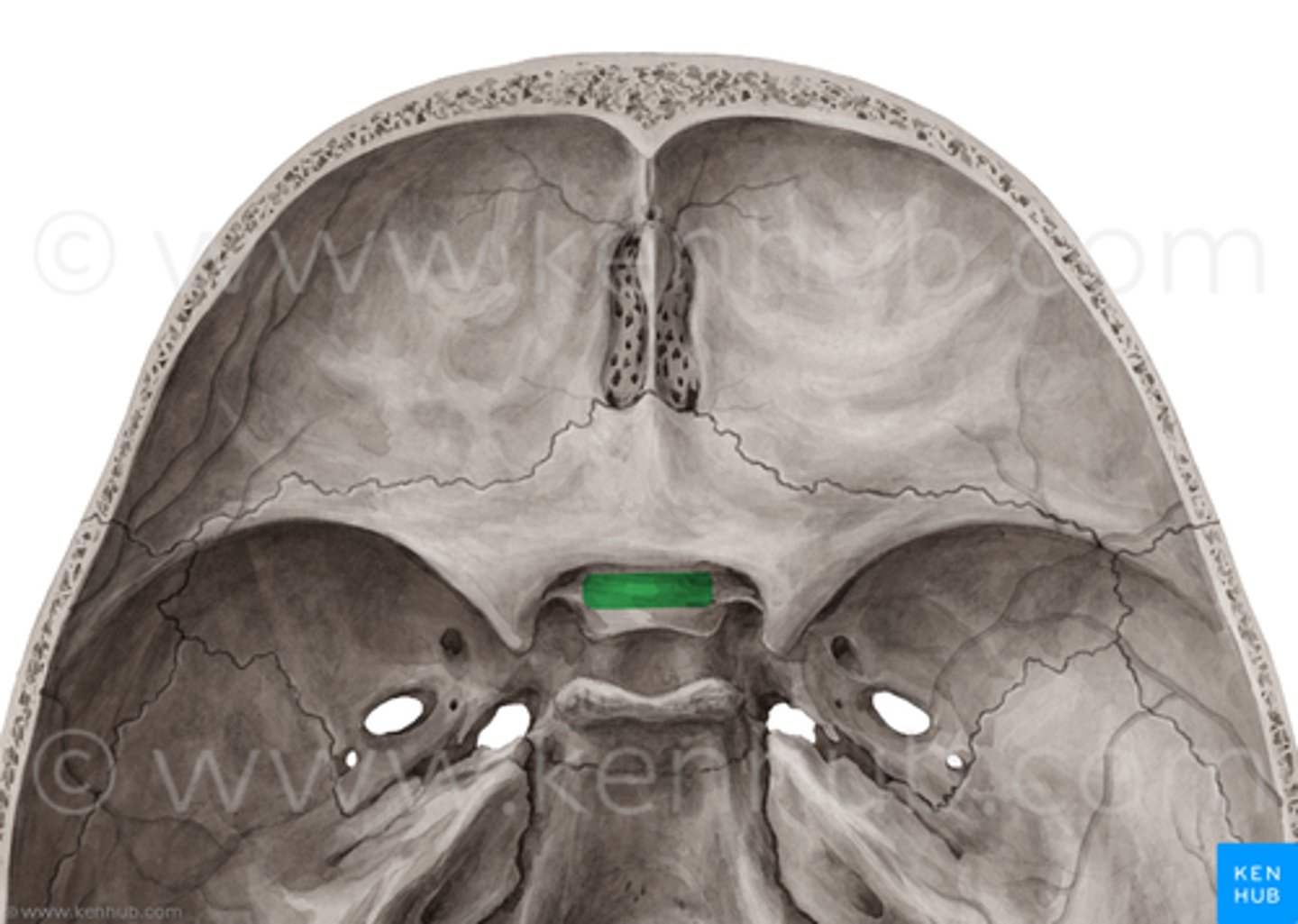
optic canals of the sphenoid
optic nerves
prechiasmatic sulcus
optic groove
superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
blood vessels and nerves of the orbit
foramen rotundum and foramen ovale
blood vessels and nerves of the face and jaw
foramen spinosum
blood vessels and nerves of membranes
ethmoid bones functions
forms the anteromedial floor of the skull, roof of the nasal cavity, and part of the nasal septum
cribriform pate of the ethmoid
Forms roof of the nasal cavity and contains crista Galli to attach falx cerebri
ethmoidal labyrinths
air-filled cavities that consist of ethmoidal cells, located in the superior nasal conchae and middle nasal conchae
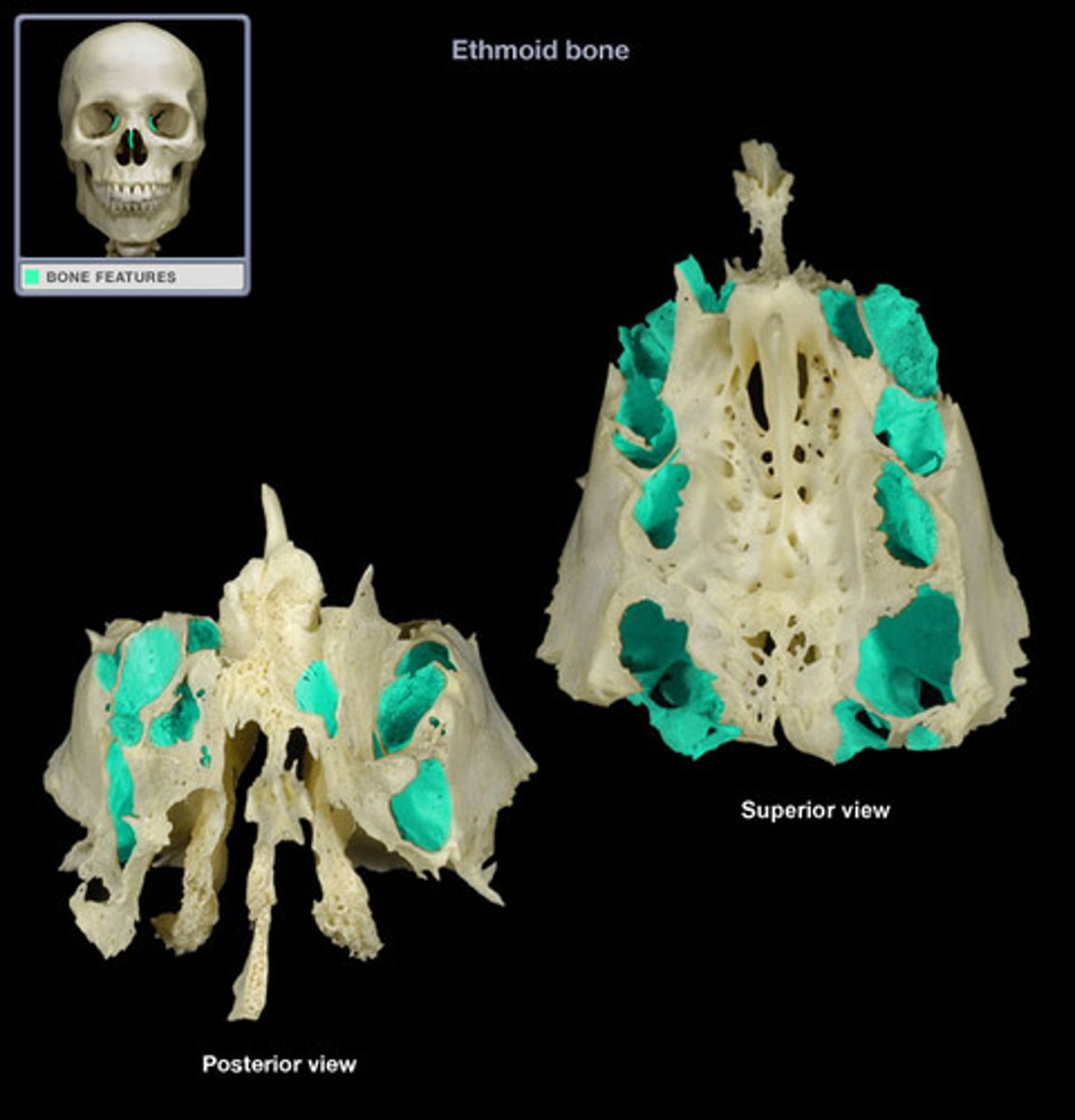
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
forms part of the nasal septum
olfactory foramina of ethmoid bone
located in the cribriform plate (tiny holes) for the olfactory nerves
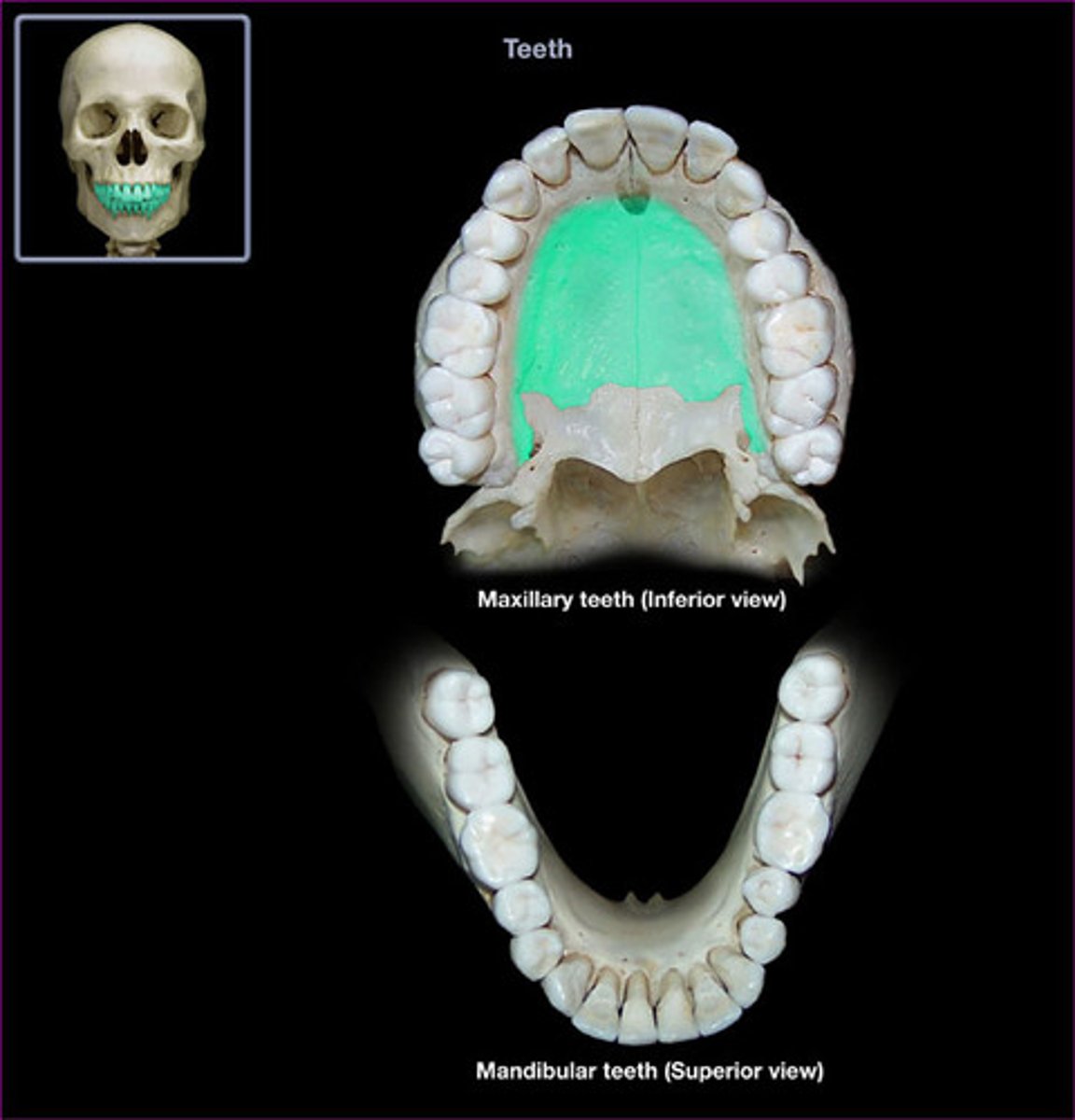
maxilla functions
- support upper teeth
- form inferior orbital rims
- form lateral margins of sternal nares
- form upper jaw and most of hard palate
- contain maxillary sinuses
orbital rim of the maxillae
protects eye and other structures of the orbit
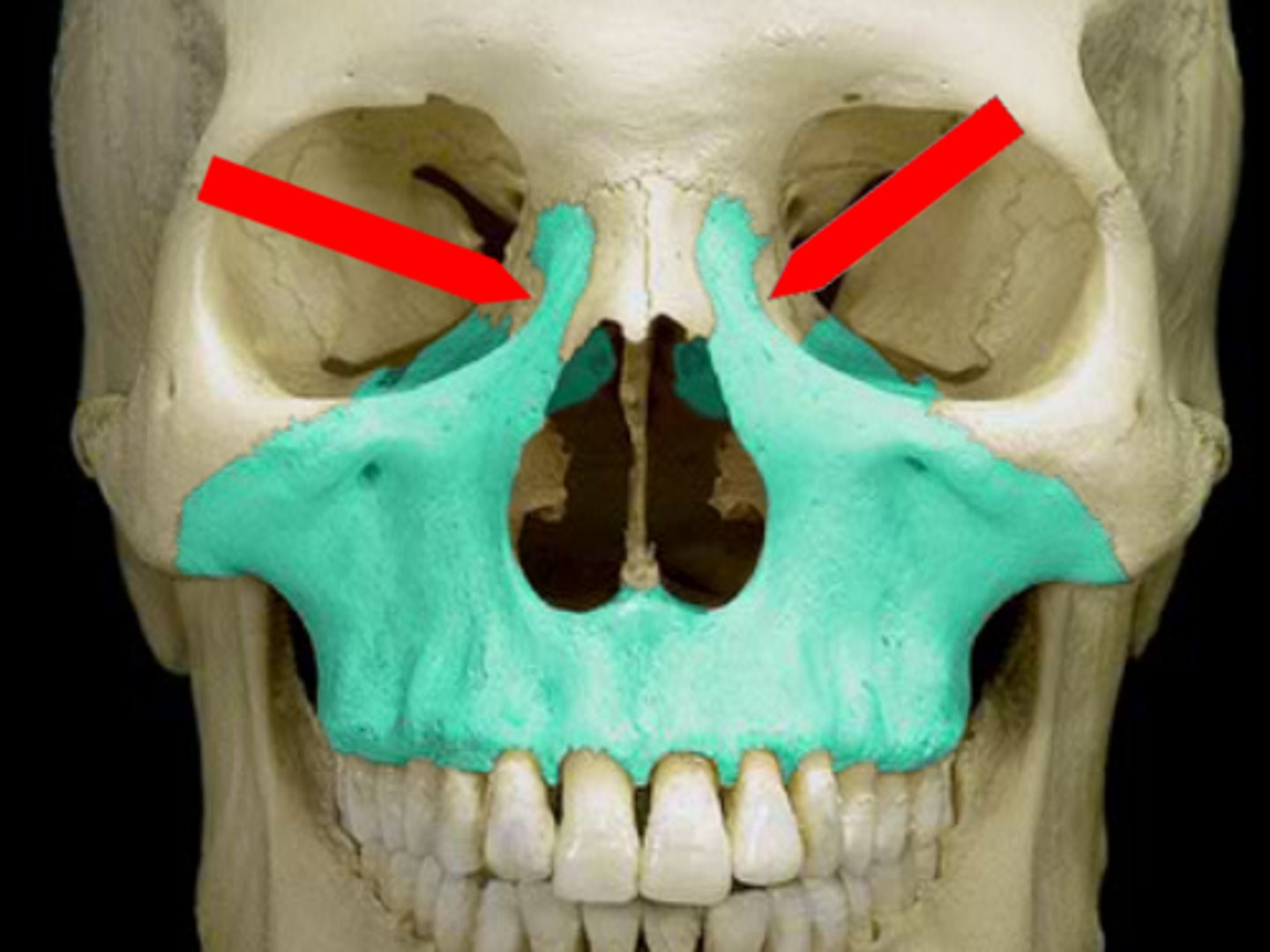
Anterior nasal spine of maxilla
attaches to the anterior nasal septum
alveolar process of the maxilla
support upper teeth
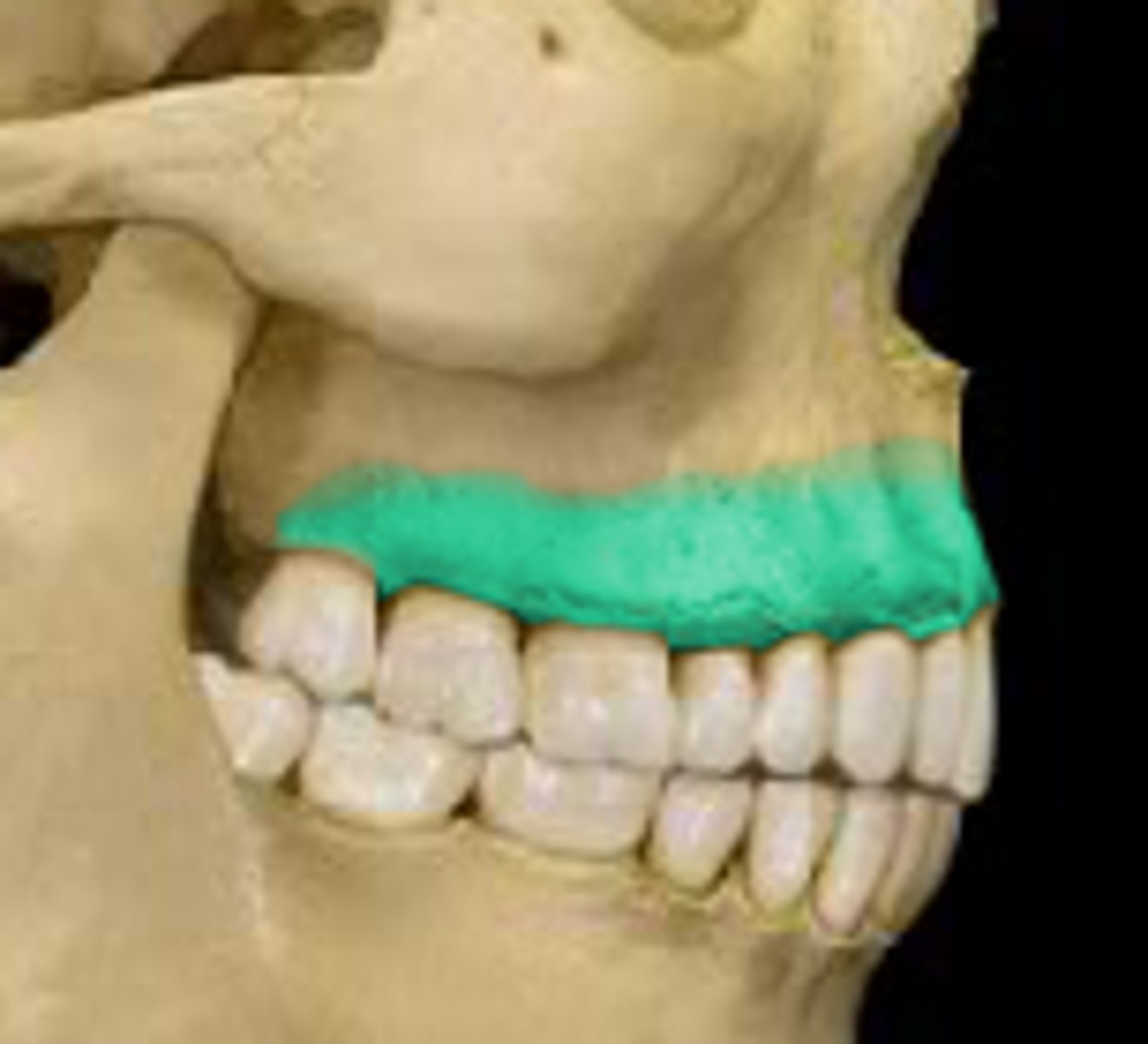
palatine process of maxilla
forms most of the hard palate
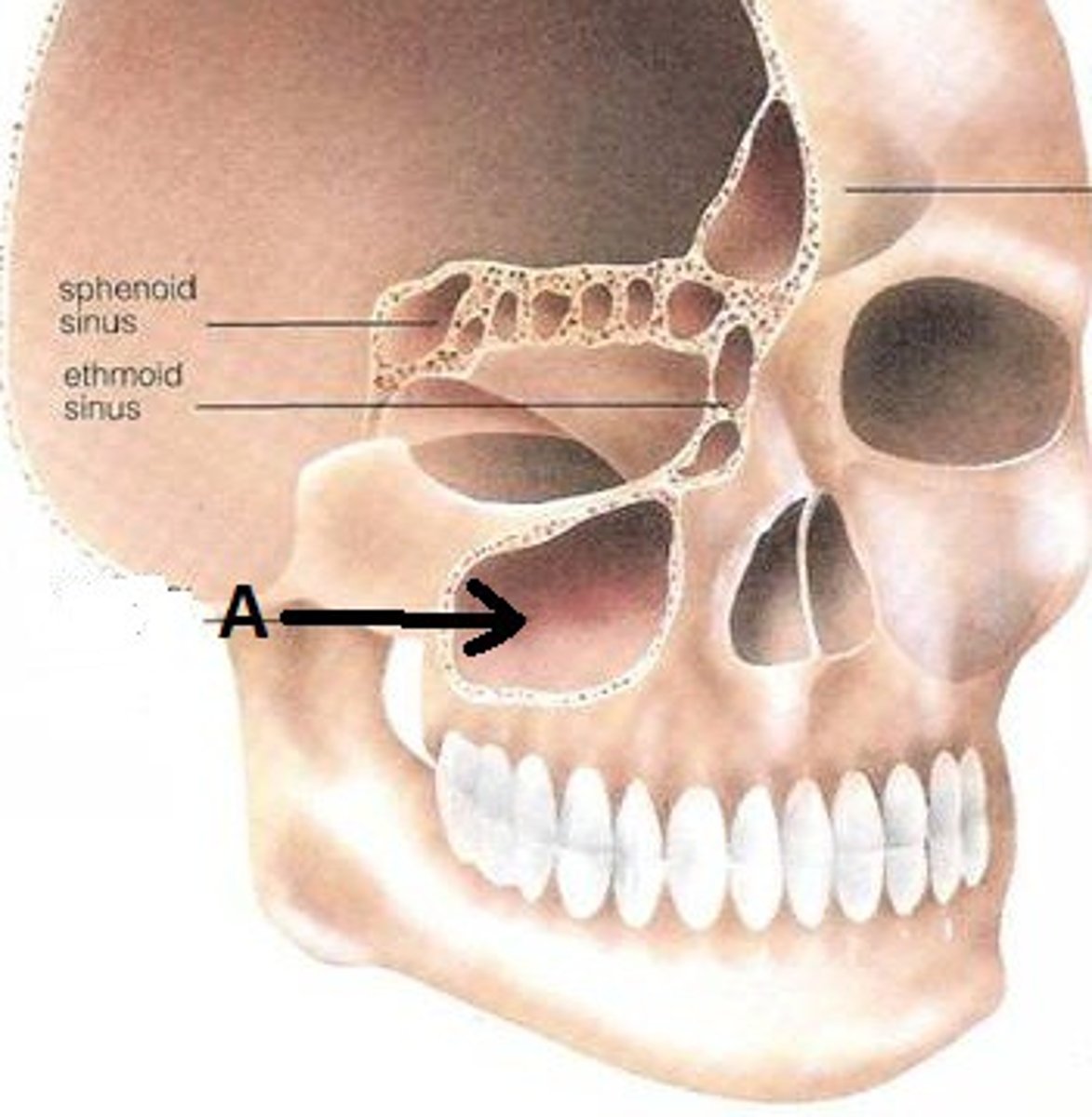
maxillary sinuses
lighten the bone
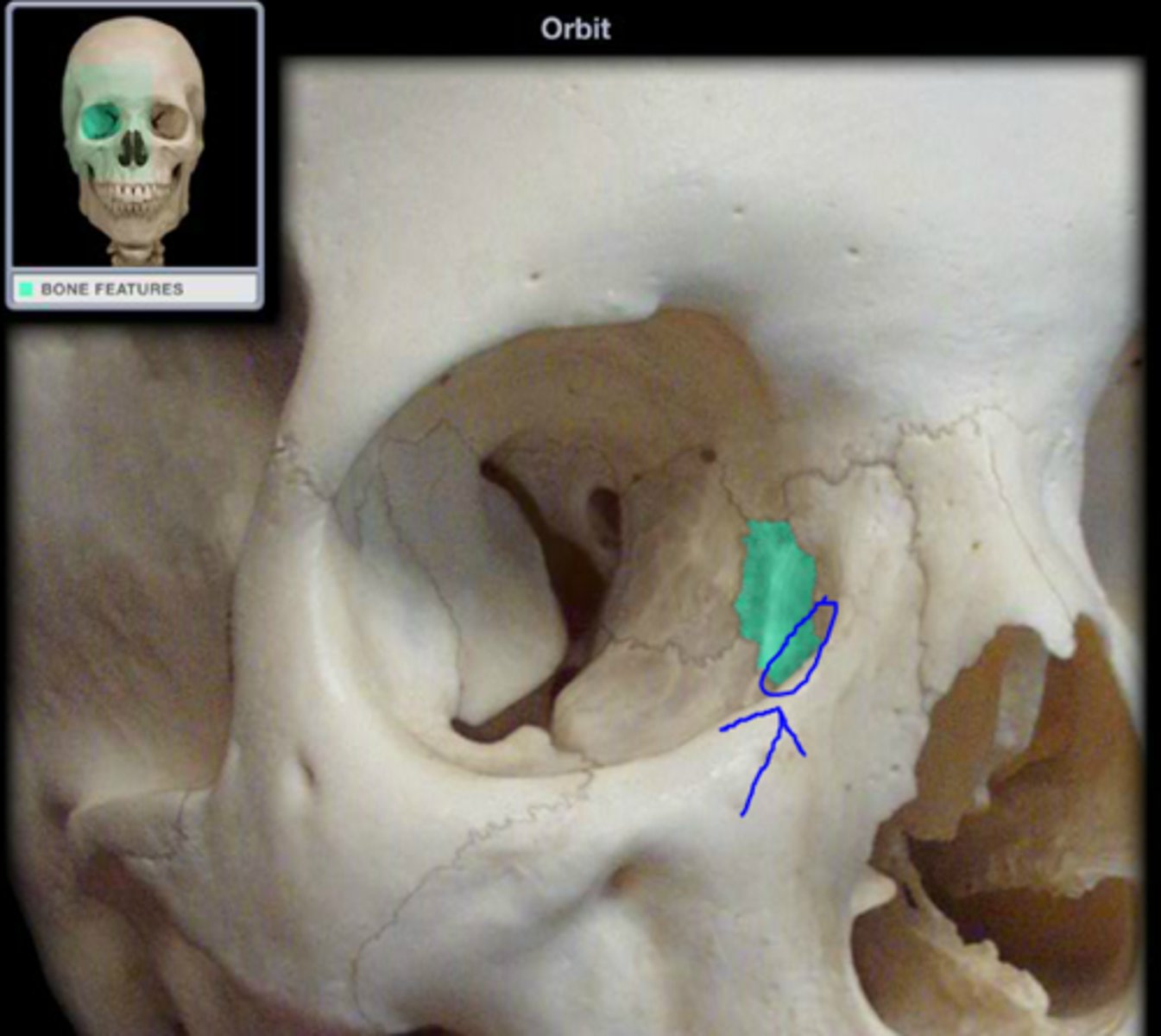
nasolacrimal canal
protect the lacrimal sac and the nasolacrimal duct
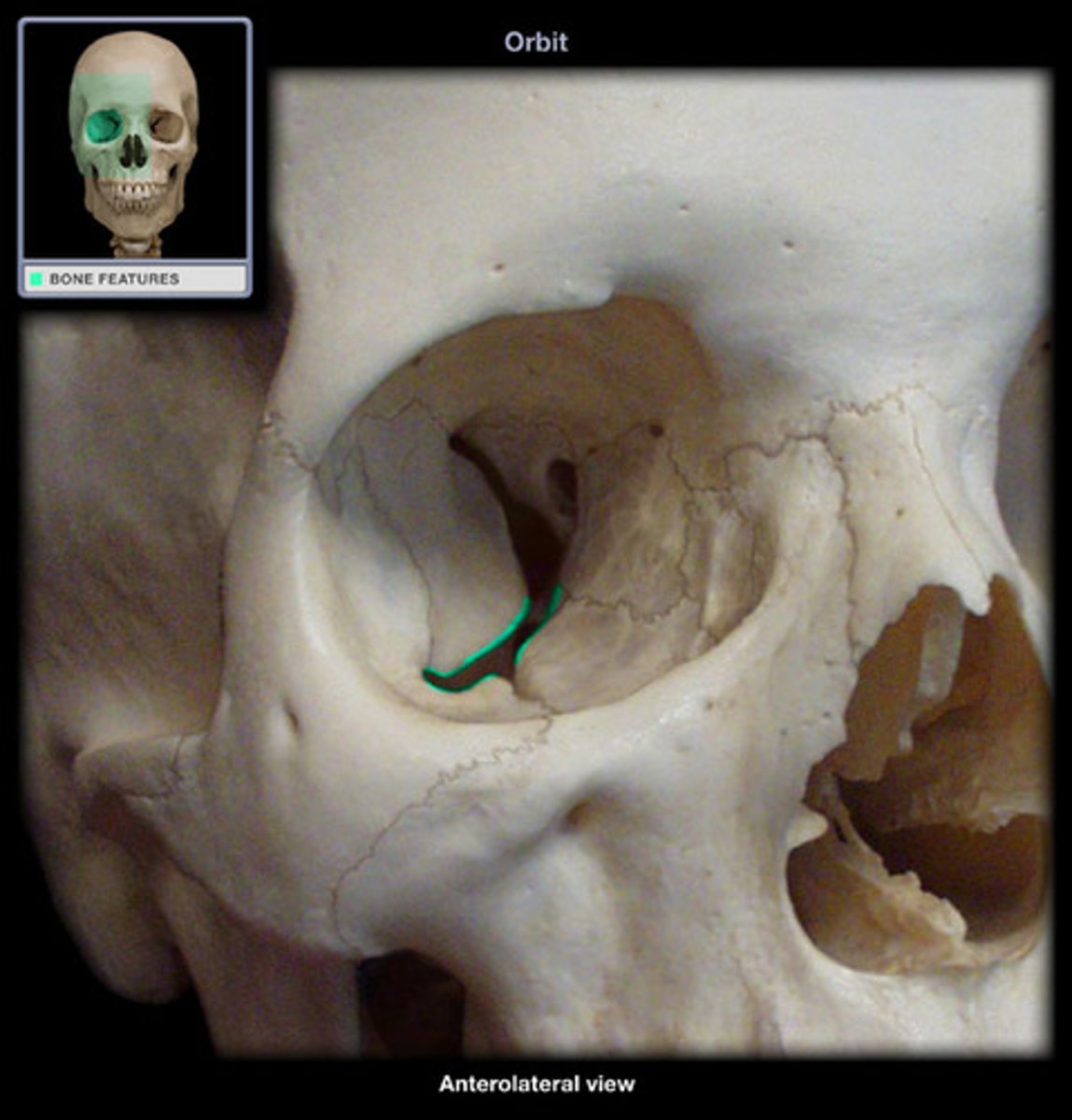
infra-orbital foramen (maxilla)
sensory nerve to the brain (via foramen rotundum)
inferior orbital fissure (maxilla)
cranial nerves and blood vessels
palatine bones functions
- forms the posterior portions of hard palate
- contribute to the floors of the orbits
horizontal plate (palatine bones)
forms posterior part of the hard palate
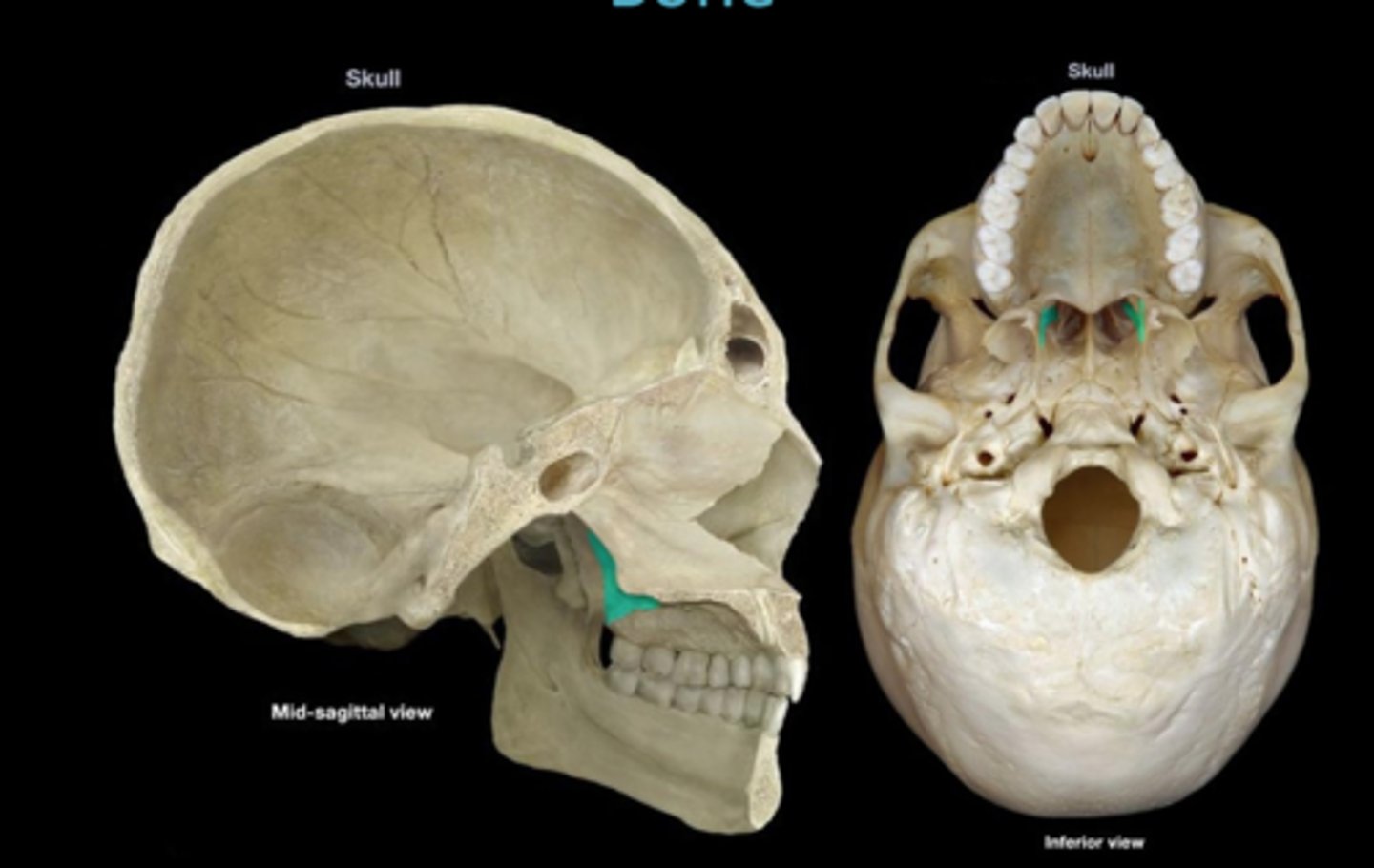
perpendicular plate (palatine bones)
extends from horizontal plate to orbital process of orbit floor
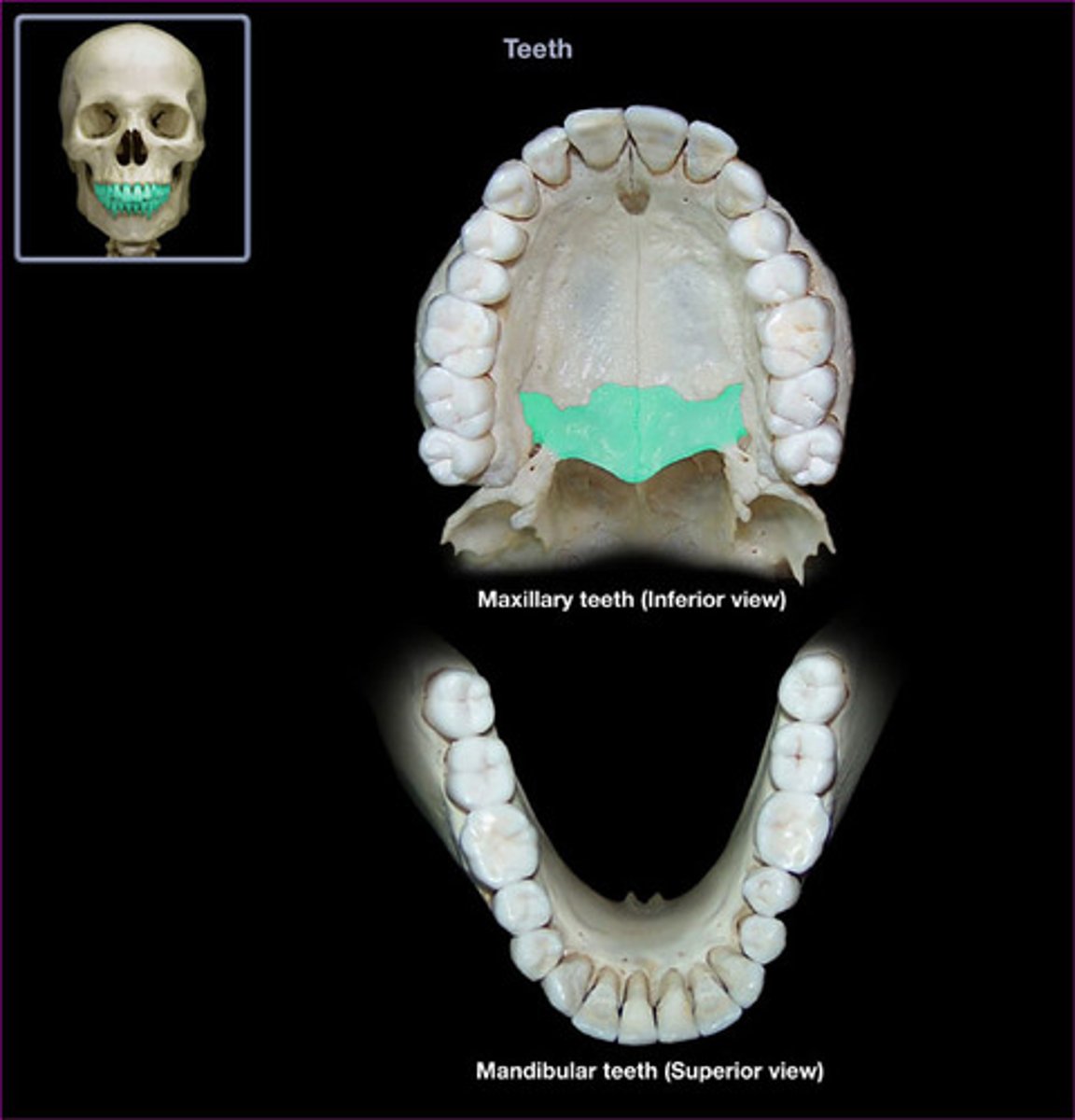
foramina of the palatine bones
small blood vessels and nerves supplying the roof of the mouth
nasal bones general function
support a bridge of the nose and connect to cartilages of distal parts of the most that extend to external nares
vomer functions
forms inferior portion of the nasal septum
inferior nasal conchae functions
slow inhaled air
create air turbulence in the nasal cavity
increase epithelial surface are to warm and humidify the air
zygomatic bones functions
contribute to rims and lateral walls of orbits and forms parts of zygomatic arches
temporal process of the zygomatic bone
meets the zygomatic process of the temporal bone
zygomaticofacial foramen
sensory nerve of the cheeks
lacrimal bones
- smallest facial bones
- form parts of medial walls of orbit
lacrimal sulcus of lacrimal bones
location of the lacrimal sac and leads to the nasolacrimal canal
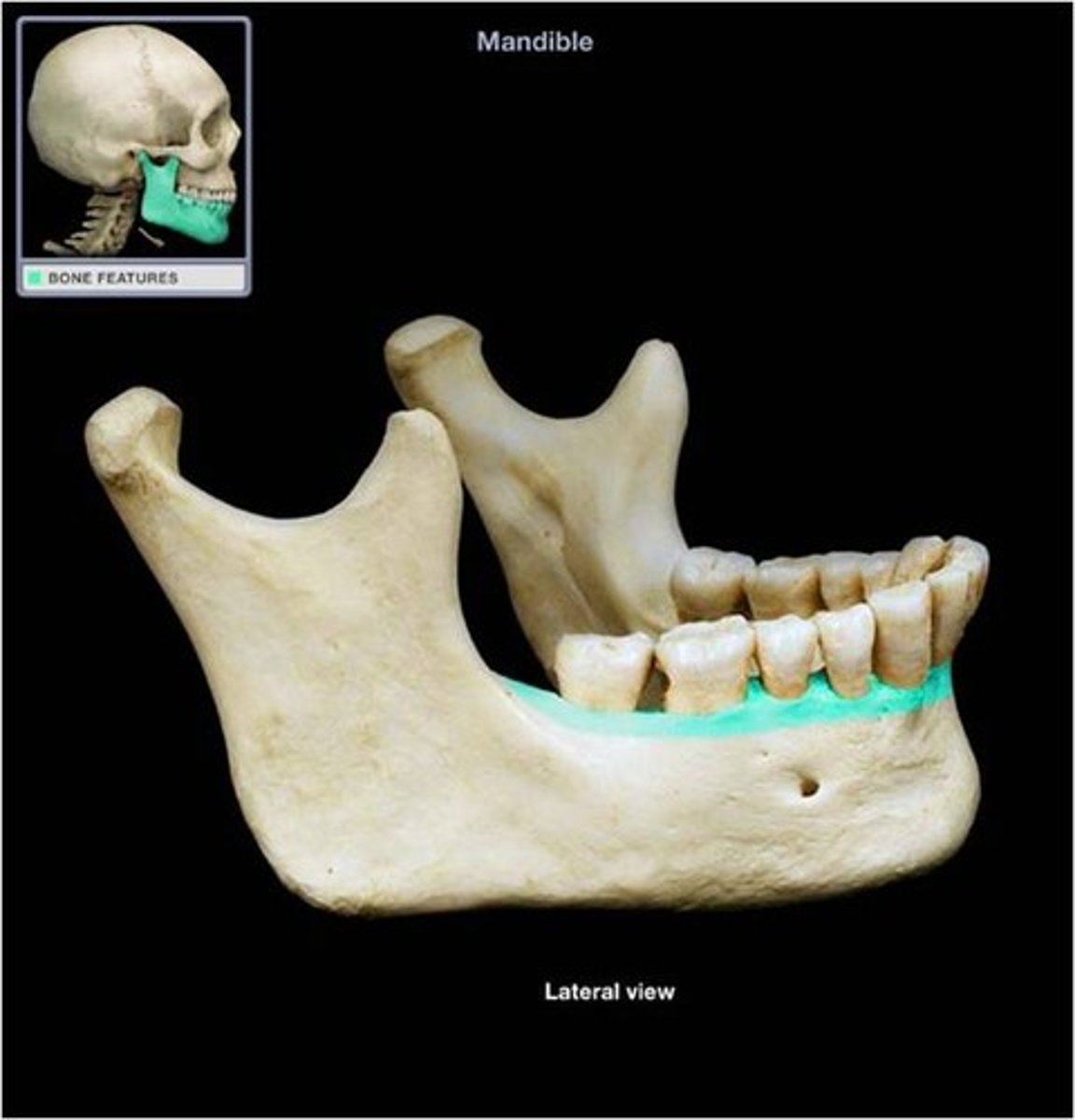
mandible functions
forms the lower jaw
body of the mandible
horizontal portion of the lower jaw
alveolar part
supports the lower teeth
mental protuberance of the mandible
attaches facial muscles
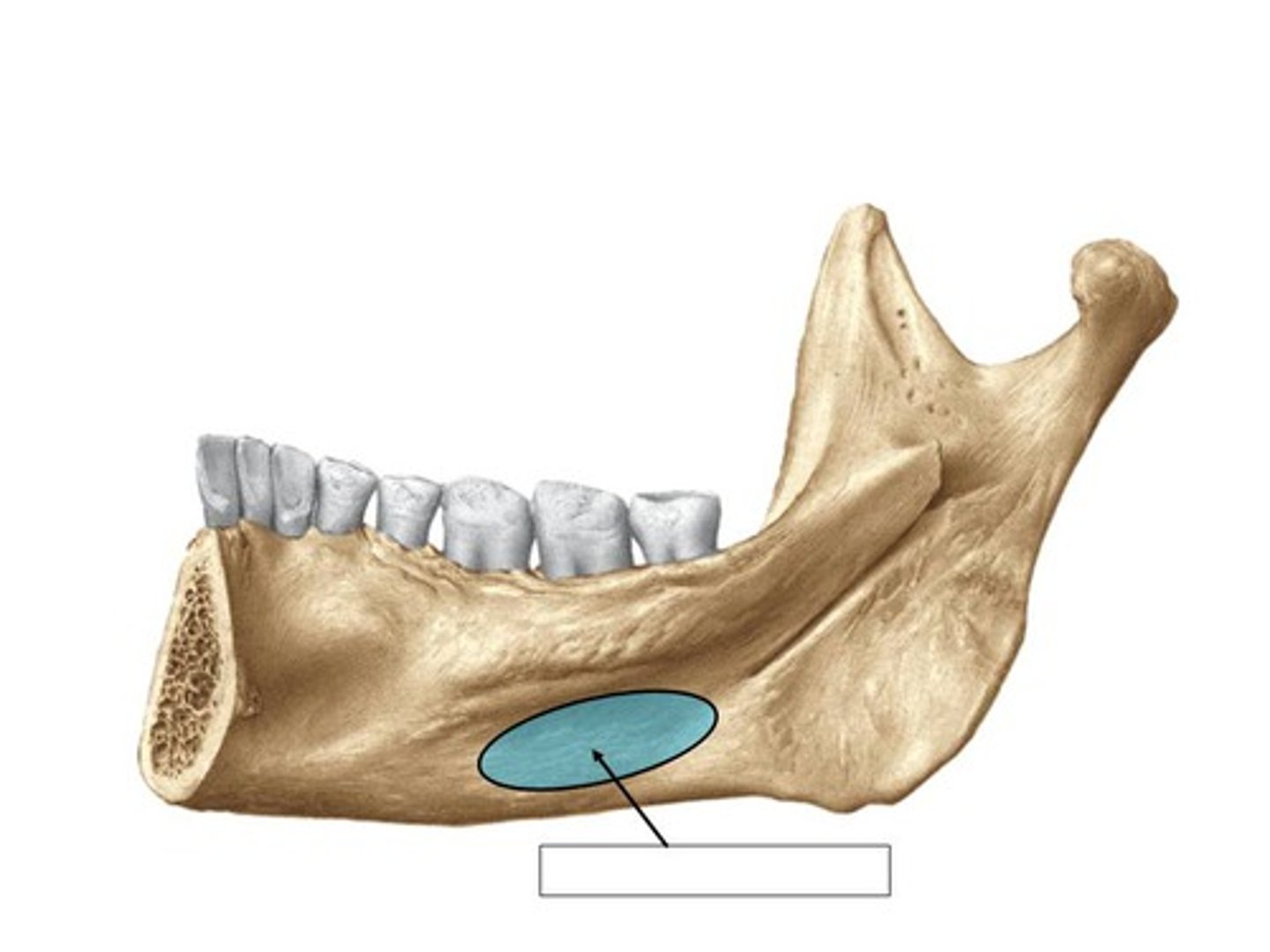
depression on the medial surface of the mandible
submandibular salivary gland
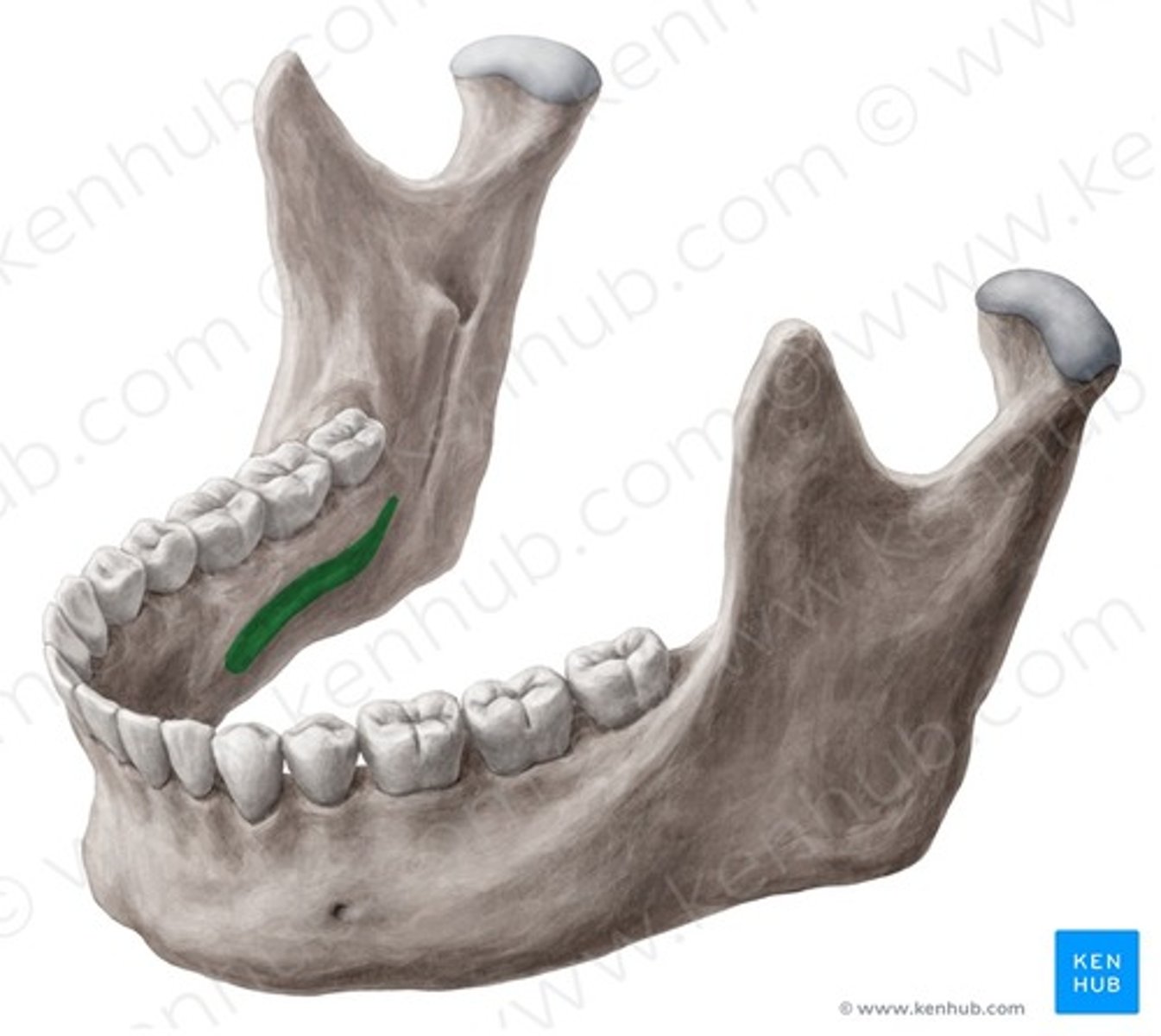
mylohyoid line of mandible
insertion of mylohyoid muscle
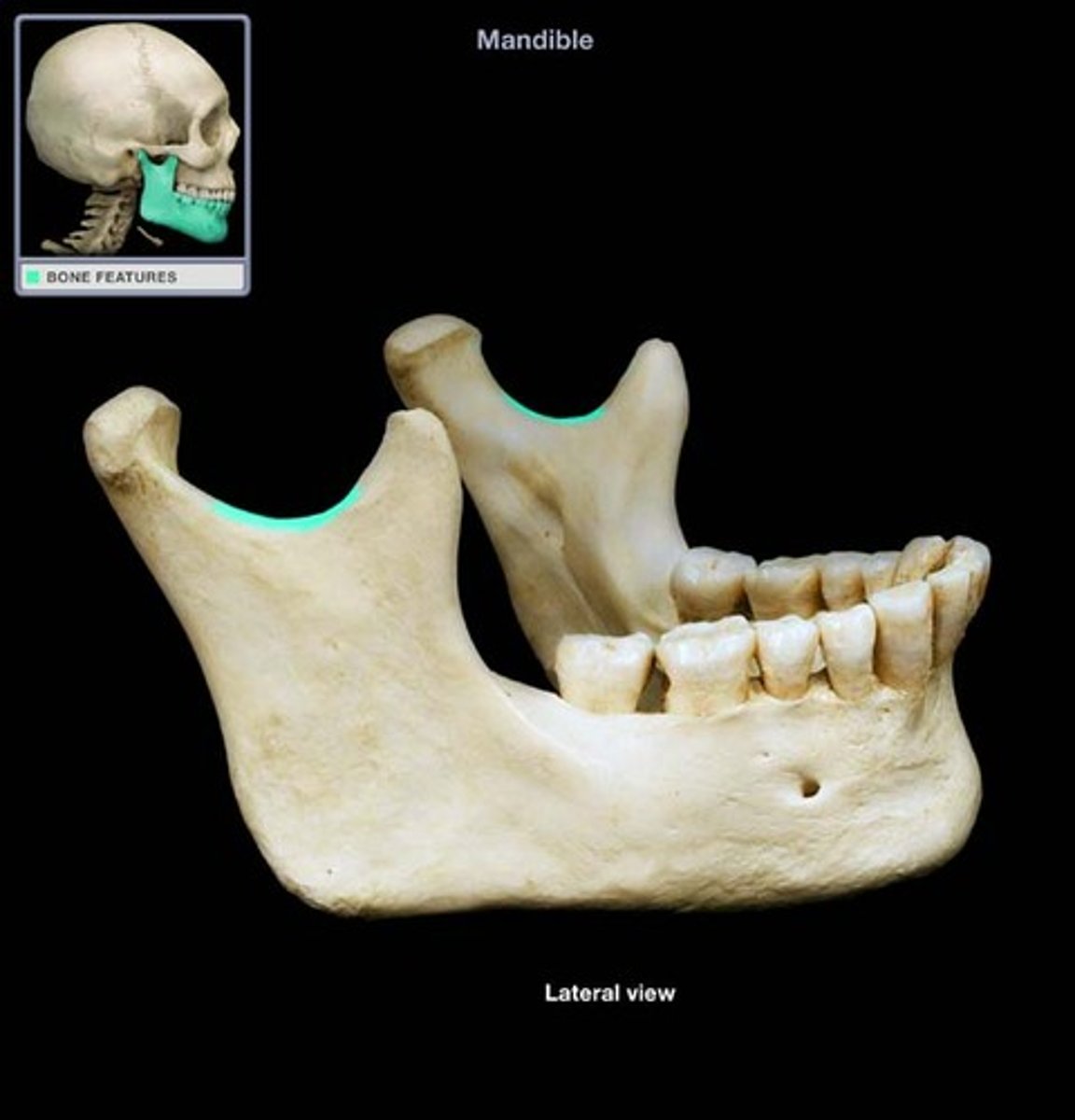
ramus of the mandible
vertical portion of the lower jaw that ascends from the angle of the mandible
condylar process of madible
articulates with the temporal bone at temporomandibular joint
coronoid process of the mandible
insertion point for temporalis muscle (closes te jaw)
mandibular notch
separates condylar and coronoid processes
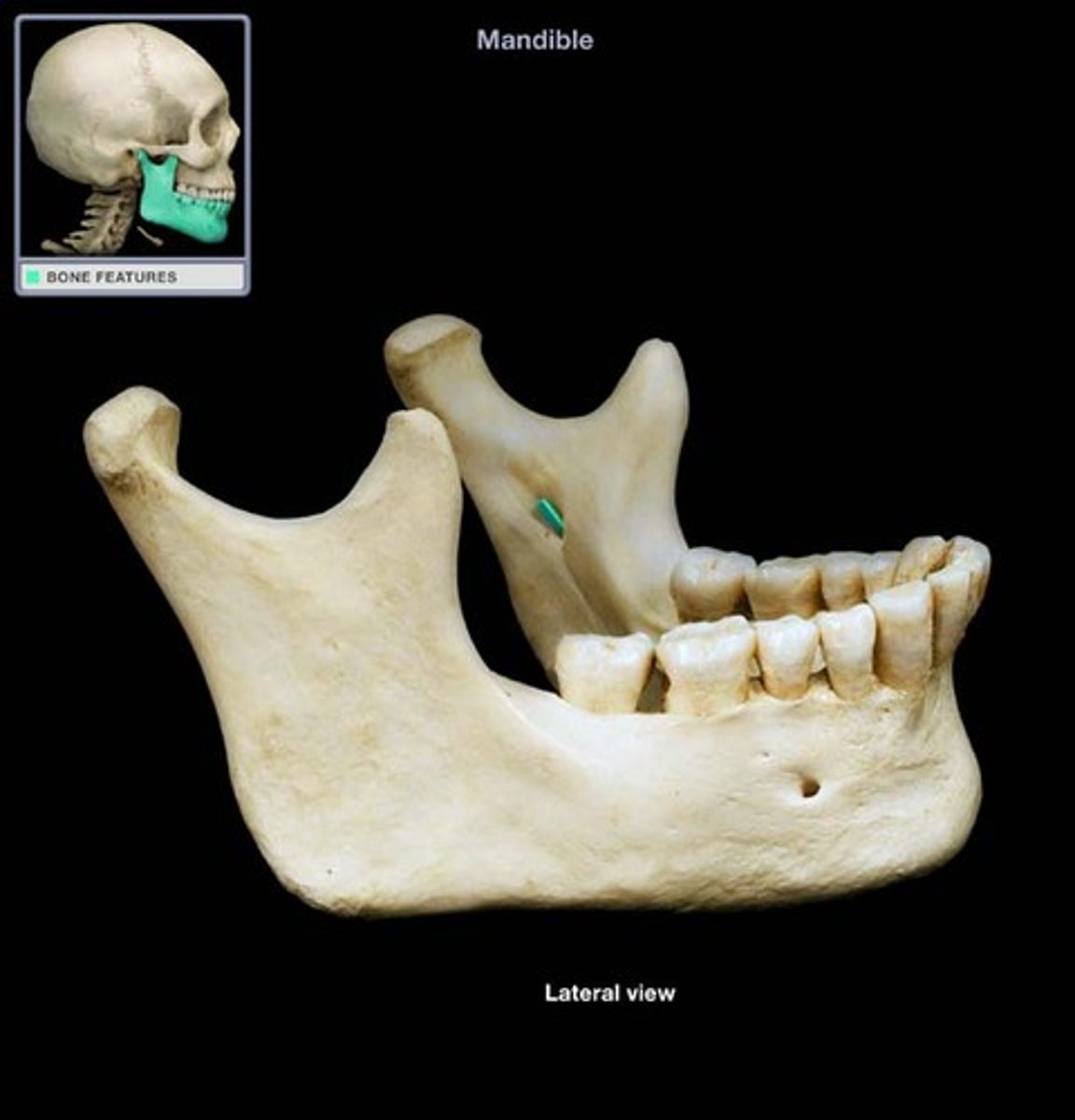
mental foramen of mandible
sensory nerves of lips and chin
mandibular foramen
entrance to mandibular canal and passageway for blood vessels and nerves of lower teeth
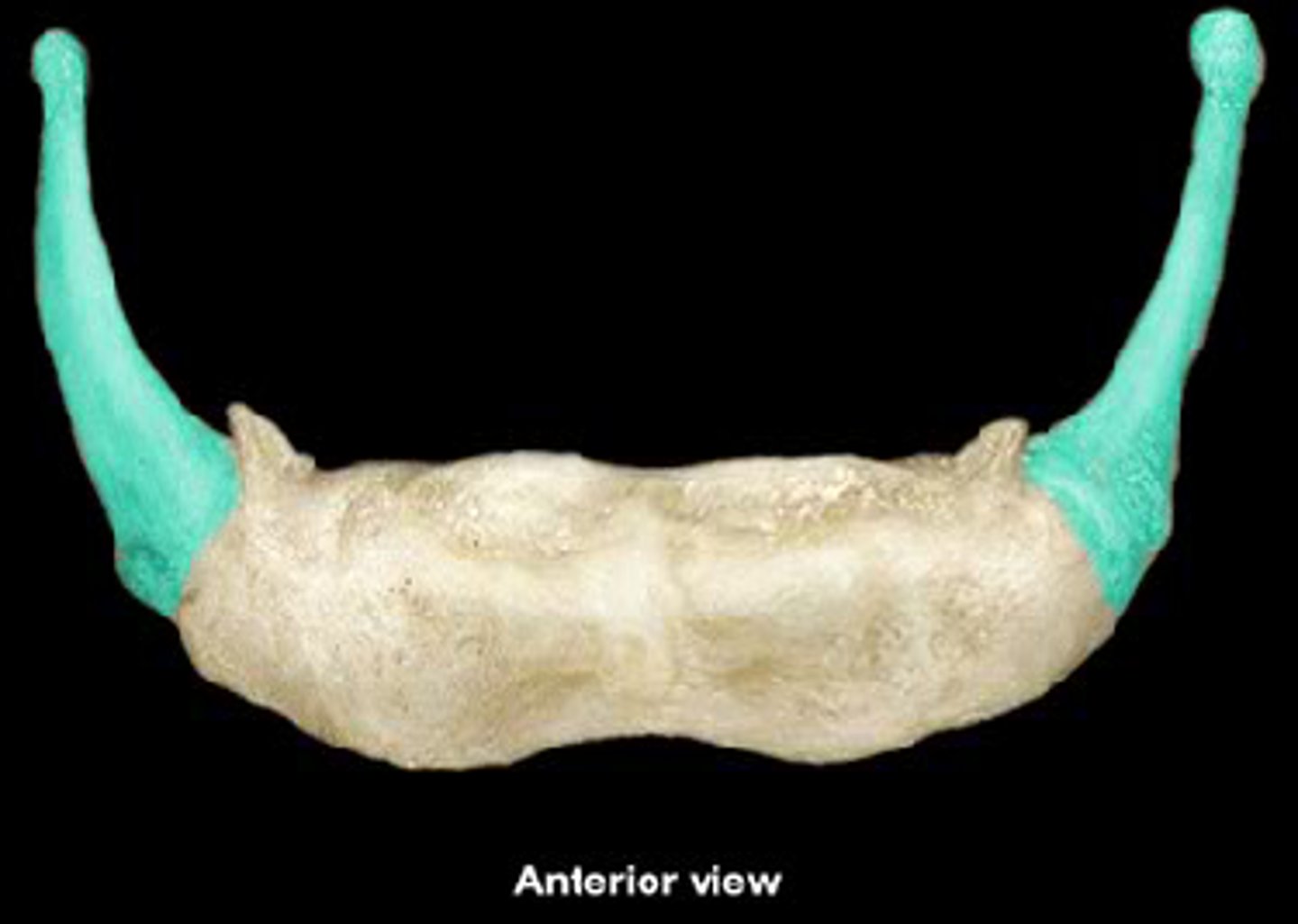
hyoid bone functions
supports the larynx and attaches muscles of larynx, pharynx, and tongue
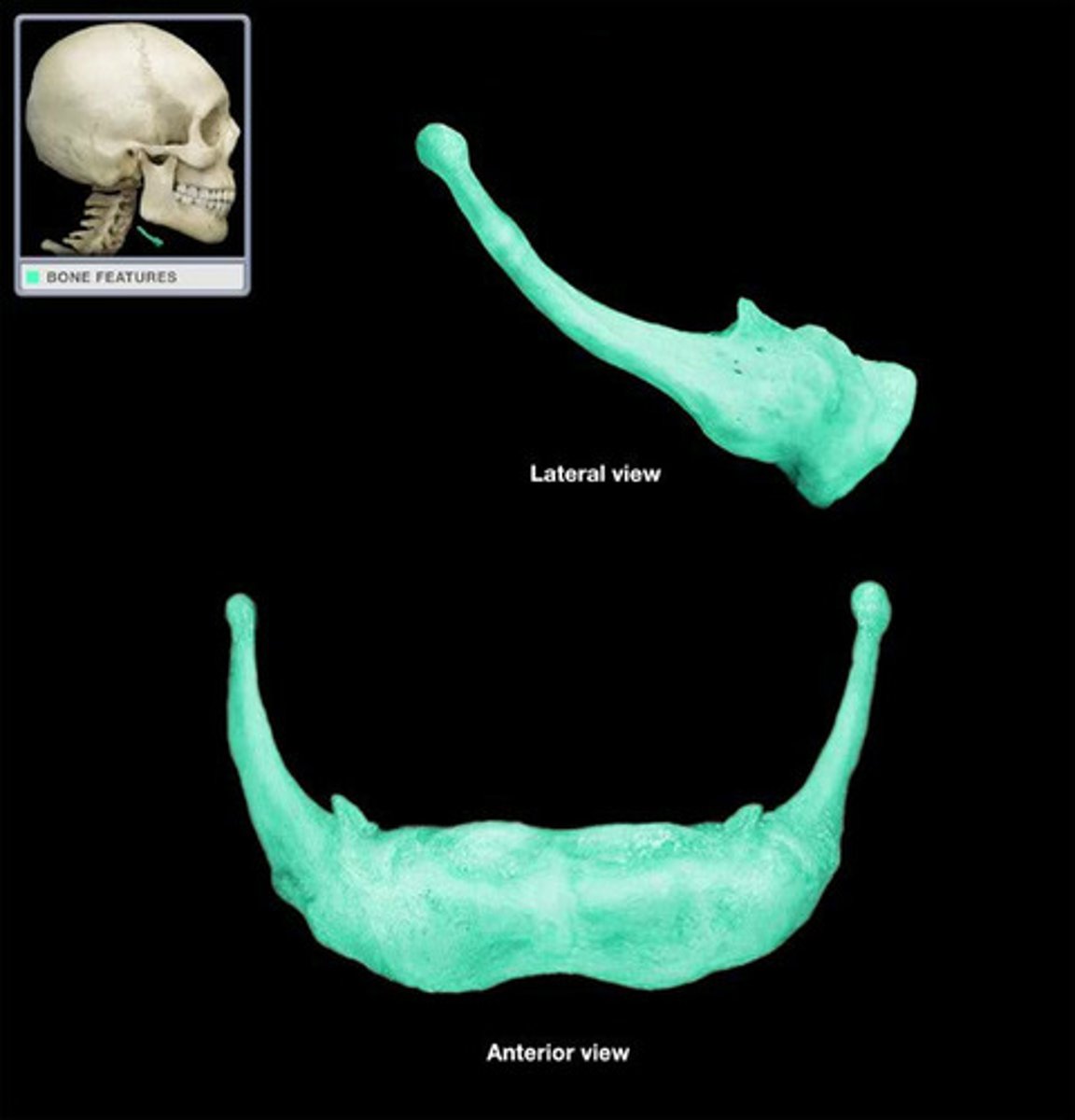
body of the hyoid bone
attaches muscles of larynx, pharynx, and tongue

greater horns of hyoid bone
supports the larynx and attaches muscles of the tongue
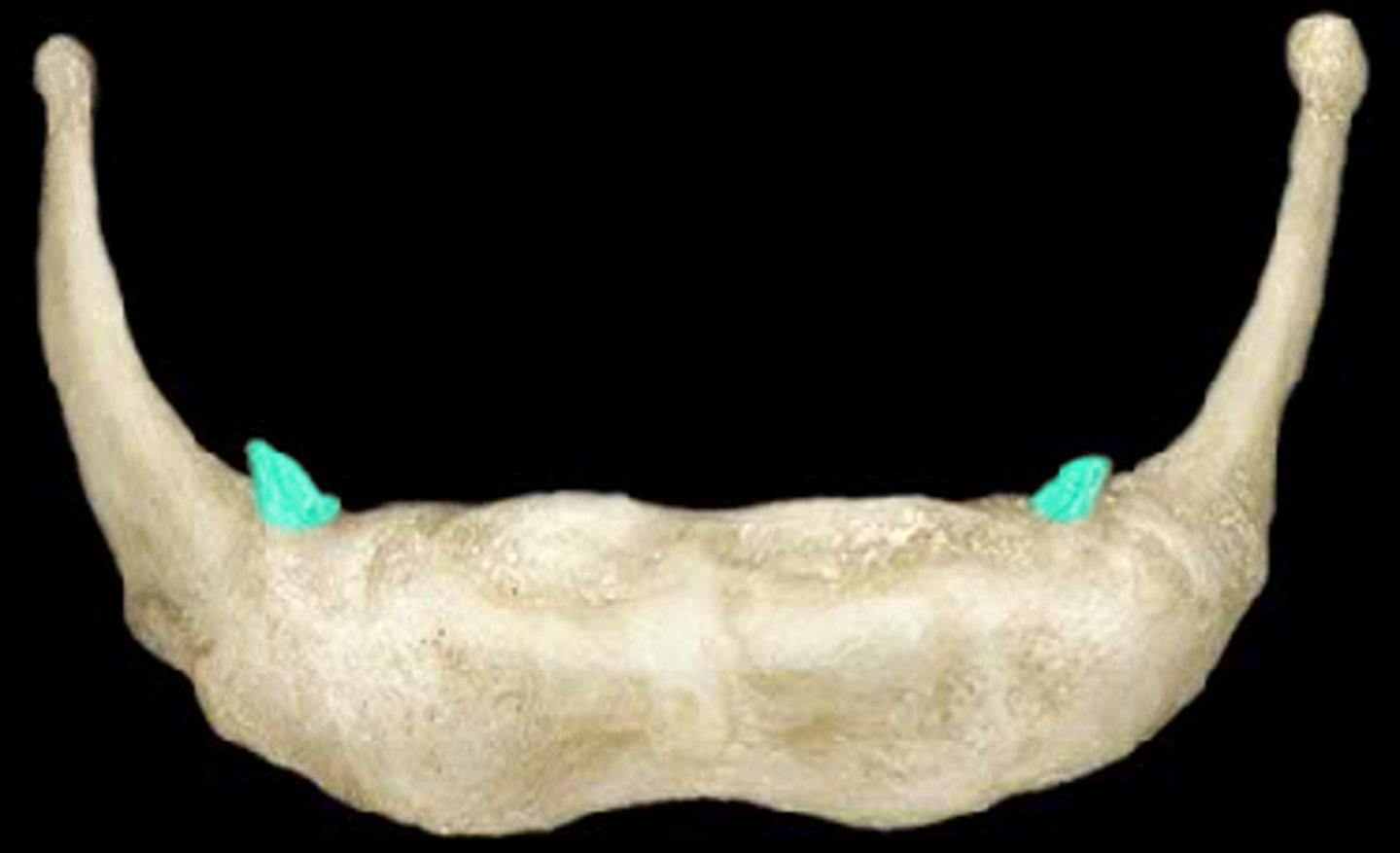
lesser horns of hyoid bone
attache stylohyoid ligaments and supports hyoid and larynx
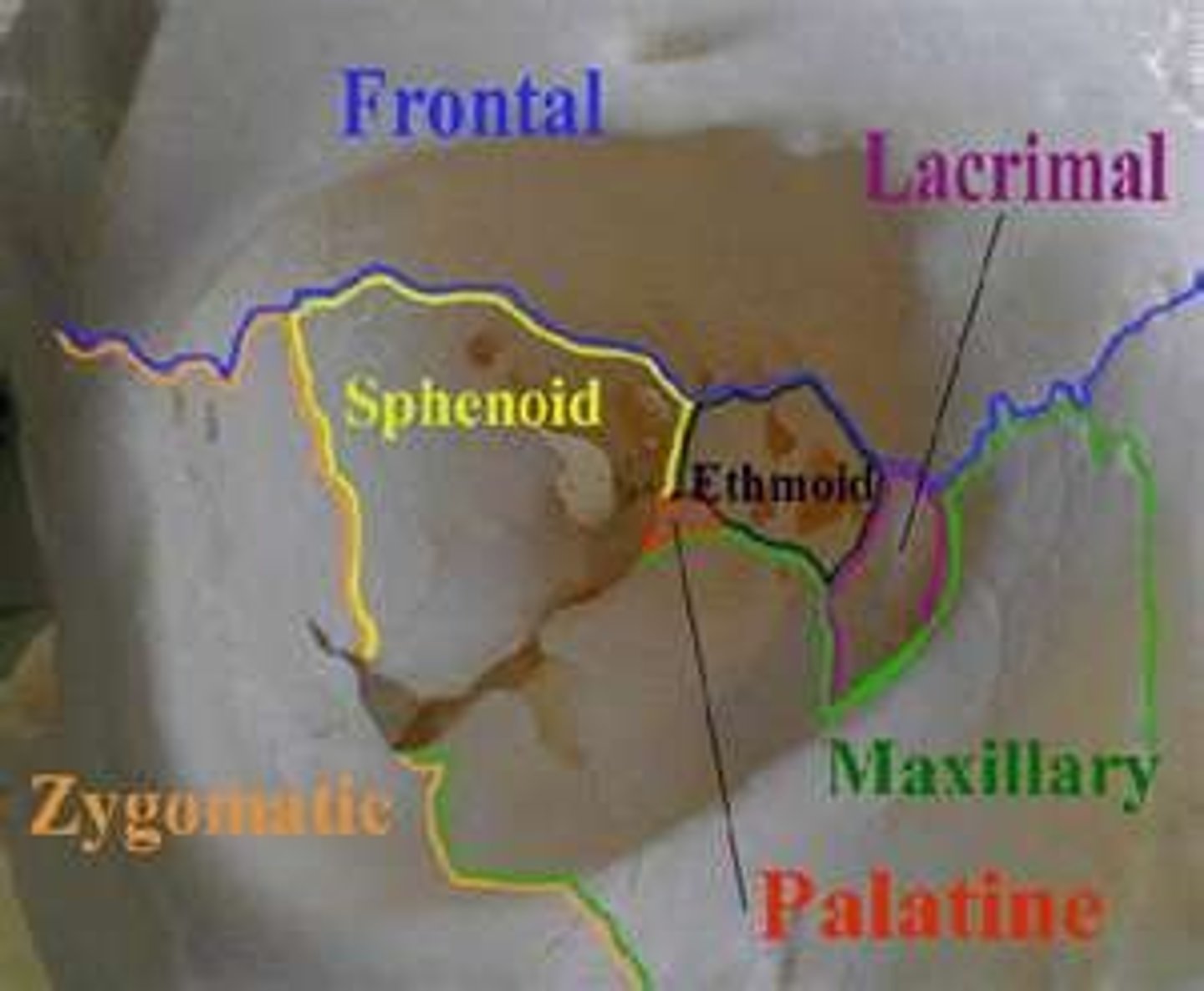
bones of the orbital complex (7)
frontal bone
maxilla
lacrimal bone
ethmoidal labyrinth
sphenoid
palatine bone
zygomatic bone
nasal complex
frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid (superior walls)
maxilla, lacrimal, ethmoid, inferior nasal conchae (lateral walls)
maxilla and nasal bones (bridge of nose)
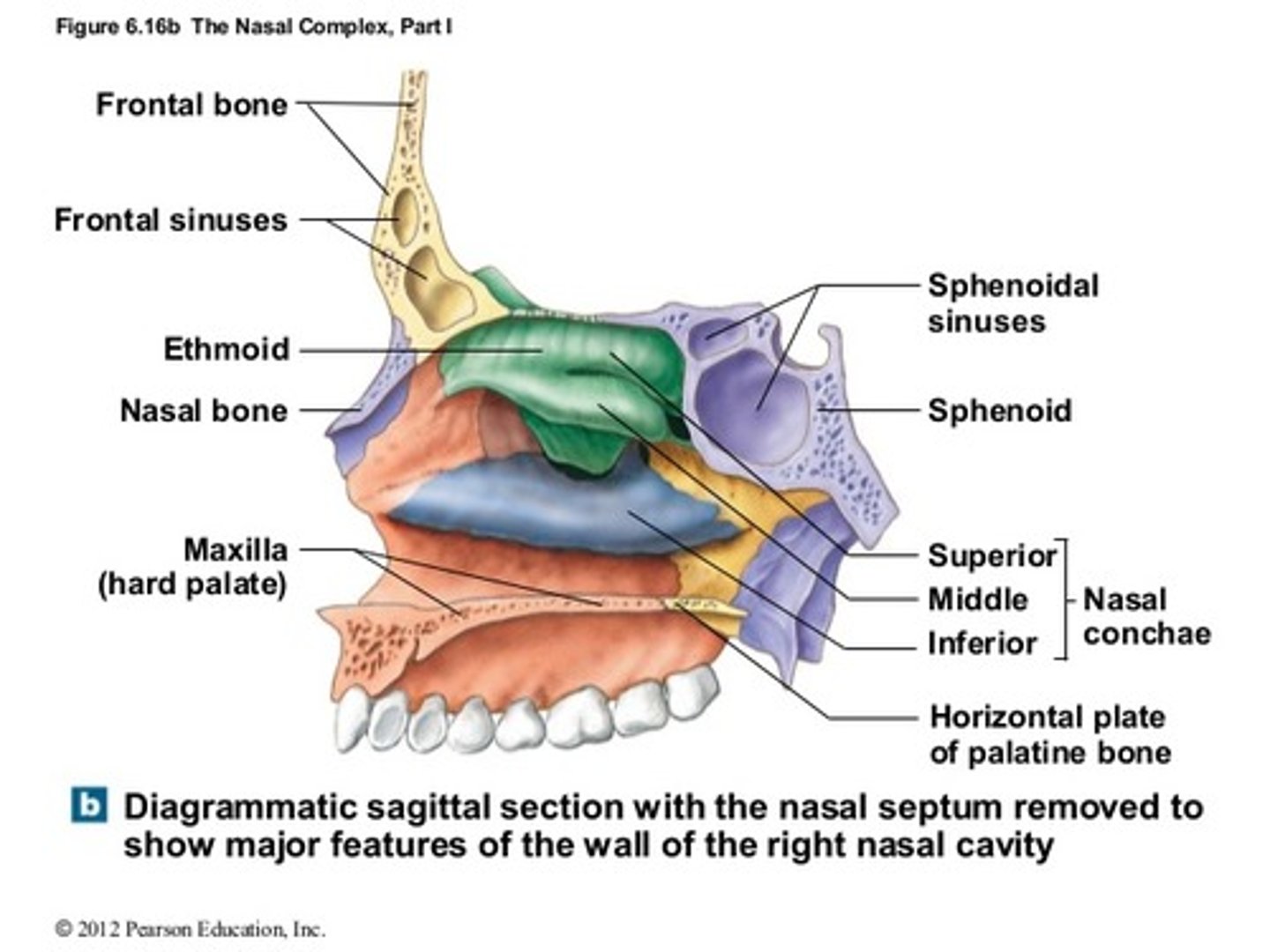
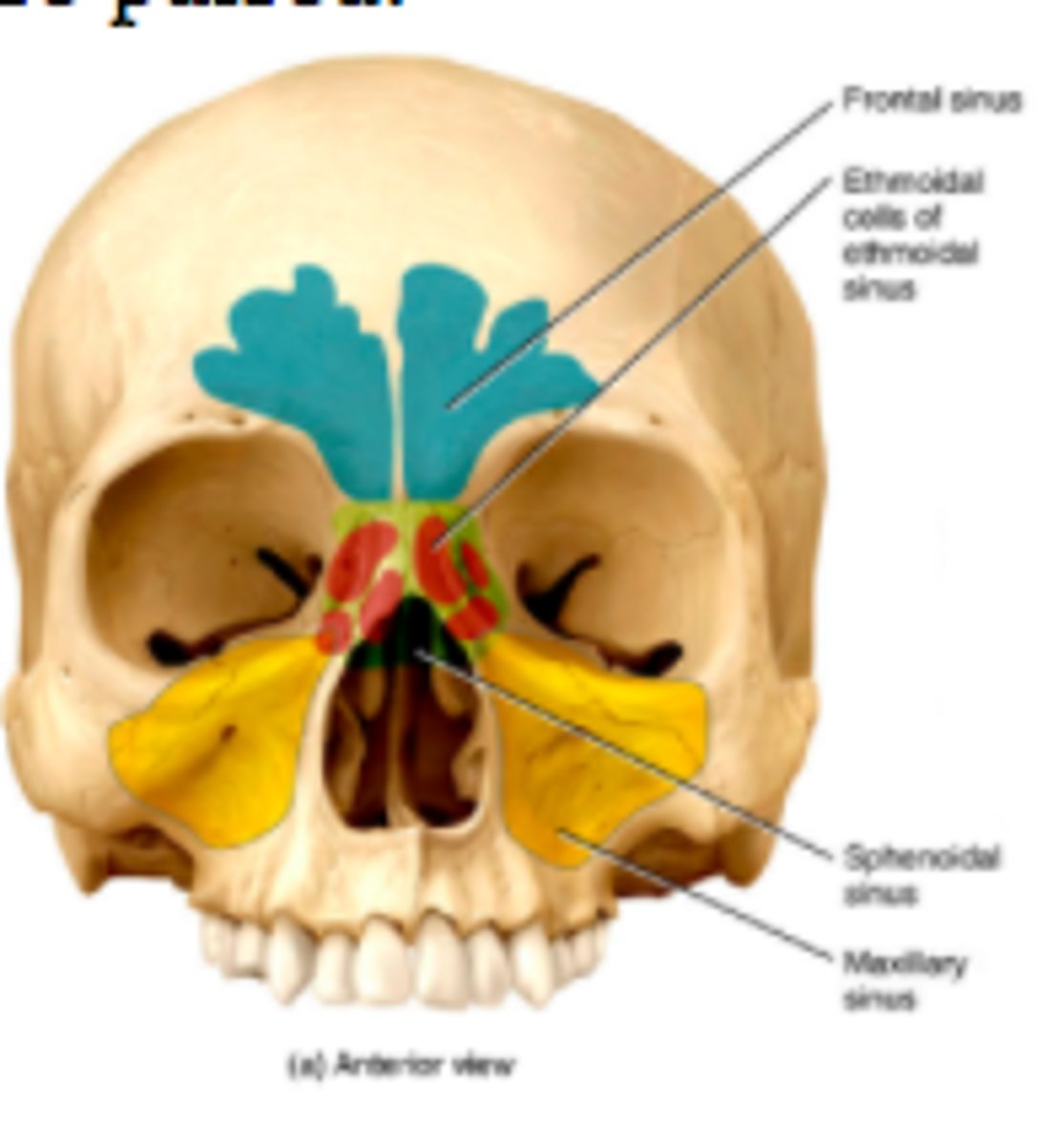
paranasal sinuses
air filled chambers connected to the nasal cavities
functions of the paranasal sinuses
lighter skull bones and release mucus into nasal cavity (mucous epithelium)
characteristics of an infant skull
- grows rapidly
- is large compared to the body
- has many ossification centers
- fusion of bones are not completed
divisions of the bones of the skull at birth
2 frontal bones
4 occipital bones
several sphenoid and temporal bones
fontanelles
- large areas of fibrous connective tissue
- covers unfused bones baby
- allow the skull to flex during birth
sphenoidal fontanelle
junction of squamous and coronal sutures
mastoid fontanelle
junction of squamous and lambdoid sutures
anterior fontanelle
at intersection of frontal, sagittal, and coronal sutures
posterior fontanelle
junction of lambdoid and sagittal sutures
vertebral column functions
protects the spinal cord and supports the head/body
divisions of bones of the spine
24 vertebrae
sacrum
coccyx
primary curves (accommodation curves)
thoracic and sacral curves that appear during fetal development and accommodate internal organs
secondary curves (compensation curves)
cervical and lumbar curves that appear after birth, shift body weight to permit upright posture