Sliding bearings
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
Machine type sliding bearings
2
New cards
How are fine (precise) design machine type sliding supperts are made?
a) moving pivot (stationary bushing),
b) stationary pivot (moving bushing).
b) stationary pivot (moving bushing).
3
New cards
Machine type slinding bearings features
\- circumferential speed of the pivot is very small, up to only 70 / 80 mm/s
\- specific pressure is insignificant
\- specific pressure is insignificant
4
New cards
How are the simplest bearings are made?
are made in the form of a hole in the housing or frame .
5
New cards
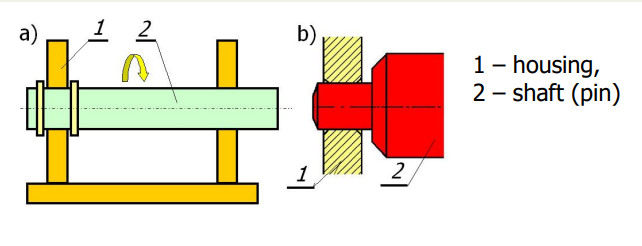
Machine type sliding bearings – moving pivot
6
New cards
How shafts are typically made?
Shafts are often made from calibrated rods and the pivots are not machined (fig. a). Turned pins (fig. b) are made with roughness Ra = 1,251,6 mu m, grounded ones Ra = 0,8 mu m.
7
New cards
how are housings must be made?
Housings which are simultaneously bearing plates must be made of proper material to made with the steel a good pair ( with the smallest coefficient of friction). Therefore often are made of brass CW508L (old M63), the CW509L (old M60) or, in the case of bodies of cast brass CB612P (old MO59).
8
New cards
When is it necessay to use bearing blocks / bushes?
**If the body is made of:**
**• materials which do not form a good frictional pair with steel , for example. light alloy (silumin AK11 AB-44100), ceramics, plastics, etc. • thin sheet metal**
**• materials which do not form a good frictional pair with steel , for example. light alloy (silumin AK11 AB-44100), ceramics, plastics, etc. • thin sheet metal**
9
New cards
From what materials are the bushings made off?
Bushings are made of materials that ensure good cooperation with steel pin, i.e. bronze CW456K (old B443) or brass CW617N (old MO58)
10
New cards
Types of bushes
* pressed in
* screwed
* mould inserted
* riveted
* fastened
* screwed
* mould inserted
* riveted
* fastened
11
New cards
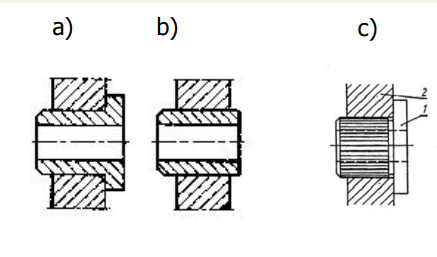
Pressed-in bushes
12
New cards
Screwed bushes
13
New cards
Mould-inserted bushes
1 – bushing (metal insert) , 2 – moulded plastic wall
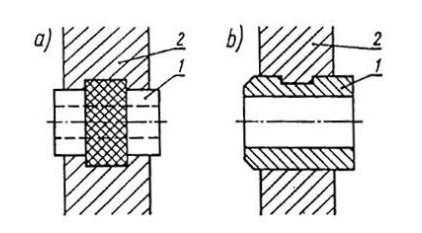
14
New cards
Riveted bushings
15
New cards
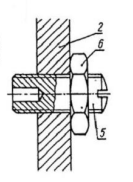
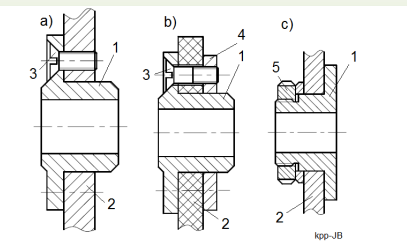
Fastened bushes
Bearing bushes fastened by a screws to : a) a metal plate , b) moulded plastic wall c) metal plate / plastic wall 1- bush, 2 – housing wall, 3 – screw, 4 – metal plate, 5 – locking nut
16
New cards
How are Bearing bushes fastened by a screws to :
a) a metal plate , b) moulded plastic wall c) metal plate / plastic wall
17
New cards
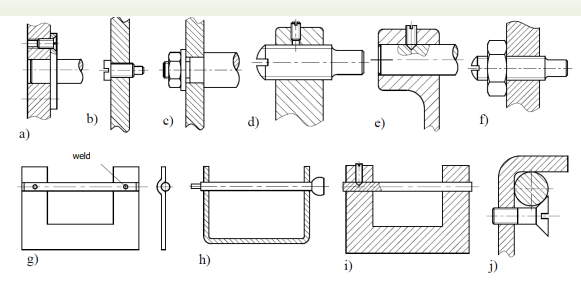
Machine type sliding bearings – stationary pivot
Pins are secured by : a, b, c, d, e, f, i, j) – fasteners , g) – point welding, h) – kneading
18
New cards
how are pins secured in stationary pivot
* fasteners
* point welding
* kneading
* point welding
* kneading
19
New cards
Types of sliding bearings in stationary pivot
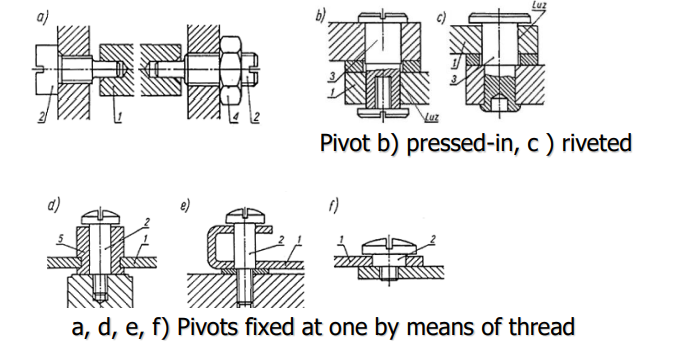
20
New cards
Clock type sliding bearings
Direct bearings in mechanism plates
21
New cards
clock type bearing with conical recess to retain lubricating oil
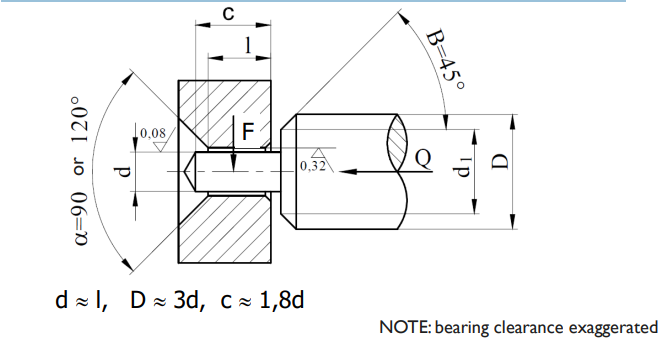
22
New cards
Clock type bearing, friction torque
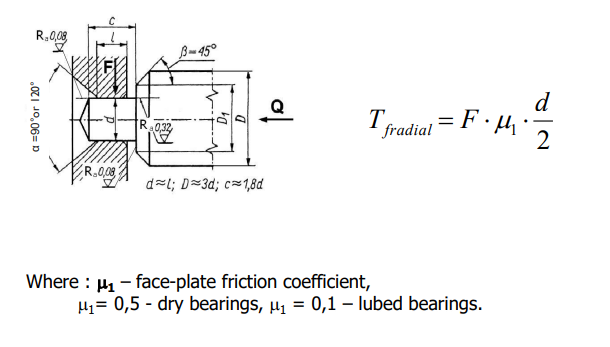
23
New cards
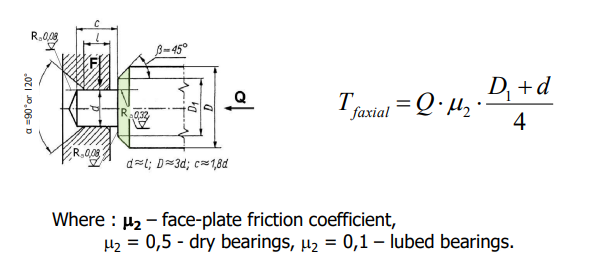
Clock type bearing, chamfer functions bita = 45 degrees
* reduction of friction torque caused by axial load Q,
* prevents the grease from outflowing (capillarity/wicking),
* serves as a basis for the manufacturing of the pinion teeth
* prevents the grease from outflowing (capillarity/wicking),
* serves as a basis for the manufacturing of the pinion teeth
24
New cards
reduction of friction torque caused by axial load Q
25
New cards
Diameters D, d i D1 have to be made allowing existence of the face.
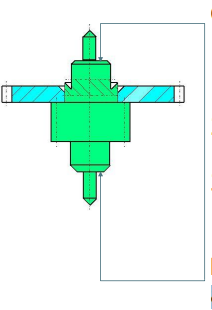
26
New cards
Clock type bearing, Materials
Pin: steel 10S20 (old A11) plate: brass CW508L (old M63) brass CW509L (old M60) Pin diameters : 0,1 up to 3 mm, Pin bushing fits: H9/d9, H9/cd9
27
New cards
How are the bushings made when the plates are thin?
bushings are made in a form of inserts.
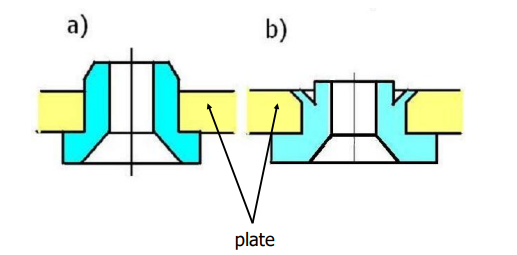
28
New cards
MINERAL BUSH (JEWEL) BEARINGS FITTED INTO MECHANISM PLATES

29
New cards
Clock type bearing, mineral bushes - materials
Corundum: dyed red or pink, grind-able.
Chalcedony: porous and dyed (red, brown).
Chalcedony: porous and dyed (red, brown).
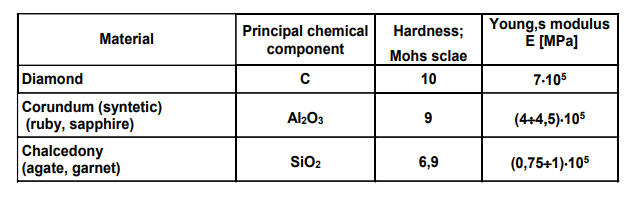
30
New cards
Clock type bearing, mineral bushes - design types
(a) with rounded (olive shaped) hole,
(b) flat, pressed-in,
(c) rounded, with German (Glashütte) type mounting
(d) rounded, with Swiss type mounting,
(e) flat, with Swiss type mounting
(b) flat, pressed-in,
(c) rounded, with German (Glashütte) type mounting
(d) rounded, with Swiss type mounting,
(e) flat, with Swiss type mounting
31
New cards
with rounded (olive shaped) hole,
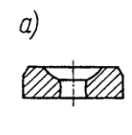
32
New cards
flat, pressed-in
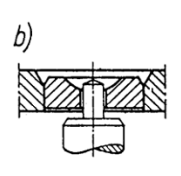
33
New cards
rounded, with German (Glashütte) type mounting
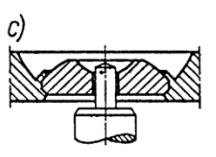
34
New cards
rounded, with Swiss type mounting
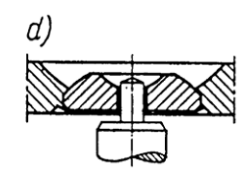
35
New cards
flat, with Swiss type mounting
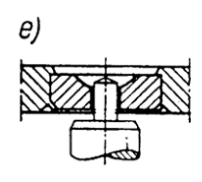
36
New cards
Clock type bearing, mineral bushes - features
* Pin nominal diameter from 0,1 up to 4 mm,
* pin material: steel 10S20 (A11), Ra = 0,08 micro m (burnished, roll-polished),
* bush ID tolerance H4 / H8,
* bush OD tolerance : h7,
* extremely small drag, small wear, long endurance, lubricated during assembly,
* usage: precise bearings(supports) in measuring equipment
* pin material: steel 10S20 (A11), Ra = 0,08 micro m (burnished, roll-polished),
* bush ID tolerance H4 / H8,
* bush OD tolerance : h7,
* extremely small drag, small wear, long endurance, lubricated during assembly,
* usage: precise bearings(supports) in measuring equipment
37
New cards
Porous – metal bushes slide bearings;
sintered bushes
38
New cards
sintered bushes
Most porous-metal bearings consist of either bronze or iron which has interconnecting pores. These voids take up to 10 to 35% of the total volume
39
New cards
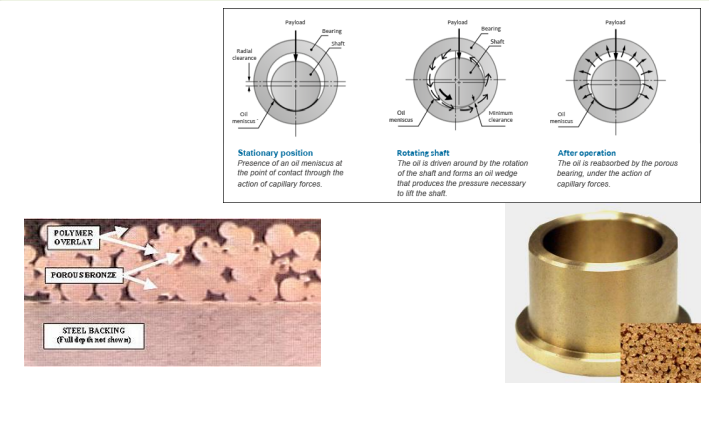
what is the operational purpose of the porous metal bearings
In operation, lubricating oil is stored in these voids and feeds through the interconnected pores to the bearing surface. Any oil which is forced from the loaded zone of the bearing is reabsorbed by capillary action. Because these bearings can operate for long periods without additional lubricant, they can be used in inaccessible or inconvenient places where re-lubrication would be difficult.
40
New cards
Porous – metal bearings
41
New cards
Pressed-in bush with additional lubrication
42
New cards
Self-aligning bushes with additional lubrication
43
New cards
Types of porous metal bearings
* Pressed-in bush with additional lubrication
* Self-aligning bushes with additional lubrication
* Self-aligning bushes with additional lubrication
44
New cards
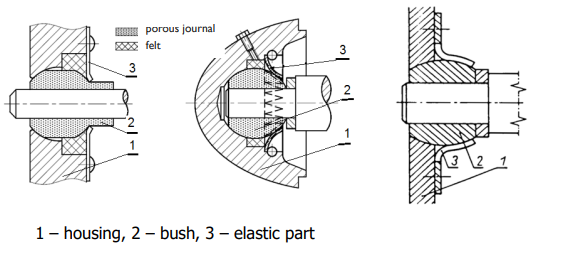
Porous – metal bearings; recommended fits
Pressed-in bushes are located by fit H7/r7 or H8/r8 Hole basis fit (H) is beneficial due to the easy selection of reamers designed to comply with holes.
45
New cards
Porous – metal bearings; features
Pin features recommendations:
\- higher grade carbon steel (C35, C55)
\- Surface roughness Ra = (0,04 / 0,08) microm !
\- hardness at less 50 HRC, when sintered iron powder bushes are used
Oil features recommendations :
\- Working temperature range from –12 up to +900 C,
\- viscosity at 500 C:
3 / 5 E (Engler degree) or 20 35 cSt ( centi-Stokes)
\- higher grade carbon steel (C35, C55)
\- Surface roughness Ra = (0,04 / 0,08) microm !
\- hardness at less 50 HRC, when sintered iron powder bushes are used
Oil features recommendations :
\- Working temperature range from –12 up to +900 C,
\- viscosity at 500 C:
3 / 5 E (Engler degree) or 20 35 cSt ( centi-Stokes)
46
New cards
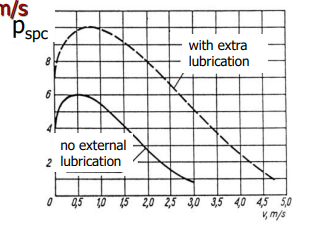
Working limits of porous metal bearings
• maximum slide velocity vmax = (610) m/s,
• maximum specific pressure pspc = (1020) MPa,
• maximum static load, that does not cause the deformation of a diameter of more than 0.1%, pmax = (50 100) MPa,
• the limit value of (p·v)max (1,81,6) MPa·m/s
• maximum specific pressure pspc = (1020) MPa,
• maximum static load, that does not cause the deformation of a diameter of more than 0.1%, pmax = (50 100) MPa,
• the limit value of (p·v)max (1,81,6) MPa·m/s
47
New cards
Porous – metal bearings; usage
• low power electric motors,
• mechanized household appliances,
• power tools,
• machines for textile, food industry
• endoprosthesis,
• high speeds at low and medium loads,
• mechanized household appliances,
• power tools,
• machines for textile, food industry
• endoprosthesis,
• high speeds at low and medium loads,
48
New cards
Sintered silicon carbide bushes
Silicon carbide is one of the hardest known materials. This material apply due to its characteristic properties.
49
New cards
Properties of sintered silicon carbide:
• very high hardness (2500 HV)
• excellent abrasion resistance,
• very good chemical resistance and mechanical strength. up to 2000° C,
• high thermal conductivity, resistance to thermal shocks (Δ \~ 250° C)
• low thermal expansion (4.3 / 5.8 x 10-6 K),
• low density (approximately 3.1 g/cm3 )
• excellent abrasion resistance,
• very good chemical resistance and mechanical strength. up to 2000° C,
• high thermal conductivity, resistance to thermal shocks (Δ \~ 250° C)
• low thermal expansion (4.3 / 5.8 x 10-6 K),
• low density (approximately 3.1 g/cm3 )
50
New cards
Polymer plain bearings
Polymer bearing bushes may be made of fabric reinforced laminates or polyamides. Bushes made of some of these materials may be impregnated with lubricant before assembly. Consequently, such supports are lubricated for life. Polymer bushes have a low coefficient of friction and a high resistance to wear (higher than that of bronze bushes).
51
New cards
Polymer plain bearings
As plastics have a low thermal conductivity and heat resistance, they may not be used for heavily loaded supports working at high rotational speeds or the large amount of heat generated by friction would cause them to be damaged. Specific loads for these bearings should not exceed 0,1 MPa
52
New cards
General features of polymer plain bearings
• Lubricant-free
• Corrosion resistance
• Maintenance-free
• Media resistant
• High compressive strengths
• Low coefficients of friction
• High mechanical dampening
• maintenance-free
• High dirt resistance
• Lightweight
• Best wear-resistance
• Very good price/performance ratio
• Corrosion resistance
• Maintenance-free
• Media resistant
• High compressive strengths
• Low coefficients of friction
• High mechanical dampening
• maintenance-free
• High dirt resistance
• Lightweight
• Best wear-resistance
• Very good price/performance ratio
53
New cards
Disadvantages of polymer plain bearings:
Absorb moisture from the environment (hygroscopy). I.e water absorption: polyamide 6 ÷10% polymethanals (PFA) 1.5%, PTFE-0%
\- are dimensionally unstable over time:
• different casting contraction,
• structural changes in the material,
• ability of hygroscopy
\- are dimensionally unstable over time:
• different casting contraction,
• structural changes in the material,
• ability of hygroscopy
54
New cards
Disadvantages of polymer plain bearings:
\- low thermal conductivity restricts the carrying capacity of the bearings:
• lower values of unit pressure plimit,
• unfit to work at high speeds to slip v
• Permitted p∙v value is crucial
\- mechanical properties changes over time (the aging of the material)
\- unsuitable for work at higher temperatures (e.g. lowered hardness)
\- harder to maintain lubricant, which means they are more likely to work on dry - the unacceptable pair: plastic-brass
• lower values of unit pressure plimit,
• unfit to work at high speeds to slip v
• Permitted p∙v value is crucial
\- mechanical properties changes over time (the aging of the material)
\- unsuitable for work at higher temperatures (e.g. lowered hardness)
\- harder to maintain lubricant, which means they are more likely to work on dry - the unacceptable pair: plastic-brass
55
New cards
What is p∙v product ?
The p∙v value can be seen as a measurement of frictional heat and can therefore be used as an analytical medium to justify the applicability of a bearing. For this purpose the actual p∙v value is compared with a permitted p∙v value calculable for the height. The permitted p∙v value is dependent on the material of the glide partner, ambient temperature and the on-time. „
56
New cards
Permitted p∙v value
K1 , K2 Constant for heat conductivity (K1 = 0,5; K2 = 0,042)
s Bearing wall thickness in mm
b1 Bearing length in mm
μ Coefficient of friction
λs Heat conductivity of the shaft
λk Heat conductivity of the bearing
ΔT (Ta - Tu ) where
Tu - ambient temperature;
Ta - max. ambient temperature
s Bearing wall thickness in mm
b1 Bearing length in mm
μ Coefficient of friction
λs Heat conductivity of the shaft
λk Heat conductivity of the bearing
ΔT (Ta - Tu ) where
Tu - ambient temperature;
Ta - max. ambient temperature
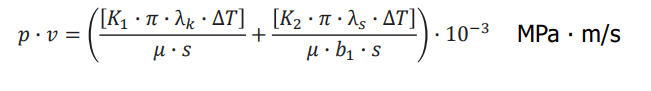
57
New cards
Permitted p∙v; correction factors
The permitted p∙v value can be raised in the intermittent service, if the bearing temperature has not at all reached the maximum due to the short turn-on times. Tests have shown that this is the case in turn-on times under 10 minutes. The shorter the turn-on time, naturally lower is the highest bearing temperature attained

58
New cards
Polymer plain bearings Limits of working conditions:
\- permitted value p∙v:
* from 0,3 N/mm2 \* m/s PA6.6
* up to 3,5 N/mm2 \* m/s iglidur X,
\- maximum working temperature 100 2500 C
\- maximum slide velocity v = 3 / 5 m/s,
* from 0,3 N/mm2 \* m/s PA6.6
* up to 3,5 N/mm2 \* m/s iglidur X,
\- maximum working temperature 100 2500 C
\- maximum slide velocity v = 3 / 5 m/s,
59
New cards
Polymer plain bearings Pin quality recommendations:
\- High grade carbon steel,
\- Surface roughnes Ra = (0,4 / 0,63) micro m,
\- Hardness c.a 50 HRC
Both worse roughness and greater smoothness cause wear increase !
\- Surface roughnes Ra = (0,4 / 0,63) micro m,
\- Hardness c.a 50 HRC
Both worse roughness and greater smoothness cause wear increase !
60
New cards
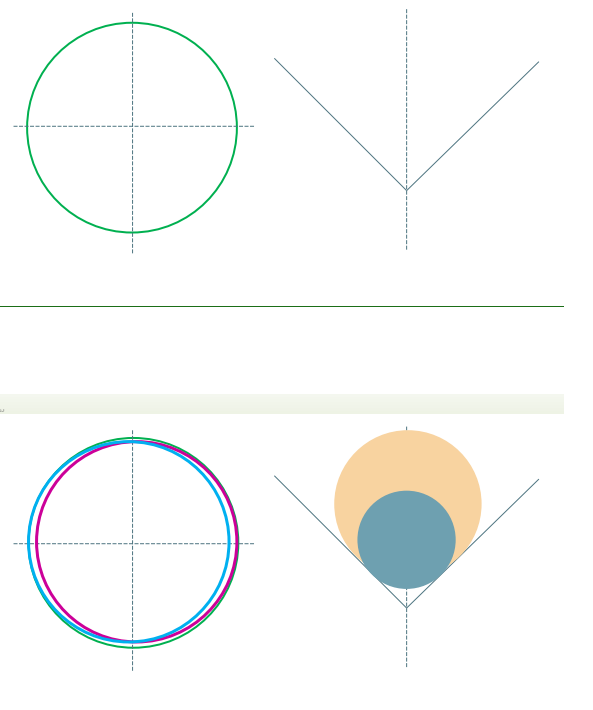
Prismatic (V-block) sliding bearings
61
New cards