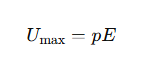7- The electric dipole
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is an electric dipole?
An electric dipole consists of a pair of equal and opposite charges (±Q) separated by a distance d.
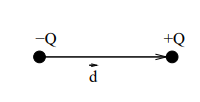
How is the electric dipole moment (p⃗) found?
d⃗ = the vector pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
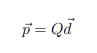
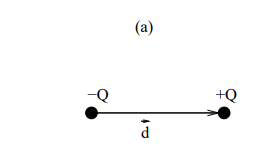
In which direction does the displacement vector (d⃗) point in an electric dipole?
It points from the negative charge (-Q) to the positive charge (+Q).
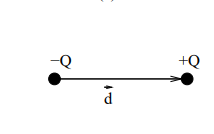
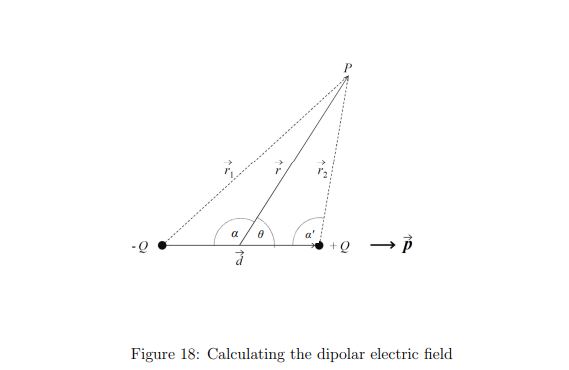
What is an ideal electric dipole?
An ideal dipole is one where:
The charge separation d is negligible compared to the distance r to the point P
The dipole moment p = Qd remains finite.
What is the general formula for the potential VP due to a point charge Q?
rP = the distance from the charge to the point P.
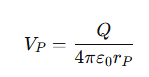
How is the potential due to multiple point charges calculated?
The total potential is the sum of the potentials from each charge:
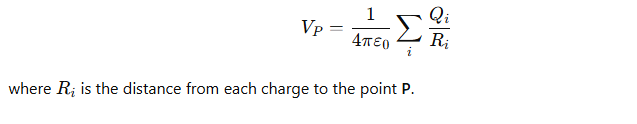
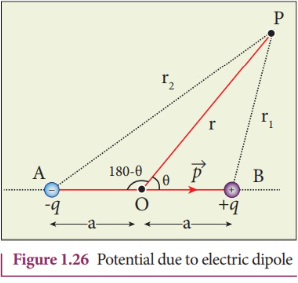
What is the expression for the potential due to a dipole?
r1 and r2 = the distances from the dipole charges to the point P.
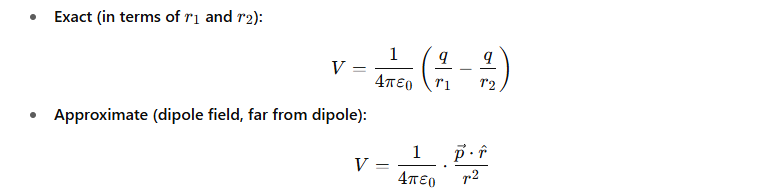
How does the dipole potential simplify in the ideal dipole approximation?
For an ideal dipole (d≪r):
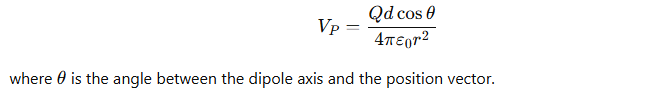
How is the dipole potential expressed using the dipole moment p⃗?
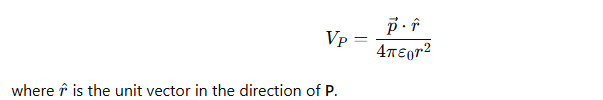
How is the electric field related to the electric potential?
The electric field Er is the negative gradient of the potential V:
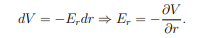
What is the radial component Er of the dipole's electric field?
p= the dipole moment
θ = the angle between the dipole axis and the position vector.
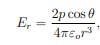
What is the angular component Eθ of the dipole's electric field?
θ= the angle between the dipole axis and the position vector.
How does the dipole field compare to a point charge field?
The electric field of a point charge falls off as r−2, while the dipole field falls off faster as r−3.
Why does the dipole field decrease faster than a point charge field?
The opposite charges in the dipole nearly cancel each other’s fields
This leaves only a small residual field that falls off more rapidly.
Where are the ideal dipole field equations valid?
The equations are valid in the far field (large distances from the dipole) but not in the near field (close to the dipole).
What is the formula for the torque (τ) on a dipole in an external electric field?
p= the dipole moment
E= the external electric field
α= the angle between them.
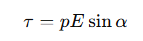
What is the expression for the work done by an external force in rotating a dipole?
The external work done in rotating the dipole from α=π/2 to α=θ
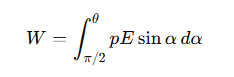
What is the potential energy U of a dipole in an electric field?
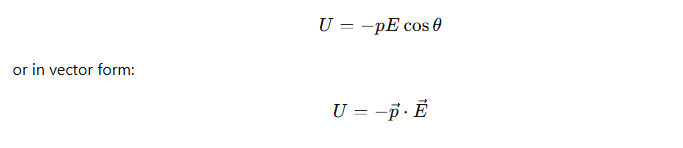
When is the potential energy of a dipole minimum in an electric field?
The potential energy is minimum when the dipole aligns with the field (θ=0∘), where:
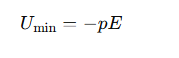
When is the potential energy of a dipole maximum in an electric field?
The potential energy is maximum when the dipole is anti-aligned with the field (θ=180∘), where: