5) Intro to CT simulation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Main advantage of CT over conventional radiography (EXAM; review Qs)
1) eliminate superimposed structures
2) differentiate small differences in density of anatomical structures/abnormalities
3) superior quality of images
(LO1) What are the main components of a CT simulator?
1) flat table top
2) external laser system
3) virtual sim workstation
4) circle of reconstruction
5) physical aperture
What is the importance of appropriate acquisition parameters?
Why is it important to set up the machine the right way when taking images
1) axial images are accurate localization of tissue
2) DRR (digital reconstructive radiograph) resolution is high enough
3) Scan time is balanced w/:
- ALARA
- tube heat capacity
- likelihood of image artifact (ex. pt moving)
What is the Z axis coordinate? (EXAM)
THICKNESS of x-sectional slice
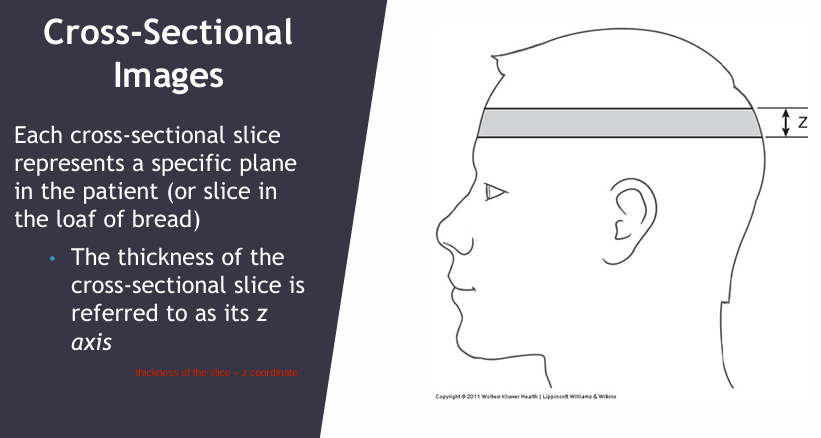
Each cross sectional slice represents a specific plane in a patient.
How would you define the x & y axis in a CT scan? (EXAM)
X = width
Y = height
(cross sectional image)
What is a pixel?
What is a voxel?
Pixel = x * y
Voxel = x, y, z
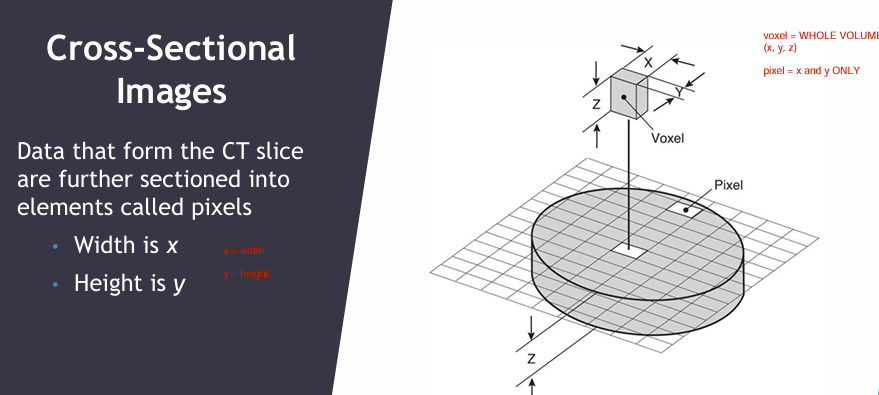
(LO)
What is the role of a CT sim in RT planning? (EXAM)
1) Target + normal tissue localization
2) Tx field design
3) Pt marking (tattoos)
4) Tx monitoring (monitor response of tx if there are any changes. Ex. throat cancer, there neck is getting small so current plan might need adjustments)
5) Pt information for planning
- contour
- tissue density (attenuation coefficient)
What are commonly used landmarks for CT sim?
sternal notch, xiphoid, iliac crist
For anatomical marks, we “referecning the table”. What does this mean?
set table readout to 0
Describe the CT sim process & procedure in logical steps (exan)
1) Pt enters room & positioned in tx position on CT table
2) Immobilization device made
3) Ensure correct position to get ant-post-lateral images
4) place PRELIMINARY reference marks on patient using lasers
5) Record CT couch position of preliminary lasers
—
6) Choose appropriate scanning protocol
7) Set CT scan limits → to include region of superior & inferior to Tx volume
😎 administer contrast if required
9) place external markers if needed
(scars, tattoos, palpable mass)
10) scan patient
—
11) patient leaves
12) transfer data to virtual simulation workstation
13) contour critical organs for dose volume constrains
14) reconstruct DRR
15) transfer data to tx planning
(LO)
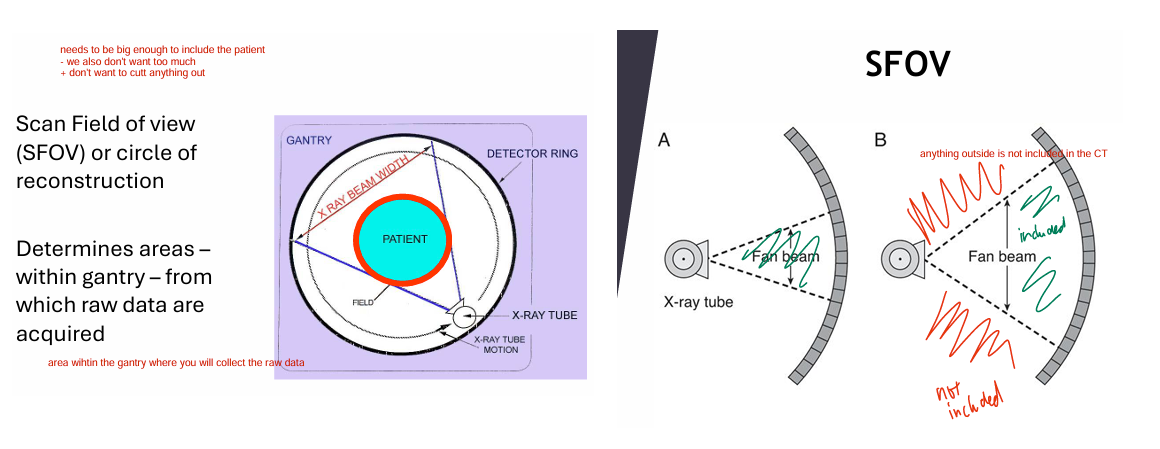
Define SFOV (EXAM)
Scan field of view (circle of reconstruction)
area within gantry where raw data is acquired
diameter of area being scanned
Anything outside SFOV is NOT imaged
- highest quality = SFOV comes very CLOSE to the patient
Things very close to the outside of SFOV may cause image artifacts
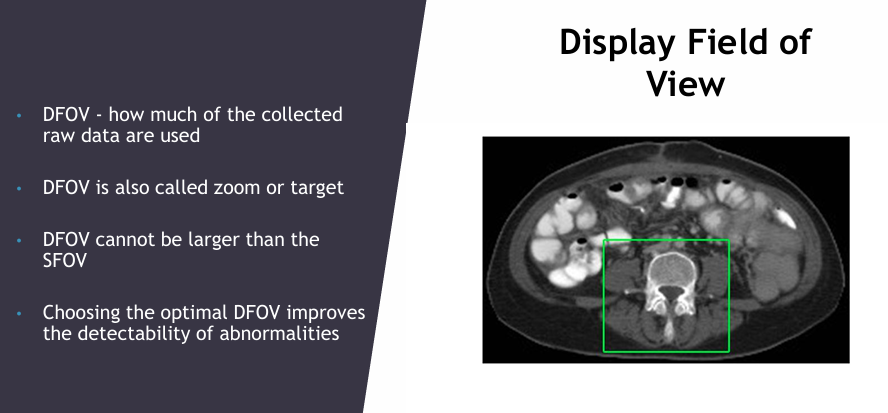
What is DFOV? (EXAM)
Display field of view (zoom or target) = how much raw data is used
- cannot be larger than SFOV
- optimal DFOV = improves detectability of abnormalities
For RT tx planning, SFOV must be __
large enough to cover periphery of the patient
Discuss SFOV selection.
Matrix comprised of individual pixels (1 CT value) placed over SFOV
- bigger the pixel = less quality
- smaller pixel = high quality (but more radiation/photons entering body = bad) [maybe use on head and neck for fine details]
![<p>Matrix comprised of individual pixels (1 CT value) placed over SFOV<br>- bigger the pixel = less quality<br>- smaller pixel = high quality (but more radiation/photons entering body = bad) [maybe use on head and neck for fine details]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4b8e256e-66b4-45fe-901e-505964497eca.png)
When is a CT acceptable?
1) individual aware of risk
2) benefits outweigh the risk
3) everything else reasonable has been done to reduce the risk
(LO)
What are the general principles of pediatric CT? (EXAM)
1) child/parents told about the risks
2) only used when it is needed, not for other means
3) effort made to REDUCE (amps/voltage) radiation dose as low as possible
4) use shielding when possible

What are strategies for reducing dose? (EXAM)
1) don’t do repeat scans
2) use iterative reconstructive methods
3) verifying that a CT is really needed
4) customize CT exam when possible (reduce dose)
5) shield patient
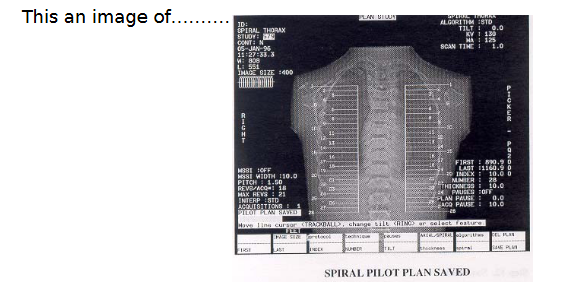
(EXAM): This is an image of ___
Give examples:
Preliminary image = localizer scan
Ex.
- topogram (siemens)
- scanograb (toshiba)
- scout (GE healthcare)
- pilot (picker) normogram
(EXAM)
1) Density of each pixel is determined by __ reach the detector.
2) To maintain statistical reliability and increase the # of pixels, we will record __ after they exit the body.
3) More photons ENTERING the body would __ the radiation dose.
1) how many photons
2) more photons
3) increase
(EXAM)
1) Average background radiation for Americans is __ mSV
2) Exposure from chest x-ray is about __mSv.
3) Exposure from a CT is __ mSv.
1) 3mSv
2) 0.1mSv
3) 10mSv
Knowledge on radiation dose to patients from CT scan:
1) avg radiation in american = 3mSv
2) exposure to chest x-ray = 0.1mSv
3) chest, abdomen, pelvis CT = 10mSv
TLDR: CT is high dose
- want to avoid inappropriate/unnecessary scans
- lack of awareness b/w healthcare professionals