Algebra 1 vocab-Lorcan Neamon
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Last updated 3:02 AM on 5/13/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
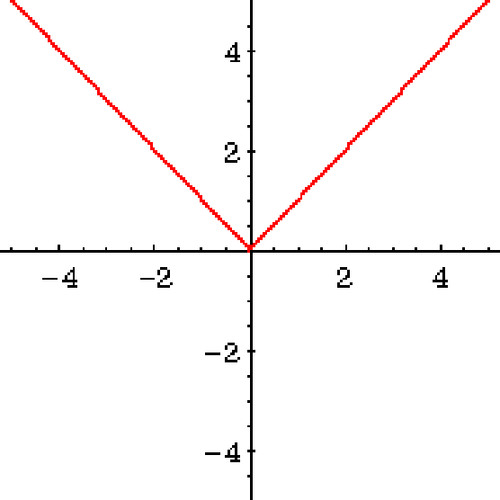
Absolute value
the distance a number is from 0
2
New cards
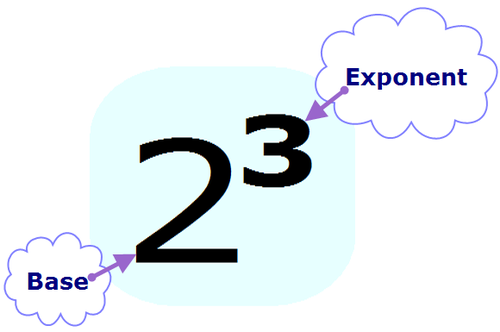
Base
A number that is raised to a power.
3
New cards
Coefficient
A constant that a variable or expression is multiplied by.
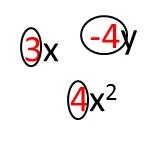
4
New cards
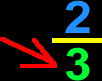
Denominator
The bottom number or expression in a fraction.
5
New cards
Difference
The distance between two quantities, or the answer to a subtraction problem.
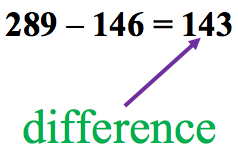
6
New cards
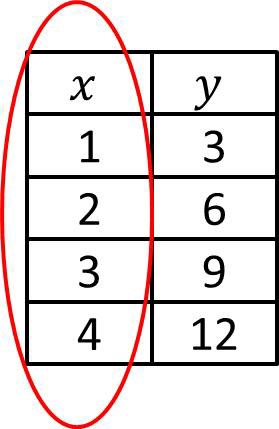
Domain
The set of inputs (x-coordinates) of a relation or function
7
New cards
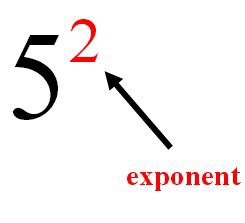
Exponent
In a power, the number of times the base is multiplied by itself.
8
New cards
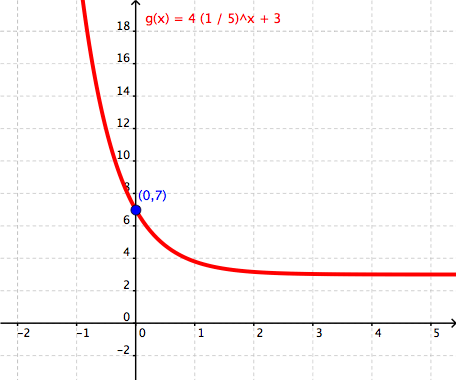
Exponential decay
When an initial amount decreases by the same percent over a given period of time
9
New cards
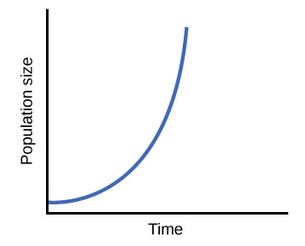
Exponential growth
growth whose rate becomes ever more rapid in proportion to the growing total number or size.
10
New cards
Monomial
A product of variables and numbers, like 3x or 5x2. A monomial is also sometimes called a term.
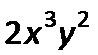
11
New cards
Polynomial
A sum of monomials. Usually terms with higher powers are written first.
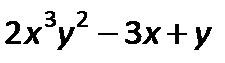
12
New cards
Range
The set of outputs (y-coordinates) of a relation or function.
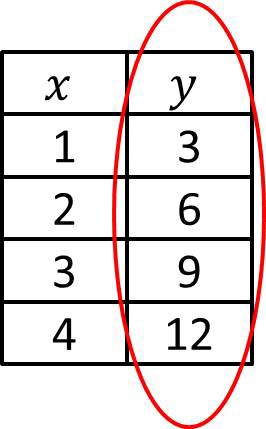
13
New cards
Reflection
A transformation that "flips" a figure over a mirror or reflection line.
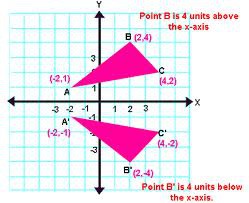
14
New cards
Rotation
Rigid motion around a fixed center , with turning but no reflection.
15
New cards
Scatter plot
Dots in the coordinate plane representing pairs of linked measurements, such as heights and weights for a group of people.
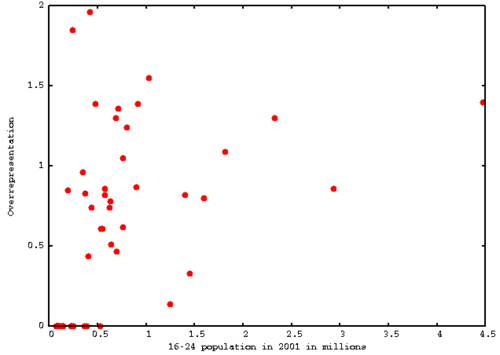
16
New cards
Sequence
A list of numbers that may be generated by some rule.
17
New cards
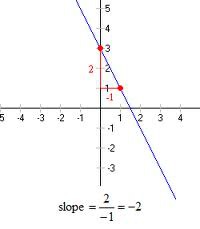
Slope
A number that measures how steep a line is. It shows the amount of change in the height of the line as you go 1 unit to the right. The slope of the line y=mx+b is m.
18
New cards
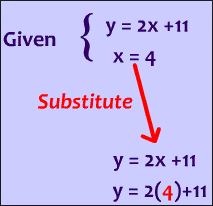
Substitution
In an expression or equation, eliminating a variable by replacing it with another expression that it is equal to.
19
New cards
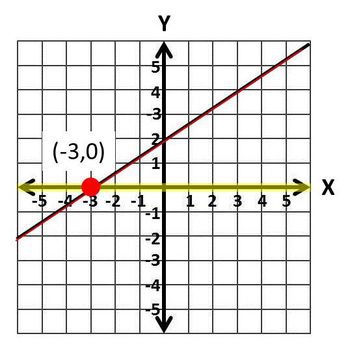
x-intercept
A point where a curve meets the horizontal axis (the x-axis).
20
New cards
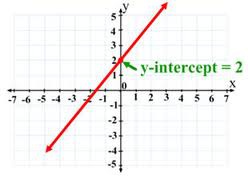
y-intercept
A point where a line or curve meets the vertical axis (the y-axis). The y-intercept of the line y=mx+b is the point (0,b).