use of bio resources (food production: crop plants, microorganisms, fish farming)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
microorgs and fish farming not done yet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
greenhouse conditions that can be manipulated and how that helps crop production (4)
Artificial heating (enzymes controlling photosynthesis can work faster at slightly higher temperatures - only used in temperate countries such as the UK)
Artificial lighting (plants can photosynthesise for longer)
Increasing carbon dioxide content of the air inside (plants can photosynthesise quicker)
helps control water supply - limiting factor will not be water, needs water for photosynthesis.
controlling the climate inside an enclose space (greenhouse) requires knowledge of l___ ____
limiting factors
can manipulate that to have no factors limiting = more photosynthesis
what are polythene tunnels
large plastic tunnels that cover crops
how polythene tunnels help crop yield (3)
They can protect crops grown outside from the effects of the weather, including excessive wind, rain and extreme temperatures
They also increase the temperature slightly inside the tunnel
They can prevent the entry of pests that can damage plants or diseases that can kill plants
If a plant is given unlimited light, carbon dioxide and water and is at a warm temperature:
the only thing limiting the rate at which it can photosynthesise is…..
If a plant is given unlimited light, carbon dioxide and water and is at a warm temperature:
the only thing limiting the rate at which it can photosynthesise is its own ability to absorb these materials and make them react
how do all these things actually make crop yield more
plants will grow bigger and faster, higher crop yields
what are fertilisers
fertilisers increase the amount of key nutrients in the soil for crop plants, meaning that they can grow larger and are more healthy, which increases yields
why are fertilisers needed e.g. for the same reused field
As crop plants take up these mineral ions from the soil, the mineral ions need to be replaced if crops are grown repeatedly in the same field (i.e. year after year)
Fertilisers are used to replace these mineral ions
what are pesticides
why do they help (2)
these chemicals kill off unwanted insects and weed species, meaning that there is less damage done to crop plants by insects, as well as reducing competition from other plant species, which increases yields
NPK fertiliser and why they are useful
Nitrogen:
Absorbed in the form of nitrates
Needed to make amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins
Lack of nitrogen causes weak growth and yellowing of the leaves of plants
Phosphorous:
Absorbed in the form of phosphates
Needed to make DNA and cell membranes
Lack of phosphorus can cause poor root growth and discoloured leaves
Potassium:
Absorbed in the form of various compounds of potassium
Allows enzyme reactions to take place to produce ATP in respiration as well as being needed for the enzymes involved in photosynthesis
Lack of potassium can cause poor growth of flowers and fruits, as well as brown spots on leaves
def:
insecticides
herbicides
fungicides
Insecticides kill insect pests
Herbicides kill plant pests
Fungicides kill fungal pests
why are pests, weeds and fungi bad for crop yield
Pests such as insects and other animals can damage crops by eating them
Weeds can outcompete crop plants for space, water and soil nutrients
Fungi can infect crop plants and spread disease which can affect growth and yield
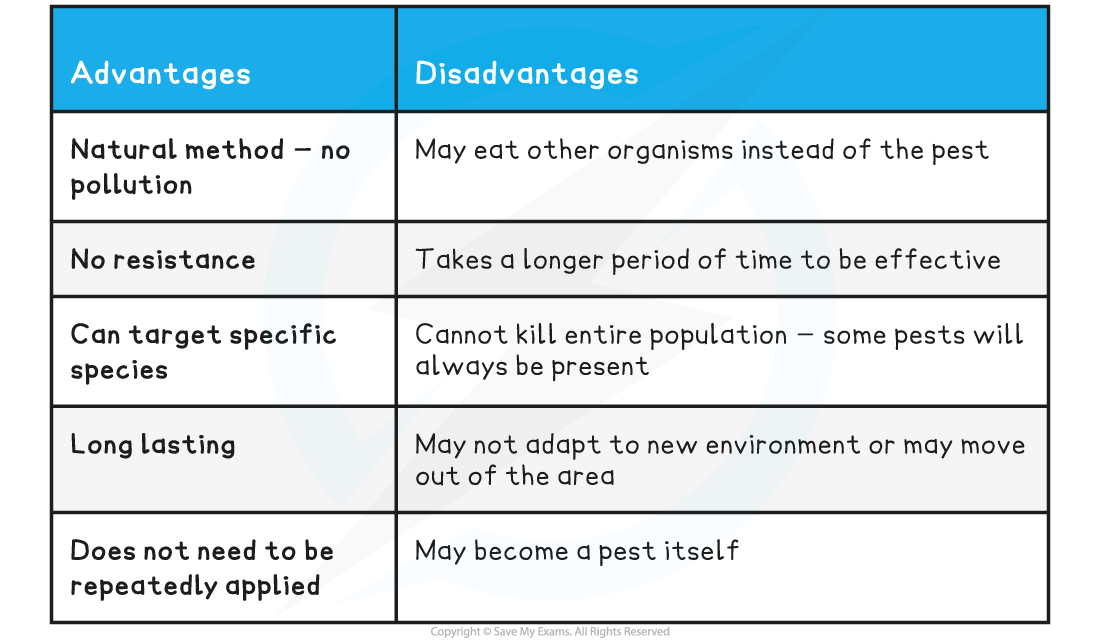
what is biological control, can it happen naturally?
it does not _____ remove a pest, but keeps it at _____ levels
Can happen naturally – for example, ladybirds eat aphids
Usually, a species is introduced specifically to prey on the pest species – for example, parasitic wasps can control whitefly in glasshouse tomato crops
As they are based on a predator-prey cycle, they do not completely remove a pest, but keep it at lower levels
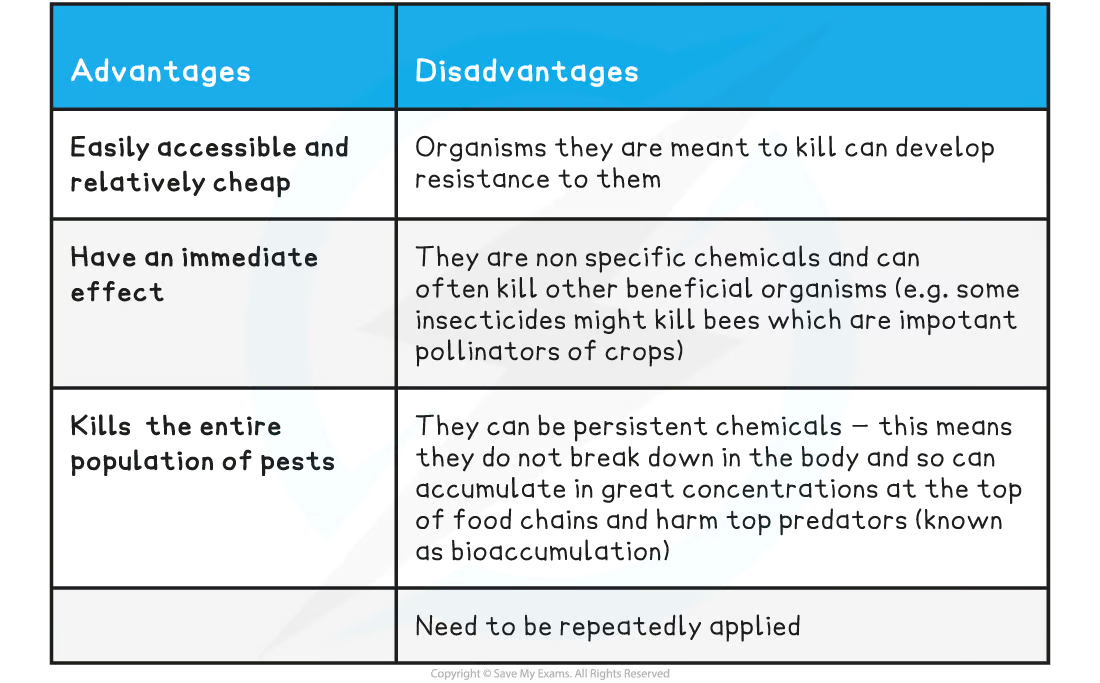
pesticides advantages (3) and disadvantages (4)
think: effect is _____, organisms can devlop______
biological control advantages (5) and disadvantages (5)
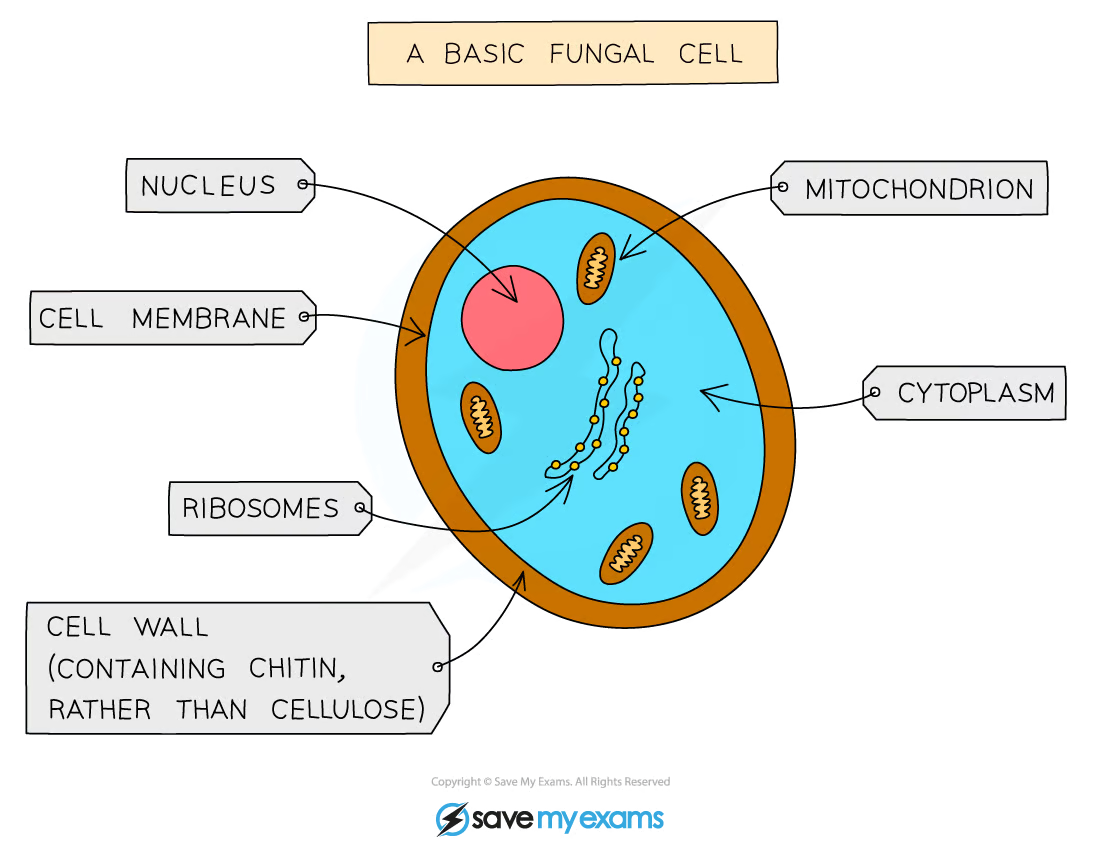
draw yeast fungus cell
what does yeast anaerobic respiration equation have
glucose → ethanol + CO2
how does yeast help make bread
what happens to the ethanol
is the yeast killed? how?
(after O2 runs out, yeast respires anaerobically)
bread rises because of the CO2 produced when yeast respires anaerobically
the bubbles make the dough rise
the ethanol is evaporated in the heat (no alcohol in bread)
then yeast is killed by high temperatures during baking
Practical: Investigating Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast
(see how temperature affects rate of anaerobic respiration in yeast)
DIAGRAM
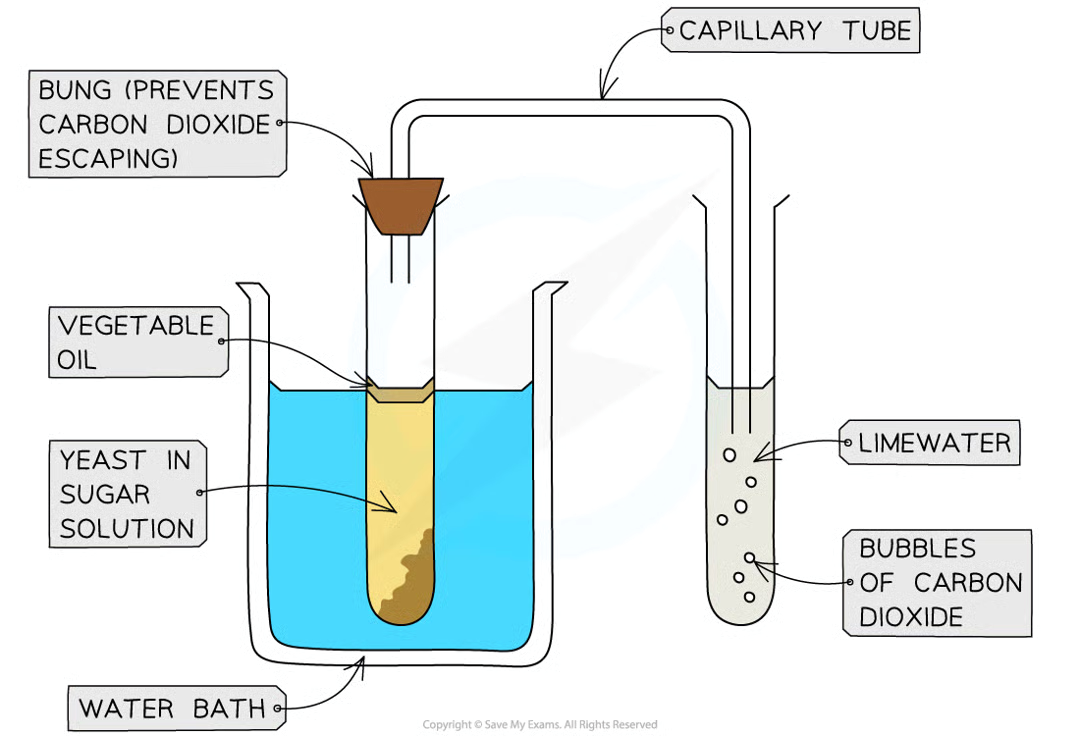
method for yeast experiment
Mix yeast with sugar solution in a boiling tube
The sugar solution provides the yeast with glucose for anaerobic respiration
Carefully add a layer of oil on top of the solution
This prevents oxygen from entering the solution (prevents aerobic respiration in the yeast)
Using a capillary tube, connect this boiling tube with another boiling tube that is filled with limewater
Place the boiling tube with yeast and sugar solution into a water bath at a set temperature and count the number of bubbles produced in a fixed time (e.g. 2 minutes)
The rate that carbon dioxide is produced by yeast can be used to measure the rate of anaerobic respiration (i.e. the rate of fermentation)
Change the temperature of the water bath and repeat
what should the results show and why
the higher the temperature, more CO2 bubbles
(higher temperature is closer to optimum temperature of enzymes in yeast, increase enzyme activity (FOR RESPIRATION) so more anaerobic products)
if its too high though enzymes will denature/yeast will die
yeast temperature CORMMSS
C – We are changing the temperature in each repeat
O – The type (species) of yeast we are using must be the same
R – We will repeat the investigation several times at each temperature to make sure our results are reliable
M1 – We will measure the number of bubbles (of carbon dioxide) produced
M2 – in a set time period (e.g. 2 minutes)
S – We will control the concentration, volume and pH of the sugar solution, as well as the mass of yeast added
how is yoghurt made
sterilise equipment + pasteurise milk
to remove competition
or spoil taste/make unhealthy
add lactobacillus to milk
incubate so it ferments
lactobacillus uses sugar lactose to anaerobically respire, producing lactic acid
this acid thickens and sours the milk
also acts as a bit of a preservative (acid)
then cooled to stop lactobacillus action
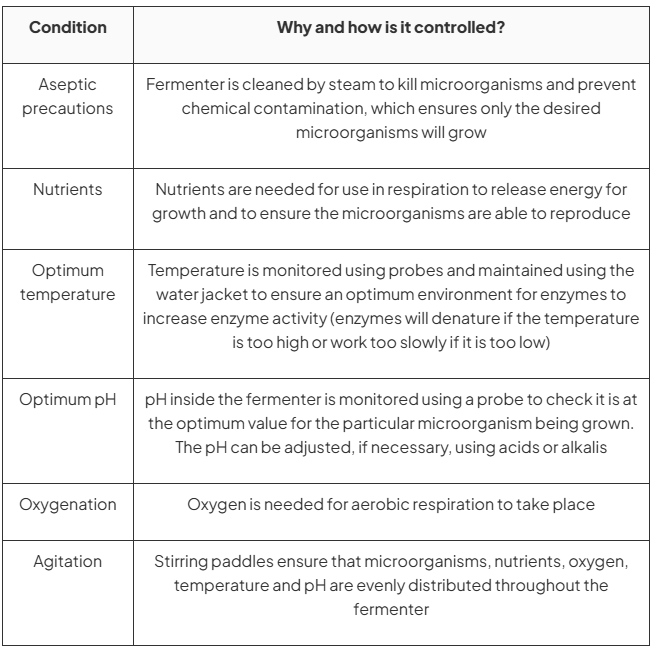
condition | why and how is it controlled |
aseptic precautions | |
nutrients | |
optimum temperature | |
optimum pH | |
oxygenation | |
agitation |

benefits of fish farming vs wild-caught (4)
The ability to selectively breed fish to ensure high quality, fast-growing fish
The ability to protect against predators
The ability to control water quality (many wild-caught fish have significant levels of pollutants such as mercury in their flesh)
The ability to control feeding to ensure rapid growth
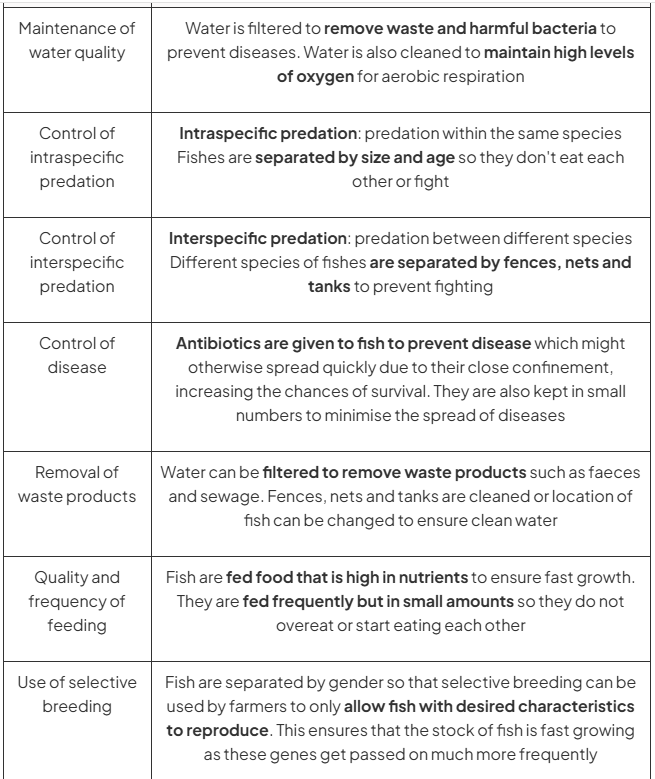
methods of good fish farming (acronym)
WPD WFS
wise practises drive well functioning systems
w
what does each stand for
W - water quality
P - predation - intra/inter
D - disease
W - waste removal
F - feeding
S - selective breeding
explain each
why to fix
how to fix