4.1 Plate Tectonics
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
continental drift
the theory that continents move relative to one another; proposed by Alfred Wegener
deep sea trench
a long, steep-sided depression in the ocean floor formed by subduction
fault
a fracture within a tectonic plate
igneous rock
a type of rock formed from magma or lava
island arc
a volcanic archipelago situated on a convergent plate boundary
lava
magma above the surface of the crust
magma
molten rock
mantle
the majority of Earth's volume, between the crust and the core
metamorphic rock
a type of rock formed by the application of pressure and heat to other rocks
uplift
the process by which rocks are elevated at a convergent plate boundary
Pangaea
The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents
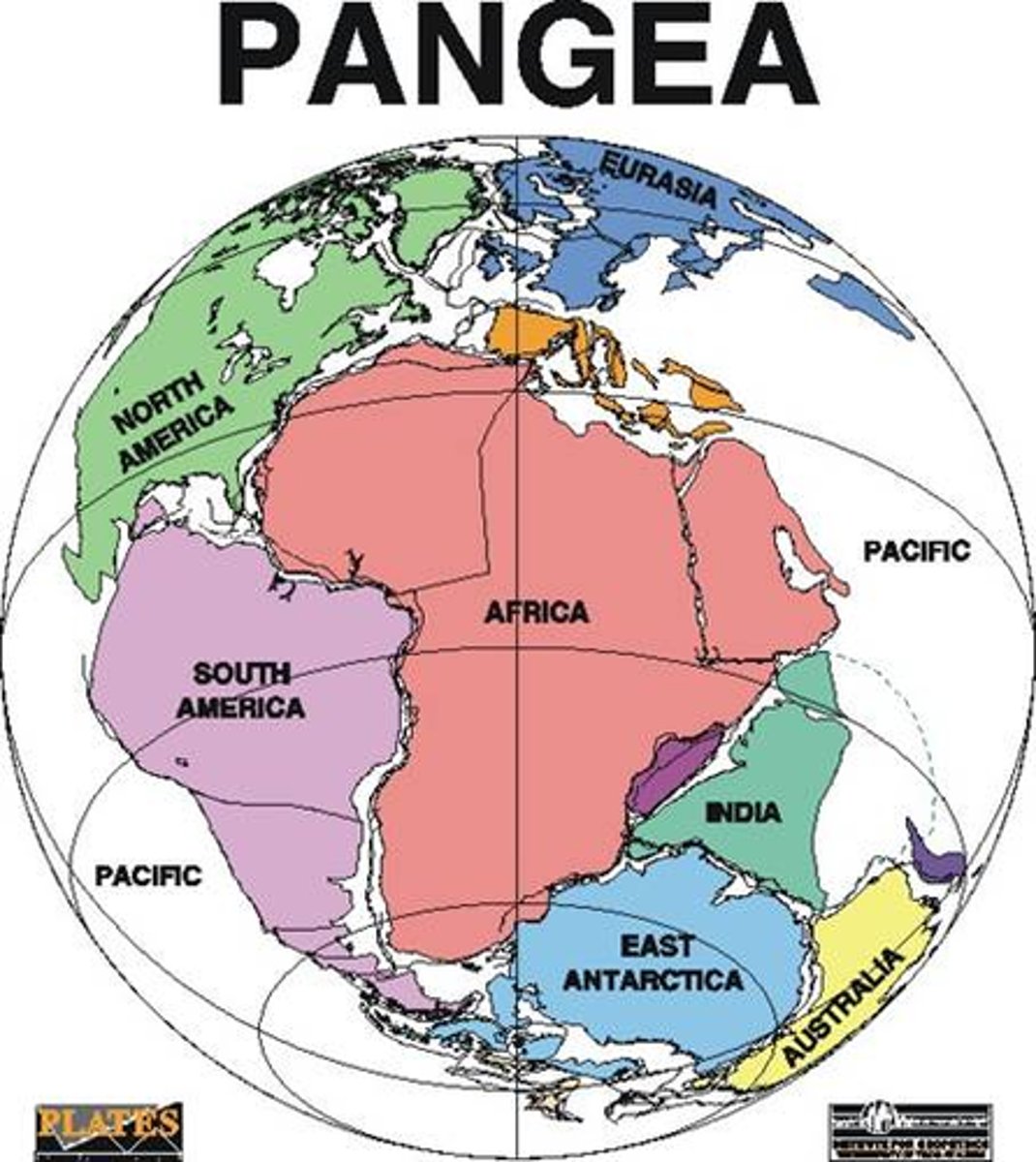
tectonic plates
Sections of the Earth's crust that move slowly over the mantle due to convection currents.
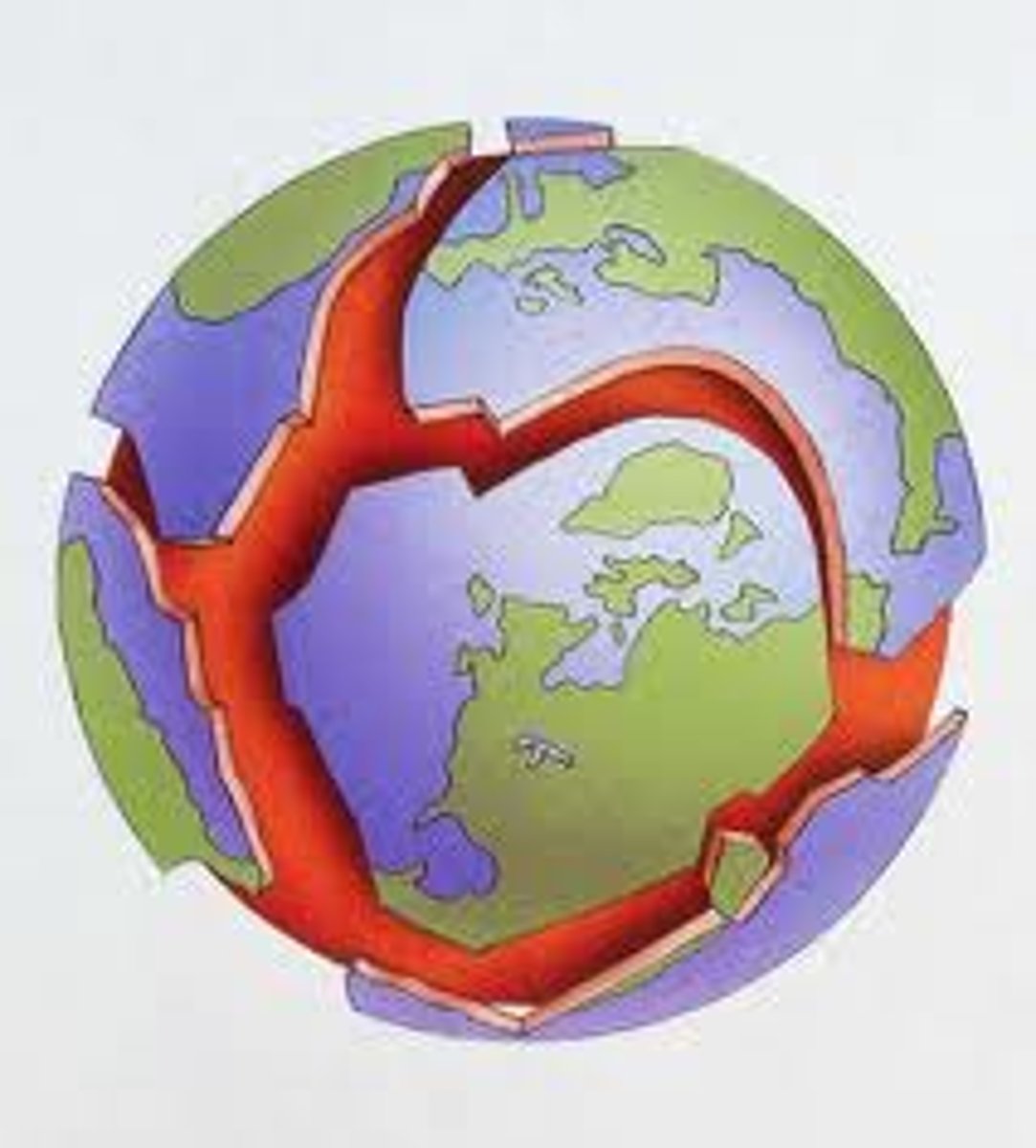

North American Plate
A tectonic plate division of the lithosphere that includes the continental crust of Greenland, North America, Siberia, and the surrounding oceanic crust, extending to the mid-Atlantic ridge.
Pacific Plate
A tectonic plate division of the lithosphere that is composed entirely of oceanic crust and lies beneath the Pacific Ocean, this is the largest tectonic plate. It includes Mexico's Baja Peninsula and southwestern California.
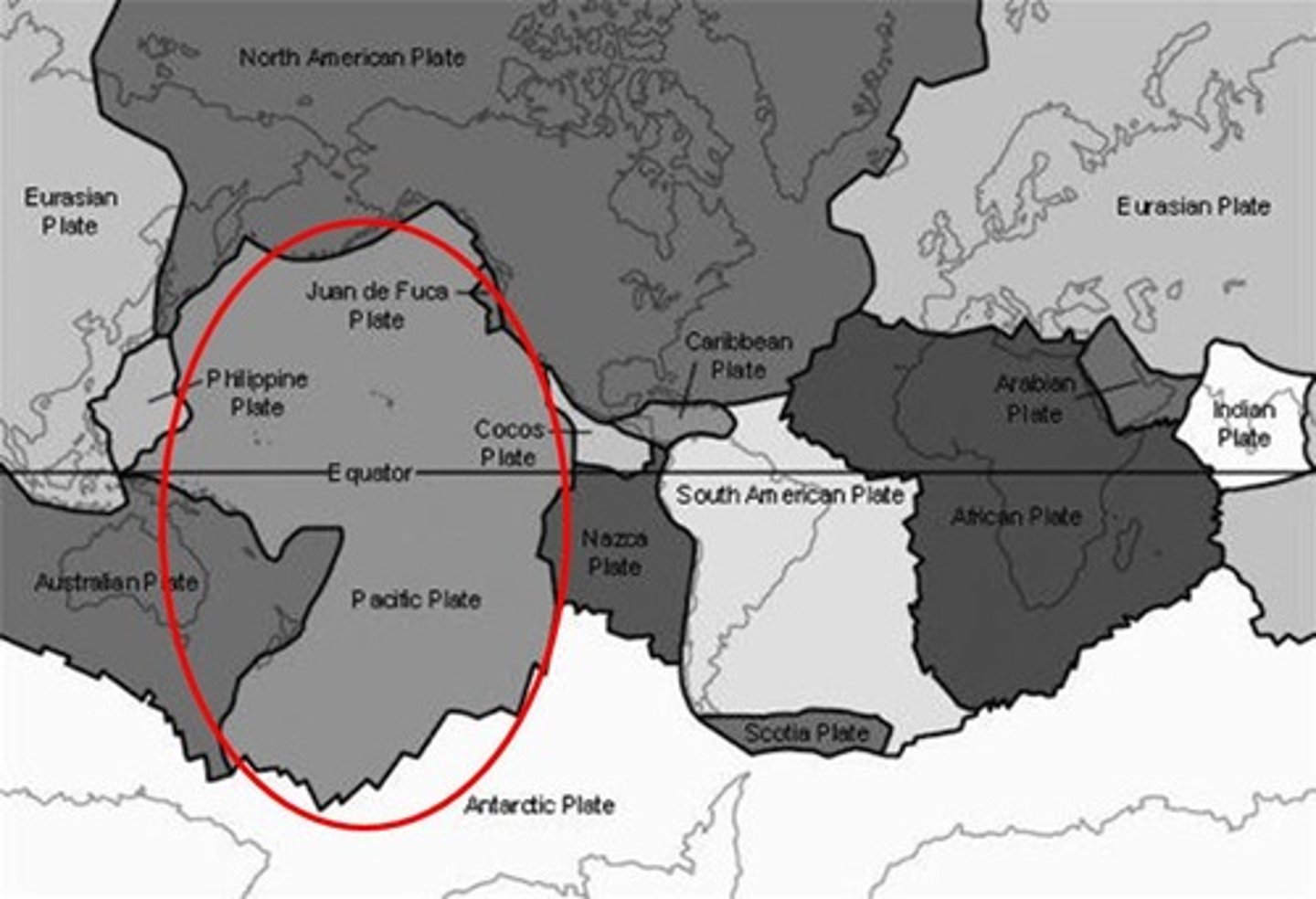
plate boundaries
At plate boundaries, Earth's crust is broken ie a fault and rocks slip past each other in one of 3 types of plate boundaries. This is where most events like seafloor spreading and most volcanoes and earthquakes occur.
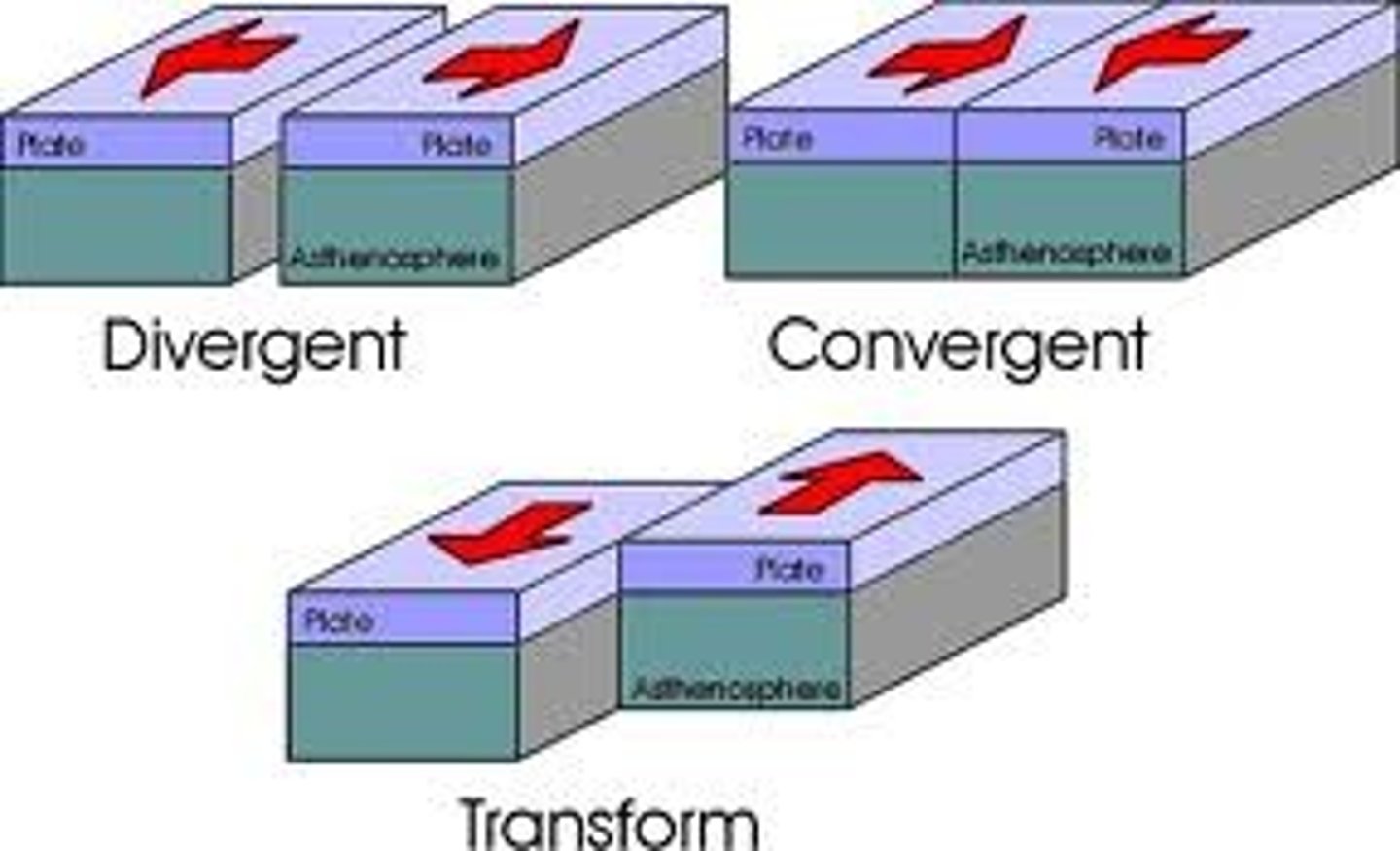
Convergent Boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates collide, come together, or crash into each other. If an oceanic plate is involved, it results in subduction zones and therefore subduction due to the higher density of oceanic plates. If both plates involved are continental plates, it results in the uplifting of plates to form large mountain chains (Himalayas)
<------- ------->
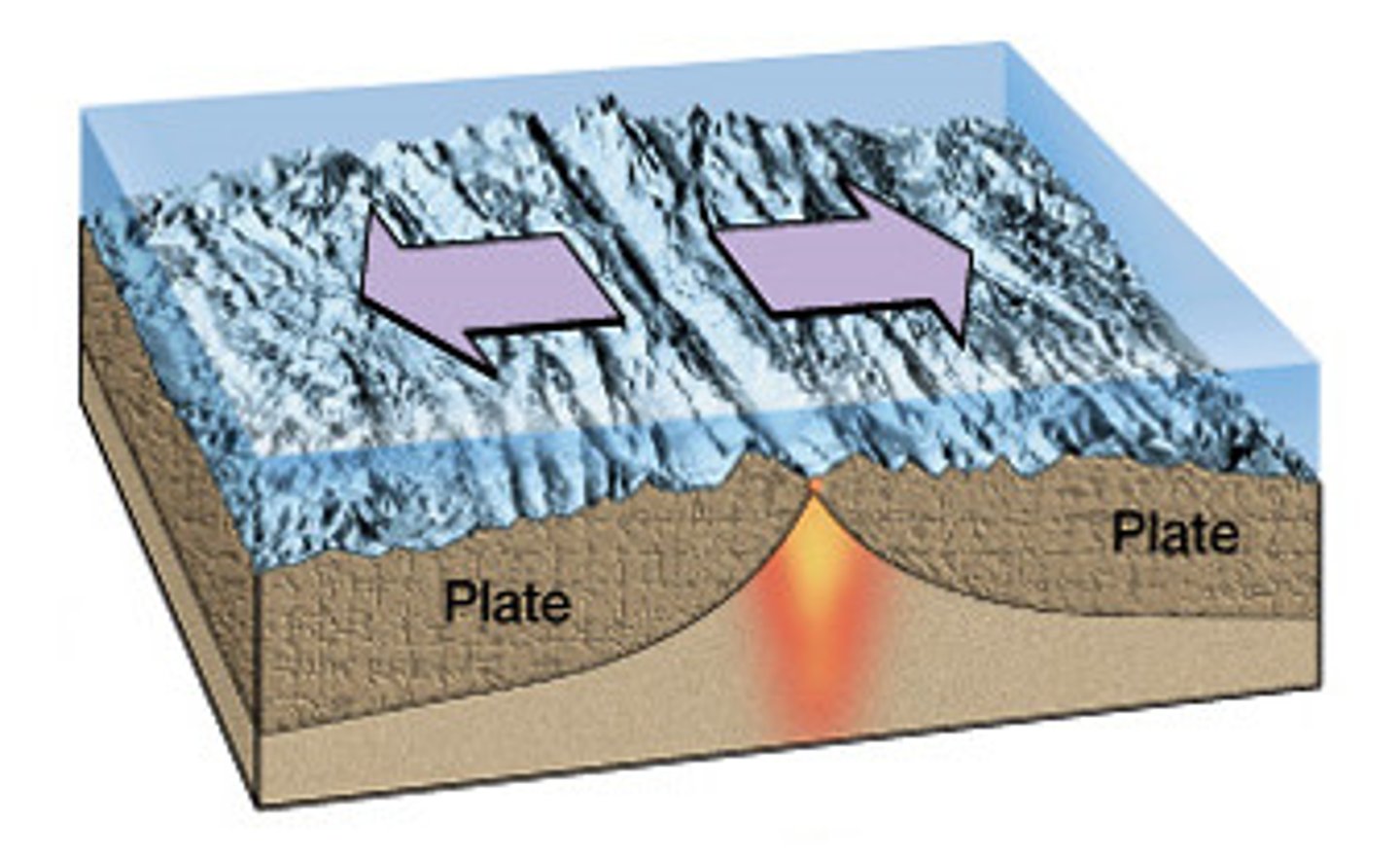
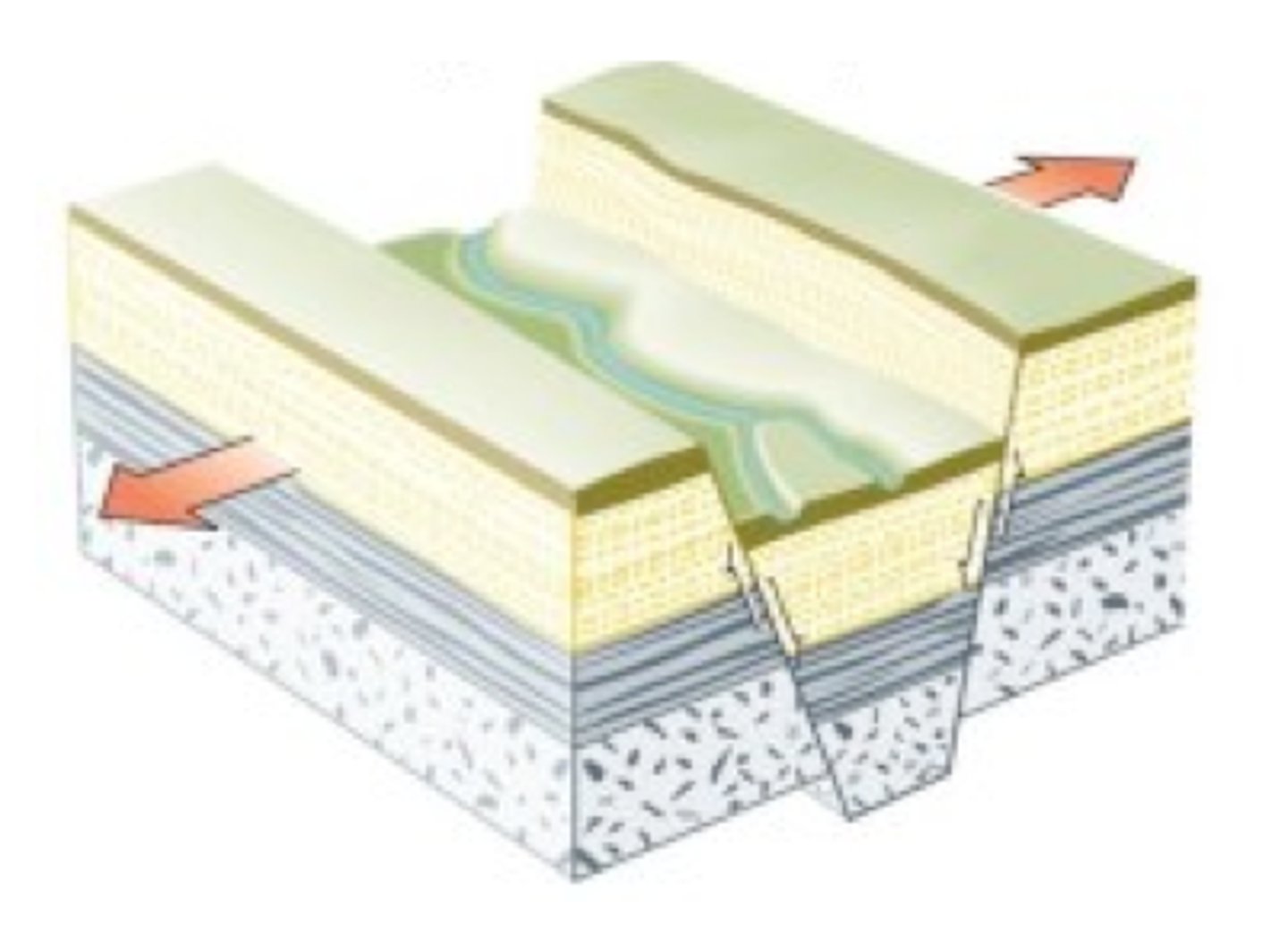
Divergent boundary
The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. This causes a gap that can be filled with magma (molten rock), and when it cools it will become new crust.
-------> <-------
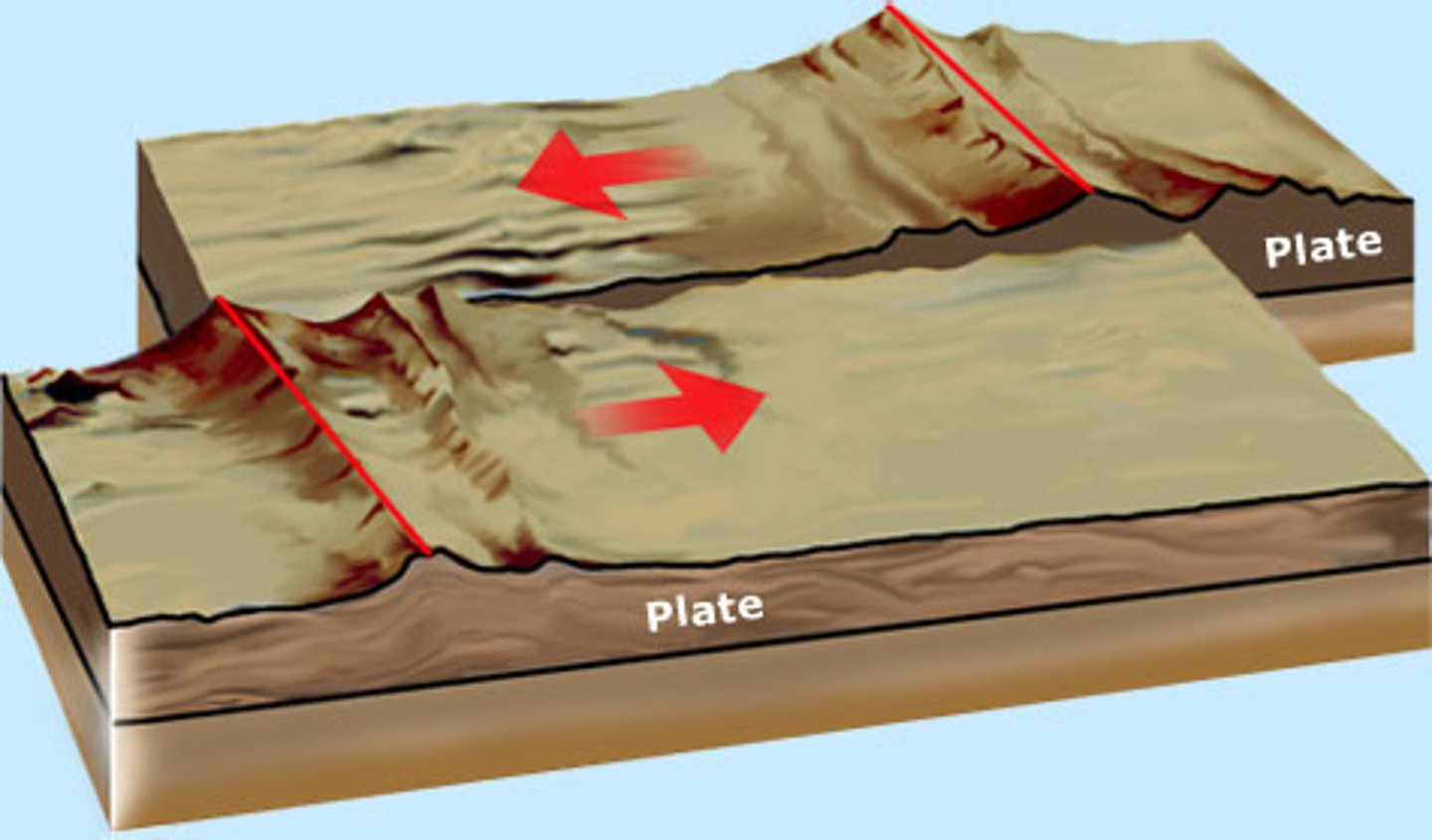
transform fault boundary
a boundary in which two plates slide past each other without creating or destroying lithosphere
---------->
<----------
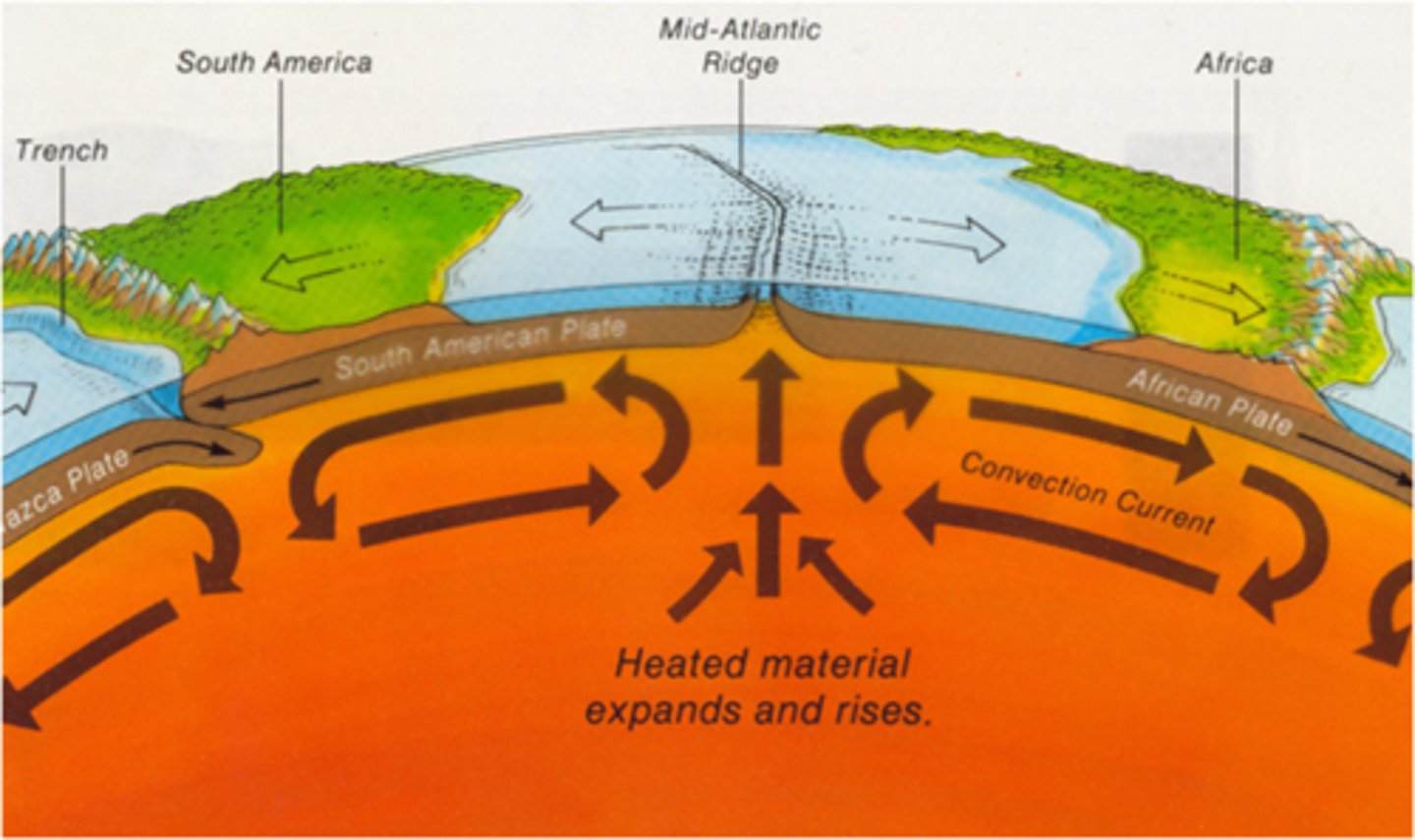
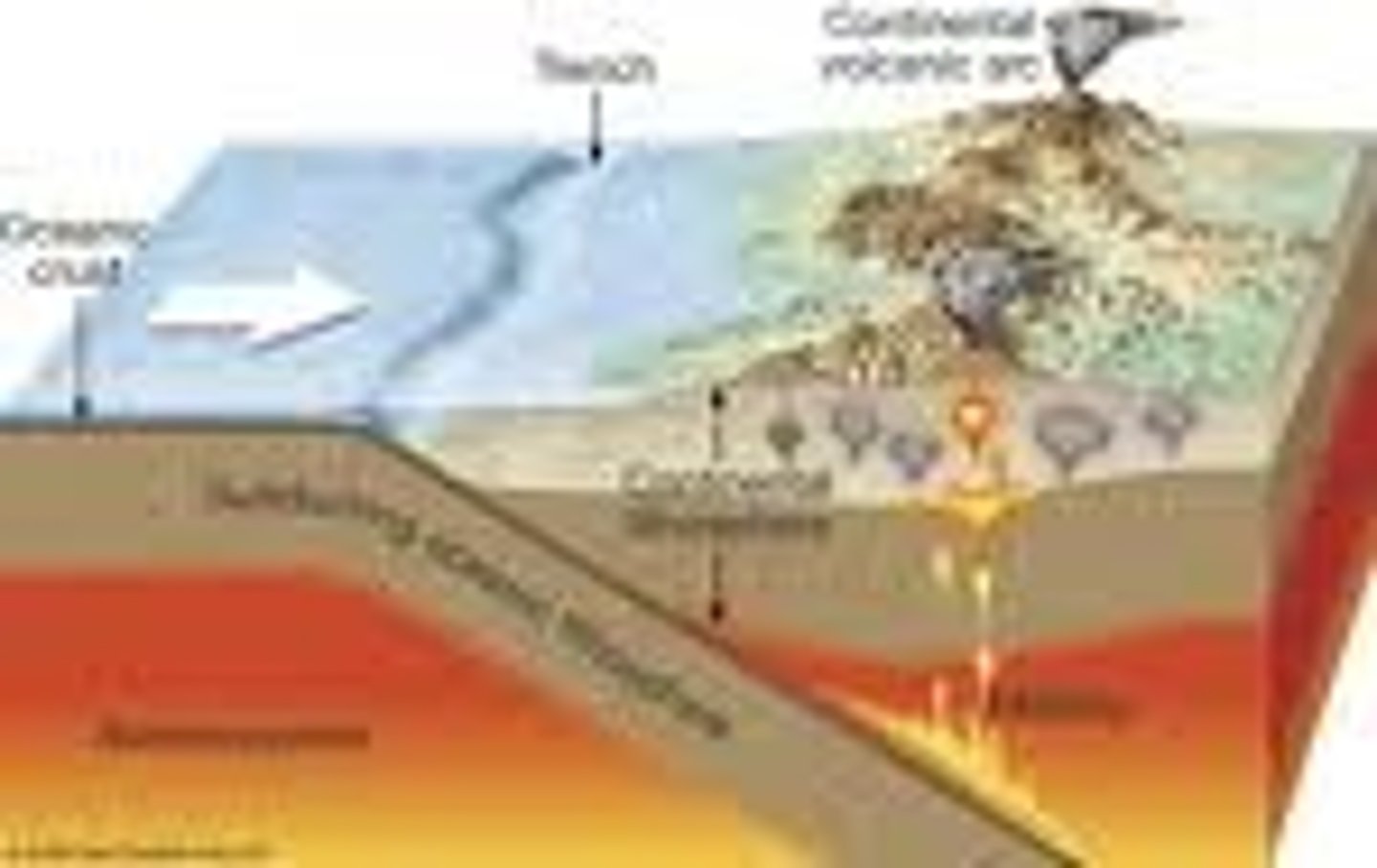
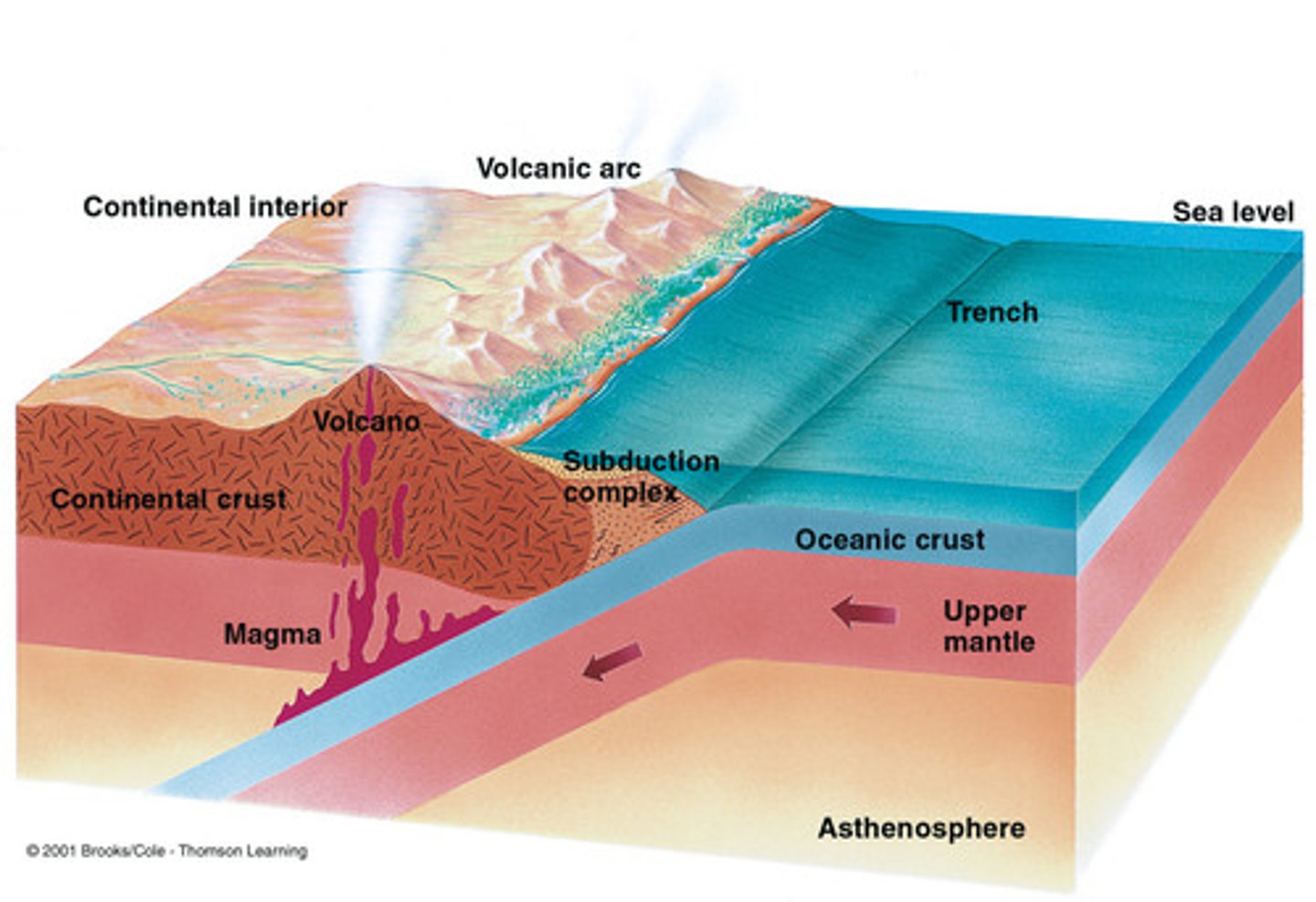
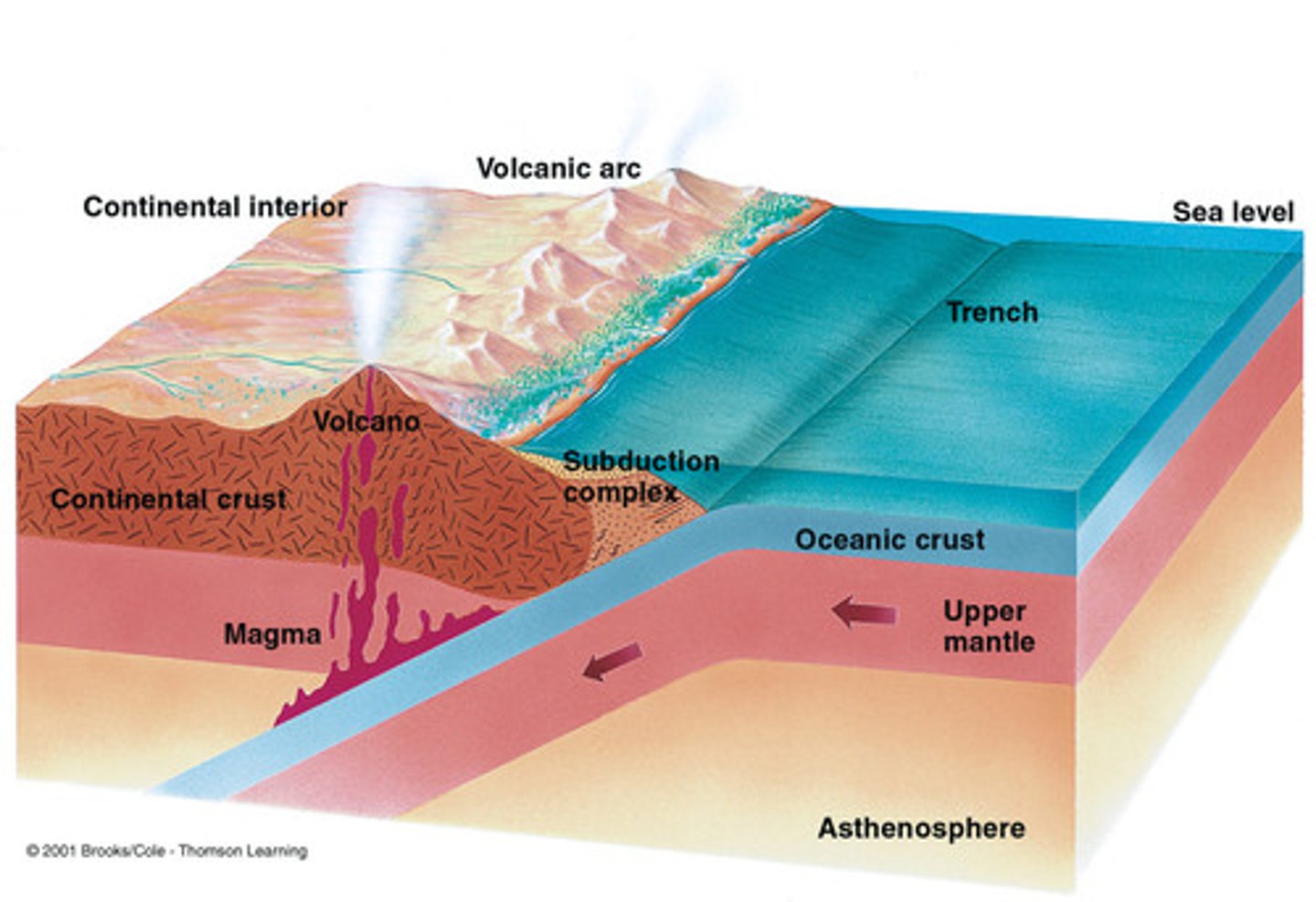
Subduction
Occurs when a tectonic plate, either continental crust or oceanic collides (converges) with oceanic crust, and the oceanic plate slides under the other plate. (occurs at a convergent boundary and usually forms volcanoes). The subducted plate is pushed under the other, deep into the mantle and melts as it encounters the mantle.
Volcanoes
mountains formed by magma from the earth's interior where tectonic plates meet
Active volcanoes
Are currently erupting, show sign of erupting in the near future, or have erupted in recorded history

Dormant volcanoes
are currently not erupting, but the record of past eruptions suggests that they may erupt again

extinct volcanoes
have not erupted in recorded history and probably will never erupt again

volcanic eruption
the sudden occurrence of a violent discharge of steam and volcanic material from inside earth resulting from built up pressure under Earth's crust

rift valleys
Occur when plates move away from each other. New ocean floor is formed as magma fills in where the plates have separated. Magma rising from this is basaltic. It is thick and forms pillow lava upon touching the cold ocean water
subduction zone
the region where an oceanic plate sinks down into the asthenosphere at a convergent boundary, usually between continental and oceanic plates but must always have an oceanic plate, it will be the subducted plate as it is denser than the other
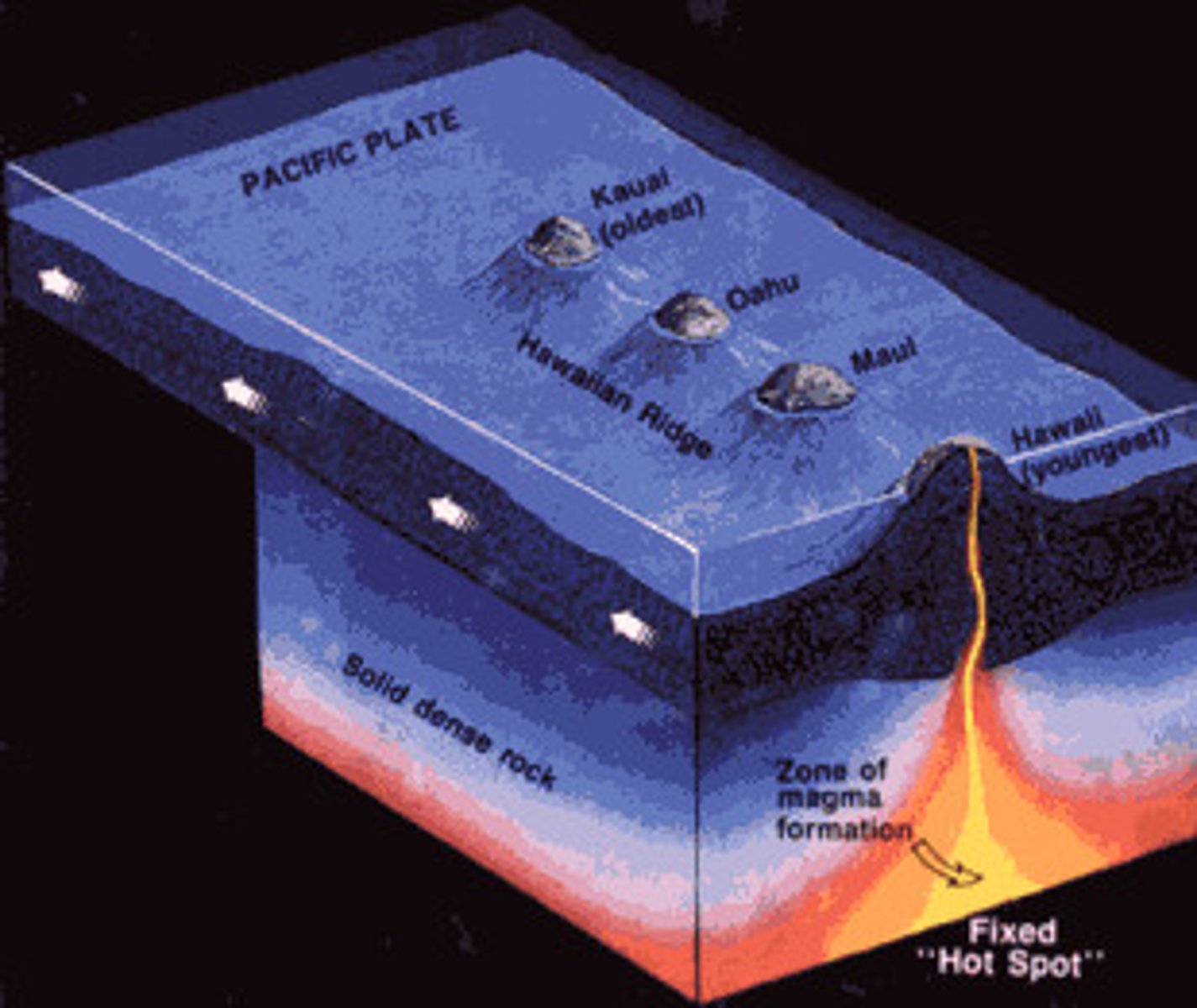
hot spots
do not form at the margin of plates. They are found over areas where magma can rise to the surface through the plates ("hot spots") The magma is often basaltic, but can also be rhyolitic which is generally associated with continental hotspots.
Ring of Fire
the chain of volcanoes that lines the Pacific Rim/Ocean
Archipelago
A chain/group of islands