Edexcel B Geography Topic 2: Development Dynamics
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
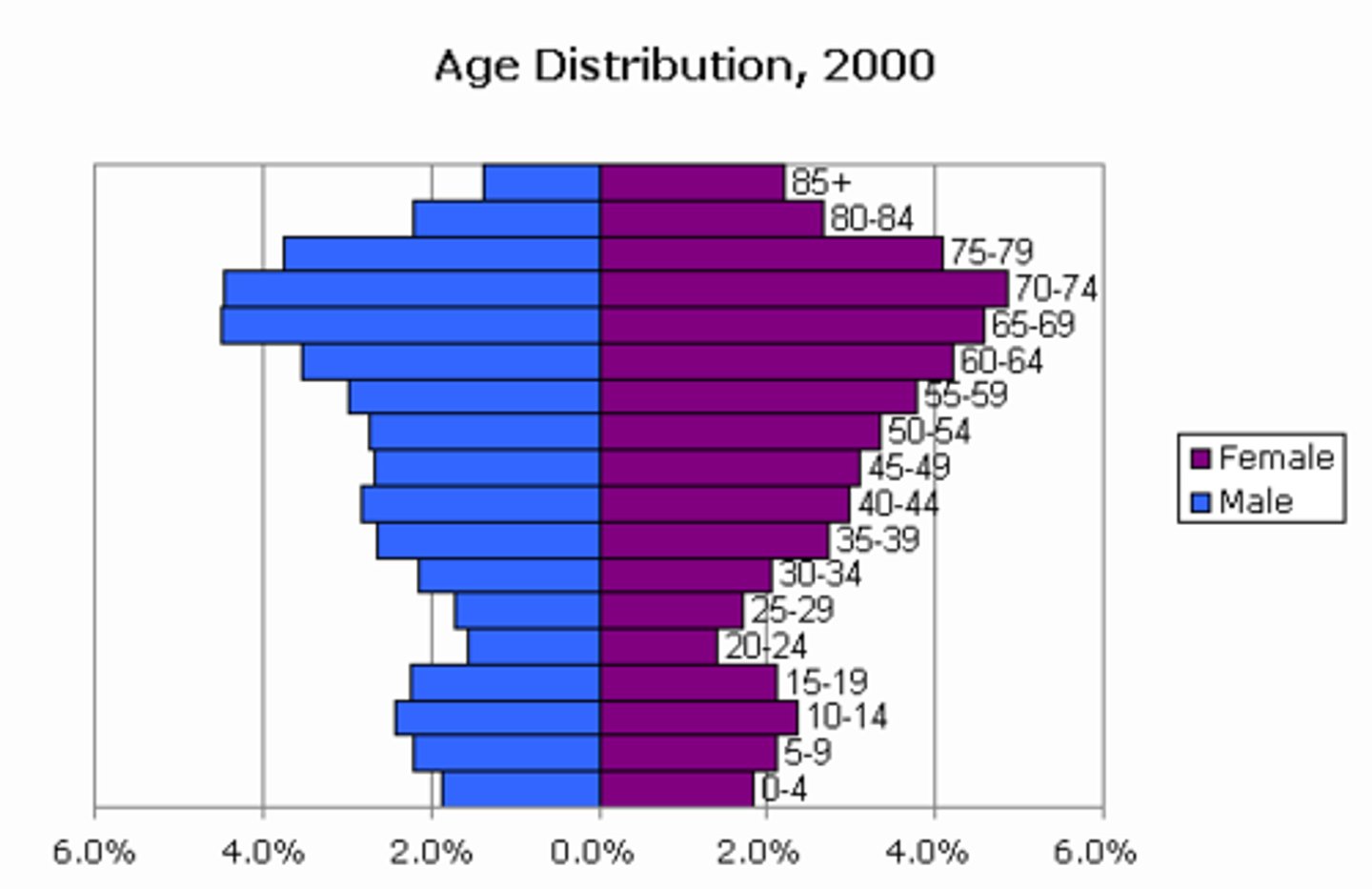
Aging population
A population in which the percentage that is age 65 and older is increasing relative to other age groups
Aid
Assistance given from one country to another. E.g. Money, equipment, education or loans
Birth Rate (BR)
The number of babies born per 1,000 people per year
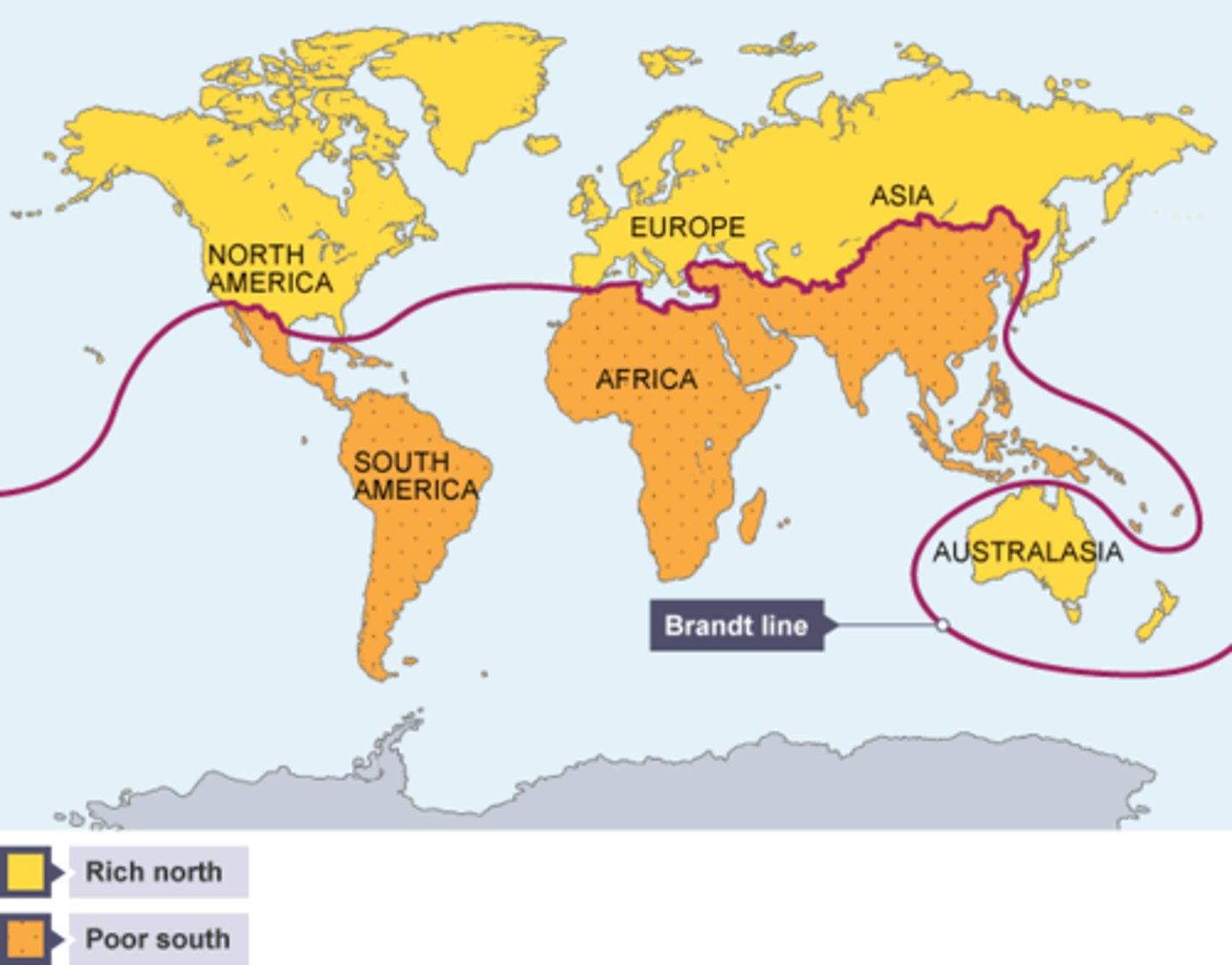
Brant Line
Economic division between the wealthy countries of Europe, both America, Japan, and Australia, and the generally poorer countries of Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Bottom-Up project
A small scheme, organised by an NGO or charity, that aims to help the poorest families.
Caste System
A Hindu social class system that controlled every aspect of daily life
Capitalism
An economic and political system which believes that richer a country is the more developed it is
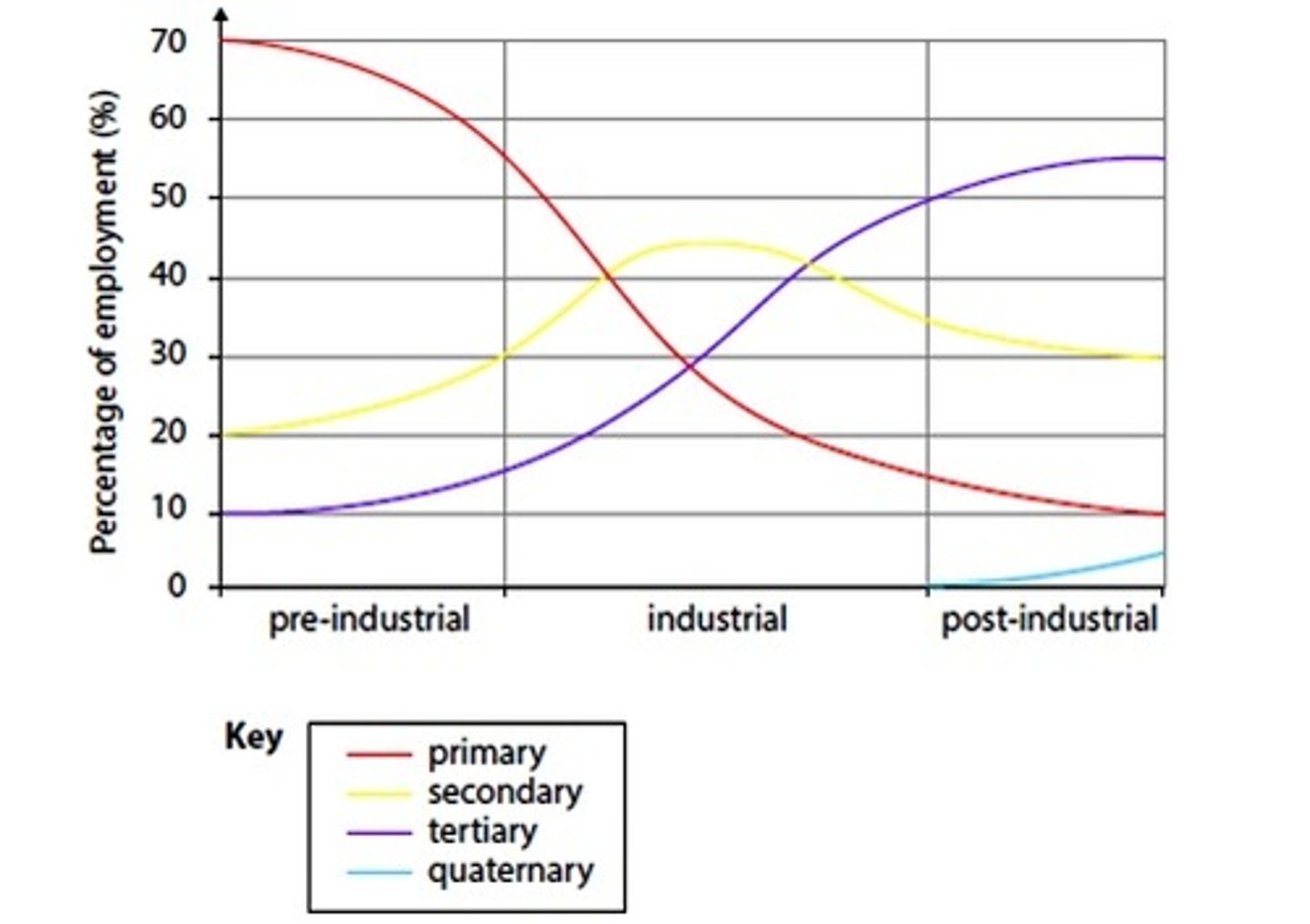
Clarke Fisher Model
Used to represent changes in employment during the 'pre-industrial', 'industrial' and 'post-industrial' periods.
Colonialism
The act of getting control over another country that occupying land and exploiting resources
Communism
A political and economic system which believes that all people should be equal. This involves all good and services being owned and distributed by the government
Corruption Perceptions Index
Ranks countries on perceived corruption 0 to 100 (0 being highly corrupt)
Death Rate (DR)
The number of deaths per 1,000 people per year
Democracy
A system of government where all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives.
Demographic data
All data linked to population. E.g. BR, DR or life expectancy
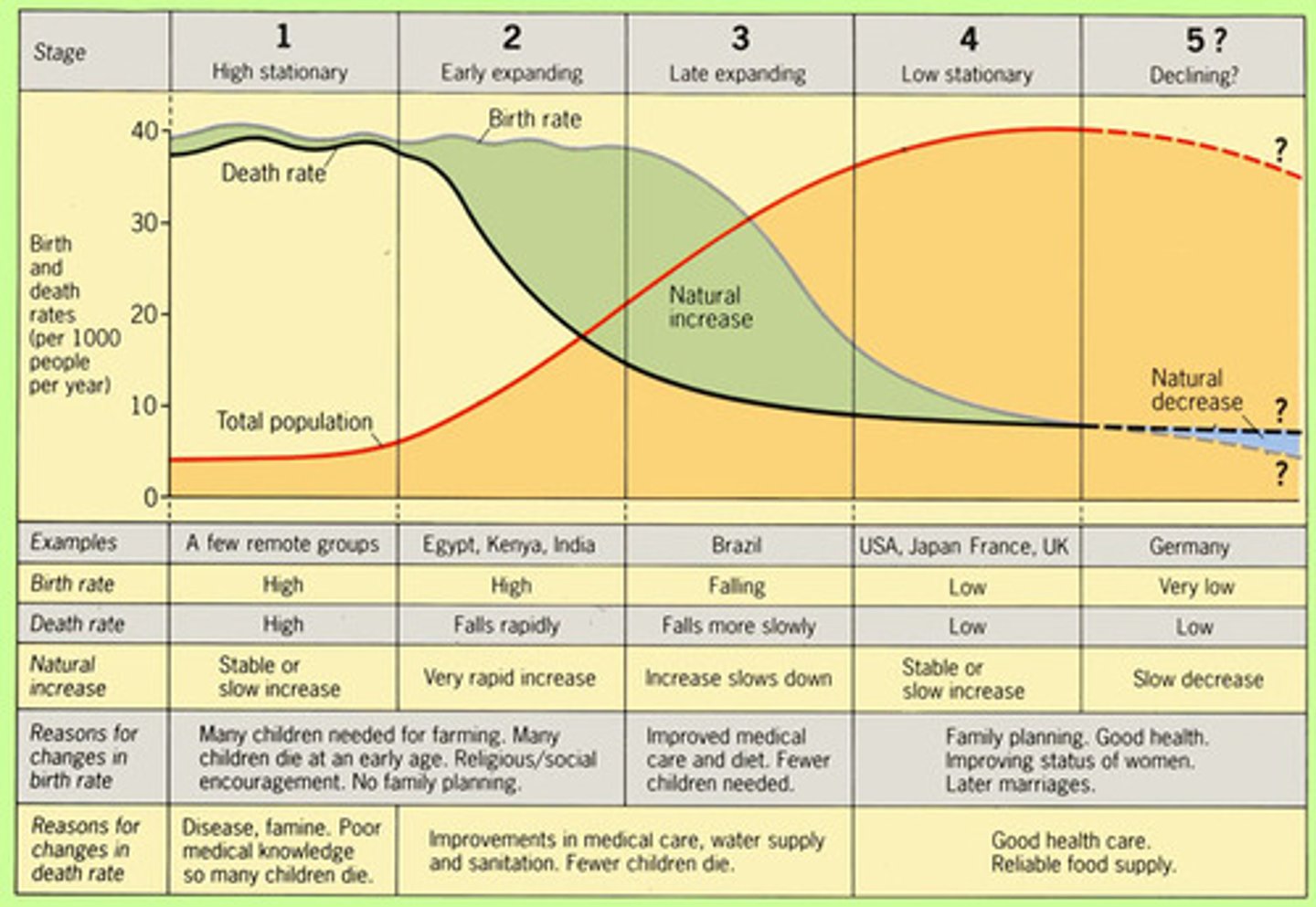
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
A model that helps explain how a country's population changes through modelling its BR, DR and overall population
Dependancy Ratio
The number of people under the age of 15 and over age 64, compares to the number of people active in the labour force.
Development
A process of improvement in the material conditions of people through diffusion of knowledge and technology, and increase in wealth.
Economic
To do with money
Economic inequality
The difference in wealth between the richest 10% of a country and the poorest 10%
Environmental
To do with the environment
Federal Direct Investment (FDI)
One country investing money into others by building factories there or investing in a large project (E.g. China's Silk Road Project)
Fertility rate
the average number of children a woman would have in her lifetime
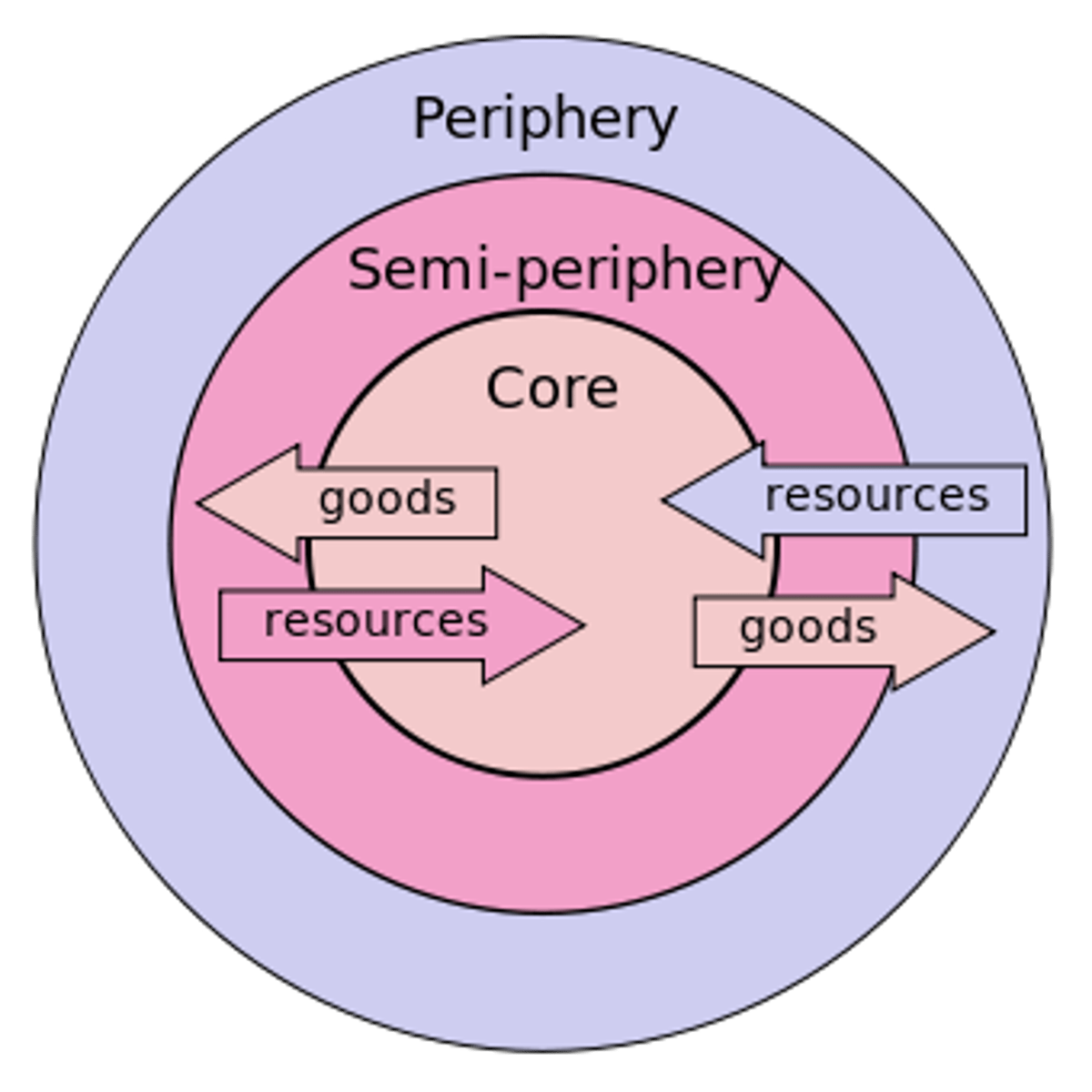
Frank's Dependency Model
A theory that peripheral nations (LICs) are dependent on core, coloniser, countries (HICs) for resources even after the core country is no longer occupying the peripheral
GDP
Gross Domestic Product- the total market value of all final goods and services produced annually in an economy
GDP per capita
Gross domestic product divided by the number of people in the population.
Gini Coefficient
A measure of income inequality within a population, ranging from zero for complete equality, to one if one person has all the income.
Globalisation
The increasing integration of economies and societies around the world particularly through international trade
Global shift
A global change where the manufacturing of goods moves from developed countries (E.g. USA) to developing countries (E.g. China)
Global Superpower
A term that describes a country that is so powerful that they affect the rest of the world
GNI
Gross national income - The value of the output of goods and services produced in a country in a year, including money that leaves and enters the country
GNI PPP
GNI Purchasing Power Parity - shows how powerful a currency is. In LICs the cost of living is cheaper so $1 USD will go further than in an HIC
Governance
The management of a place or group of people
High Income Country (HIC)
A country with GNI per capita higher than $12746 (World Bank 2013)
Human Development Index (HDI)
A measure of economic well-being that combines life expectancy, education, and standard of living as shown in GDP per capita and purchasing power.
Indicator
A way of measuring development, which focuses on social, economic or environmental development
Industrialisation
The process experienced by a country that moves away from primary industries towards secondary industries as its principal sector for national output and employment
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The number of infants that die under 1 year old per 1,000 live births per year
Infastructure
Basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society and its economy. E.g. Roads, housing, schools, hospitals etc.
Informal Sector
A sector of the economy that is not regulated or taxed by the state
Interdependence
A relationship between countries in which they rely on one another for resources, goods, or services
Inter-Governmental Organisation (IGO)
A group of countries established by a treaty such as the World Bank or United Nations.
Level of Development
A country's wealth (GDP) and its social and political progress
Life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live in a given area
Literacy Rate
The percentage of a country's people who can read and write.
Low Income Country (LIC)
A country with GNI per capita lower than $1045 (World Bank 2013)
Maternal mortality rate
Number of deaths per thousand of women giving birth.
Middle Income Country (MIC)
Group classified by the World Bank as having a per capita income between $1 025 and $12 475
Neo-colonialism
Country that displays economic dependence on another country; a country that displays so much economic independence on another country, that it seems to be a colony of the independent country
Newly Industrialised Countries (NIC)
A country where industrialisation has recently taken place
Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO)
An organisation which is not part of a government, but provides important resources or aid. E.g. Charities or universities
Outsourcing
Hiring workers in developing countries due to lower wages
Political
To do with politics or the Government
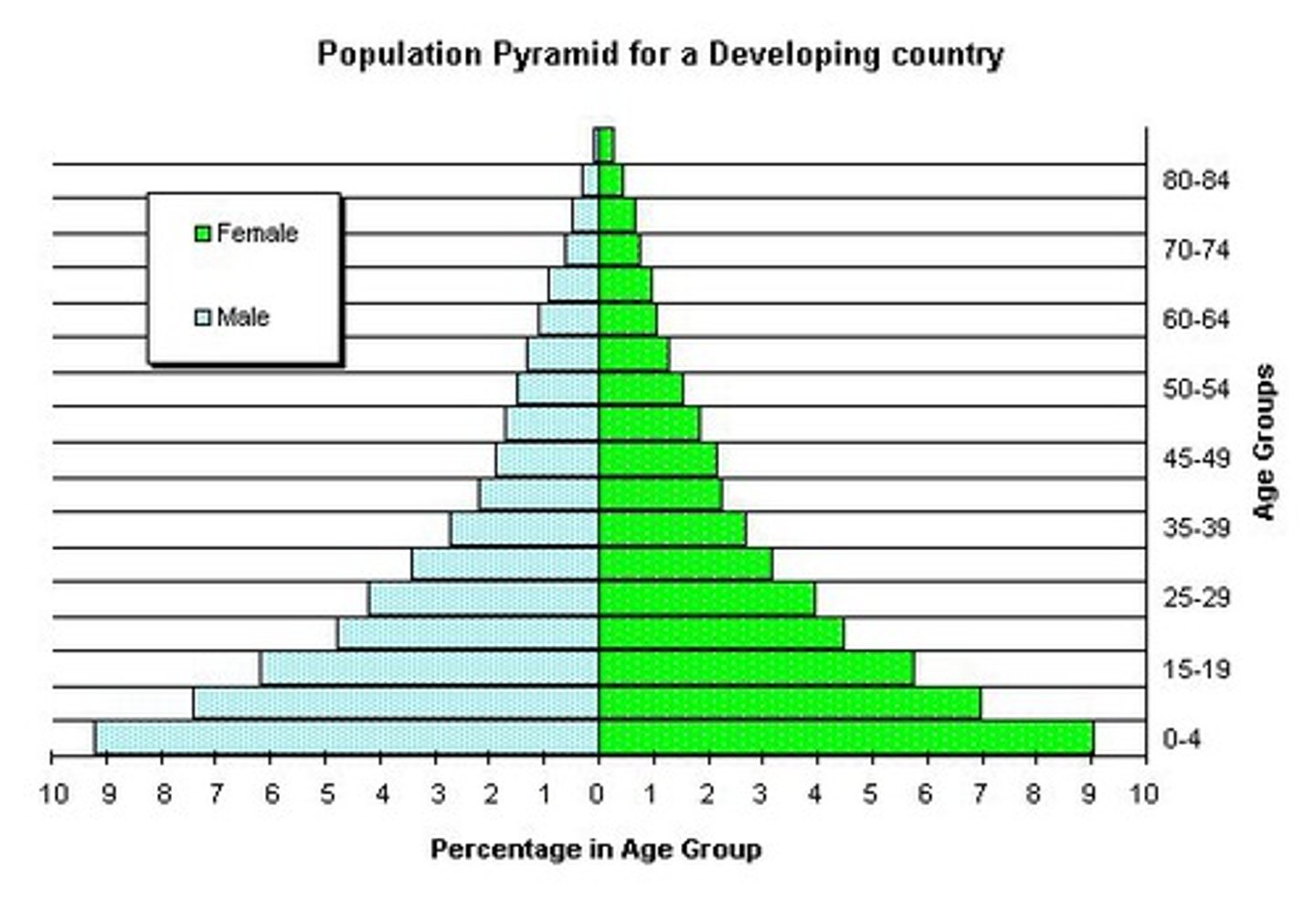
Population Structure
The composition of a population, the most important elements of which are age and sex
Post-Industrial
describing an economy in which the tertiary sector has become more important than the secondary sector
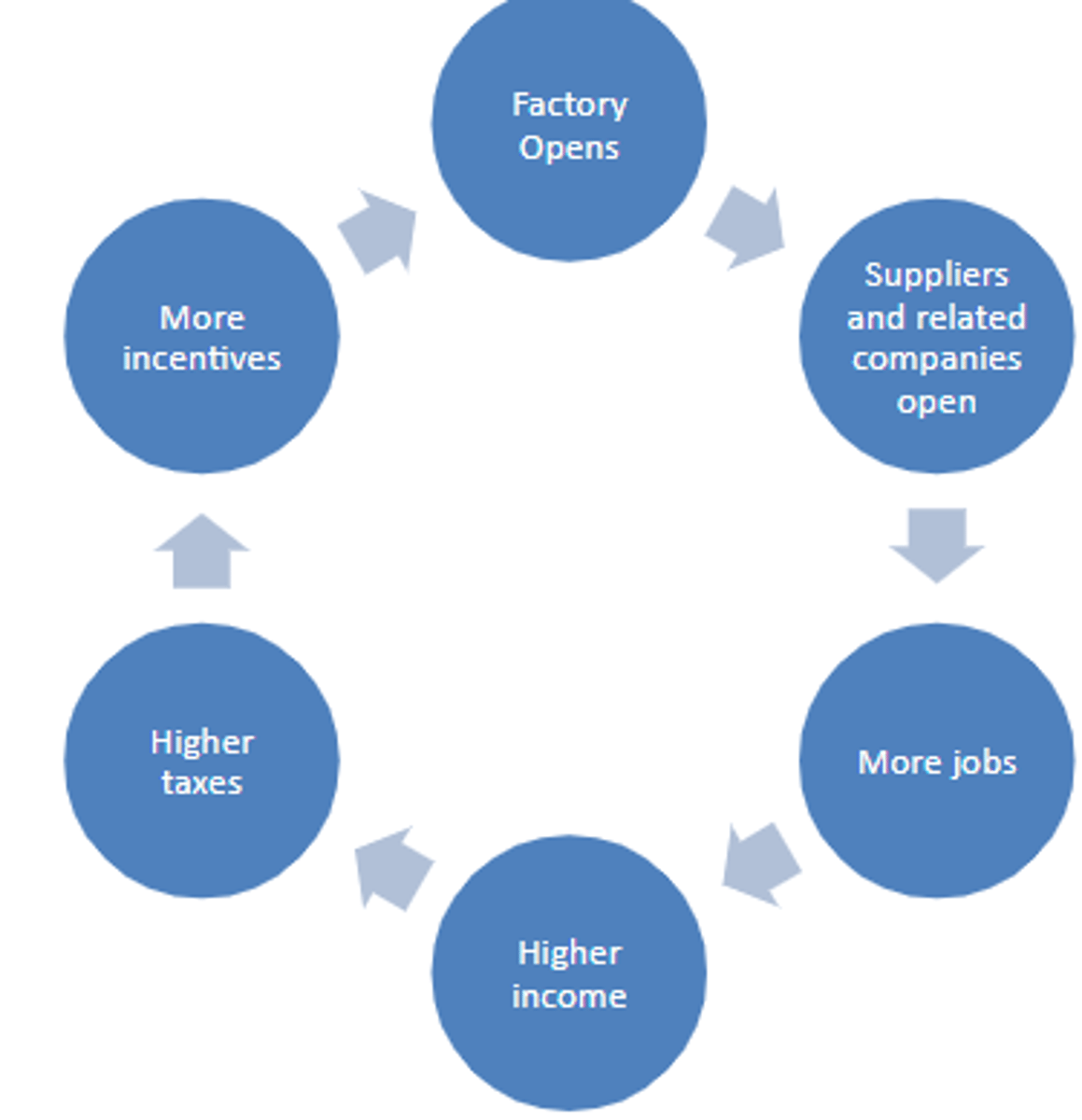
Positive multiplier effect
When an initial investment in a community (building a new school) leads to positive knock on effects (more jobs and increase in migration to the area)
Poverty Line
Minimum income required to meet basic needs in a given area
Pre-industrial
A period in development of a society when farming employment is high and a manufacturing industry has yet to develop
Primary Industries
An industry that extracts natural resources from the Earth. E.g. Farming
Quality of life
The standard of health, comfort, and happiness experienced by an individual or group.
Quaternary Industry
An industry provide information services like research and computer technology. E.g. Computer Scientist
Recourses
Items used in the production of goods, land, labour etc.
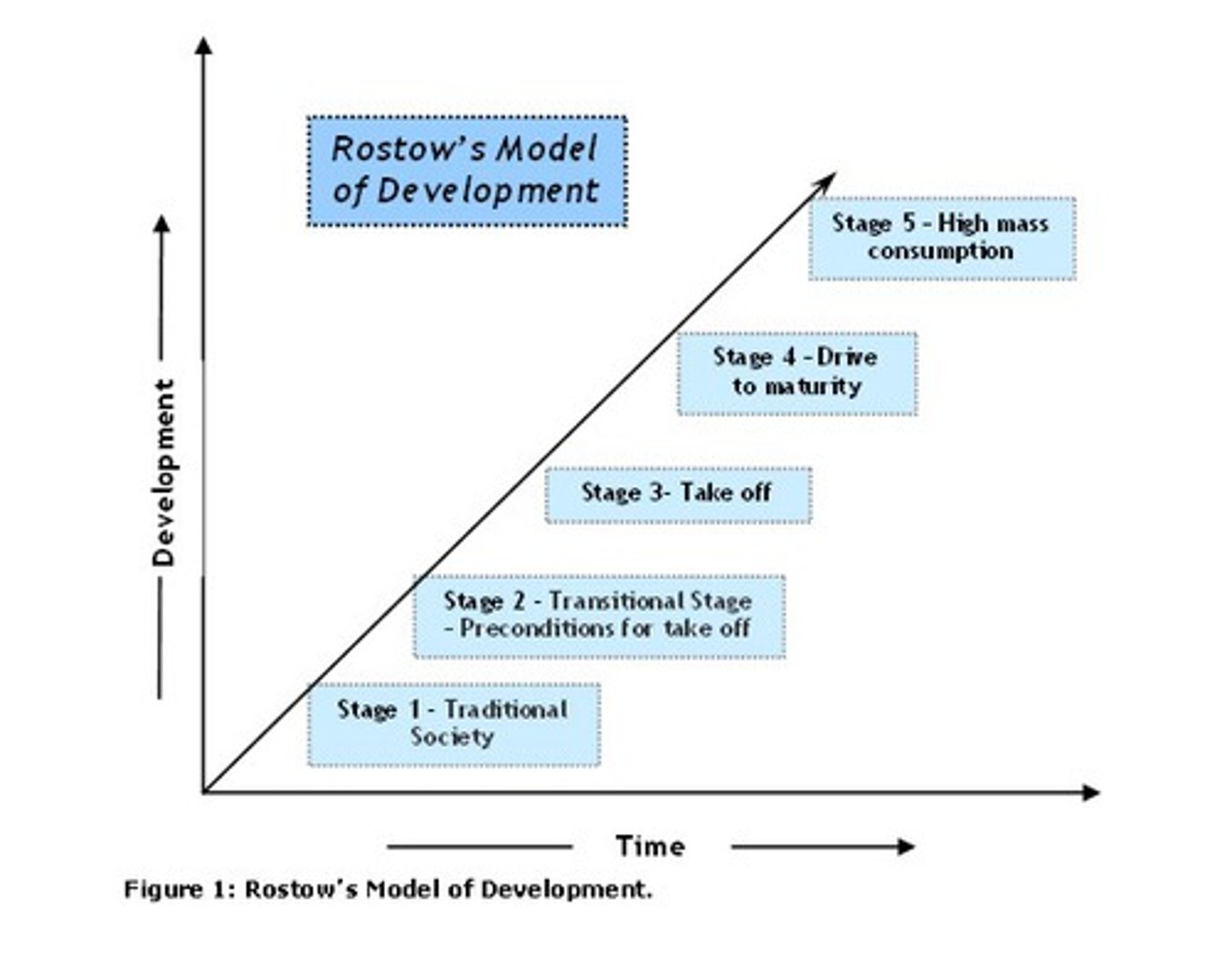
Rostow's Modernisation Theory
The development of a country takes five stages of growth: Traditional Society, Pre-Conditions for Take Off, Take Off, Drive to Maturity, Mass Consumption.
Rural area
The countryside
Rural-urban migration
The movement of people from the countryside to the city
Secondary Industries
An industry that assembles, processes, or converts raw materials into fuels or finished goods. E.g. Factory Workers
Social Inequality
The unequal distribution of wealth, power, or prestige among members of a society
Squatter Settlement
An area in a LIC city where people illegally build homes on land they do not own. They are known by different names around the world. E.g. slum, favela
Tertiary Industry
Provides goods and services to people and businesses. E.g. Doctor or Teacher
Top-Down Project
A large-scale scheme to improve development, organised by the government or a large TNC. The benefits of the scheme should trickle down to poorer families in the community.
Trade
Exchange of goods and services between people, companies or countries
Trans-National Corporation (TNC)
Global companies which operate in more than one country. E.g. Nike
Tariffs
Taxes on imports or exports
Topography
The shape of the land (how hilly it is)
Urban area
Cities or built up area
Urbanisation
The increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities
Youthful population
A population in which there is a high percentage of people under the age of 16 (or sometimes 18)