Ohm’s Law
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Ohm’s law
The current that flows through most substances is directly proportional to the voltage applied to it.
Georg Simon Ohm
The German physicist after whom the Ohm’s law is named
voltage, current
In the cause and effect relationship, _______ is the cause and _______ is the effect.
Ohmic material or ohmic component
Any material or component that obeys Ohm’s law (current through the device is proportional to the voltage applied)
Nonohmic material or nonohmic component
Any material or component that does not obeys Ohm’s law (current through the device is not proportional to the voltage applied)
1827
What year did Georg Ohm described an experiment in which he measured voltage across and current through various simple electrical circuits containing various lengths of wire?
To observe the current through a resistor that results from an applied voltage.
What is the objective of the experiment that was shown by Georg Ohm?
A resistor is connected in series with a battery
Explain the arrangement of the circuit that Georg Ohm used
Across the resistor (in parallel with the resistor)
How must the voltmeter be placed in order to measure the voltage
In line with the resistor (in series with the resistor)
How must the ammeter be placed in order to measure the current?
Ammeter’s positive terminal should face the entering direction of the current and voltmeter’s positive terminal should be on the higher voltage side of the component.
How can we get positive readings on our Ammeter and Voltmeter?
+9V, 0
A battery of 9V will have ___ at its positive terminal and __ at its negative terminal.
By switching the terminals of the battery.
How to get a current flow in the opposite direction?
V = IR
Mathematical representation of the Ohm’s law
across, through
Voltage is ______ the object and the current is _______ the object
linear
In the Ohm’s law, voltage and current have a ______ relationship with each other.
V(t) = Vmax * sin(2πft)
What is the equation that describes how the voltage supplied to a house varies over time in an AC circuit?
Diode
A circuit device that allows the current flow in only one direction. Is a semiconducting circuit element. It’s one example of a nonohmic device
Symbol of a diode
(1)
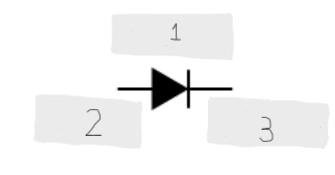
Anode (+)
(2)
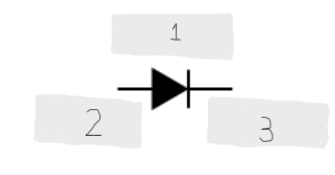
Cathode (-)
(3)
y-axis
In A v/s B, A belongs on what axis?
x-axis
In A v/s B, B belongs on what axis?
Voltage v/s Current
Resistor’s operation is usually shown as what?
Current v/s Voltage
Diode’s operation is usually shown as what?
When its anode is at a negative potential and cathode is at positive potential.
When is the diode said to have reverse bias?
Reverse bias
A phenomenon where the diode has an extremely large resistance and there is very little current flow (essentially zero)
As the voltage is increased, the current still essentially remains zero
Until it reaches the breakdown voltage, leading the diode to conduct.
When its anode is at a positive potential and cathode is at negative potential.
When is the diode said to have forward bias?
Forward bias
A phenomenon where the diode conducts and current flows through it only if the voltage is greater than 0.7V.
As the applied voltage increases so does the current, but the voltage across the diode remains approximately 0.7V,
And here the resistance of a diode is close to zero
Because diode’s resistance in its forward bias is close to zero, the resistor needs to be placed for the current to not become very large.
Why is resistor also placed with the diode in the circuit?
microscopic, current density, conductivity, electrical field
Ohm’s law was originally stated as a ___________ view, in terms of the _______________, the ____________, and the ________________
Current density
The applied electrical field is proportional to what?
The proportional relationship between Voltage and Current in the Ohm’s law comes from the drift velocity of the free electrons in the metal that results from an applied electrical field.
What does the microscopic view suggests?