Chapter 15 Treatment of Psychological Disorders
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
psychotherapy
generic name givent o formal psychological treatment
involve interactions between practicioner and client
limitation: some disorders are characterized by apathy or indifference
requires engagement from the client
biological therapies
approaches to disease and illness
therapies are based in idea that psychological disorders come from abnormalities in body
psychopharmacology
the use of medications that affect the brain or body to treat psychological disorders
limitation: long-term success requires indefinite treatment sometimes
Who first developed psychological treatments?
Freud
Free association
client says whatever is on the come and therapist looks for unconscious conflict
developed by Freud
dream analysis
looking for hidden meaning in dreams
developed by Freud
general goal od psychoanalysis
to increase clients’ awareness of their own unconscious and how it affects their daily functioning
psychodynamic therapy
reformulated Freud’s ideas as those were largely ineffective
aims to help clients examine their needs, defenses, and motives to understand why there is distress
couch is replaced with chair
features of contemporary psychodynamic therapy
exploring the clients’ avoidance of distressing thoughts
looking for recurring themes and patterns in thoughts and feelings
discussing early trauma experiences
focusing on interpersonal relations and childhood attachments
emphasizing the relationship with the therapist
exploring fantasies, dreams, and daydreams
behavior therapy
behavior is learned and therefore can be unleaded
behavior modification
exposure
exposing someone can reduce their anxieties by exposing them to their fears and changing how they think about said fears
cognitive therapy
based on the theory that distorted thoughts can produce maladaptive behaviors and emotions
cognitive restructuring
advocated by Aaron T. Beck
clinician seeks to help a person recogniza maladaptive though patterns and replace them with ways of viewing the world that are more in tune with reality
rational-emotive therapy
advocated by Albert Ellis
therapist acts as a teacher explaining the clients errors in thinking and demonstrating adaptive ways to think and behave
maladaptive pattern vs. after cognitive restructuring
see image
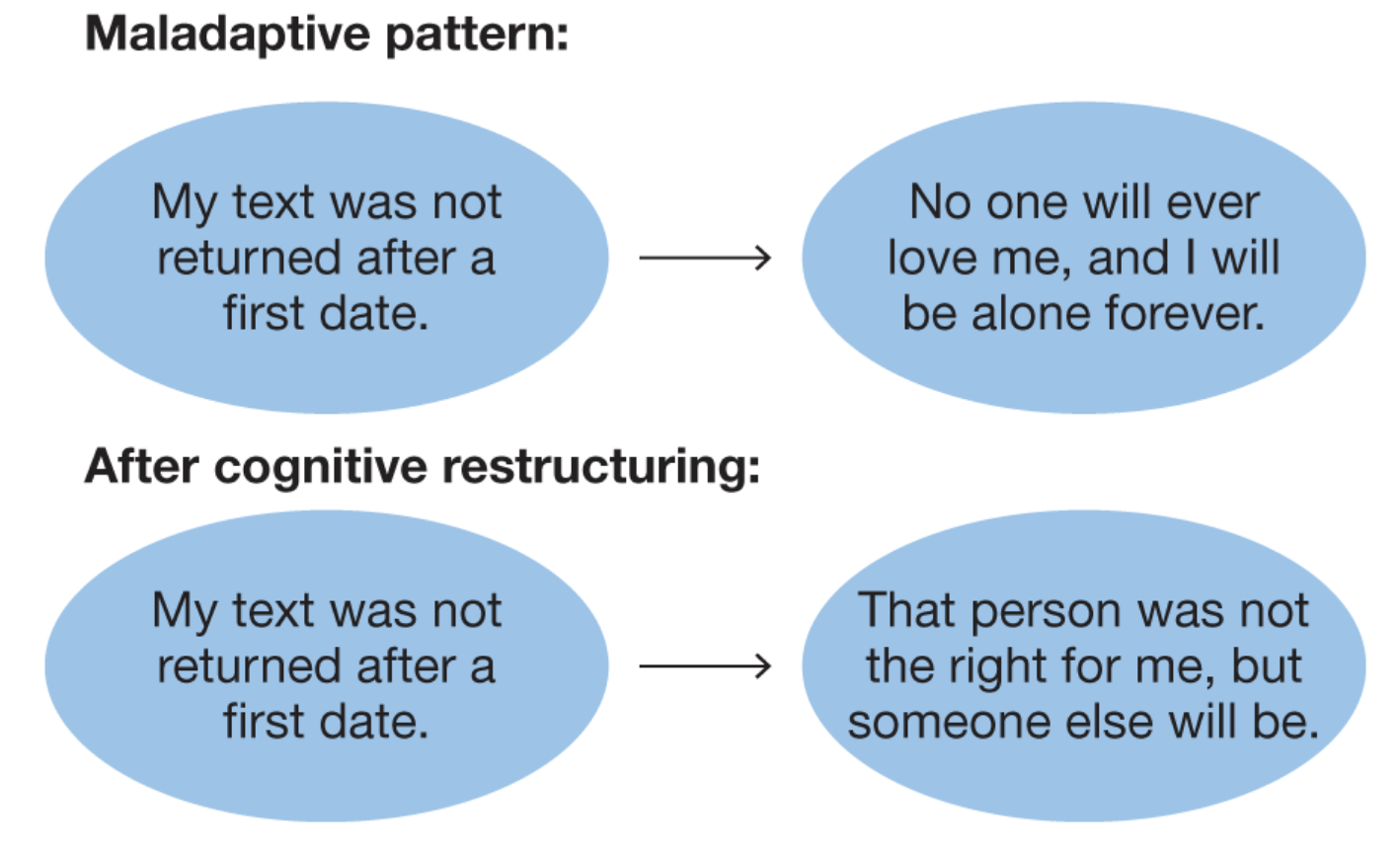
interpersonal therapy
focuses on circumstances, mainly relationships the client attempts to avoid
developed out of ideas on how people relate to one another
mindfulness-based cognitive therapy
created by John Teasdale and colleagues
people who recover from depression are vulnerable to faulty thinnking
goals: to help clients become more aware and help them learn to disengage from ruminative thinking through meditation
Cognitive-behavioral Therapy
uses cognitive and behavior therapy
goal: correct the client’s faulty cognitions and to train the client to engage in new behaviors
client-centered therapy
developed by Carl Rogers
encourages people to pulfill their potentials for personal growth through greater self-understanding
key ingredient: creation of a safe and comforting setting
form of humanistic therapy
reflective listening
therapist repeats clients’ concerns to help them clarify their feelings
motivational interviewing
uses a client-centered approach over a very short period
helps clients identify discrepancies between current state and where they would be in their lives
created by William Miller
systems approach
individual is part of a larger context
Family therapy
each person is a part of the larger system
changing one’s behavior affects the whole system
family involvement is key
group therapy
less expensive than individual therapy
rose in popularity after WW2
many are organized around a specific problem
structure varies depending on topic and therapist
psychotropic medications
act by changing brain chemistry
may provide relief from symptoms of psychological disorders
3 categories: antianxiety drugs, antidepressants, and antipsychotics
Antianxiety drugs
aka anxiolytics
one class is benzodiazepines (Xanax and Ativan)
induces drowsiness
antidepressents
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is the first antidepressent to be discoveres
second category: tricyclic antidepressents
inhibit reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine
SSRIs
inhibit reuptake of serotonin but to a significantly lesser extent
critics say they are overperscribed
How do SSRIs work?
see image
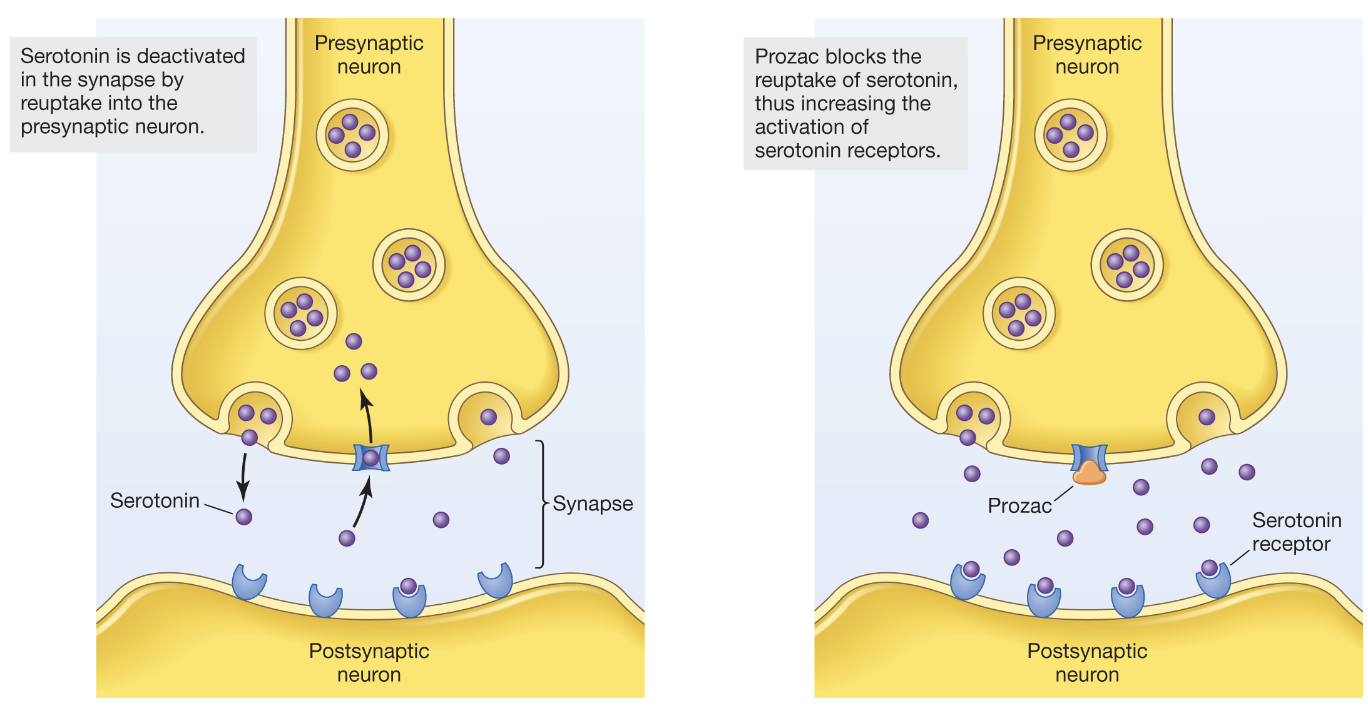
antipsychotics
long-term use sideeffect: tardive dyskinesia (involuntary muscle twitch)
treatment resistant
not all people are treated successfully with therapy , medication or both
trepanning
holes in head to heal from psychological disorder
psychosurgery
in which areas of the brain were selectively damaged
credited to Antionio Egas Moniz
creator of the lobotomy
electroconvulsive therapy
involves placing electrodes on a person’s head and administering a strong enough electric current to cause a seizure
commonly used to treat schizophrenia and depression
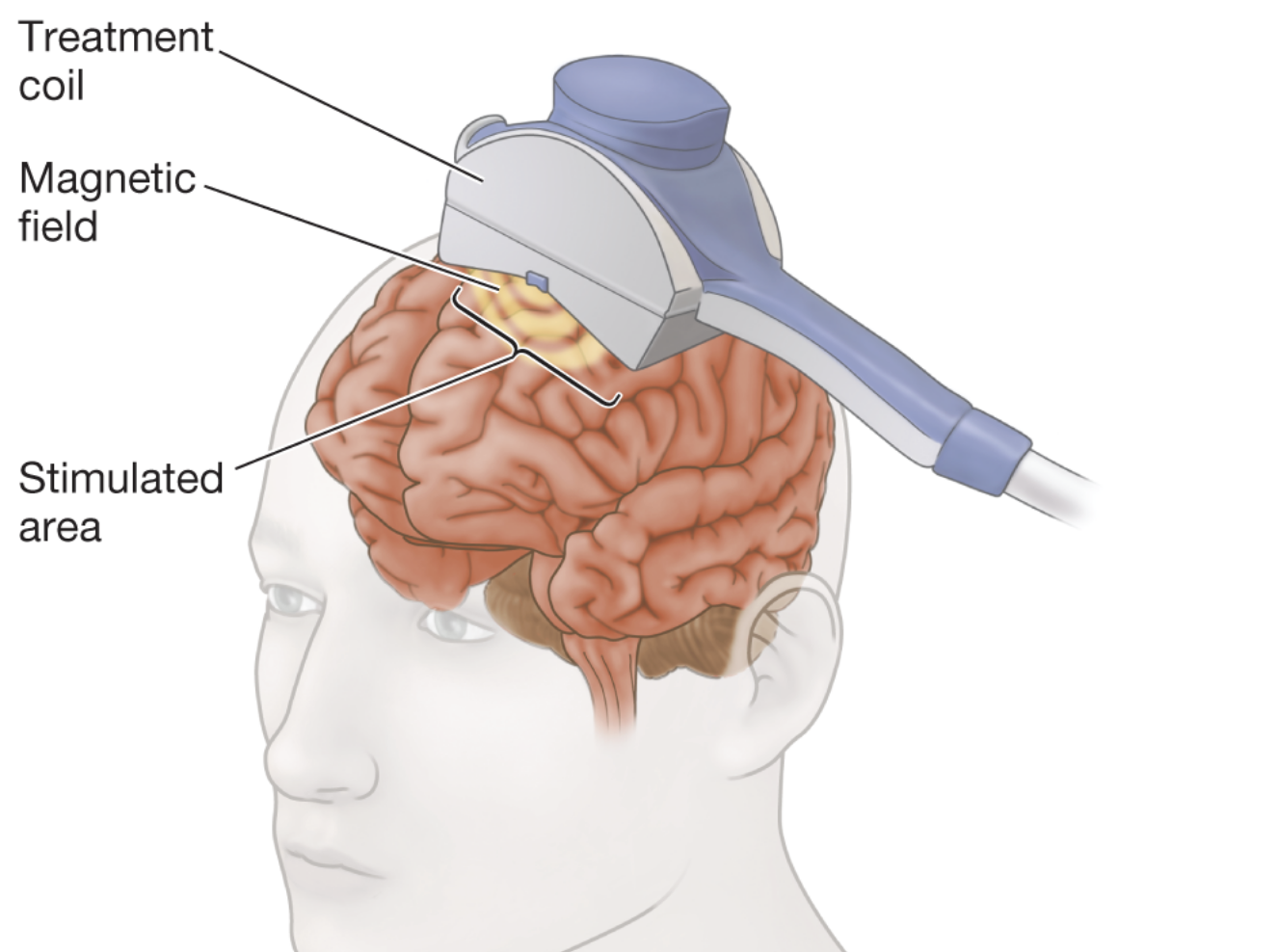
transcranial magnetic stimulation
used to treat severe depression
interrupts neural function in that region
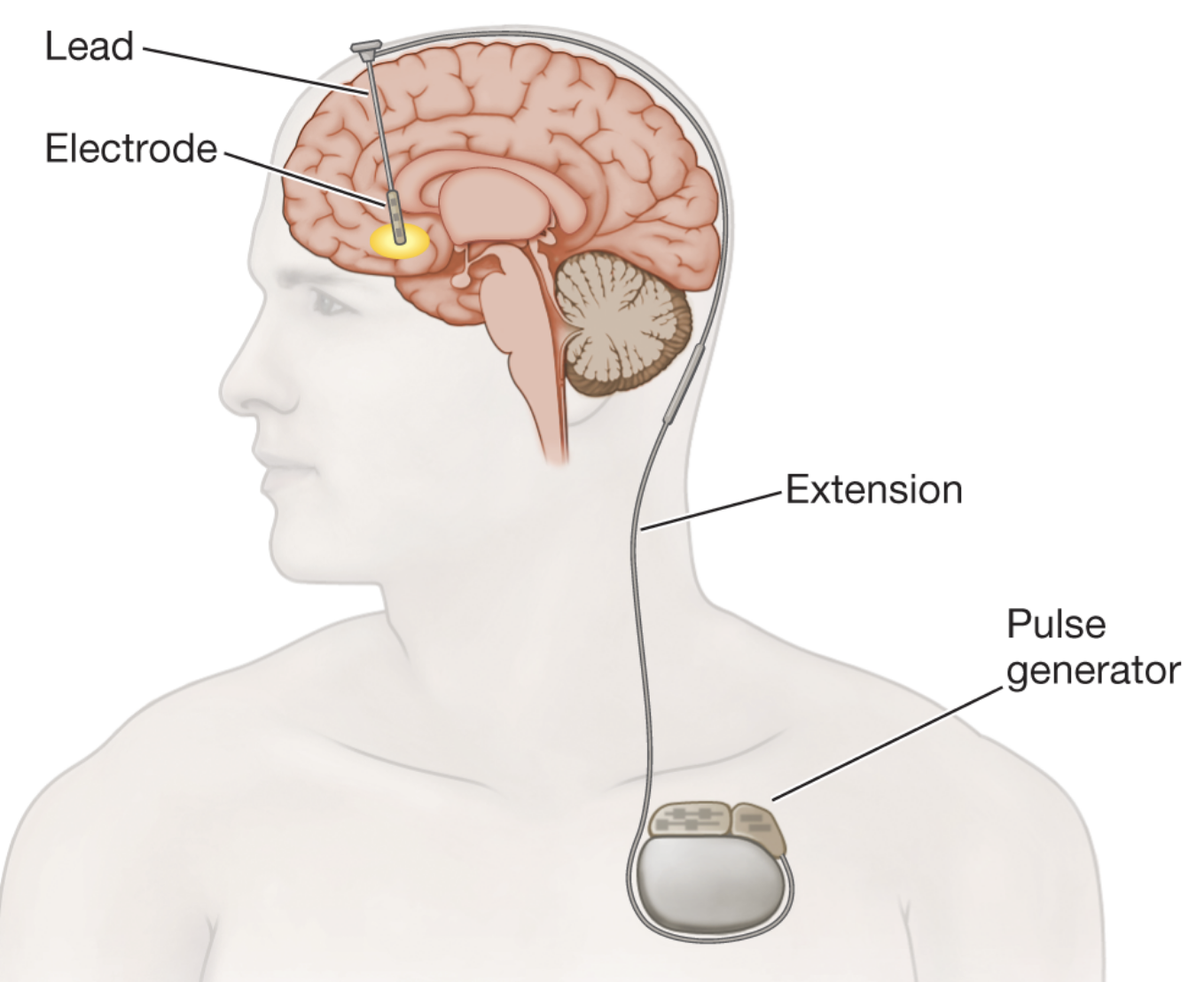
deep brain stimulation
mild electricity stimulated the prain much like a pacemaker
used to treat Parkinson’s OCD and major depression
placebo effect
improvement based on inert drug or minimal contact
more complicated for psychotherapy than drug research
David Barlow
pointed out that medical studies often lead to dramatice treatment practice changes
John Shedler pointed out that evidence-based treatments can be statistically significant without providing any practical improvement in symptoms (relief might not even be sufficient for patients’ needs)
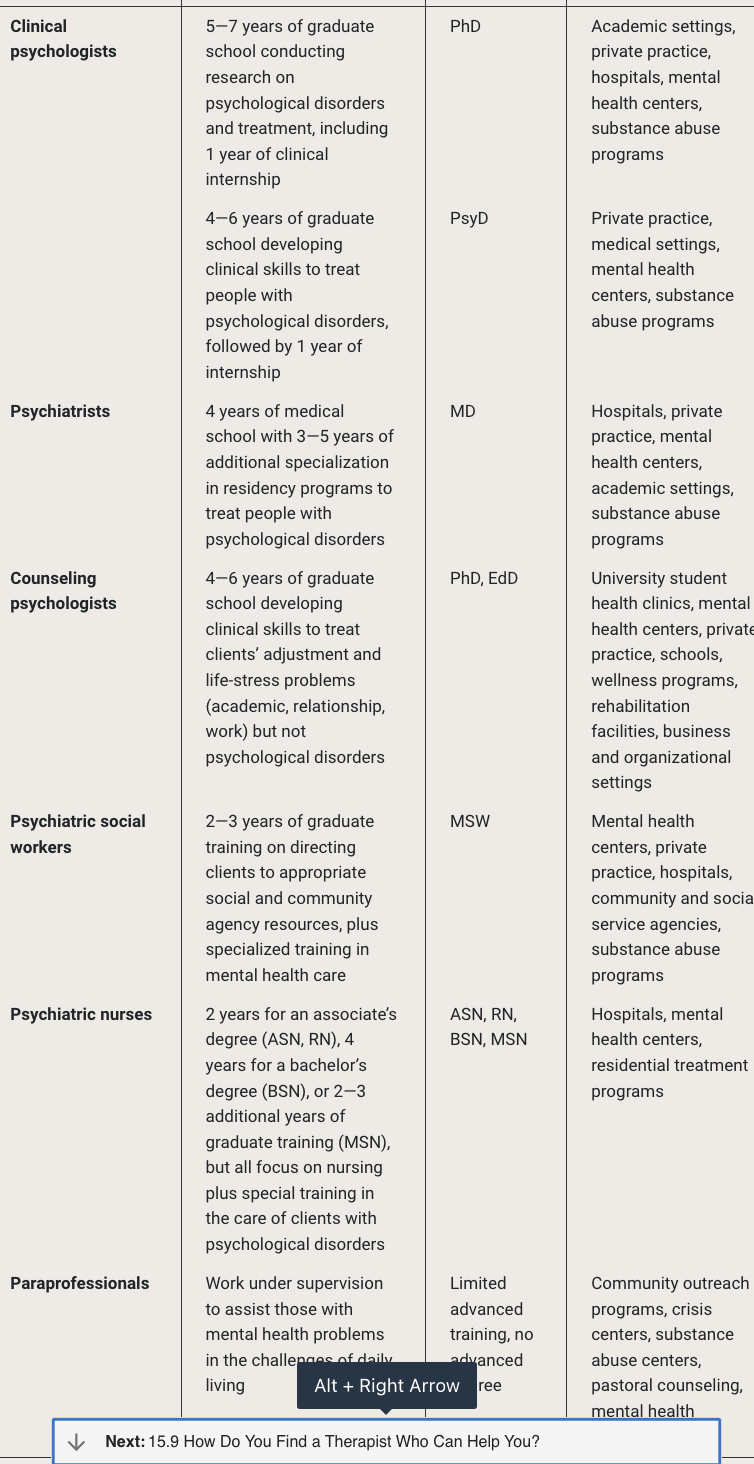
Providers for mental health and their training requirements
see image
technology-based treatments
use of minimal contact with therapists and rely on smartphones, computer programs or internet for treatment
ex. using app to track moods
What does CBT work best to treat
most adult anxiety disorders
panic disorders (in some cases more effective than medication)
systematic desensitization
make a fear hierarchy, expose, fear becomes extinguished
best for phobias
Effective treatment for OCD
CBT
SSRI called clomipramine (not a true ssri but very potent)
Deep Brain Stimulation might be effective for those with no relief from medication or CBT
Addiction treatment success requirements
1) stop using drugs
2) stay drug free
3) be a productive member of family, society, work, etc.
Addiction treatments
CBT
exposure therapy
family and group therapy
growing knowledge of medication to help addiction
challenge: many with addiction also have other psychological disorders
iproniazid
MAO inhibitor
in 1957, used to treat depression
alternative threatments
phototherapy for Seasonal Affective Disorder
gender issues in treating depressive disorders
women are twice as likely to be diagnosed
men might be less likely to seek help
John Cade
found that the urine of manic patients was toxic
believed uric acid might be causing the symptoms of mania
using lithium salts to treat manic patients
lithium is not yet well understood as a treatment
atypical antipsycholotic
medications have been found to be effective in stabilizing moods and reducing mania
combination of lithium and atypical antipsycholotics may improve treatment outcomes
SSRIs and bipolar disorder
generally not recommended
SSRIs and other antidepressants may trigger manic episodes
reserpine
used in the 1950s and before to treat symptoms of schizophrenia
chlorpromazine replaces this
schizophrenia treatment
atypical antipsychotics are first line
because of sideeffects most others are only used in severe cases
schizophrenia treatment must include medications in addition to other therapies
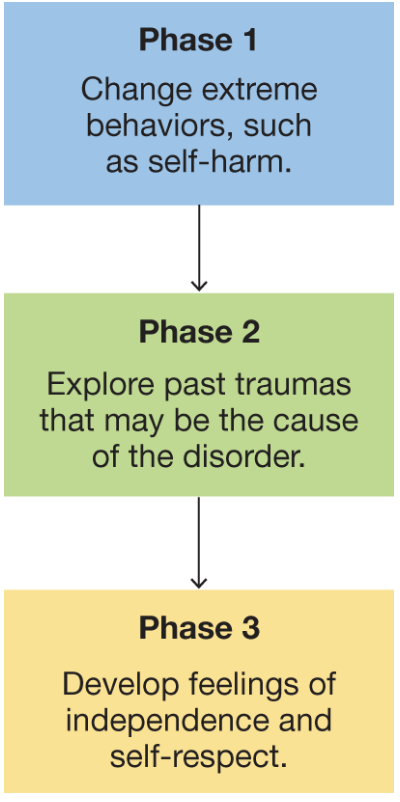
dialectal behavior therapy
created by Marsha Linehan in 1980s
combines elements of CBT with a mindfulness approach based on Eastern meditative practices
patients are seen in both group and individual sessions
three stages in image
used for personality disorders
no other threatment exists for personality disorders
DBT is most successful for borderline personality disorder
why is treatment for personality disorders so difficult
often patients percieve things other than themselves as the problem
cause is unknown
Treating antisocial personality disorder
often patients manipulate therapists
stimulants have been shown to work in short term due to diminished cortical arousal
does not work in long term
conduct disorder
childhood condition known to be a precursor to antisocial PD
Treatment for ADHD
methyphenidate (Ritalin)
only barely increases positive behaviors → significantly decreases negative ones
Adderall
parents are often pressured to medicate children
parents then pressure physicians
bahvior therapy may be the most effective in the long run
Issues with medication and ADHD
increased risk of substance abuse issues
medication effects may not be long-term
Autism spectrum disorder treatment
ASD children are less likely to respond to rewards
Applied Behavioral Analysis (AVA)
uses operant conditioning
requires a minimum of 40 hours per week
speculation on brain functions which could cause symptoms of autism
subsyndromal disorder
a level below the DSM5 diagnostic criteria but still problemsome