Chemistry - Unit 8 Organic IUPAC
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
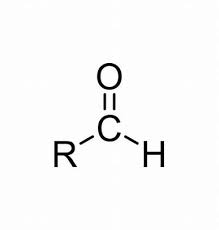
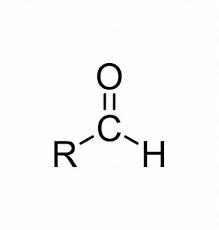
Aldehyde
C=O (carbonyl at the end of the carbon chain) (Class)
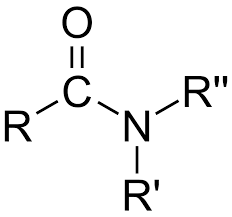
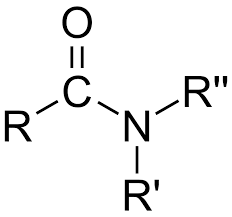
Amide
-CONH2, -CONHR, -CONR2 (Class) bonded to carbon chain after
Amine
-NH2 (Class) no carbon bond after

Phenyl
C6H5- (Functional Group for benzene)
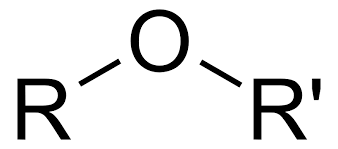
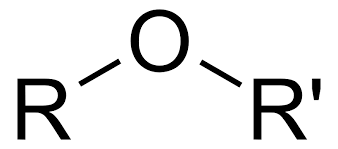
Ether
-OR (alkoxy group) (Class)are in the middle of the carbon chain
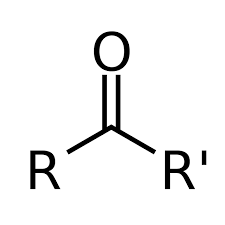
Ketone
-C=O (carbonyl group in the middle of a carbon chain) (Class)
alkenyl
C=C bond (Functional Group for alkenes)
Alkynyl
Carbon-to-carbon triple bond (functional group for alkynes)
Carbonyl (A)
CHO (functional group for aldehyde)
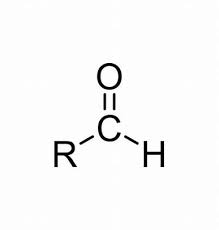
Carbonyl (K)
RCOR' functional group for ketones
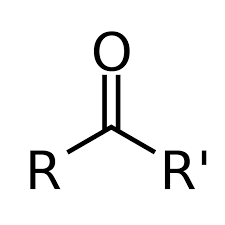
Carboxyl acid
COOH (class ) end of the chain
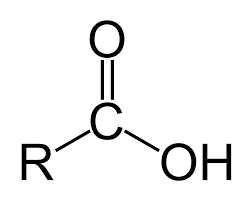
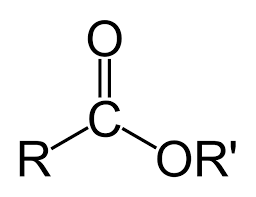
Carboxyl
COOC, RCOOR (functional group at the end of carbon chain)
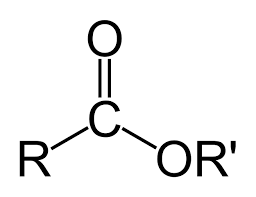
Alkoxy
ROR' (functional group for ethers)
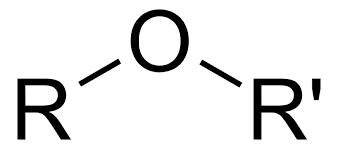
Amido
CONH2 (functional group for amide)
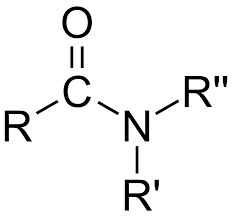
Amino
-NH2 (functional group for amine)

-oxyalkane
ROR (IUPAC suffix for ether class)
-al, -anal
CHO (IUPAC suffix for aldehyde)
-one, -anone
RCOR (IUPAC suffix for ketone’s)
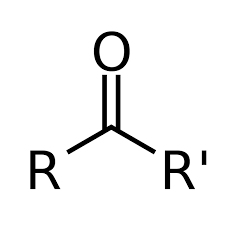
-oic acid, anoic acid
COOH (IUPAC suffix for carboxylic acid)
-anoate
COOC, RCOOR (IUPAC suffix for carboxyl ester)
-anamide
CONH2 (IUPAC suffix for amide)
-anamine
NH2 (IUPAC suffix for amine)

amino-
NH2 (IUPAC prefix for amine)

how are esters formed
esters form when the alkyl group of an alcohol replaces the hydrogen of a carboxylic acid in a condensation reaction