Module 2: Sampling (marj)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Population
The set of all individuals in a particular study (Gravetter & Wallnau, 2017)
Sample
A set of individuals selected from a population, usually intended to represent the population in a research study (Gravetter & Wallnau, 2017)
Sampling
• It is measuring a small portion of something and then making a general statement about the whole thing.
• In actual research, a small portion of a large population is studied and the results of such a study are alluded to the whole population.
Parameter
It refers to the characteristic that summarized the data of a population.
Statistics
It refers to the data that describes a sample.
concept of estimate
The term statistics is synonymous to the?
1. Sampling enables the investigation of a large population
2. Sampling reduces cost of research
3. Sampling enables the completion of a study within a reasonable period of time
4. Sampling makes data more relevant and accurate
5. Sampling avoids consuming all the sources of data
Why do we need sampling? (Purposes and Advantages)
Sampling enables the investigation of a large population
The universe or population to be studied may be too large, or even infinite, that it is almost impossible to reach all the persons in the population.
Hint: Purpose or Advantage of Sampling
Sampling enables the completion of a study within a reasonable period of time
When there is sampling, the researcher deals with fewer respondents and so the work is finished very much sooner than when he deals with the whole population.
Hint: Purpose or Advantage of Sampling
Sampling reduces cost of research
Because sampling makes possible the use of a small portion of a study population, the cost of research may be reduced to a level that the researcher can afford.
Hint: Purpose or Advantage of Sampling
Sampling reduces cost of research
We can make generalization without gathering data from the whole population
Hint: Purpose or Advantage of Sampling
Sampling makes data more relevant and accurate
If there is no sampling, the collection of data may take a very long period of time, so much so that by the time the gathering of data has been completed, the first data gathered may already be obsolete and are no longer relevant and accurate.
Hint: Purpose or Advantage of Sampling
Probability Sampling
Non-probability Sampling
General Types of Sampling
Accidental sampling/Convenience sampling
Quota Sampling
Snowball Sampling
Purposive Sampling/Judgment Sampling
Types of non-probability sampling
Purposive Sampling/Judgment Sampling
A type of Non-probability Sampling that:
Is done based on previous ideas of population composition and behavior. An expert with knowledge of the population decides which units in the population should be sampled. In other words, the expert purposely selects what is considered to be a representative sample.
It is subject to the researcher’s biases.
Snowball Sampling
A type of Non-probability Sampling that:
New units are recruited by other units to form part of the sample. It can be a useful way to conduct research about people with specific traits who might otherwise be difficult to identify (e.g., people with a rare disease).
Quota Sampling
A type of Non-probability Sampling that:
Many sectors of the population may be represented in the sample but there is no proportional representation
Accidental Sampling/Convenience Sampling
A type of Non-probability Sampling that:
The persons included in the sample are those who are met by chance or accidentally met by the researcher interviewer.
Simple Random Sampling
Systematic Random Sampling
What are the Types of Probability Sampling?
Simple Ranndom Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
• Every member’s name of the population is included in a list (may be manual or automated), and samples are chosen randomly.
Cluster Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
Is used when the total population of a big geographical area is studied.
Then, random selection of clusters is done to choose the sample of the study.
Simple Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
• More appropriate to use if the population is more or less similar with respect to the characteristics of the population.
Stratified Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
Is used when the population is segmented into differential groups or sections called stratifications or strata (singular: stratum).
Systematic Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
• Being used when the elements or subjects in the study are arrayed or arranged in some systematic or logical manner such as alphabetical arrangement, residential or house arrays, geographical placement etc.
Multistage (Cluster) Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
Is used especially when the subjects of an investigation are scattered all over a big geographical area.
Stratified Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
• The differentiated groupings may be horizontal or vertical.
• Selection is done in every stratum or section using either pure random sampling or systematic random sampling.
Multistage (Cluster) Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
Is best used if the population list is available and if the population covers a wide area.
Simple Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
Is easy to understand and apply. However, it may become difficult to utilize when dealing with a large population. The sample chosen may be distributed over a wide geographic area.
Multistage (Cluster) Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
Is a combination of cluster sampling and stratified random sampling. Sample samples are chosen by repeatedly doing cluster sampling until you reach the desired number. Stratified random sampling may be the last step of this method.
Systematic Random Sampling
A type of Probability Sampling that:
• Every nth sampling unit in the sampling frame is chosen to be included in the sample.
• A starting point is selected at random
Sampling Interval
“K” means?
Population
“N” means?
sample size
“n” means?
margin of error
“e” means?
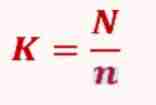
What is the formula of K = Sampling Interval

What is the formula of strata?
Sampling error
It is the difference between measurements from a sample and corresponding measurements from the respective population. It is caused by the fact that the sample does not perfectly represent the population.
Non-sampling error
It is the result of poor sample design, sloppy data collection, faulty measuring instruments, bias in questionnaires, and so on.
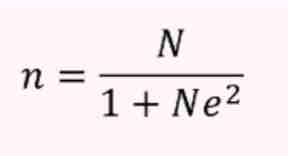
What is the formula of n=Sample Size?