Physical assesment Exam 2
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Amblyopia
lazy eye, one eye has poorer vision than the other
astigmatism
irregular curvature of cornea or lens
light is not focused on the same plane
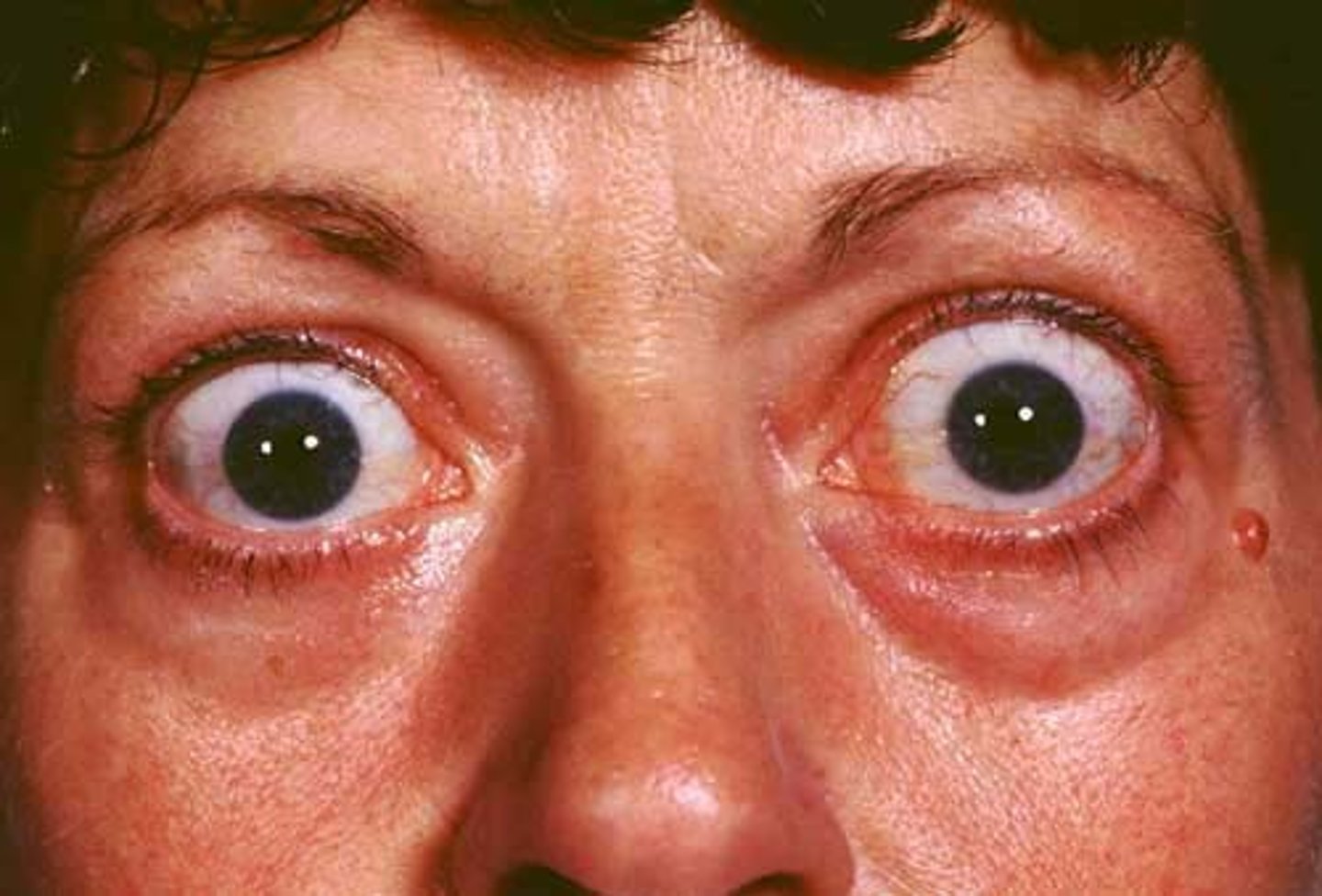
exophthalmos
abnormal protrusion of the eyeball
hyperopia
farsightedness: trouble seeing close up
miosis
small constricted pupil
seen with horner syndrome
mydriasis
dilated pupils
O.D
right eye
O.U
both eyes
O.S
left eye
presbyopia
happens with old age
loss of eye to accomodate
scotoma
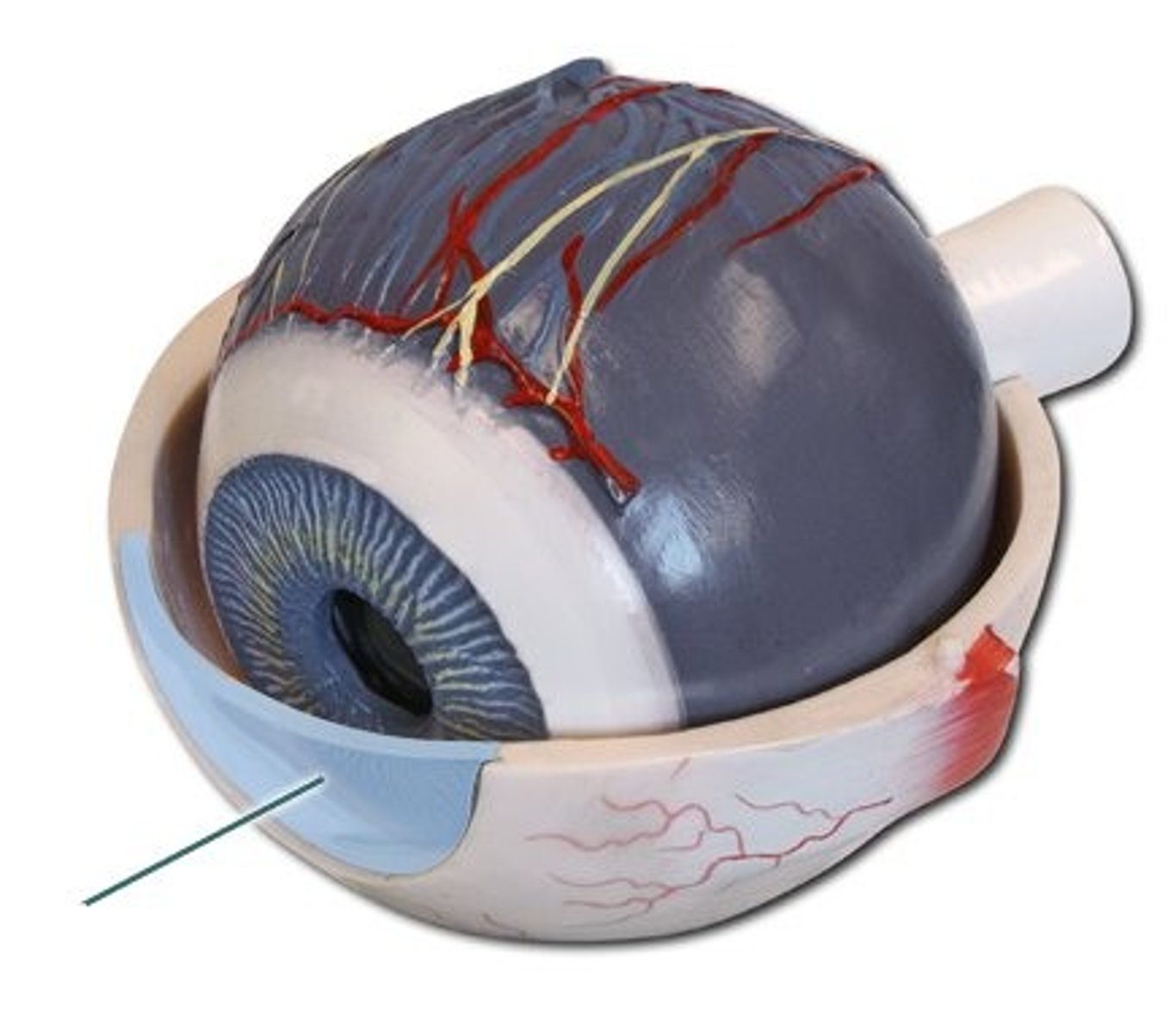
bulbar conjunctiva
covers the sclera
keeps eye lubricated and protects against microorganisms
choroid
middle layer of the eye that contains blood vessels
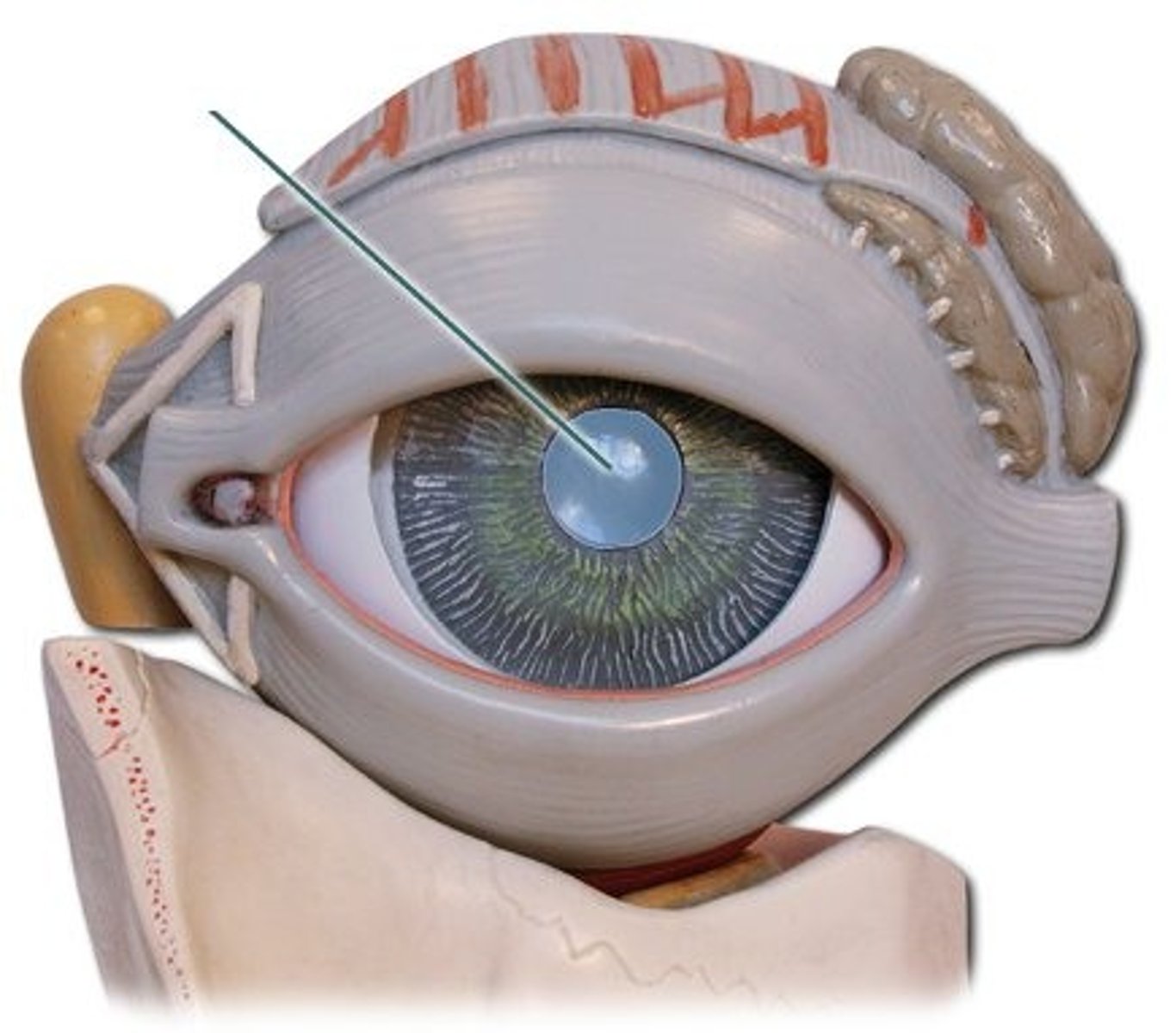
cornea
clear/dome like
protects the eye
bends/focuses light onto retina
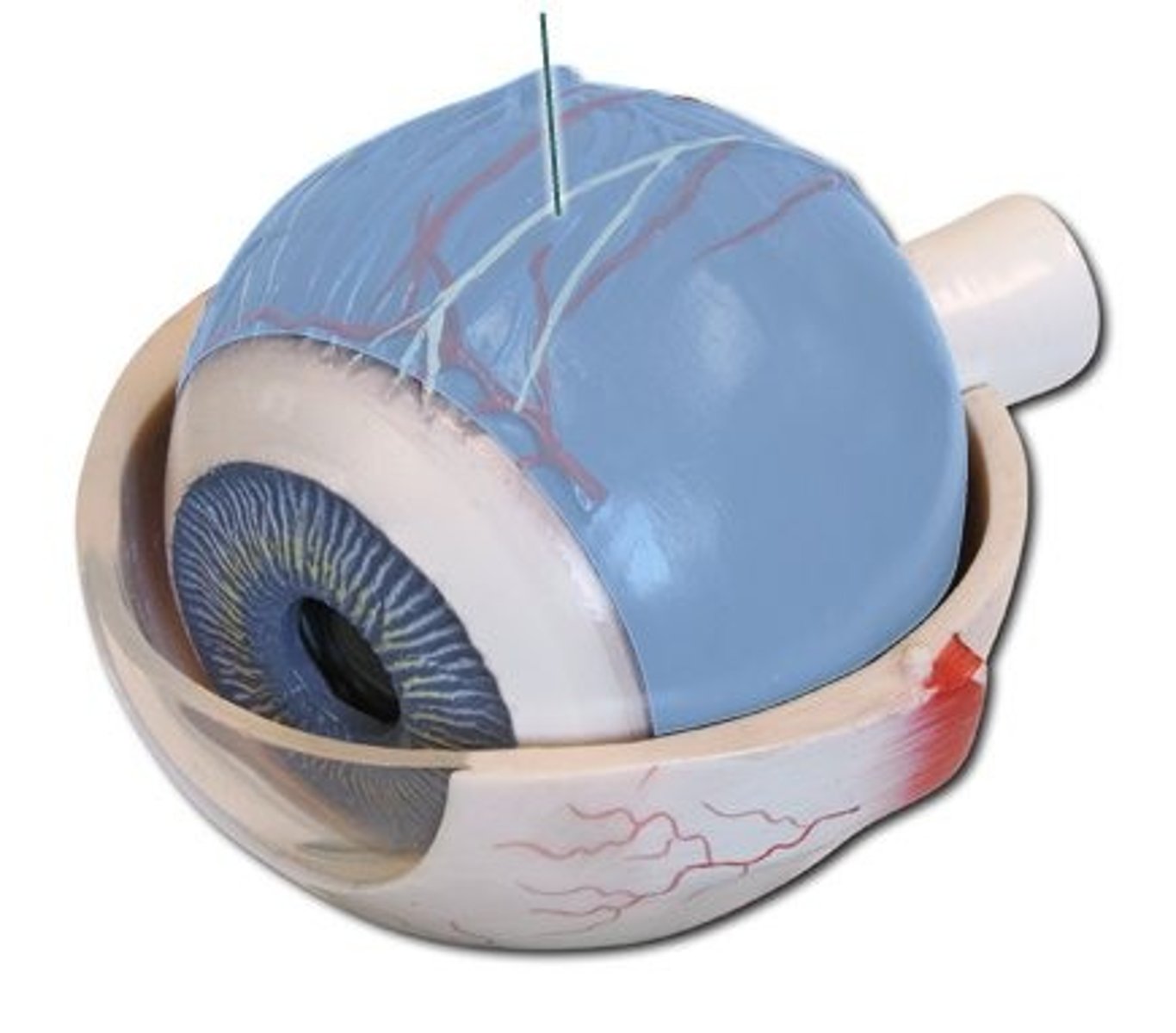
extraocular muscles
control eye movement
MR, SR, IR, LR, SO, IO
CN III lesion: MR/SR/IR/IO
CN IV lesion: SO
CN VI lesion: LR
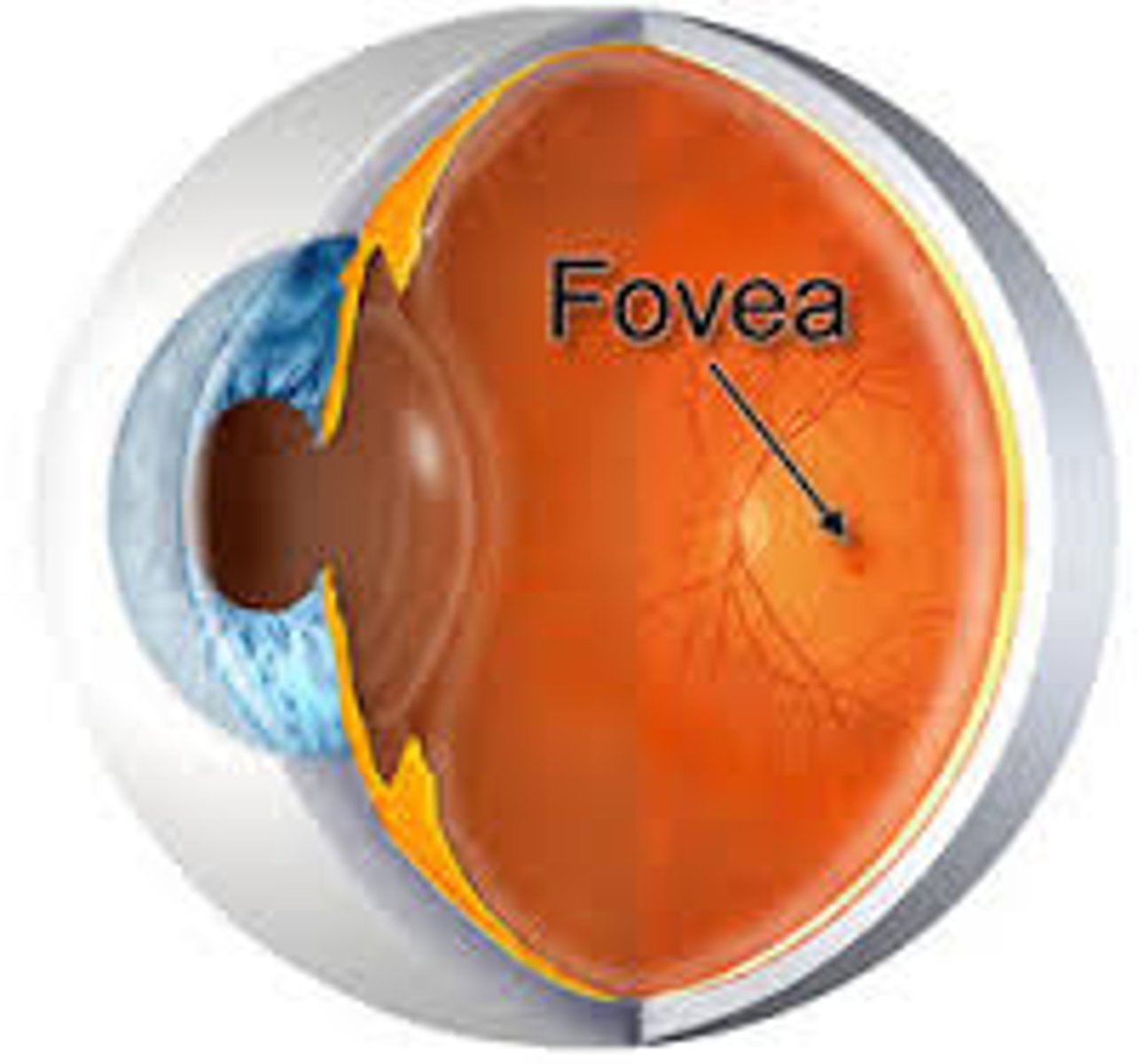
fovea
sharpest point of vision
foveal light reflex: indicated a healthy eye
iris
EYE COLOR
dilator m: makes pupils bigger
sphincter m: makes pupils small
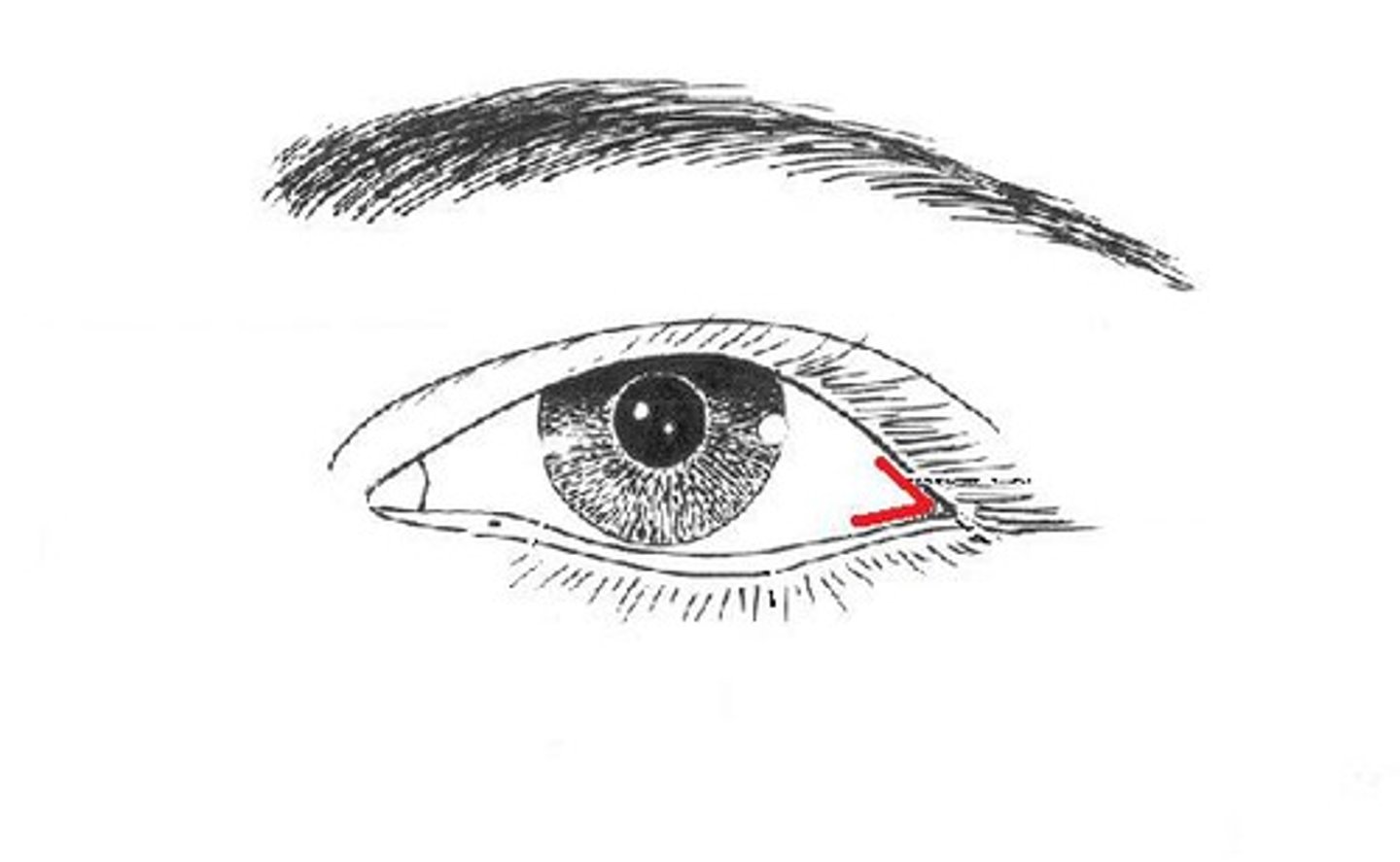
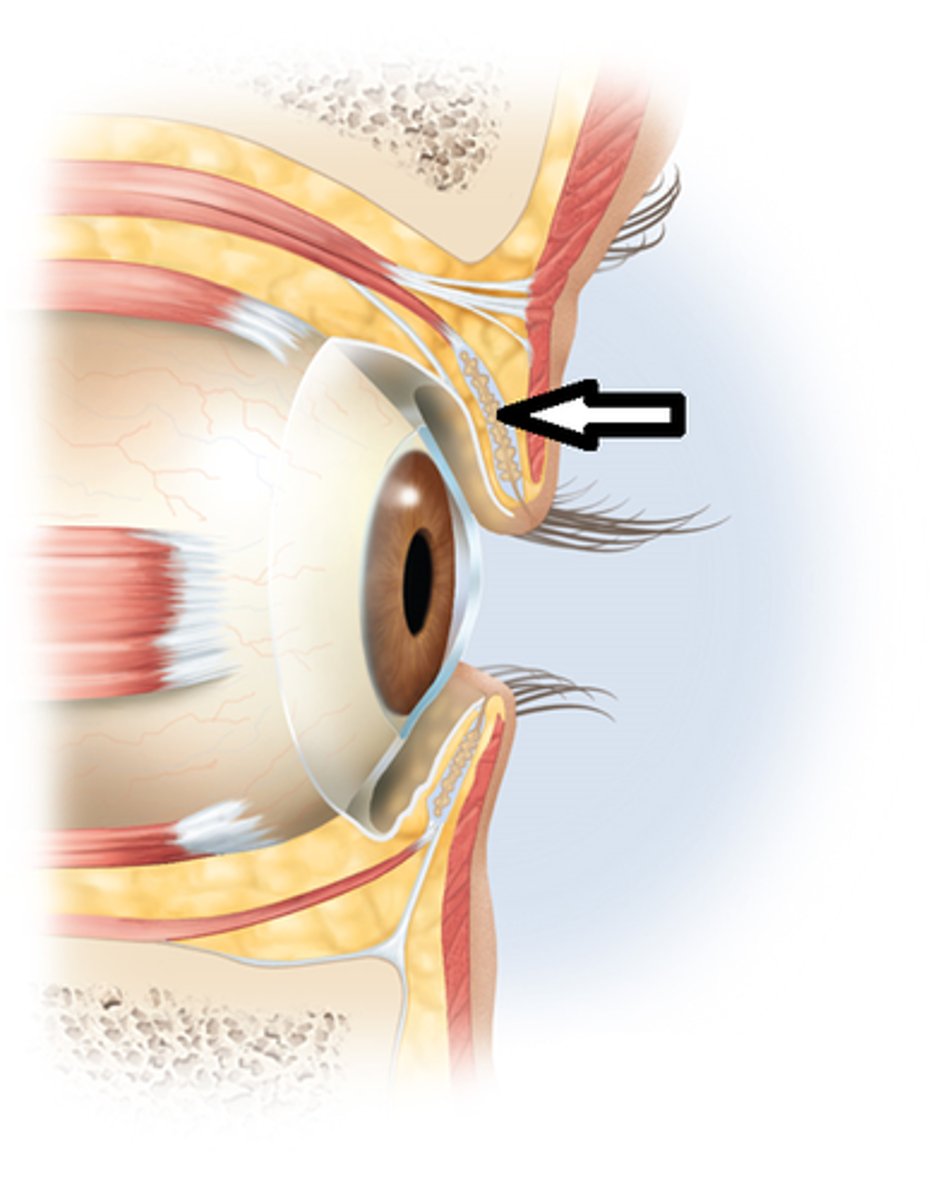
Lateral canthus
corner of eye-supports lower eyelid
helps eye blink and protects eyes surface
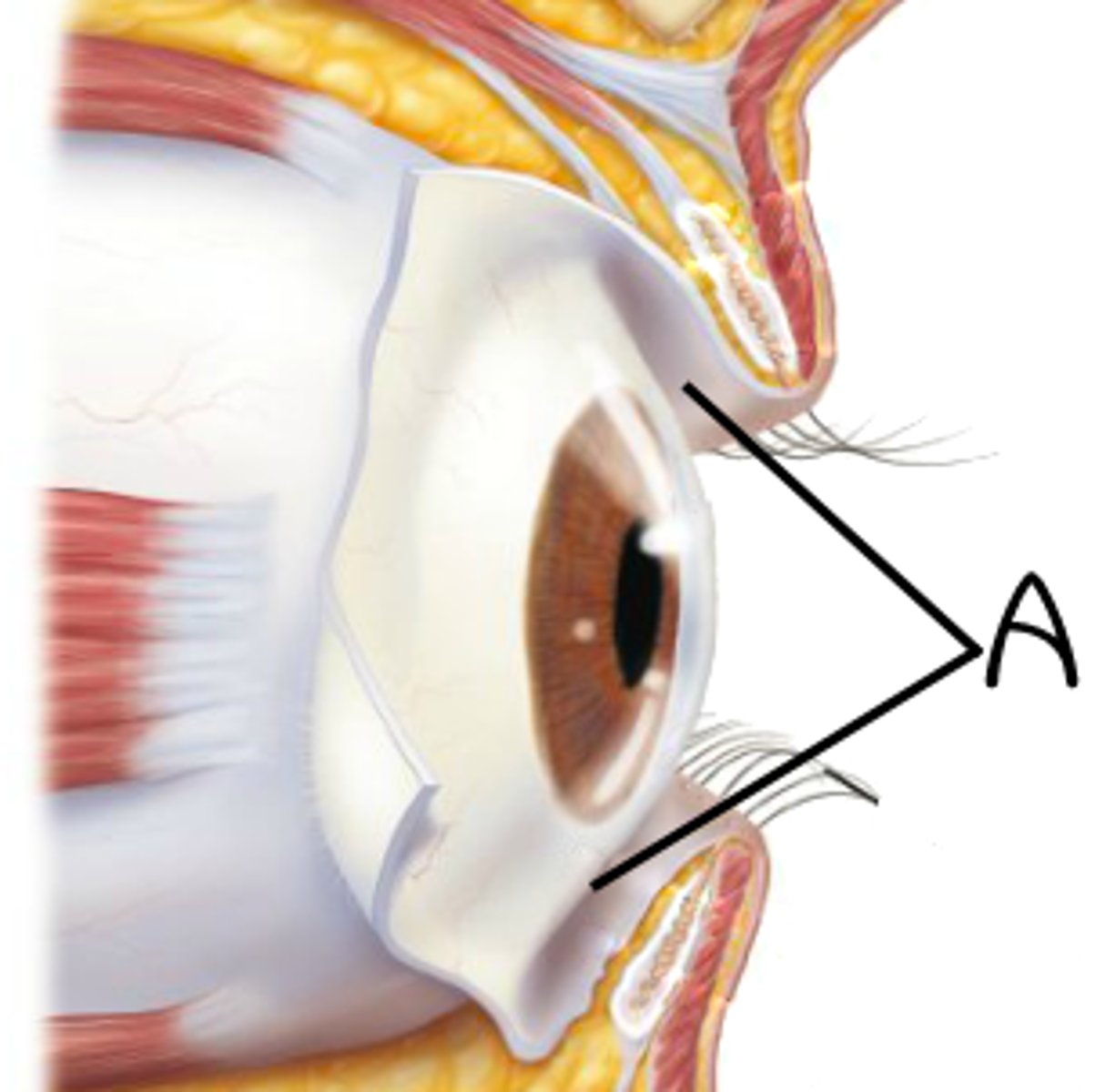
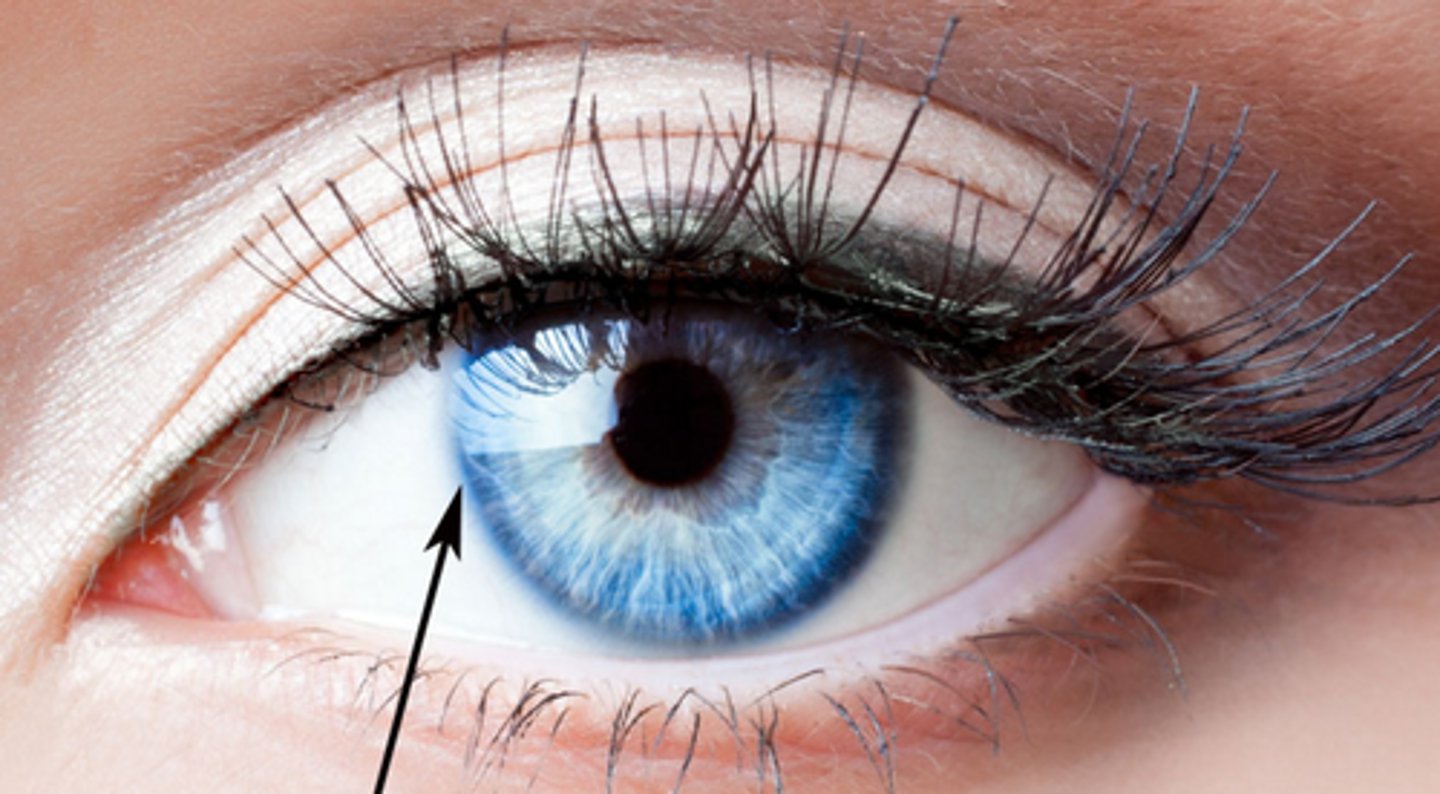
limbus
border between cornea and sclera
bluish outline

lens
focuses light onto retina
macula
central vision
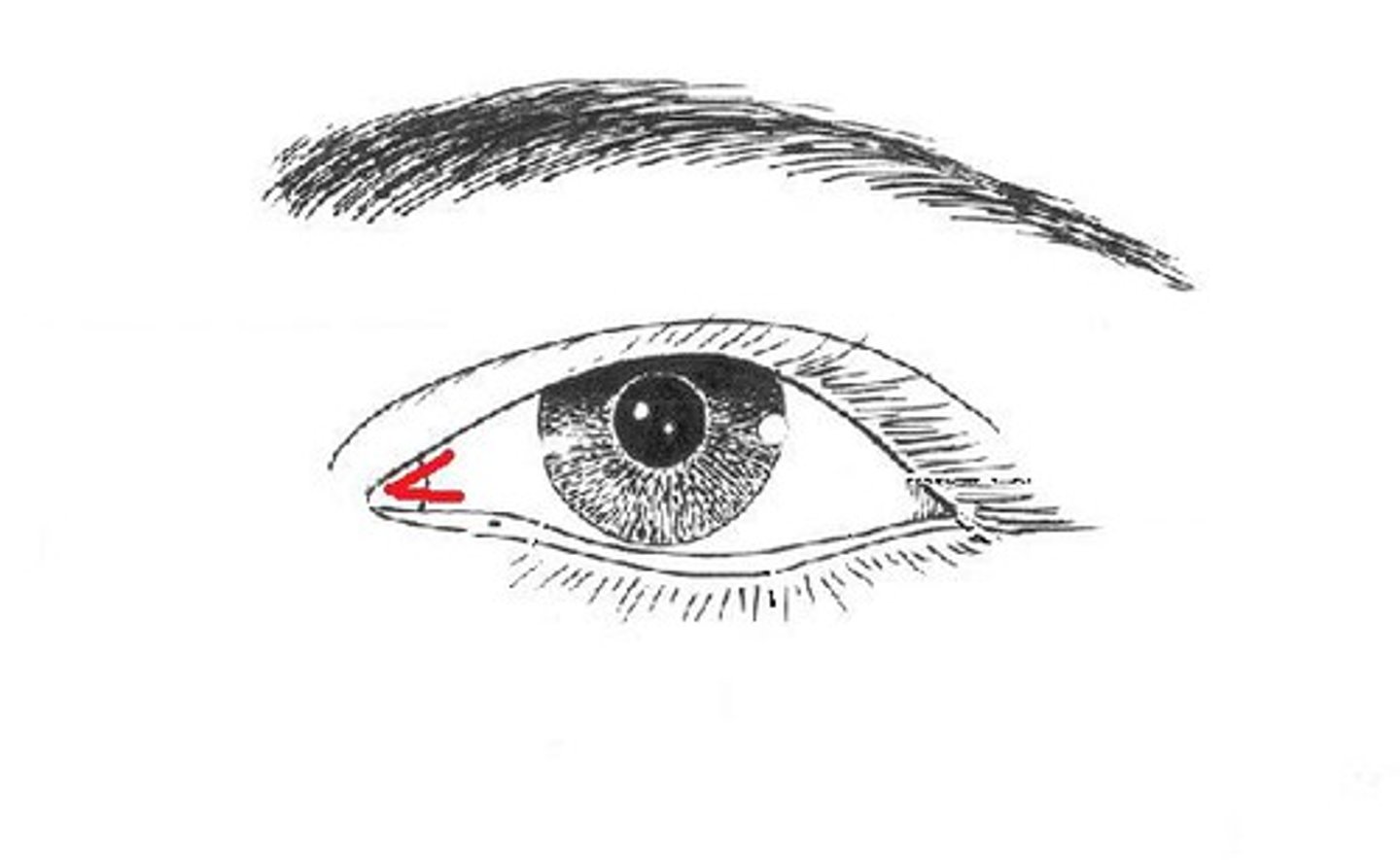
medial canthus
inner corner of the eye
assists in drainage of lacrimal sac
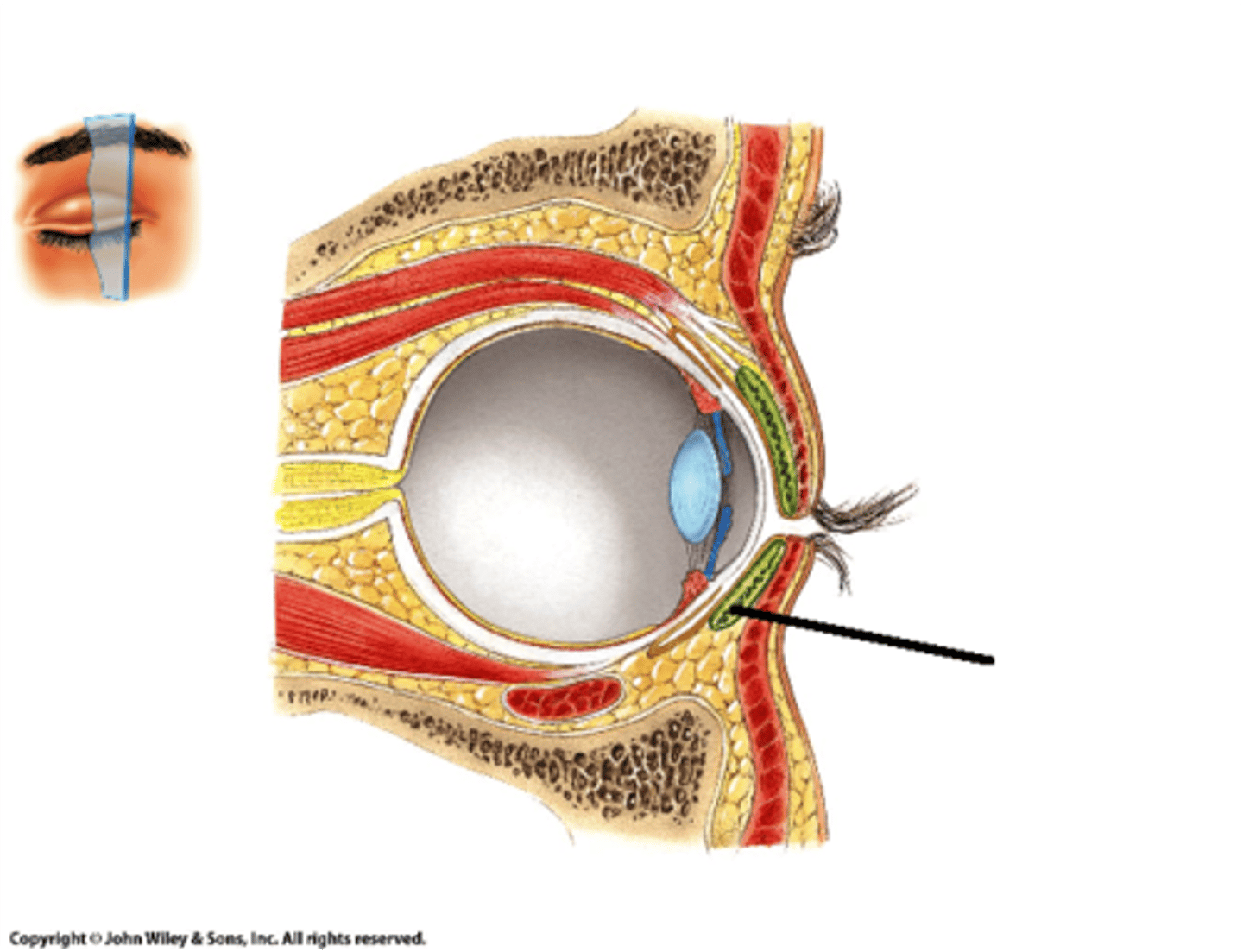
meibomian glands
sebaceous oil glands in eyelids and stops tears from evaporating
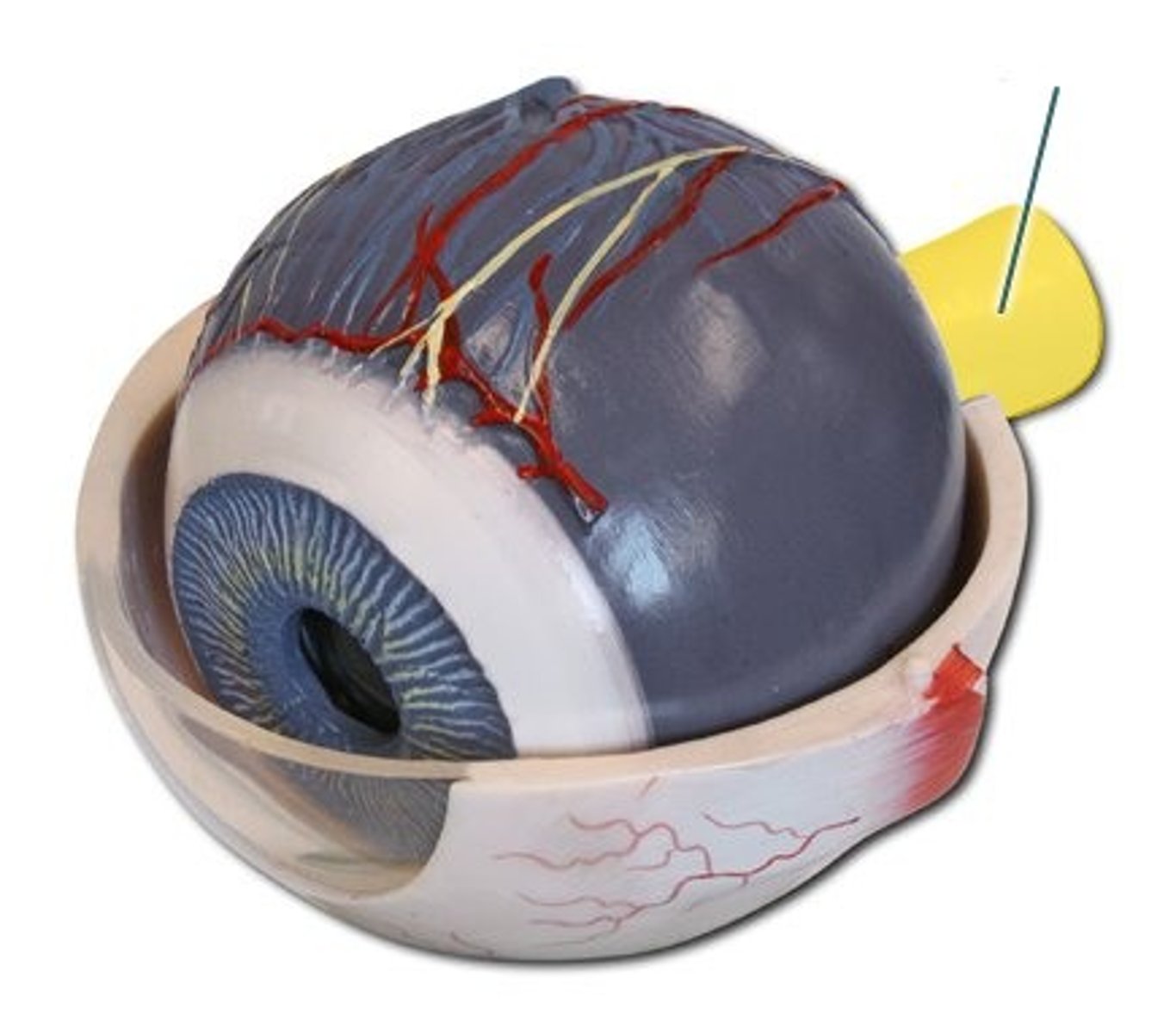
optic nerve
carries signals to the brain
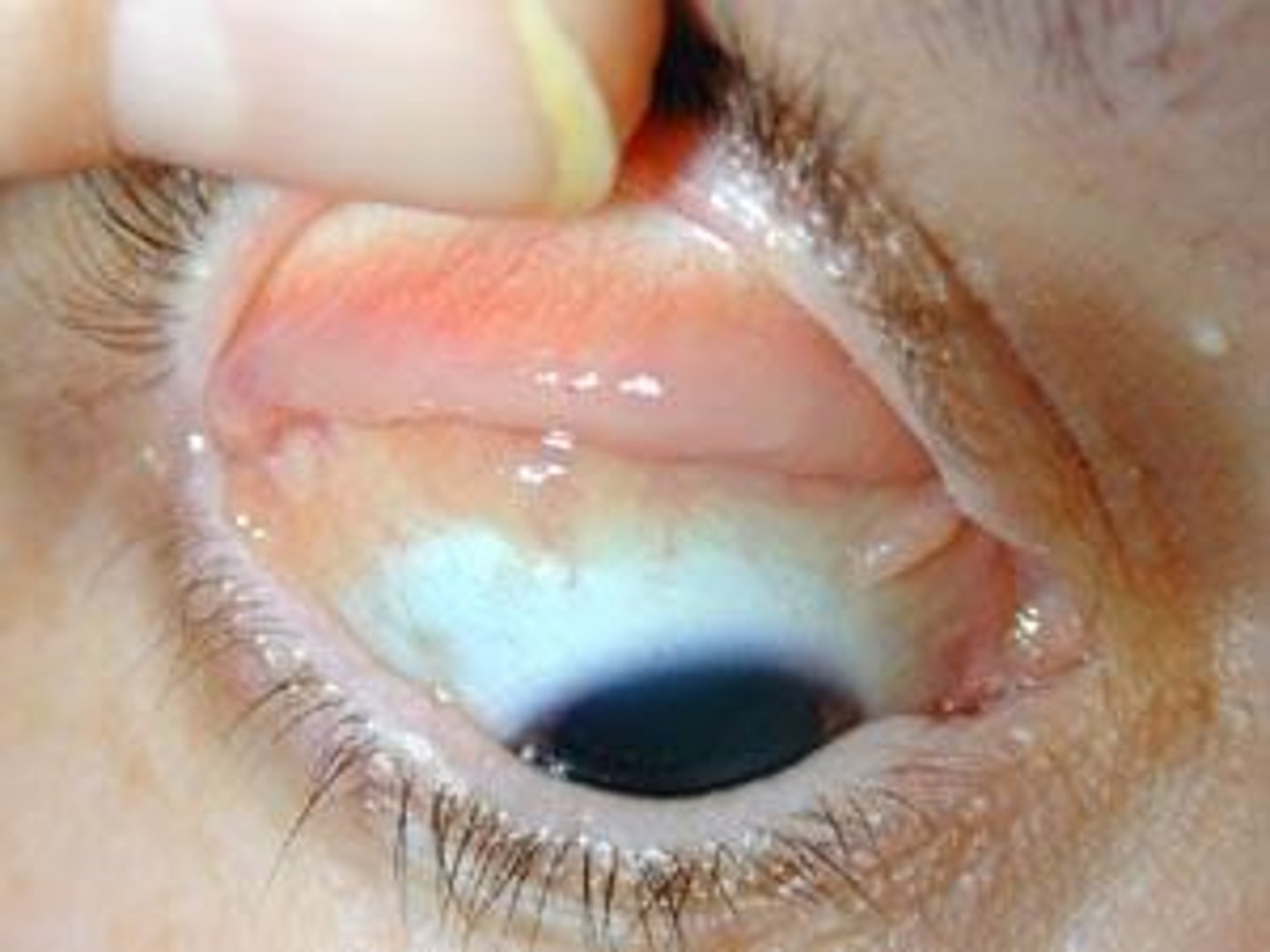
palpebral conjuctiva
covers inside of eyelids and keeps it lubricated
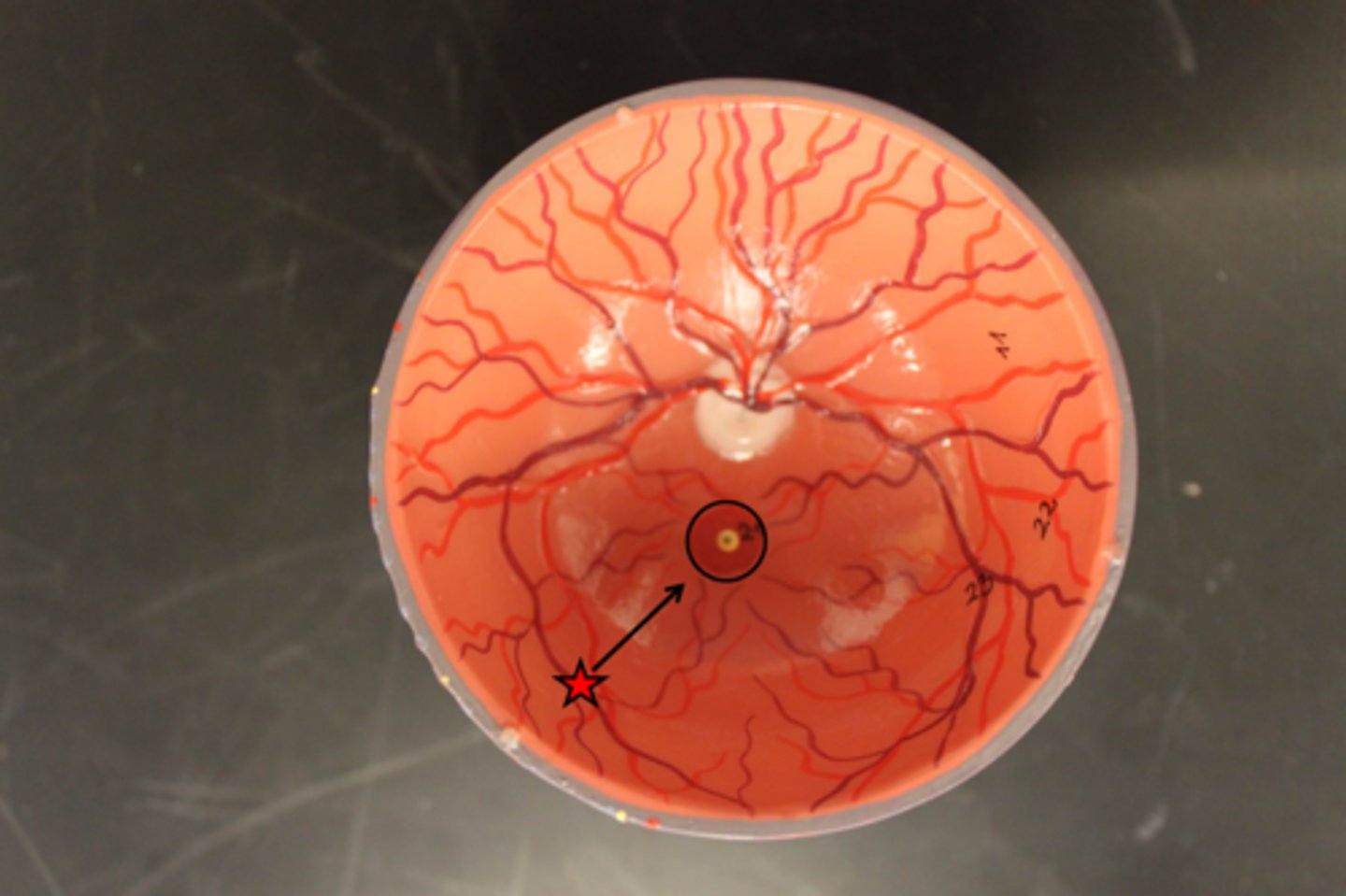
optic disc
Region at the back of the eye where the optic nerve meets the retina. It is the blind spot of the eye because it contains only nerve fibers, no rods or cones, and is thus insensitive to light.
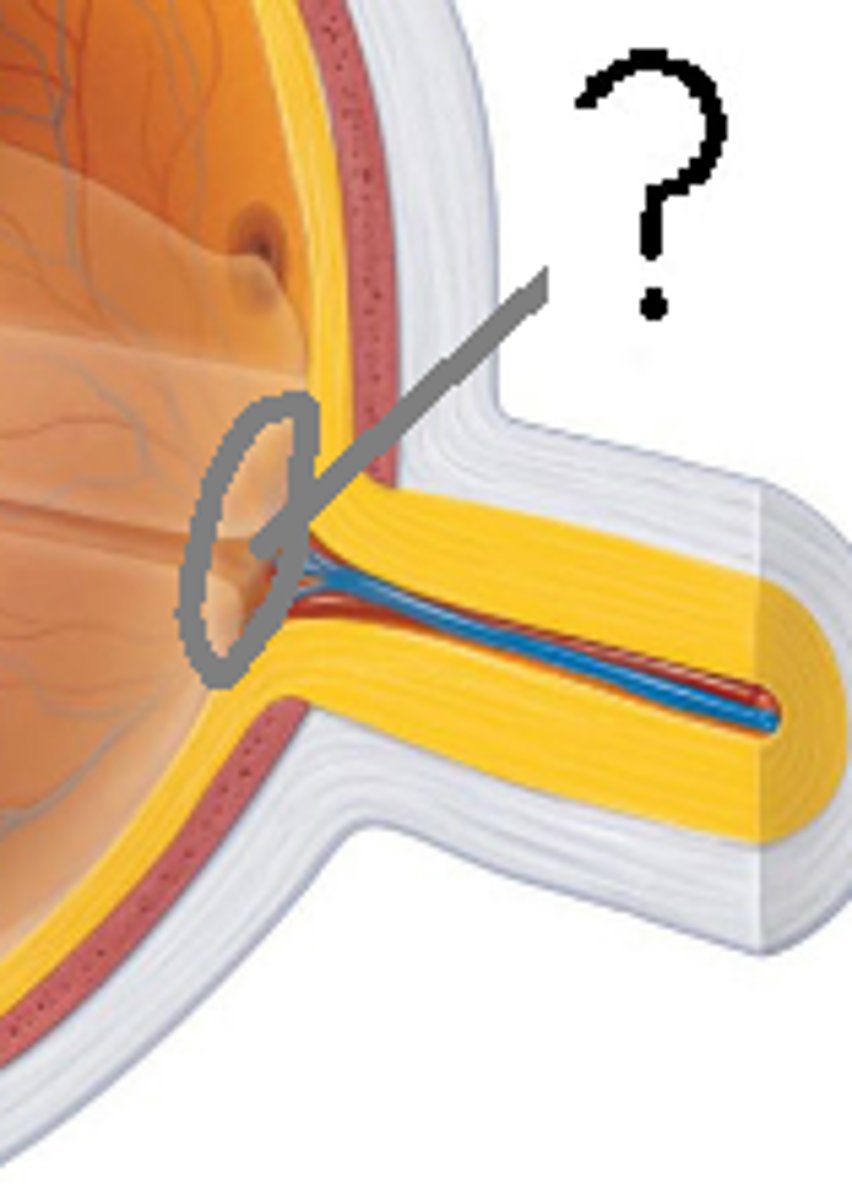
pupil
absence of tissue in center of iris
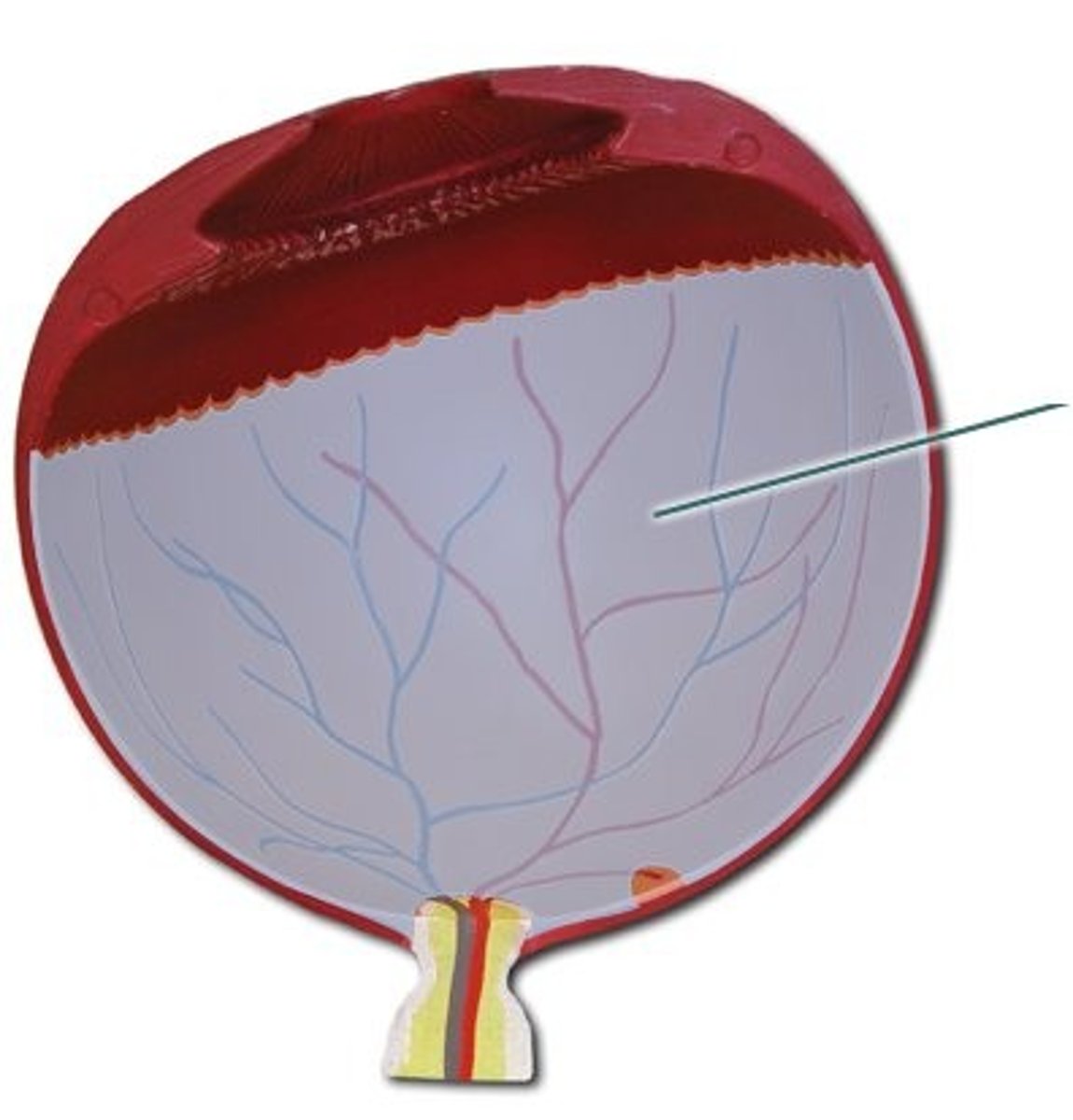
retina
neural tissue that carries messages to the brain
innermost layer
scerla
protects and maintains shape of the eye
tarsal plate
main structural component of eyelids
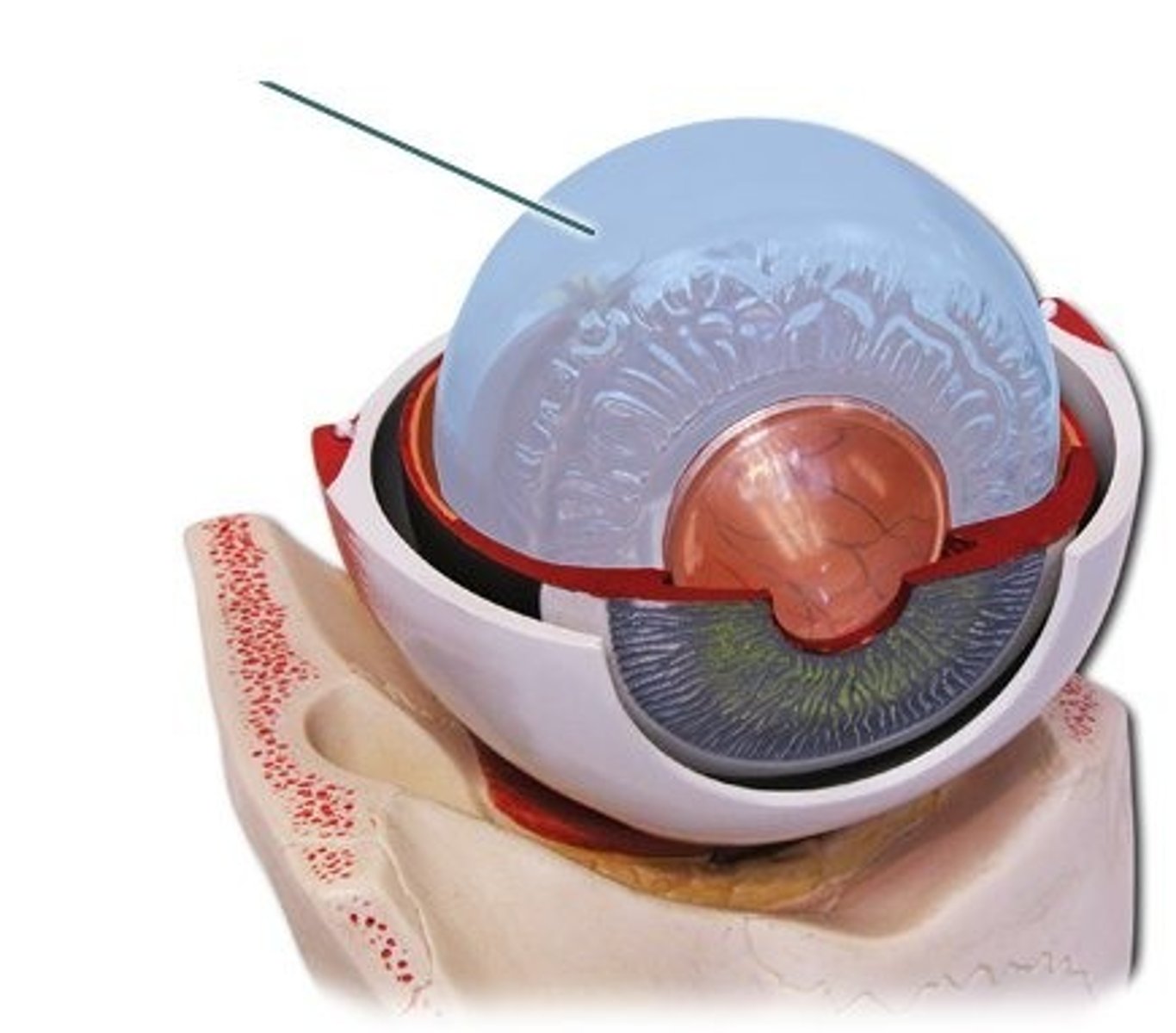
vitreous body
back of the eye that contains vitreous humor
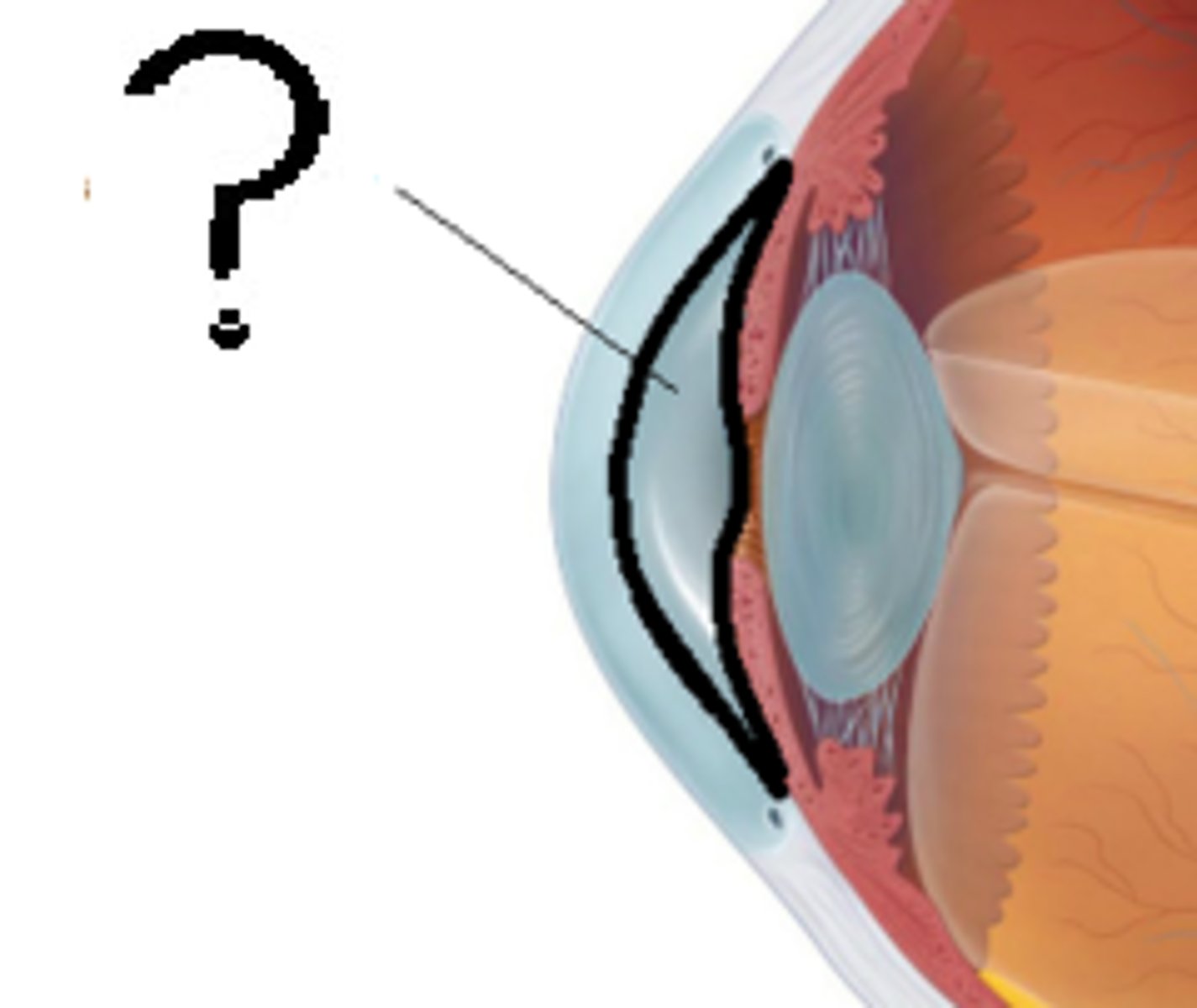
anterior chamber
fluid-filled space between the cornea and iris
contains aqueous humor
Lacrimal system pathway: TEARS drainage
tears secreted by lacrimal duct and drained :
punctum> canaliculi > lacrimal sac > nasolacrimal duct> into nose/back throat
Pathway of aqueous humor
anterior segment (ciliary body) > posterior chamber > anterior chamber > drained via trabecular meshwork
Visual pathway steps
pupil > retina > stimulates photoreceptors in retina > travels to optic nerve > signals carried to the brain
Near reaction
3 parts relfex that brings near objects into focus through lens thickening, pupillary constriction and inward rotation of eyes
Anisocria
unequal pupil size
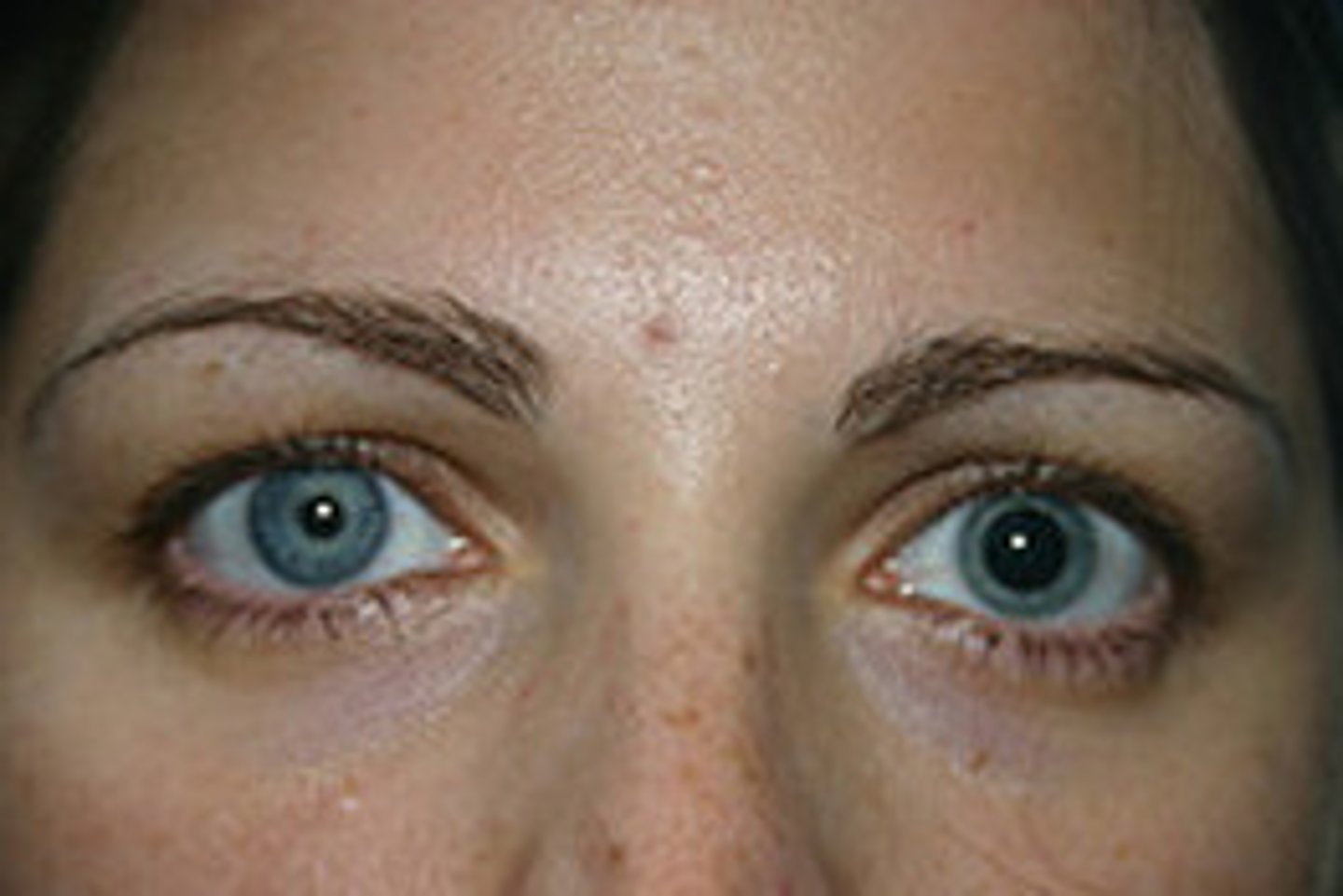
strabismus
misalignment of the eyes
Dyschromotopsia
color blind
deutan
color blind shifted more towards red
protan
color blind shifted towards green
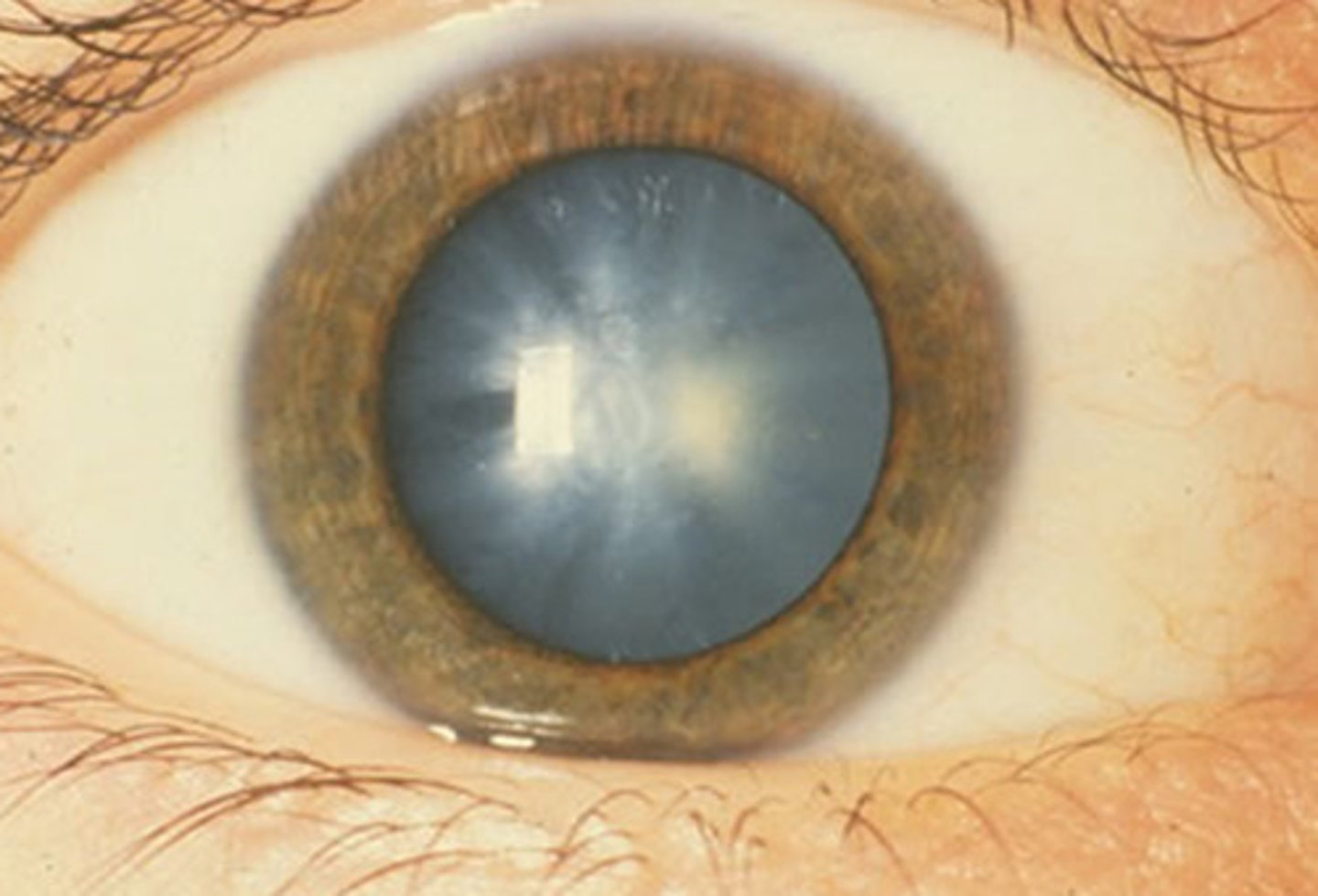
cataracts
clouding of the lens
natural age related process
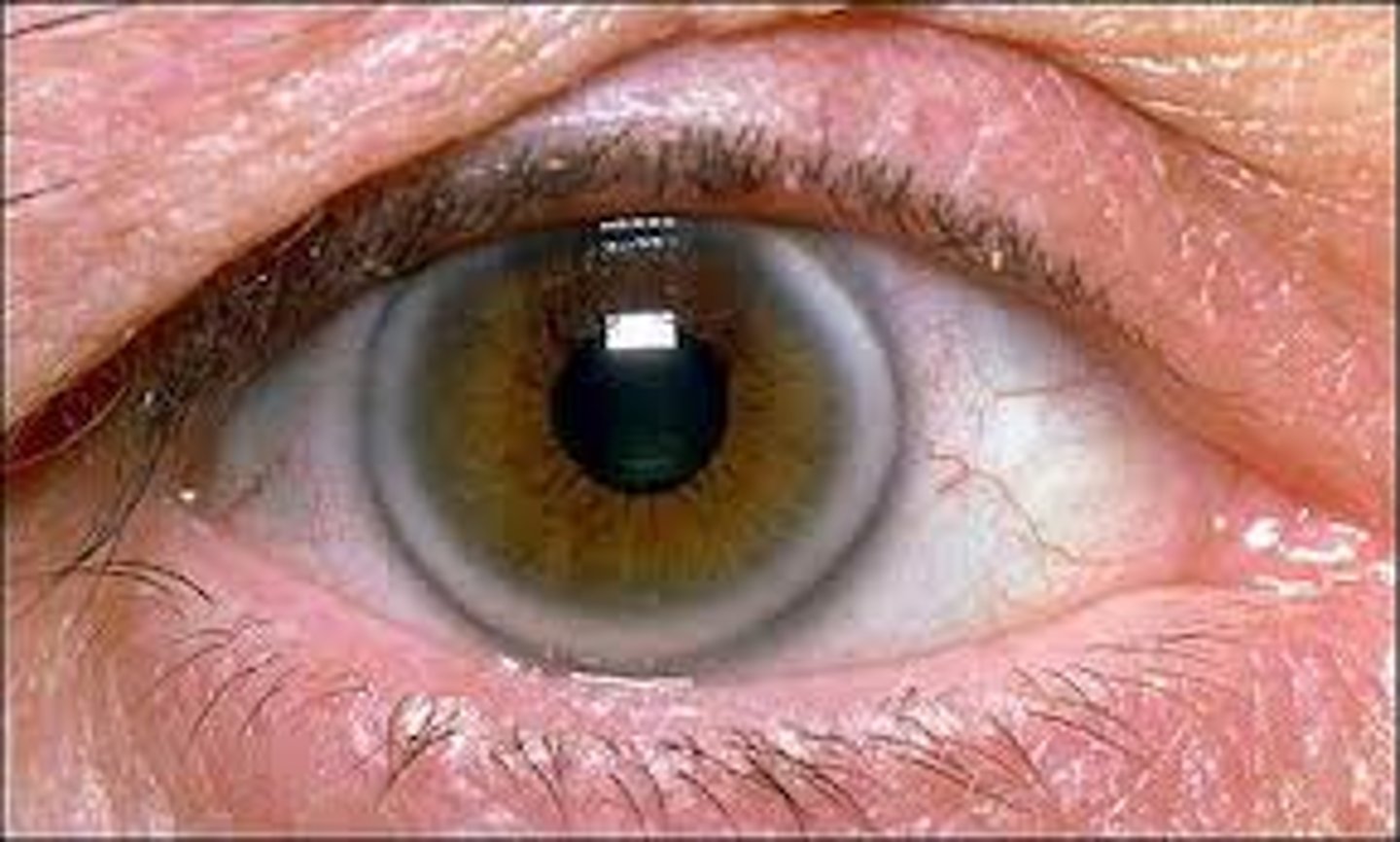
corneal arcus
lipid deposits
very common in aging population
no work up needed
intraocular pressure (IOP)
determined by rate at which aqueous humor is being made and drained
Normal IOP
10-21 mmHg
methods to test IOP
goldmann applanation tonometry( gold standard)
icare tonometer(best for kids)
Tono-pen (common in ED)
exotropia
condition where one or both eyes turn inward " wall-eyed appearance"
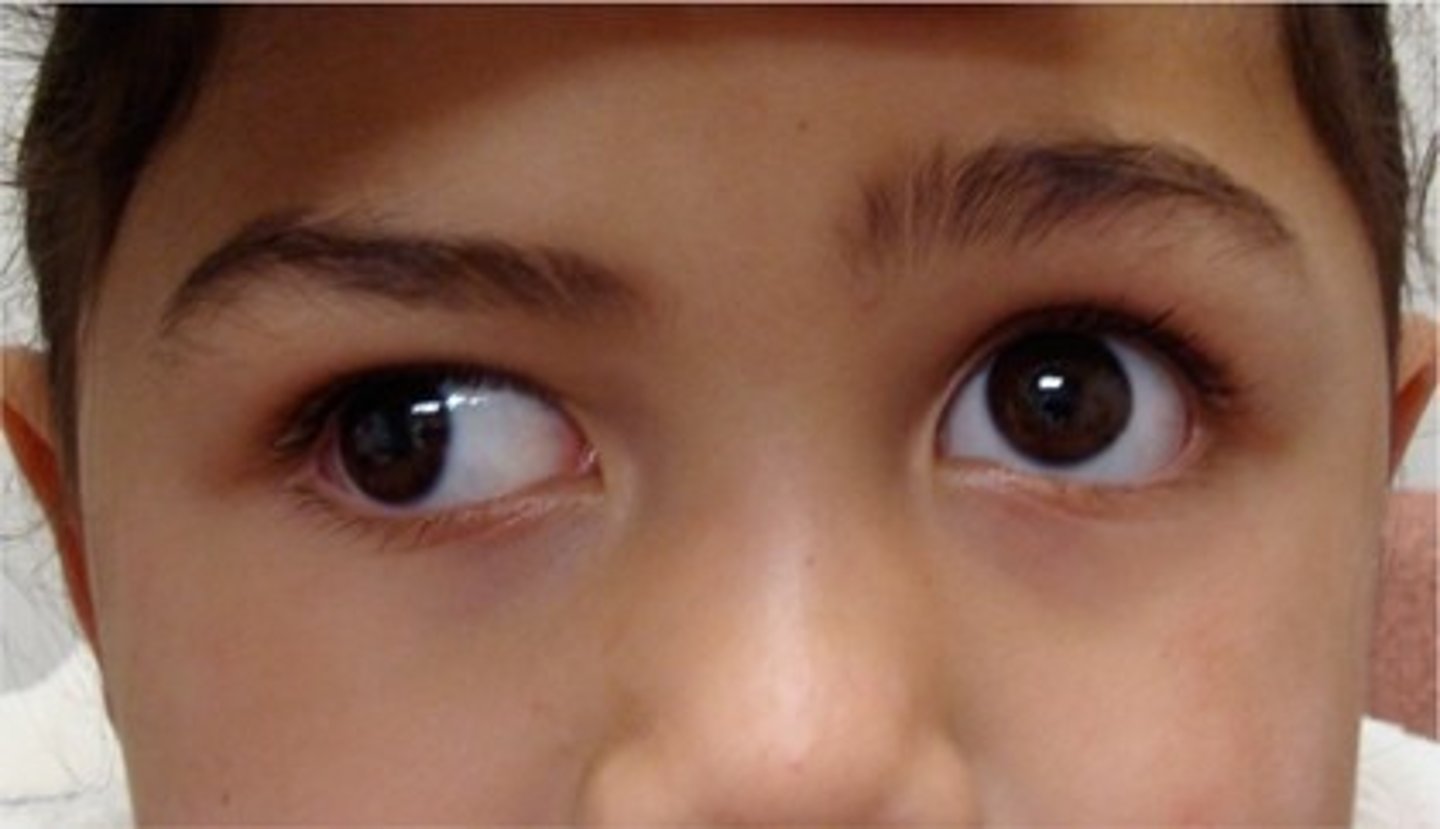
esotropia
inward turning of the eye
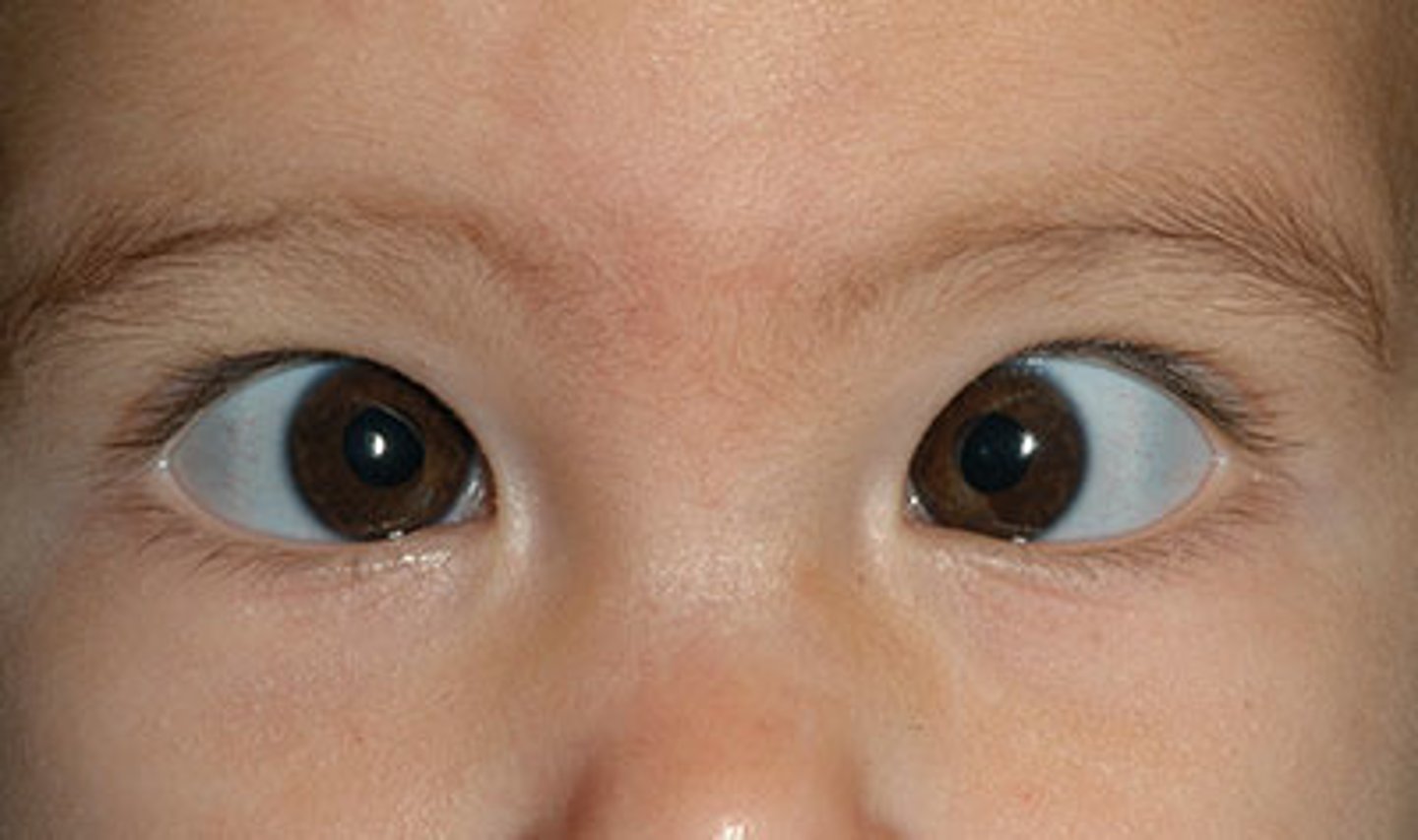
pinguecula
harmless, yellowish white bump that develops on the white part of the eye
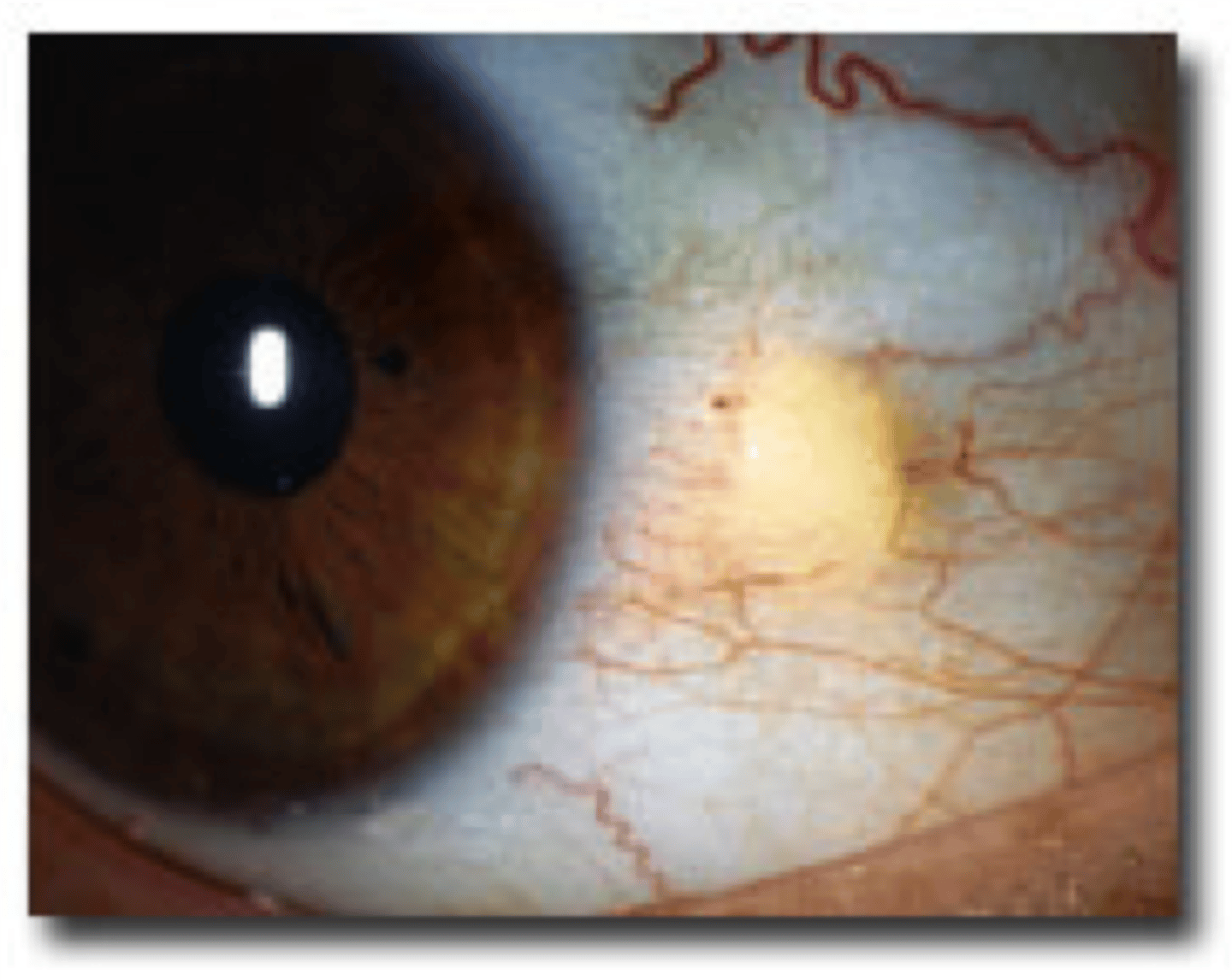
pterygium
thin tissue growing into the cornea from the conjunctiva, usually caused from sun exposure
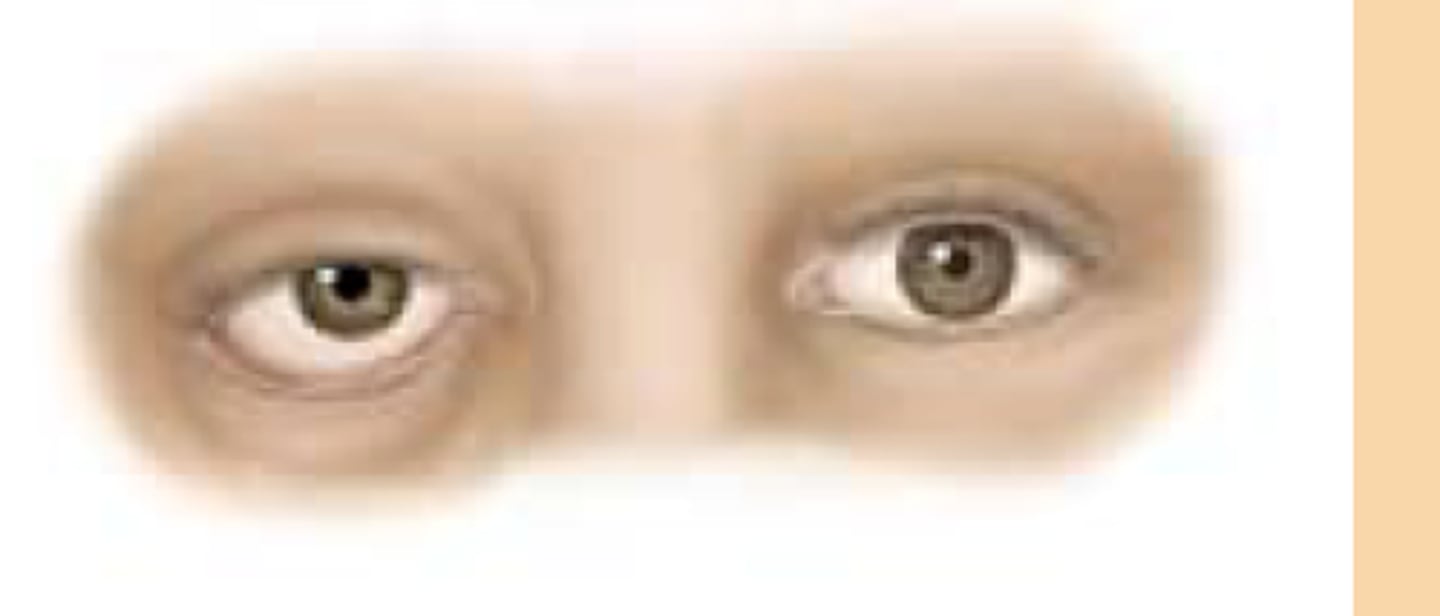
ptosis
drooping eyelid
can be aging/congenital: absence if eye crease
new onset : needs urgent FU
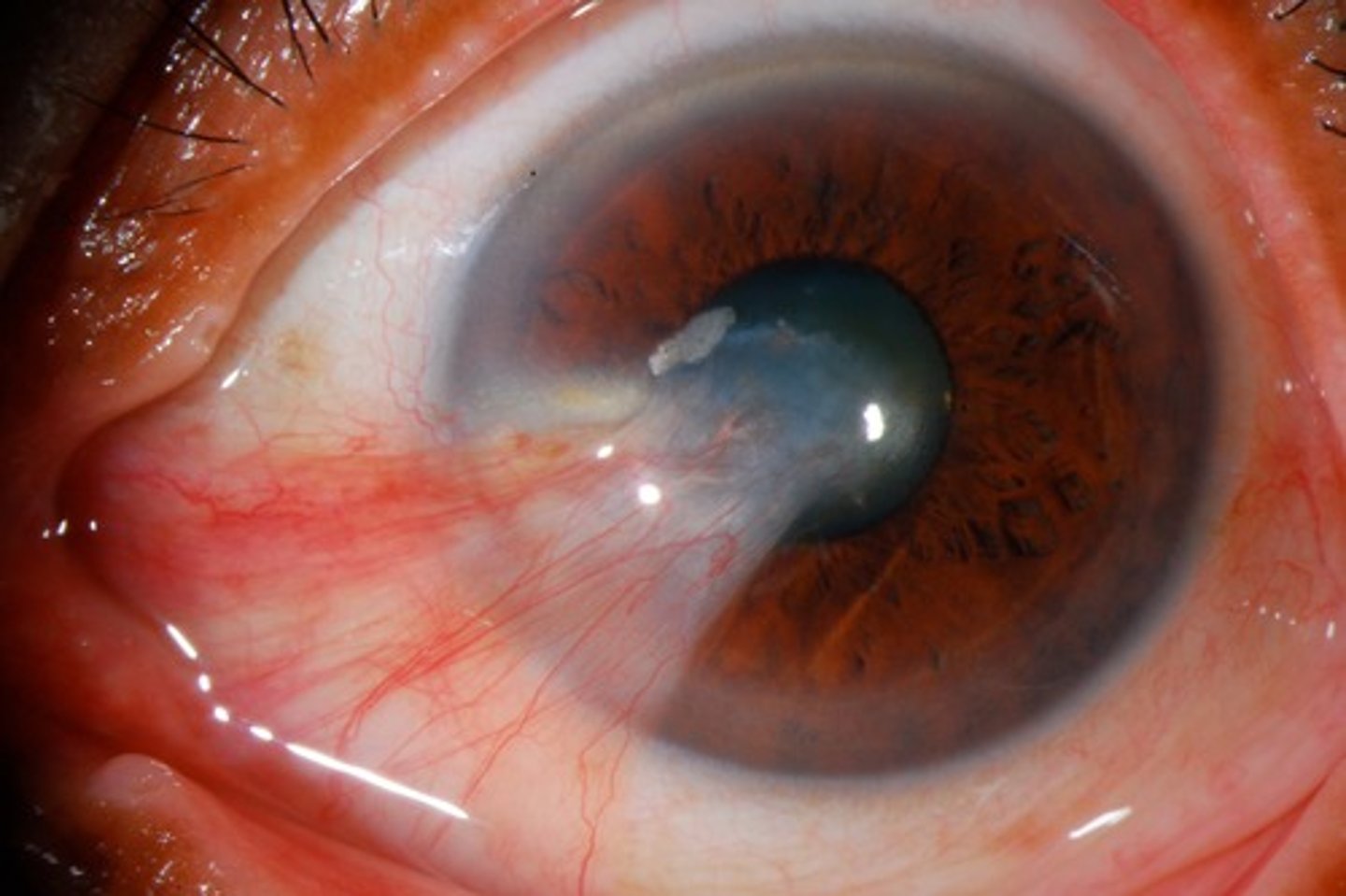
causes of pitosis
Horner's syndrome
CN III palsy
Myasthenia Gravis
entropion
inward turning of the rim of the eyelid
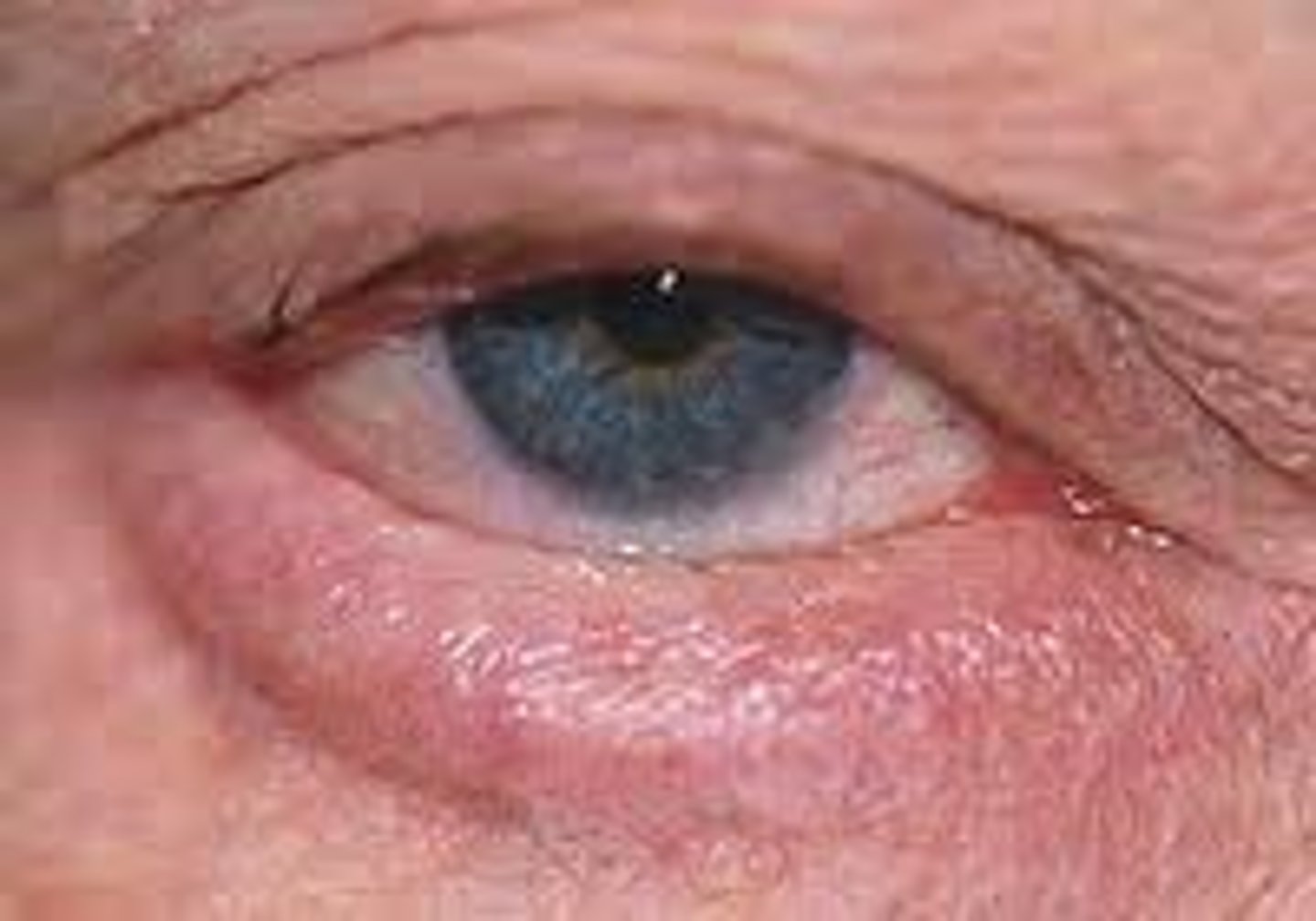
ectropion
outward turning of the rim of the eyelid
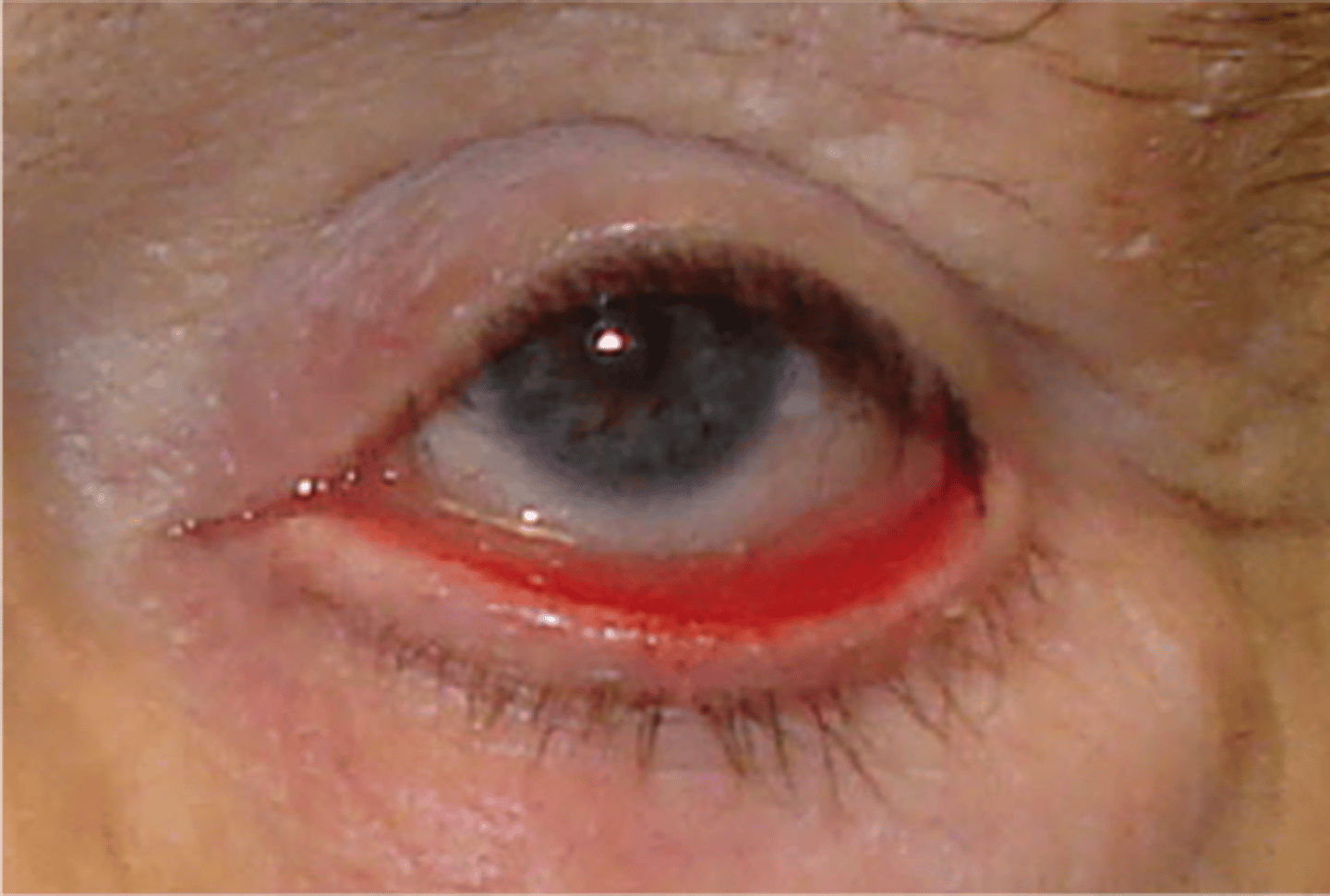
stye(chalazion)
plugging of meibomian glands
Acute: hordeolum
chronic
Treatment: warm compress and lid scrubs
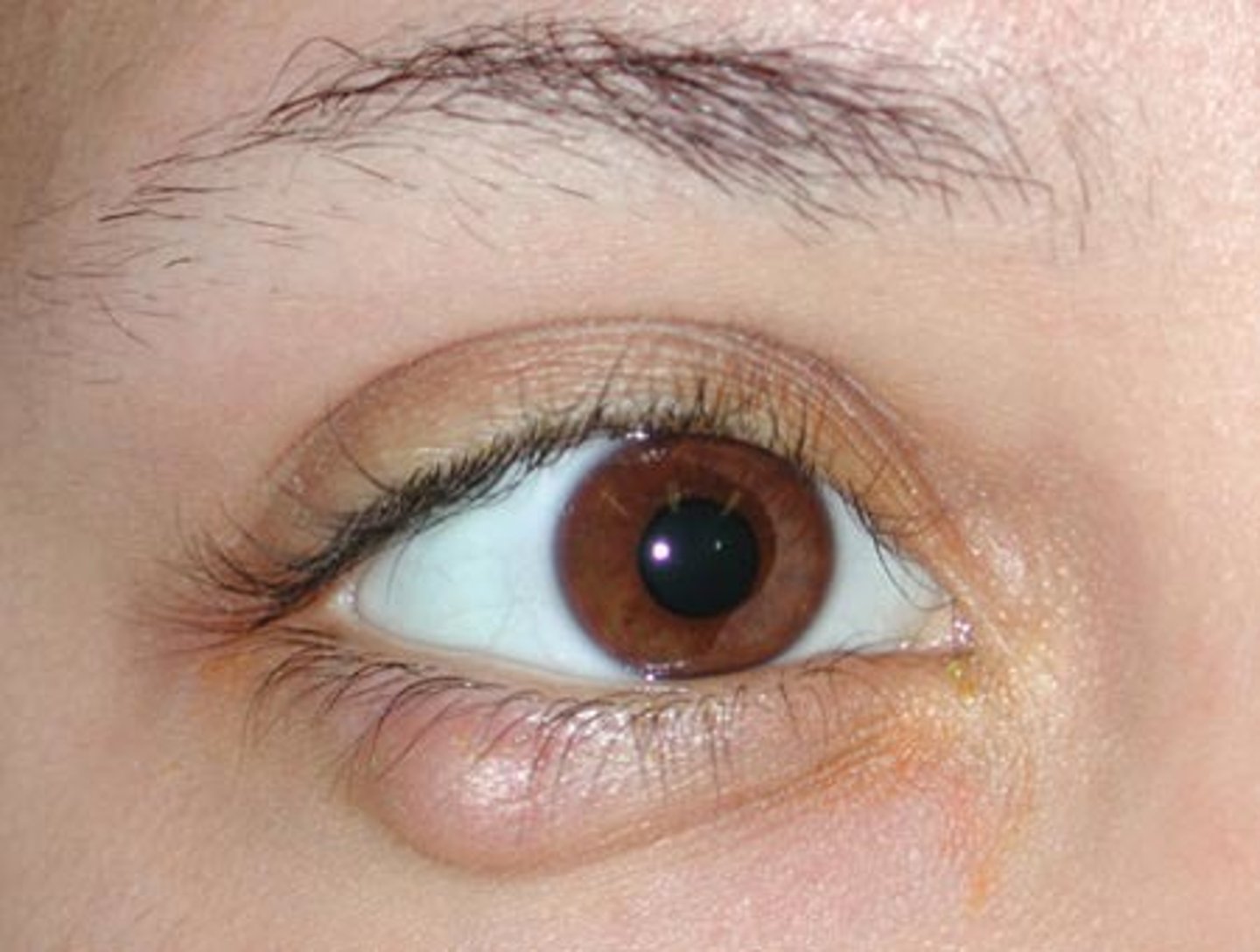
papilledema
swollen optic nerves from increased ICP
life and sight threatening
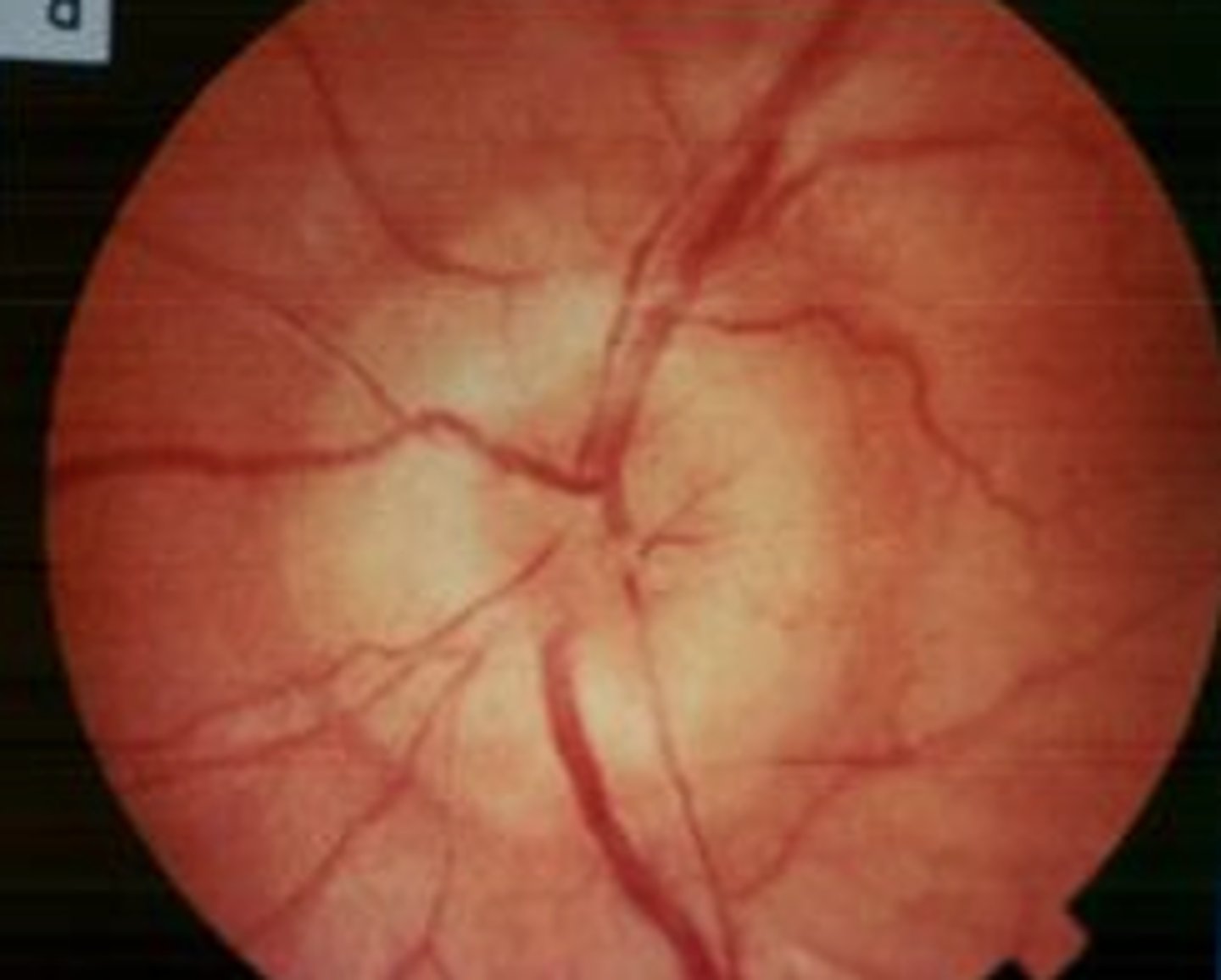
diabetic retinopathy
damage to the retina as a complication of uncontrolled diabetes
treatment:
medication, laser surgery, eye injections
hypertensive retinopathy
Disease of the retina due to high blood pressure.
treatement:
control BP, laser therapy, surgery
chest pain differentials
cardiovascular, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, psychiatric, malignancy, dermatological
apical impulse
point of maximal impulse (PMI); pulsation created as the left ventricle rotates against the chest wall during systole, normally at the 5th left intercostal space in the midclavicular line
cardiac apex
the rounded point at the bottom of the heart
diastole(s2 dub sound)
Relaxation of the ventricles
SLV close
AV open
pressure is decreased
dyspnea
shortness of breath
insufficiency
chronic condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet bodys need for O2 and nutrients
murmer
abnormal heart sound
crescendo murmur
increases in intensity
decrescendo murmur
decreases in intensity
crescendo-decrescendo murmur
increases and then decreases in intensity
plateau murmur
Constant intensity, suggests mitral regurgitation or ventricular septal defect.
orthopnea
difficulty breathing when lying down
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
episodes of sudden dyspnea and orthopnea which awaken patient from sleep
mitral regurgitation
backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium
happens during systole
plateau murmur
Tricuspid regurgitation
Backflow of blood into the right atrium during systole
aortic valve regurgitation
Backward blood flow from ascending aorta into left ventricle during diastole
aortic stenosis
calcification of aortic valve cusps that restricts forward flow of blood during systole
Mitral valve stenosis
narrowing of the mitral valve during diastole from scarring caused rheumatic fever
pulmonic stenosis
narrowing of the opening and valvular area between the pulmonary artery and right ventricle during systole
hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by a fluid at rest due to force
oncotic pressure
pressure exerted by large proteins in the blood plasma on the capillary walls
systole (s1) lub
ventricular contraction
AV close
SLV open
pressure is increasing
venous hum
continuous, low pitched murmur in the neck or upper chest
often heard in children
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
Thickening of heart muscle
Systolic
Plateau M
thickening of left ventricle
usually genetic
ventricular hypertrophy
may be a sign that the heart is working harder to pump blood to the rest of the body.
patent ductus arteriosus
congenital heart defect where the ductus arteriosus, a temporary blood vessel present in the fetus, remains open after birth.
systolic M
ventricular septal defect(VSD)
an opening in the septum separating the ventricles(hole in heart)
systolic Murmur
viens
carry blood towrds the heart
oxygenated blood
arteries
carries blood away from the heart
deoxygenated blood
PATHWAY OF BLOOD
IVC/SVC > RA > tricuspid V > RV > pulmonary valve > pulmonary artery > LUNGS to get oxygenated > pulmonary vein > LA > mitral V > LV > aortic V > aorta
splitting of S1 and S2
when the mitral/tricuspid valves do not close at the same time (S1 split)
when the pulmonic/aortic valves do not close at the same time (S2)
Two sounds instead of one
S3 gallop
rapid ventricular filling
may suggest heart failure: older patients
can be normal in: conditioned athletes, children and 3rd trimester of pregnancy
diastolic sound
S4 gallop
atrial contraction
thickening of heart muscle
diastolic sound
pathologies:
- cardiomyopathy
-aortic stenosis
- hypertension
friction rubs
rubbing of pericardial layers
pericarditis
scratchy or grating sound during expiration
clicks
short, high pitched sound heard during cardiac cycle
indicated abnormal valve function
opening snaps
associated with mitral stenosis
early diastolic sound from abrupt deceleration during opening of a stenotic mitral valve
alveoli
air sacs located in the bronchioles of the lung and main gas exchange
atelectasis
collapsed lung when alveoli become blocks or losing air
bronchophony
voice transmission test
normal= muffles noise
abnormal= louder/clear voice
sign of pneumonia
egophony
ask patient to say "ee"
normal= muffled "ee"
abnormal= ay sound
pneumonia or pleural effusion
whisphered pectoriloquy
whisper 99 to patient
normal: faint and distinct
abnormal: whispered words are louder/clearer
pneumonia or lung mass
consolidation
air spaces within the lung tissue are filled with fluid/pus/blood