1.05 Medical Sciences
1/479
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
480 Terms
nasal vestibule
stratified squamous
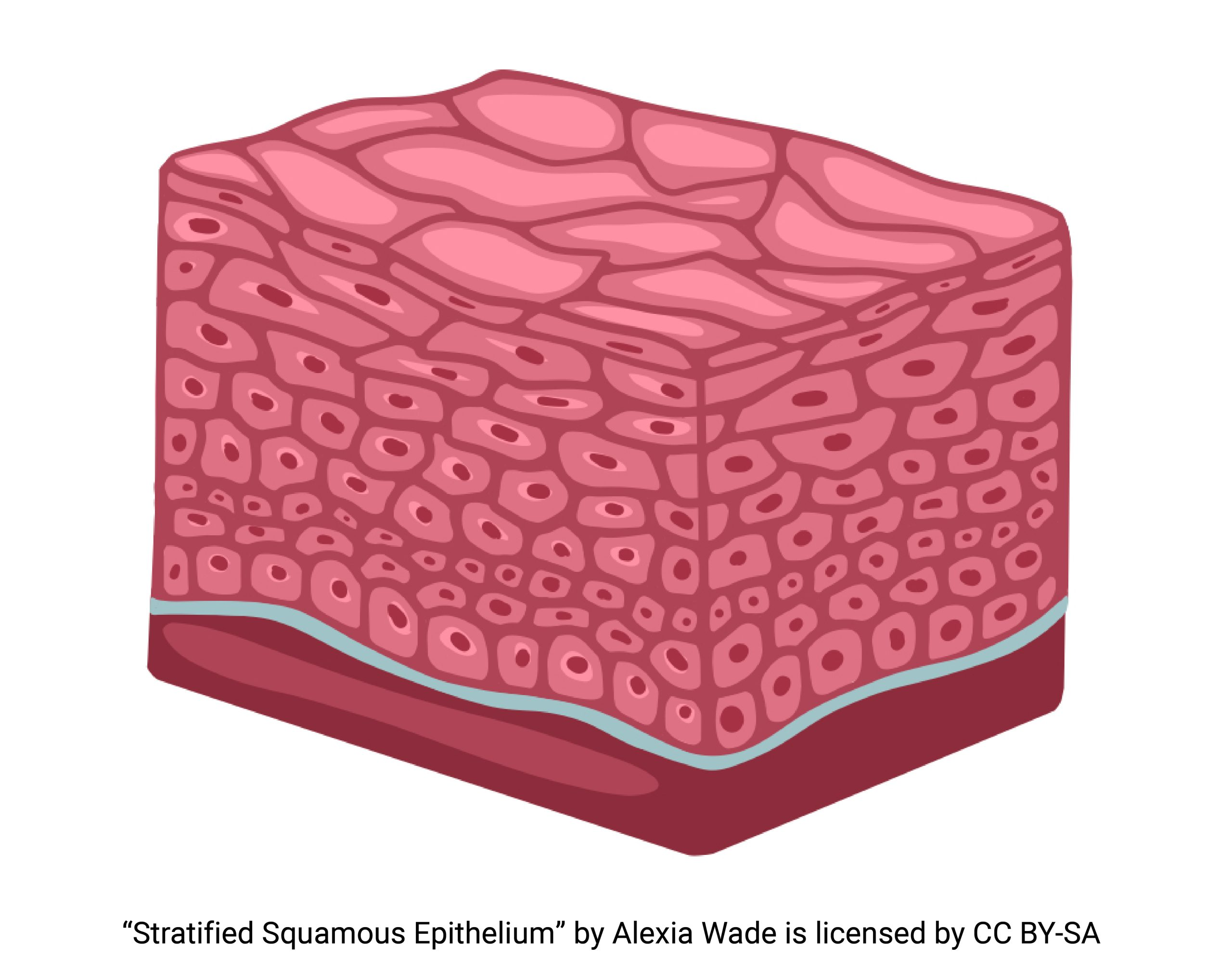
nasal cavity to lobar bronchi
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
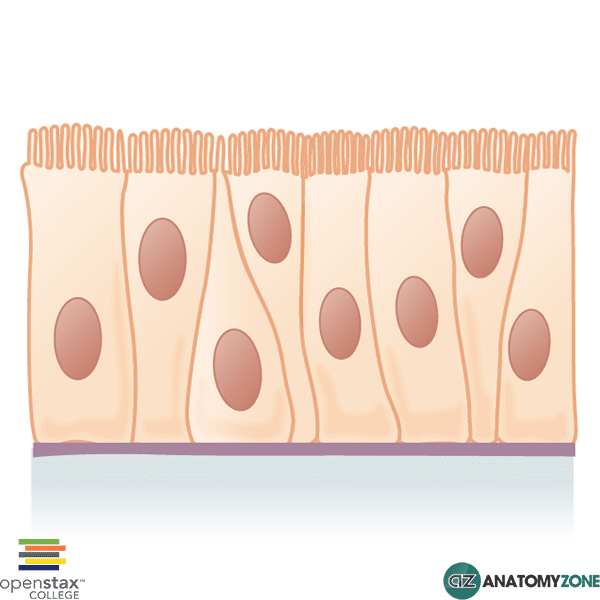
segmental bronchi to bronchioles
simple ciliated columnar epithelium
alveoli
simple squamous epithelium
exceptions
non-keratinised stratified squamous:
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
- superior larynx (vocal cords)
club cells (3)
- detoxification of inhaled pollutants
- secrete CCSP (club cell secretory protein)
- control inflammation
pulmonary neuroendrocrine cells (PNEC) or K cells
only cell type that is innervated
what type of cell can differentiate into type 1 pneumocytes after injury?
type 2 pneumocytes
what is found in the hilum of the lung?
- main bronchus
- pulmonary arteries
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial vessels
- bronchopulmonary lymph nodes
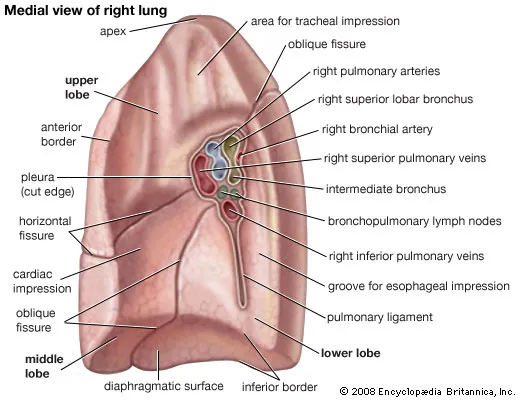
what is found anteriorly to posteriorly in the R hilum? (5)
- bronchial vessels
- R superior pulmonary vein
- R pulmonary artery
- R inferior pulmonary vein
- superior and intermediate lobar bronchi
what is found anteriorly to posteriorly in the L hilum? (5)
- L superior pulmonary vein
- L pulmonary artery
- L lobar bronchi
- L inferior pulmonary vein
- bronchial vessels
what are the 4 sections of the mediastinum?
- superior
- anterior
- middle
- posterior
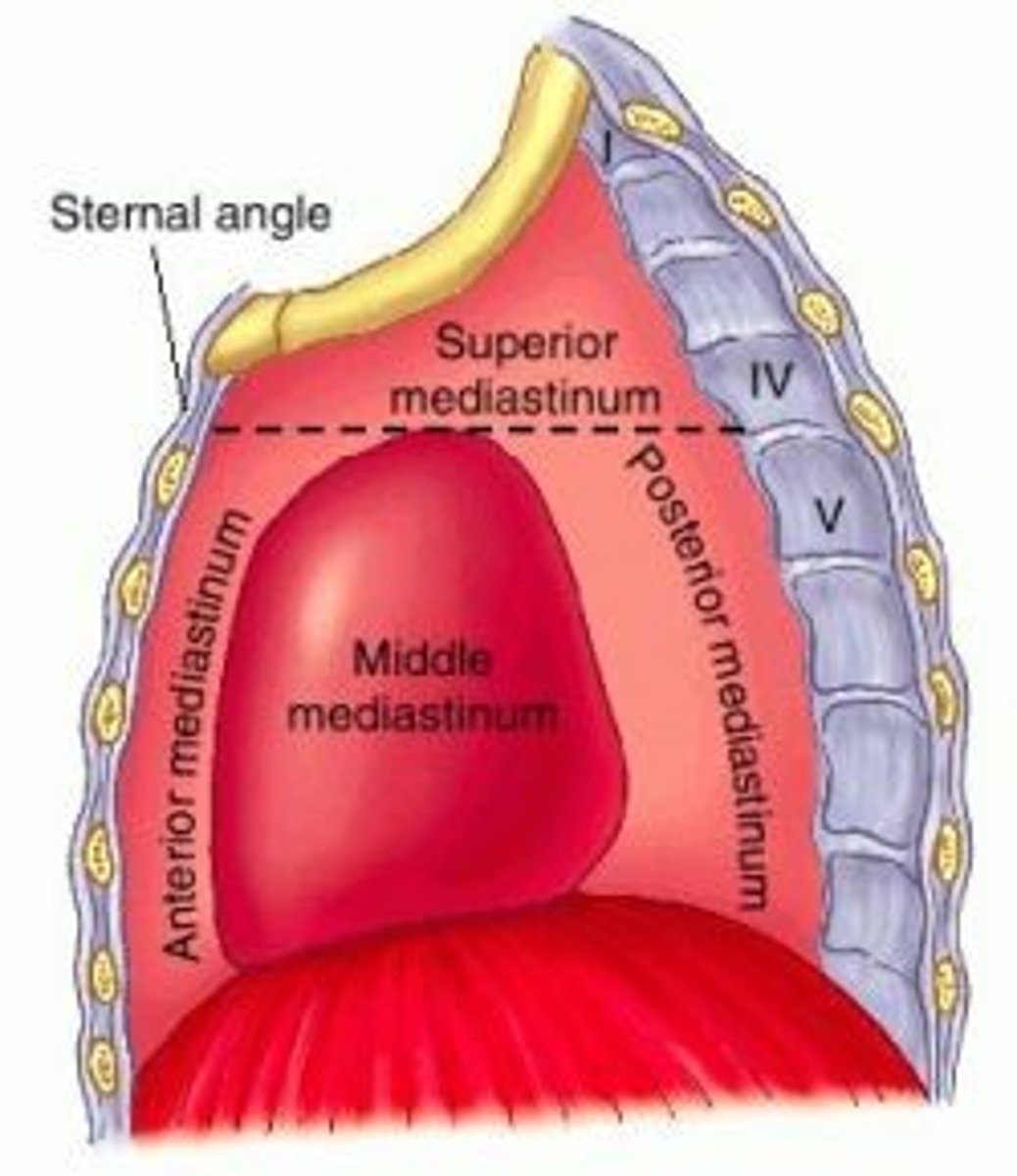
what is found in the superior mediastinum? (10)
- superior vena cava
- brachiocephalic veins
- arch of aorta
- thoracic duct
- trachea
- oesophagus
- thymus
- vagus nerve
- left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- phrenic nerve
what is found in the anterior mediastinum?
- thymus
- lymph nodes
- fat
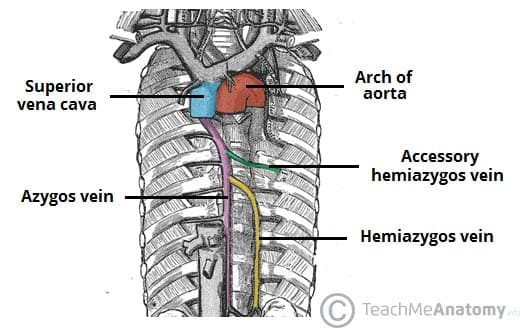
what is found in the middle mediastinum?
- pericardium
- heart
- aortic root
- arch of azygous vein
- R and L main bronchi
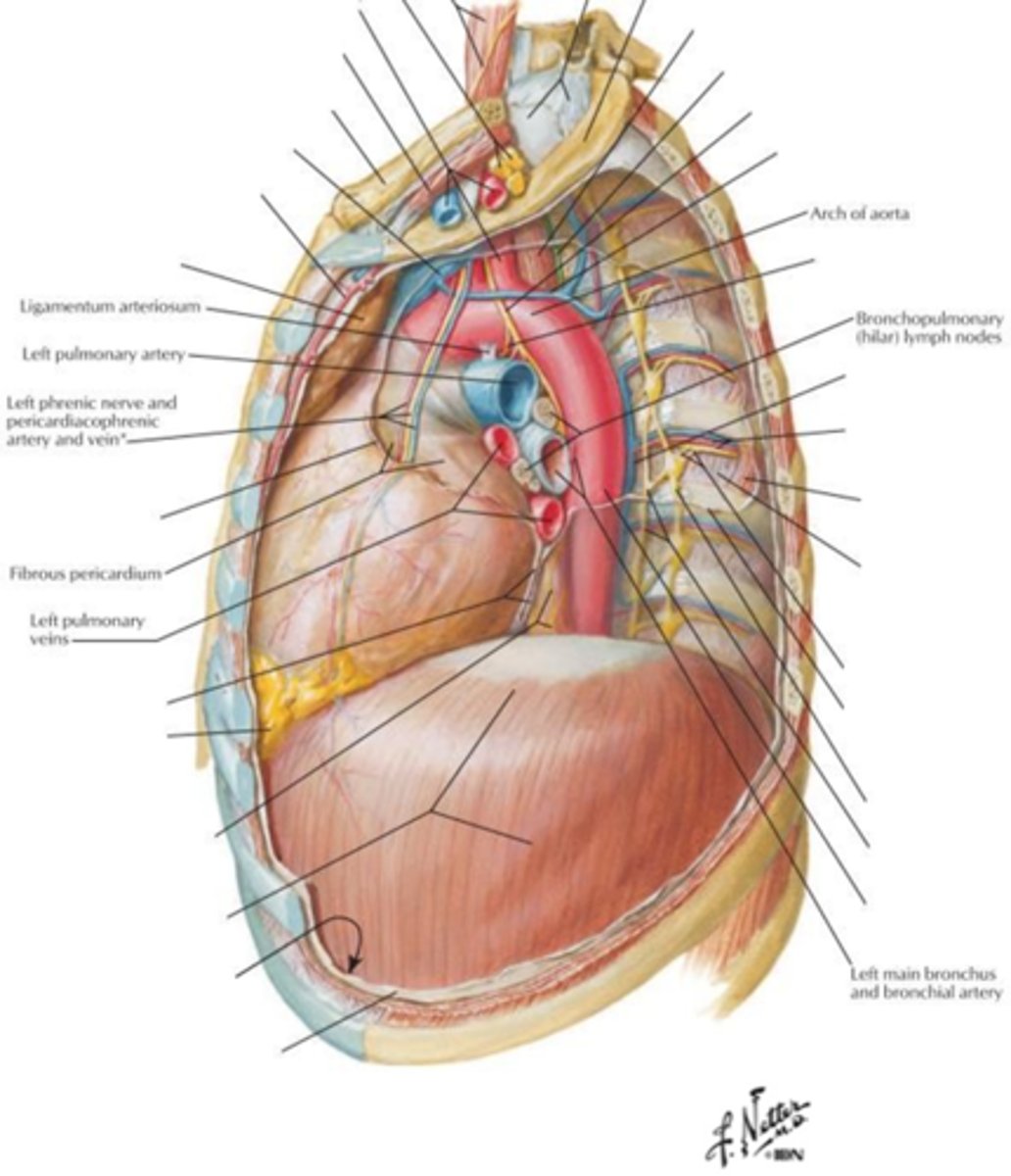
what is found in the posterior mediastinum? (7)
- oesophagus
- thoracic aorta
- azygous vein
- thoracic duct
- vagus nerve
- sympathetic nerve trunks
- splanchnic nerves
how does the aorta interact with the oesophagus?
superior mediastinum - oesophagus is posterior to aorta
posterior mediastinum - oesophagus is anterior to aorta
what is the tidal volume?
volume of air inhaled and exhaled in one breath during quiet respiration
what is inspiratory reserve volume?
extra volume that can be inspired above tidal volume during forced/maximum inspiration
what is expiratory reserve volume?
extra volume that can be expired below tidal volume during forced/maximum expiration
what is residual/reserve volume?
volume remaining after maximum expiration
what is vital capacity and how is it measured?
- volume that can be exhaled after maximum inspiration
vital capacity = inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + expiratory reserve volume
what is inspiratory capacity and how is it measured?
- volume breathed in from quiet expiration to max inspiration
inspiratory capacity = tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume
what is functional residual capacity and how is it measured?
volume remaining after quiet expiration
functional residual capacity = expiratory reserve volume + residual volume
what is total lung capacity and how is it measured?
volume of air in lungs after maximum volumes
total lung capacity = tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume + expiratory reserve volume + residual/reserve volume
what are the 2 dead spaces in respiration?
- anatomical dead space
- alveolar dead space
what is anatomical dead space?
volume of air that never reaches alveoli
what is alveolar dead space?
volume of air that reaches the alveoli but does not participate in respiration
what is the main function of the lymphatic system?
- drain excess tissue fluid, plasma proteins and other cellular debris back into the bloodstream
- involved in immune defence
what is the collection of substances called when it enters the lymphatic vessels?
lymph
what do the lymph nodes do?
filter lymph then returns to circulation via the venous system
what are the primary lymphatic organs?
thymus and red bone marrow
what is the main function of the spleen?
filter blood and remove old red blood cells
what is the main function of the thymus?
T lymphocyte maturation
what is the main function of red bone marrow?
maturation of immature lymphocytes
what are lymph nodes?
kidney-shaped structures which filter foreign particles from blood
what cells are found in the outer cortex of the lymph nodes?
B-lymphocytes
what cells are found in the inner cortex of the lymph nodes?
T-lymphocytes and dendritic cells
how does lymph enter lymph nodes?
via afferent lymphatic vessels
how does lymph leave lymph nodes?
via efferent lymphatic vessels
what are the two main systems of lymph vessels?
- superficial vessels
- deep vessels
where are superficial vessels?
arise in subcutaneous tissue and accompanies venous flow
where do superficial vessels drain to?
into deep vessels
where are deep vessels?
drain the deeper structures of the body e.g. internal organs and accompany deep arteries
where does lymph drainage begins?
lymph channels
what do lymph channels develop into?
lymph vessels
what do lymph vessels drain through?
lymph nodes
where do lymph vessels eventually end up?
into lymphatic trunks/collecting vessels
what do the lymphatics trunks eventually form?
right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct
what does the right lymphatic duct drain?
upper right quadrant of body
where does the right lymphatic duct empty into?
right venous angle - where right subclavian and right internal jugular veins join
also sometimes:
- right subclavian vein
- right external jugular vein
what does the thoracic duct drain?
the rest of the body (so not the upper right quadrant)
where does the thoracic duct empty into?
left venous angle - where left subclavian and left internal jugular vein join
also sometimes:
- left subclavian vein
- left external jugular vein
what are the the cisterna chyli and where are they located?
dilated sac at bottom of thoracic ducts draining fluid from intestinal and lumbar trunks
how is lymph fluid formed?
when fluid leaves capillaries due to hydrostatic pressure
what is the composition of lymph fluid?
95% water
5% proteins, lipids, carbohydrates
which lymphatic vessels drain the lung? (2)
- superficial lymphatic plexus
- deep lymphatic plexus
what does the superficial lymphatic plexus drain?
lung parenchyma
what does the deep lymphatic plexus drains?
structures of lung root
where do the superficial and deep lymphatic plexus drain?
into the trachebronchial nodes
what is the main muscle used in respiration?
diaphragm
what are the other muscles used in quiet respiration?
- external intercostal muscles
- internal intercostal muscles
what does the diaphragm consist of?
muscles fibres and central tendinous portion
what happens to diaphragm during inspiration? (4)
- diaphragm contracts and moves downwards
- the attached parietal pleura descends
- the visceral pleura also descends so the airways and alveoli expand
- air is sucked into the lungs
what happens to the diaphragm during expiration?
diaphragm relaxes and moves upwards
how is air expelled from the lungs in terms of muscles?
recoil of the elastic tissue in lungs
what happens to the ribcage and intercostal muscles during inspiration?
- external intercostal muscles contract and move the ribcage upwards and outwards
- the joints between posterior ends of the ribs and the transverse processes of the vertebrae enable the lower ribs to swivel upwards and outwards
what does the upwards and outwards movement of the ribcage cause?
- increases the lateral and anteroposterior diameter of thorax
- increases thoracic volume and making the negative pressure of the lungs more negative so air can be sucked in
what extra is used in forced respiration?
the accessory muscles of respiration
what are the accessory muscles of respiration? (4)
- abdominal (oblique, transversus and rectus abdominis)
- sternocleidomastoids
- scalene muscles
what innervates the diaphragm?
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
what innervates the intercostal muscles?
intercostal nerves (T1-T12)
what are the microscopic parts of skeletal muscle biggest to smallest? (5)
- muscle
- fascicle (portion of muscle)
- muscle fibre (cell)
- myofibril (bundles)
- sarcomere (short units of myofibril)
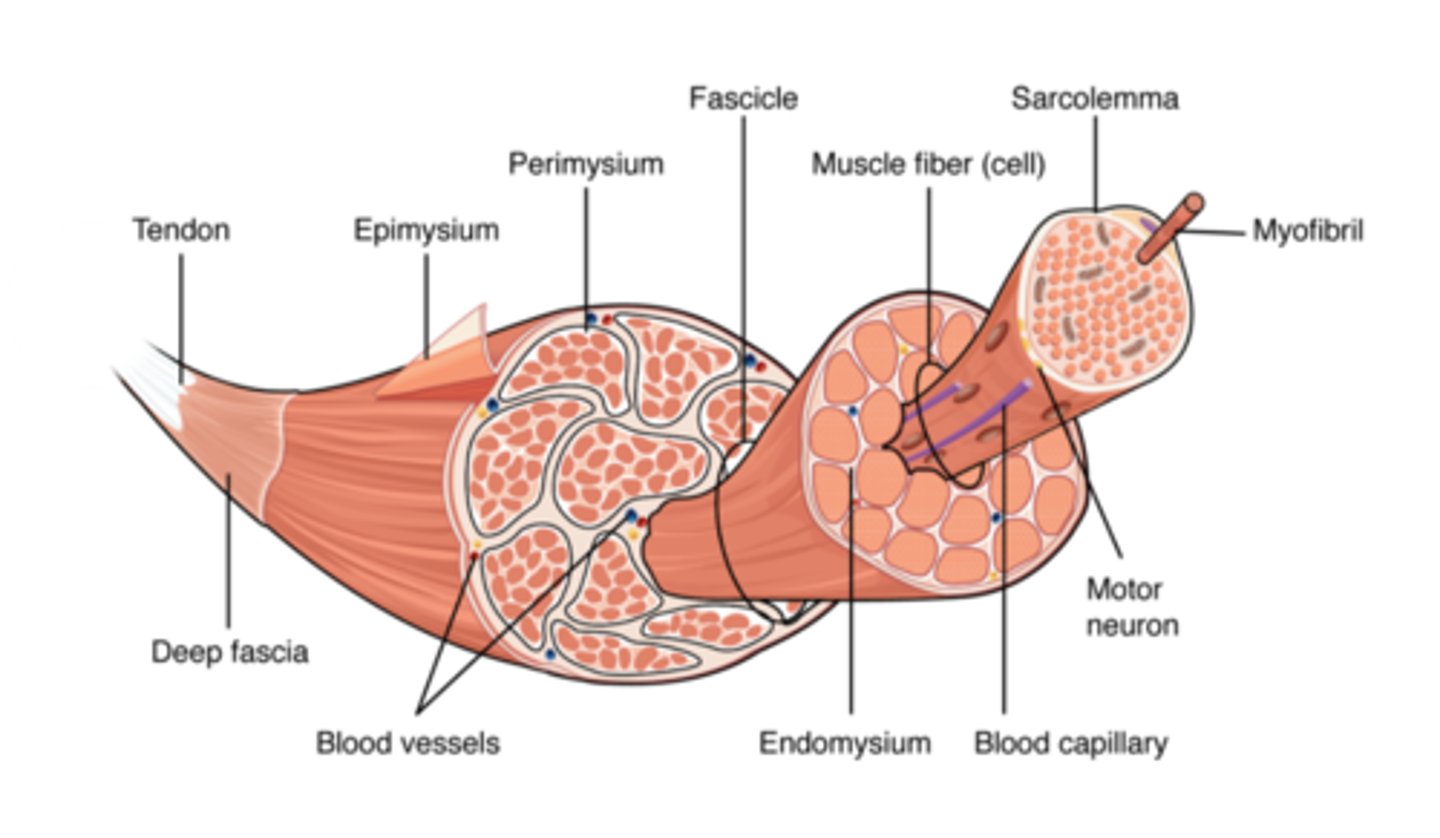
what is the structural unit of a muscle?
muscle fibre (cell)
what is the functional unit of a muscle?
sarcomere (z line to z line)
what are the two components of the sliding-filament theory?
actin and myosin
which is the thicker filament?
myosin
which is the thinner filament?
actin
what are the bands/zones/lines involved in the sliding-filament theory?
- A-bands
- I-bands
- H-zone
- Z - line
- M-line
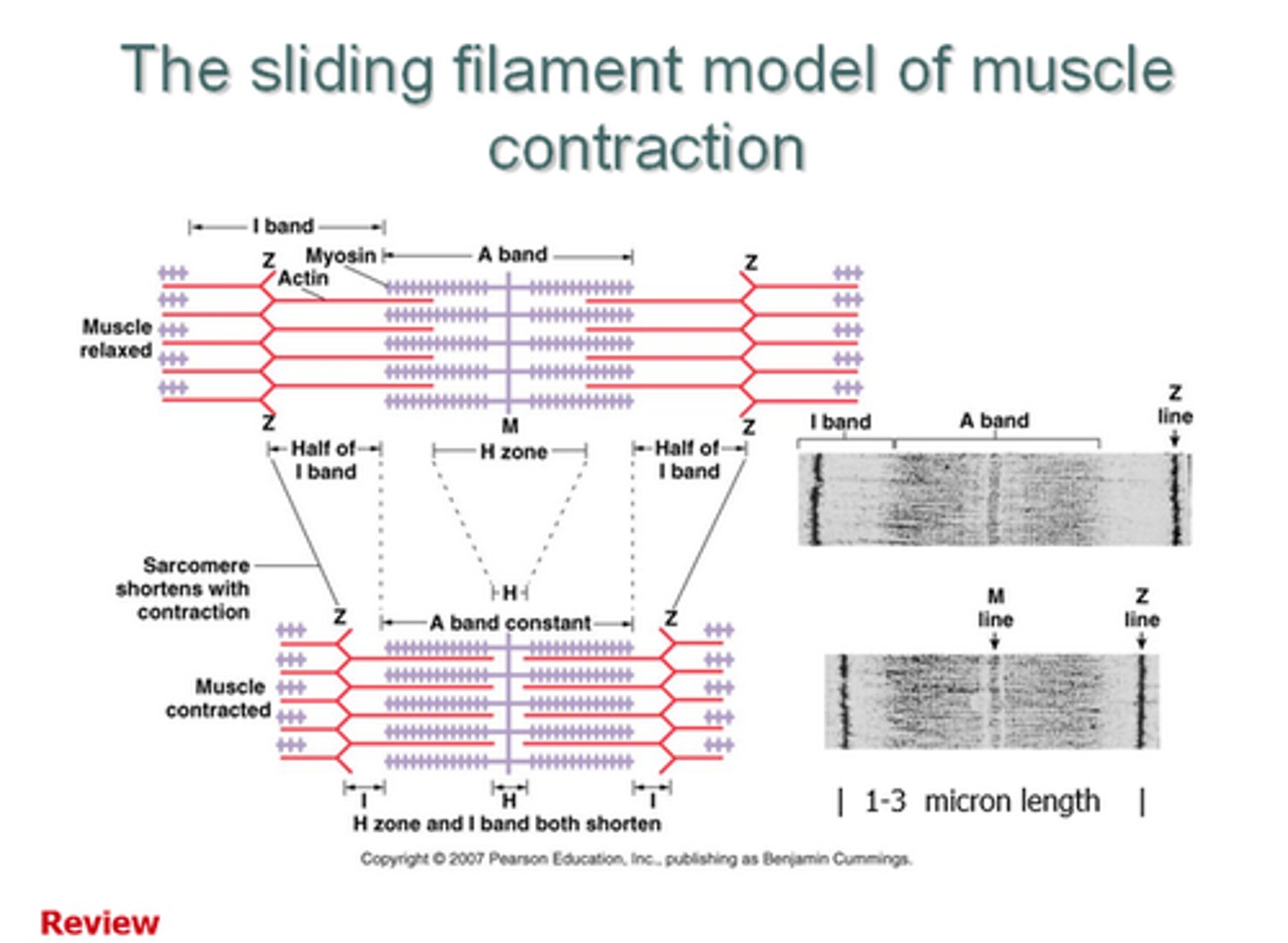
where do the A-bands cover?
entire myosin filament
where do the I-bands cover?
non-overlapping sections of actin filament
what is the H-zone?
non-overlapping sections of myosin filament
what is the Z-line?
end of sacromere
what is the M-line?
middle of sacromere
what happens to the A-band during contraction?
stays the same length
what happens to the I-band during contraction?
gets shorter
what happens to the H-zone during contraction?
gets shorter
how is are skeletal muscles stimulated to contract? (7)
- an action potential arrives at a neuromuscular junction
- causes an opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
- Ca2+ enter the cell
- causes vesicles containing acetylcholine to release contents into synaptic cleft
- ACh causes an influx of Na+ into muscle fibre causing depolarisation
- the depolarisation activates voltage-sensitive sodium channels
- causes an action potential in skeletal muscle fibre
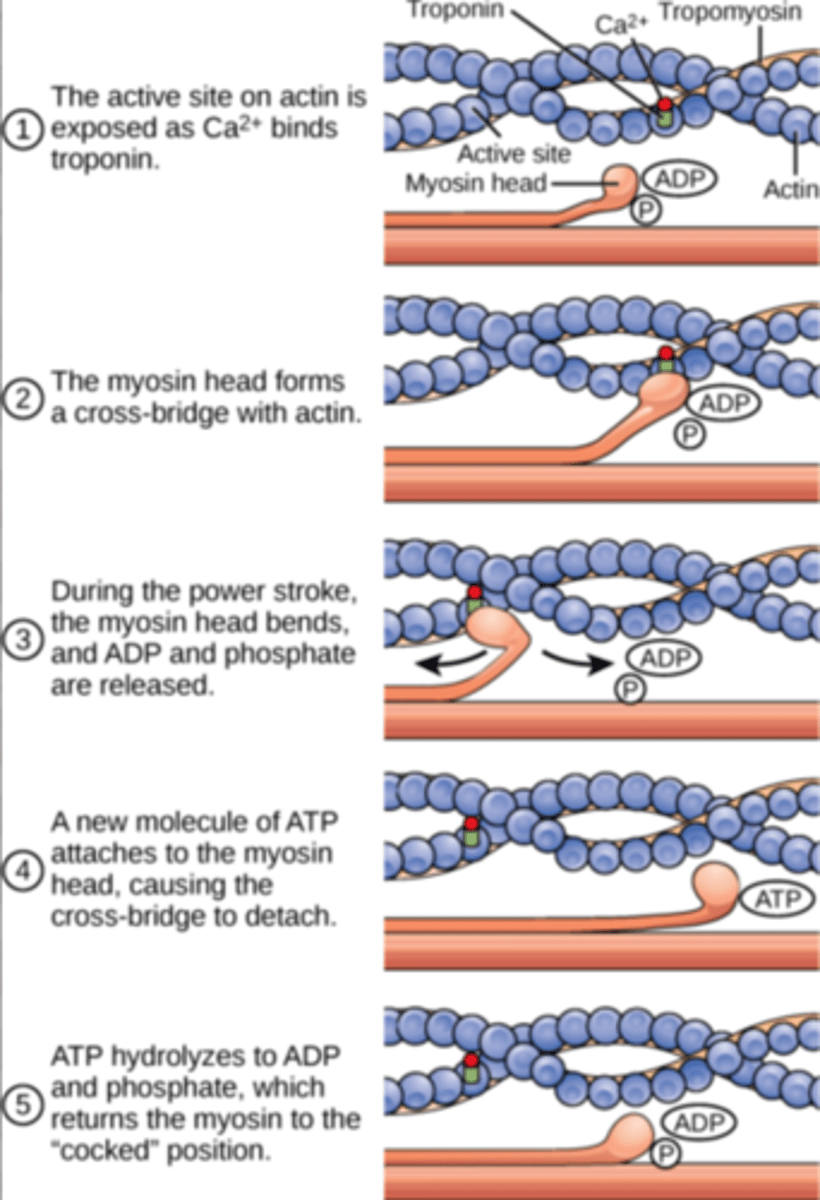
how does the skeletal muscle contract? (7)
excitation-contraction coupling:
- depolarisation at neuromuscular junction
- conducted down t-tubules
- influx of calcium ions into sarcoplasm from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- calcium binds to troponin C causing a change in conformation that moves tropomyosin away from myosin head binding sites on the actin filaments
- this allows the myosin head to bind to the actin, forming a cross-link
- a power stroke occurs as myosin heads pivot in a 'rowing motion' moving the actin past the myosin towards the M line
- ATP then binds to the myosin head causing it to release the actin so the process can repeat
what is a virus?
an infective agent that carries genetic information in DNA or RNA but is metabolically inert and can only replicate once in host cell
what are the 4 main criteria used to classify viruses?
- type of nucleic acid in genome
- number of nucleic strands and their polarity
- mode of replication
- size, structure and symmetry of virus particle
what are the common structural features of viruses? (4)
- genetic material
- capsid (made of capsomeres)
- genetic material + capsid = nucleocapsid
- sometimes outer envelope or membrane
what is the structure of the genetic material in viruses? (4)
- either single stranded (ss) or double stranded (ds)
- linear or circular
- RNA or DNA
- contained within capsid
what are the 3 different symmetry types of nucleocapsids?
- icosahedral
- helical
- complex
where does the outer envelope or membrane generally come from?
lipid bilayer of host cell origin
how does a virus infect its host cell? (6)
1) attaches to receptor on host cell
2) penetration into the host cell
3) uncoating of capsid
4) synthesis of viral RNA - proteins - capsid - nucleic acid
5) capsid forms round DNA = nucleocapsid
6) release of viruses by budding off and forming envelope
what are the most common transmissions of viruses? (6)
- inhaled droplets
- oral - food or water
- direct transfer from other infected hosts via sexual transmission or blood-borne routes
- direct skin contact
- from bites of vector arthopods
- transplacental
can a virus use any host?
no, they show host specificity so can only infect one or a restricted range of host species
what does the host specificity depend on?
the ability of the virus to attach to the host cell via a receptor