15_Cellular Communication
1/59
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
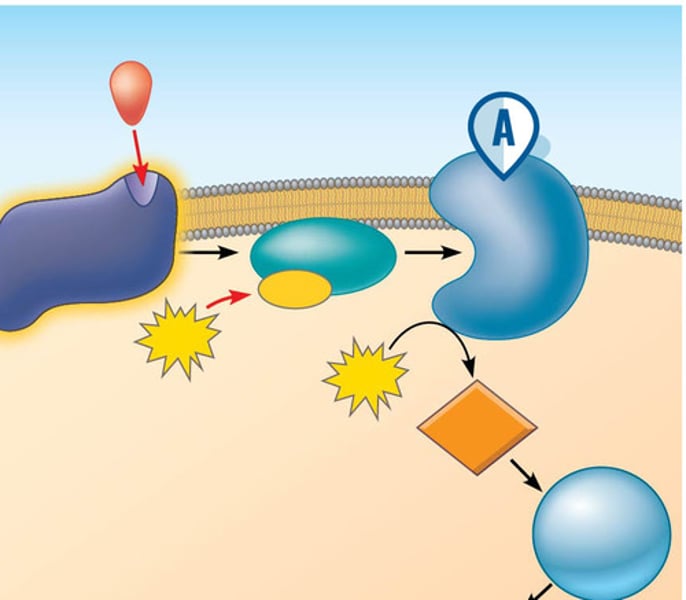
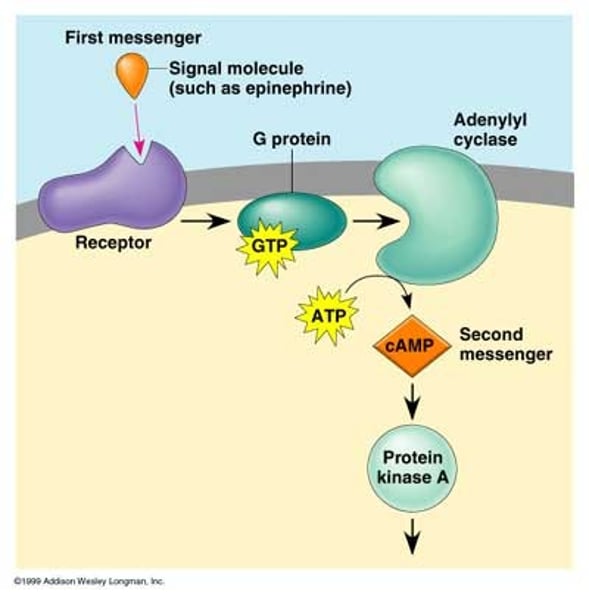
adenylyl cyclase
An enzyme in the PM that converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to an extracellular signal.
apoptosis
programmed cell death
autocrine signal
signal that is sent and received by the same or similar nearby cells
autoinducer
signaling molecule secreted by bacteria to communicate with other bacteria of its kind
caspases
enzymes responsible for cell death in apoptosis; proteases and endonucleases
Ced-4
required for activation of Ced-3; kept "off" by Ced-9 unless death signal is present
Ced-9
inhibits apoptosis unless a signal for cell death arrives
Ced-3
The chief caspase in the nematode
C. elegans
nematode; multicellular eukaryote; model organism for studying apoptosis
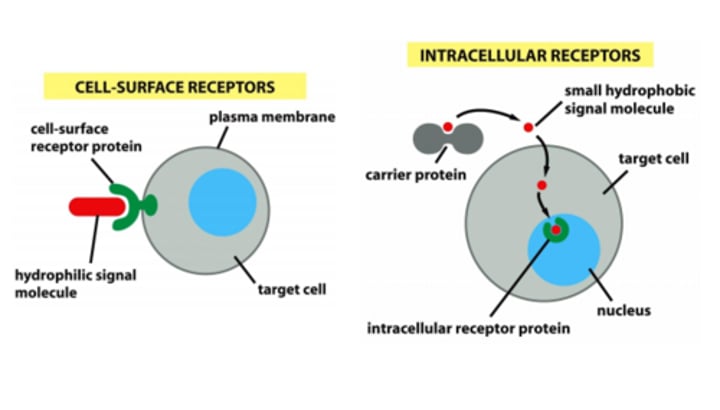
cell-surface receptor
cell-surface protein that transmits a signal from the exterior of the cell to the interior, even though the ligand does not enter the cell
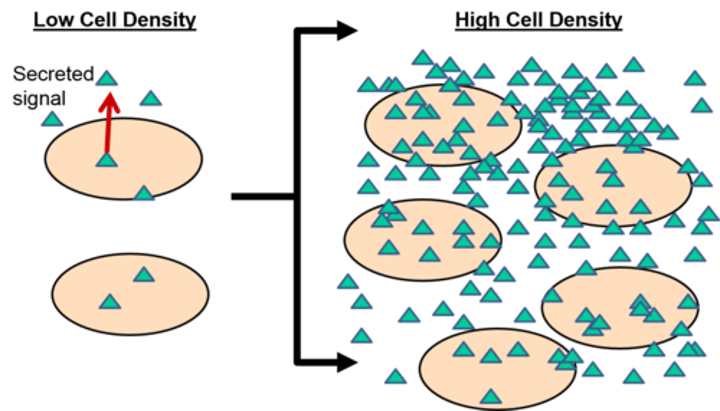
biofilm
Community of microorganisms living within a shared mass of secreted slime. Communication between cells via signaling molecules (quorum sensing).
cellular response
variety of actions possible from regulating the activity of a protein or enzyme to turning on or off synthesis of a protein.
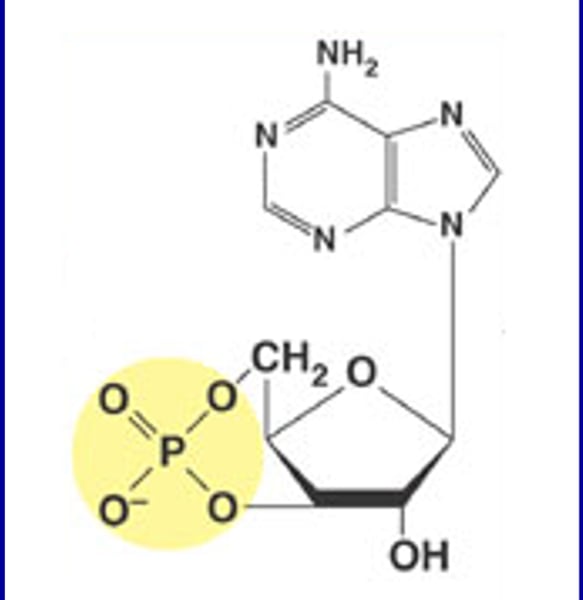
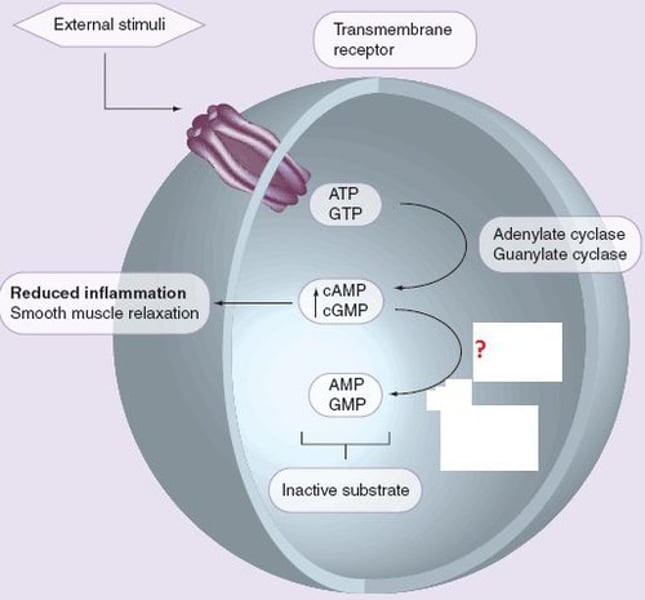
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
second messenger that is derived from ATP
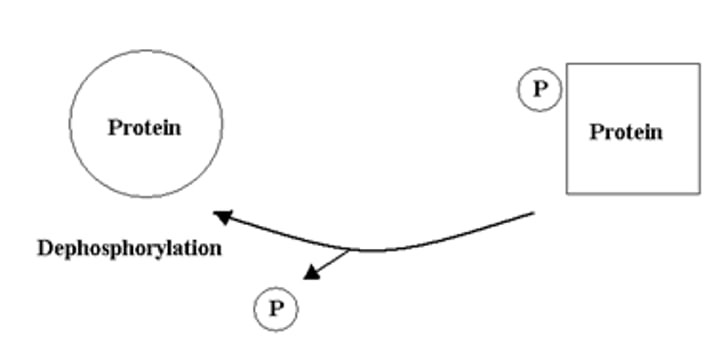
dephosphorylation
removal of a phosphate group from a molecule
cyclic AMP-dependent kinase
(also, protein kinase A, or PKA) kinase that is activated by binding to cAMP
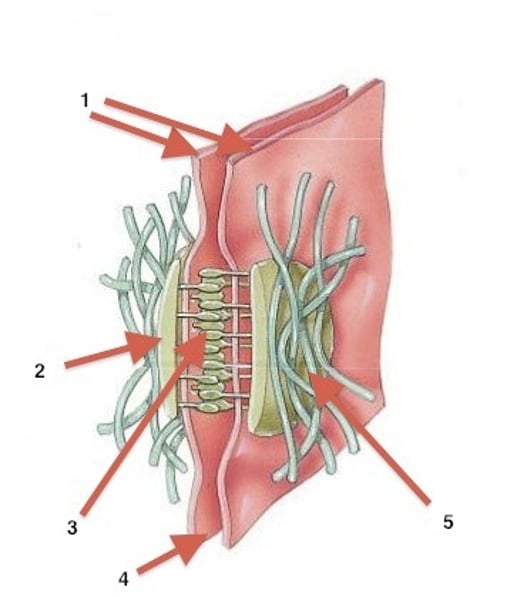
desmosome
a type of intercellular junction in animal cells that functions as a rivet, fastening cells together
diacylglycerol (DAG)
cleavage product of PIP2 that is used for signaling within the plasma membrane
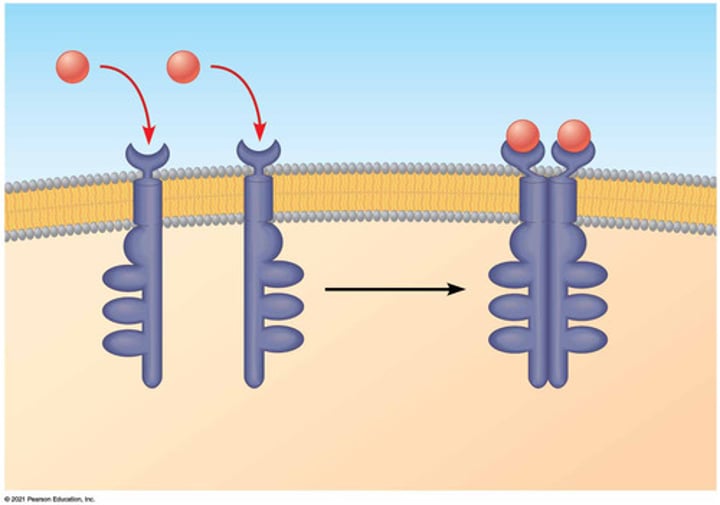
dimer
chemical compound formed when two molecules join together
dimerization
(of receptor proteins) interaction of two receptor proteins to form a functional complex called a dimer
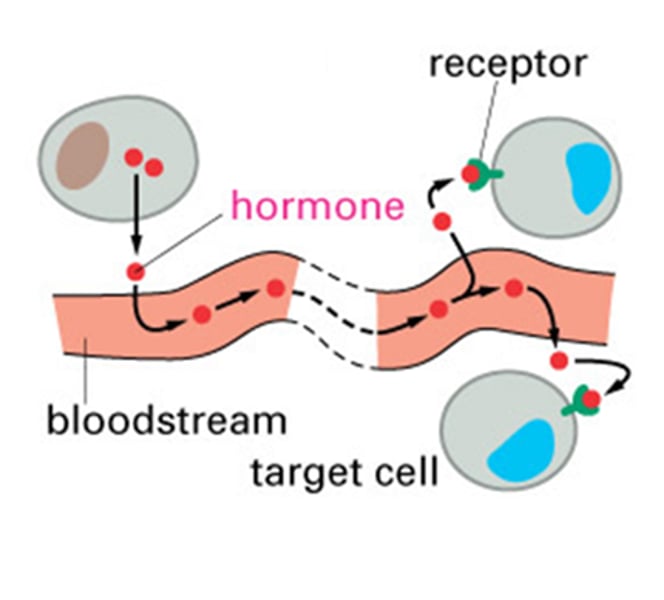
endocrine cell
cell that releases ligands involved in endocrine signaling (hormones)
endocrine signal
long-distance signal that is delivered by ligands (hormones) traveling through an organism's circulatory system from the signaling cell to the target cell
enzyme-linked receptor
cell-surface receptor with intracellular domains that are associated with membrane-bound enzymes
extracellular domain
region of a cell-surface receptor that is located on the cell surface
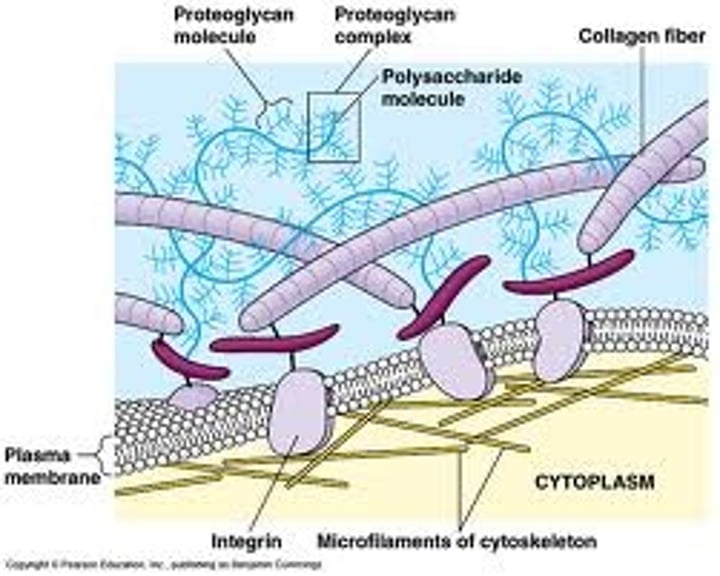
extracellular matrix
a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells.
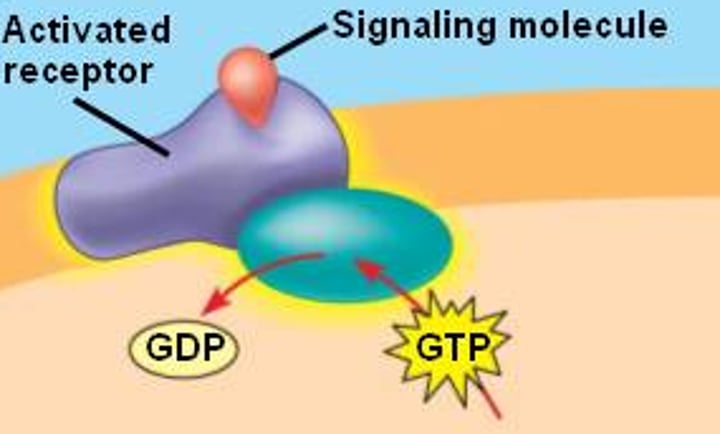
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
cell-surface receptor that activates membrane-bound G-proteins to transmit a signal from the receptor to nearby membrane components
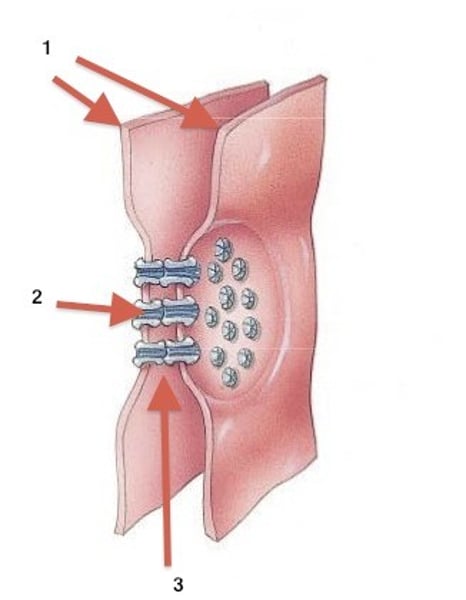
gap junctions
like plasmodesmata in plant cells in that they are channels between adjacent cells that allow for transporting ions, nutrients, and other substances that enable cells to communicate; connexins in PM arrange themselves in an elongated donut-like configuration - a connexon.
growth factor
ligand that binds to cell-surface receptors and stimulates cell growth
hormone
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
inhibitor
molecule that binds to a protein (usually an enzyme) and keeps it from functioning
inositol phospholipid
lipid present at small concentrations in the plasma membrane that is converted into a second messenger; it has inositol (a carbohydrate) as its hydrophilic head group
inositol triphosphate (IP3)
cleavage product of PIP2 that is used for signaling within the cell
intercellular signaling
communication between cells
intracellular signaling
communication within cells
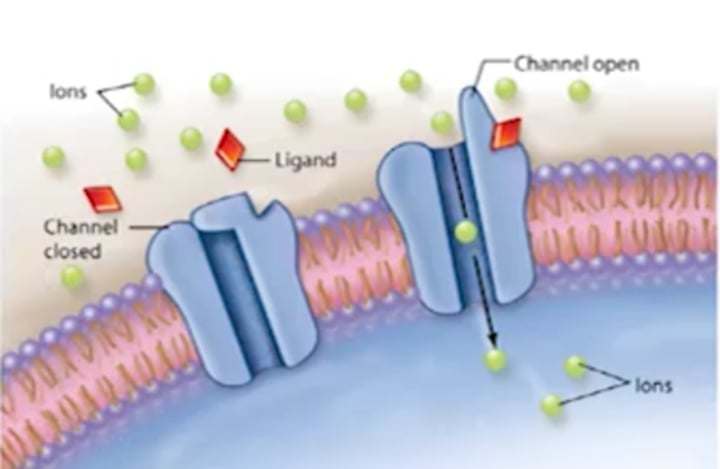
ion channel-linked receptor
cell-surface receptor that forms a plasma membrane channel, which opens when a ligand binds to the extracellular domain (ligand-gated channels)
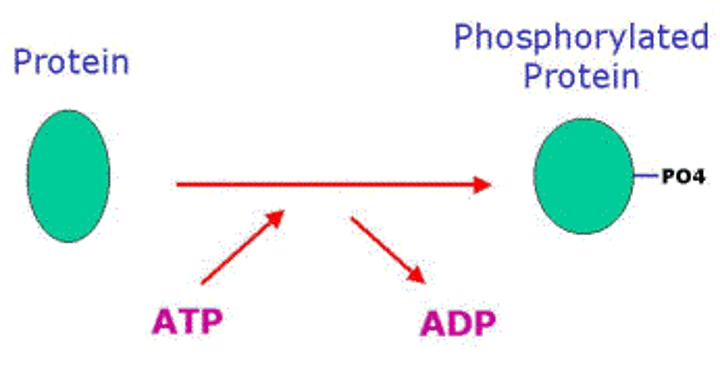
kinase
enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule
ligand
molecule produced by a signaling cell that binds with a specific receptor, delivering a signal in the process
local signaling
signaling between adjacent cells through messengers (paracrine and synaptic), direct contact (plasmodesmata, gap junctions) or cell-cell recognition
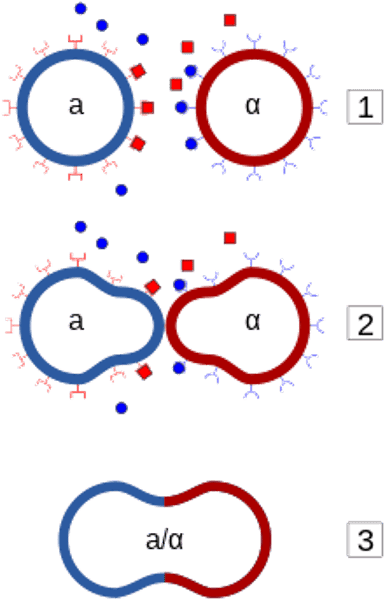
mating factor
signaling molecule secreted by yeast cells to communicate to nearby yeast cells that they are available to mate; two mating types are "a" and "alpha"
neurotransmitter
chemical ligand that carries a signal from one nerve cell to the next
paracrine signal
signal between nearby cells that is delivered by ligands traveling in the liquid medium in the space between the cells
phosphatase
enzyme that removes the phosphate group from a molecule that has been previously phosphorylated
phosphodiesterase
enzyme that degrades cAMP, producing AMP, to terminate signaling
phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule; often done by kinases
plasmodesmata
An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect from adjacent cells
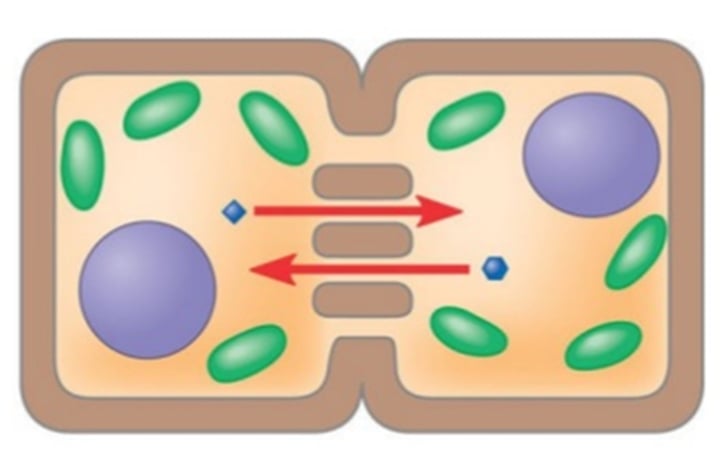
quorum sensing
method of cellular communication used by bacteria that informs them of the abundance of similar (or different) bacteria in the environment
receptors
proteins in or on target cells that bind to ligands
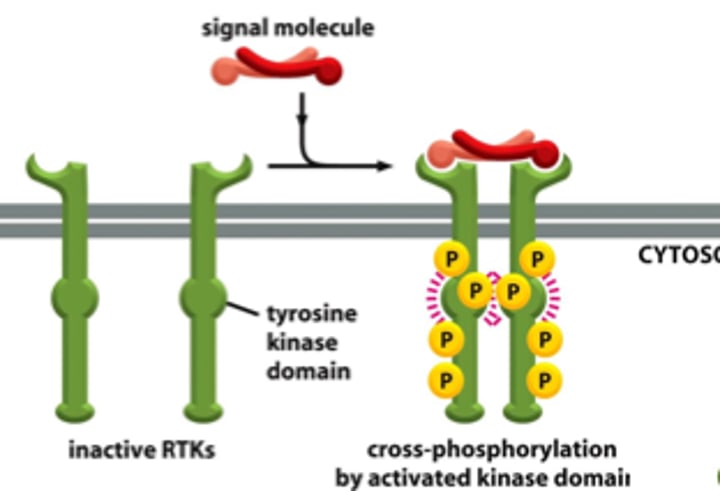
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
membrane receptors that are activated by dimerization following ligand binding and transfer phosphate groups from ATP to another protein; multiple tyrosines in their tails
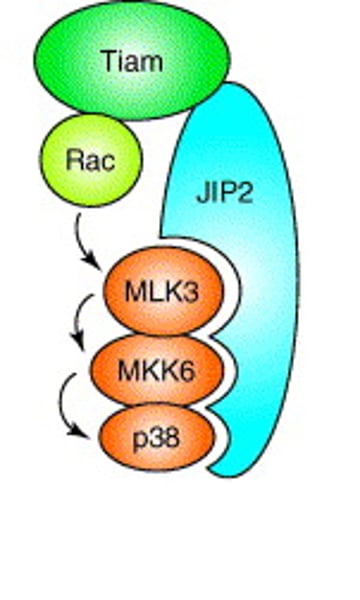
scaffolding proteins
large relay proteins to which several other relay proteins are simultaneously attached
second messenger
small, non-protein molecule that propagates a signal within the cell after activation of a receptor causes its release
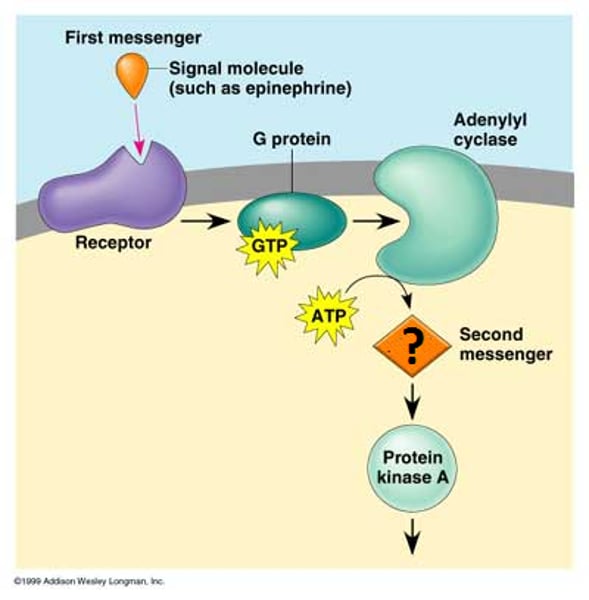
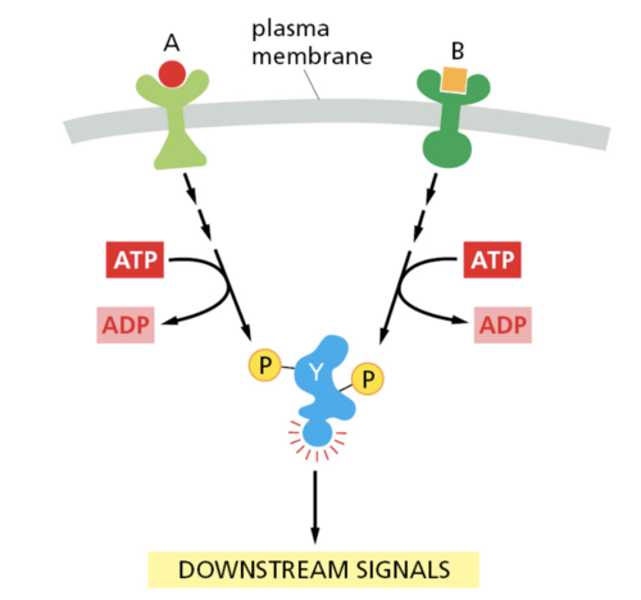
signal integration
interaction of signals from two or more different cell-surface receptors that merge to activate the same response in the cell
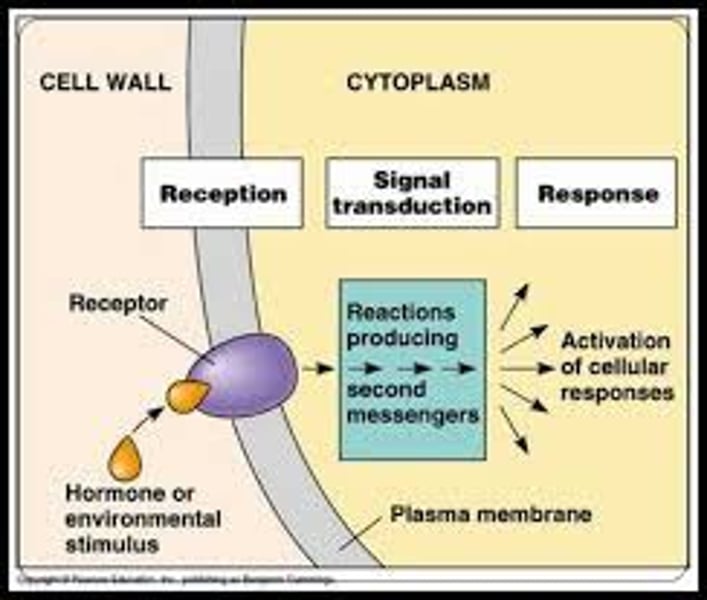
signal reception
Chemical signal binds to receptor, binding causes an alteration of receptor conformation and alteration interacts with cellular molecules causing a metabolic change.
signal transduction
propagation of the signal through the cytoplasm (and sometimes also the nucleus) of the cell
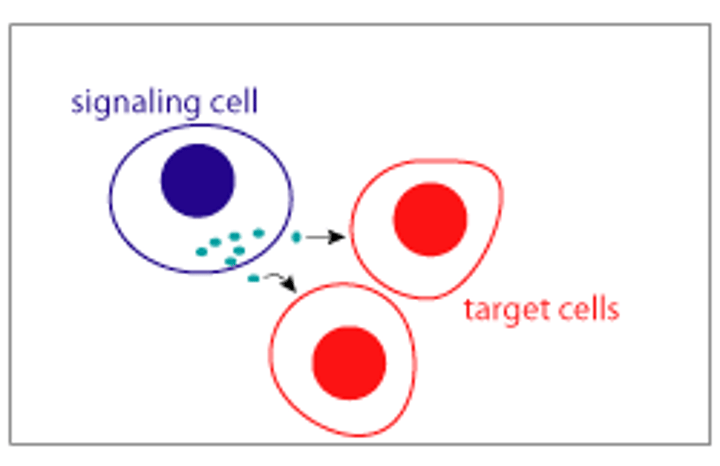
signaling cell
cell that releases signal molecules that allow communication with another cell
signaling pathway
(also signaling cascade) chain of events that occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell to propagate the signal from the plasma membrane to produce a response
synaptic signal
chemical signal (neurotransmitter) that travels between nerve cells
target cell
cell that has a receptor for a signal or ligand from a signaling cell
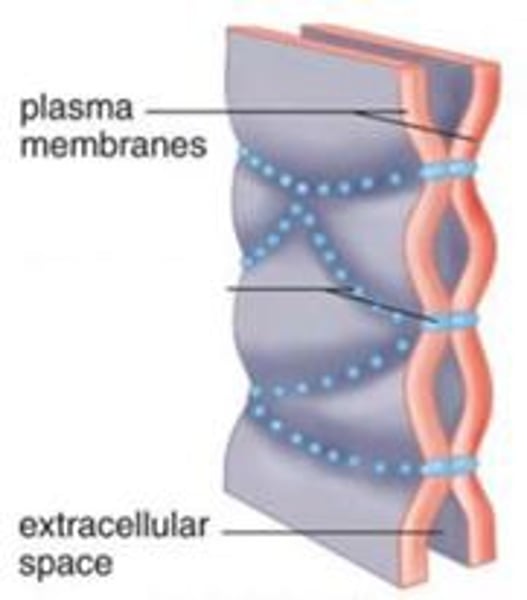
tight junction
a type of intercellular junction between animal cells that prevents the leakage of material through the space between cells; proteins called claudins and occludins tightly hold the cells against each other.
transcription factor (active)
A regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes.
transcription of a gene
RNA polymerase reads DNA of the gene to produce a mRNA complementary to it
translation
the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm