Movement In and Out of Cells Flashcards
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Diffusion
Net overall movement of particles from a high concentration to low. It is Passive transport.

Osmosis
The process of water molecules moving across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration, until equilibrium.
Passive Transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of cellular energy.
Active transport
The process of moving particles against their concentration gradient, requiring energy input from the cell, often via ATP.
Permeable
The ability to go through something.
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
A substance in which a solute is dissolved, forming a solution.
Hypotonic solution
A solution that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution, causing water to move into cells.
Hypertonic solution
A solution that has a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution, leading to the movement of water out of cells.
Isotonic
Equilibrium, same solute and solvent concentration.
Dilute solution
A solution that has a low concentration of solute relative to the solvent, leading to less saturation.
Concentrated solution
A solution that has a high concentration of solute relative to the solvent, resulting in greater saturation.
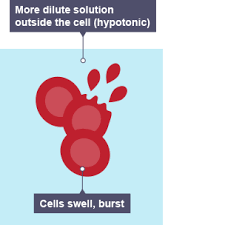
Osmosis In Animal Cells in Pure water
As more water enters the cell, it swells and may eventually burst.
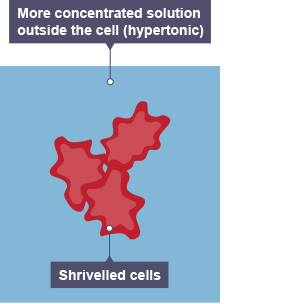
Osmosis In Animal Cells in a concentrated solution
As the water leaves the cell, the cytoplasm shrinks. The cell shrivels up.
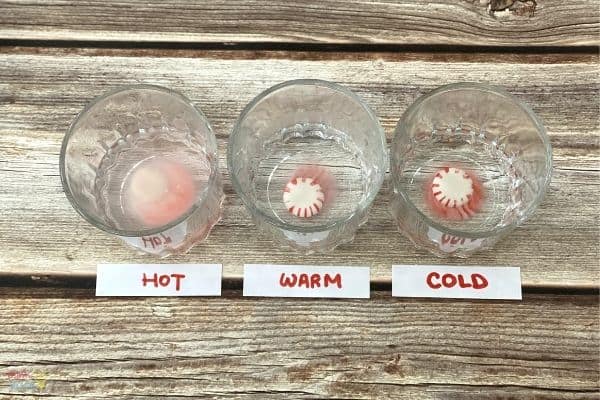
How does temperature affect diffusion?
The higher the temperature the more kinetic energy, and faster movement of diffusion. Ex: Dissolving in cold vs. Warm water

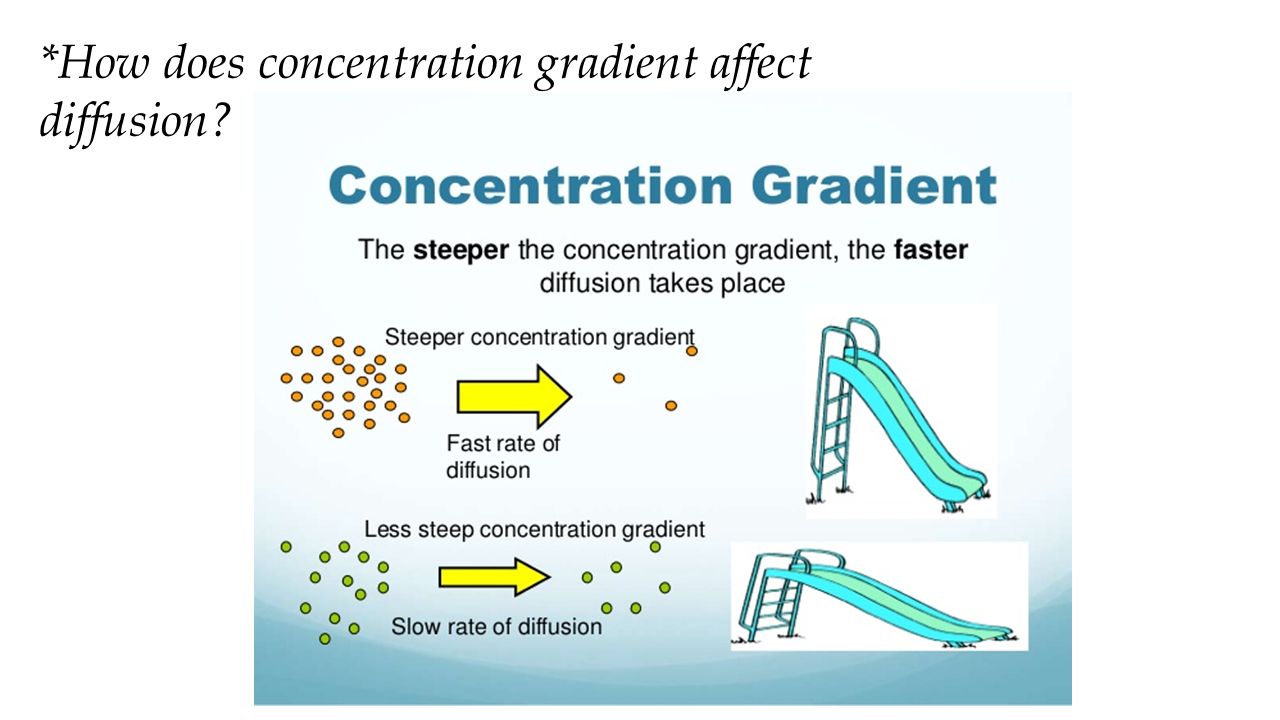
How does concentration gradient affect diffusion?
The bigger the difference in concentrations, the steeper the gradient is, and therefore there is a faster rate of diffusion. Conversely, when concentrations are similar, the rate of diffusion slows down, because molecules are moving towards equilibrium.