unit 3 honors biology-energetics
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
, ex. primary producers, algae, plants
heterotroph
an organism that relies on other organisms for food
ex.bunnys, snakes,squirrels
decompistion is the ____ stage in the recycliing of nutrients
first
detritivore
a feeder of dead or decaying matter
examples of decomposers
ex. fungi, bacteria, beetles, flys
1st trophic level
producers
2nd trophic level
primary consumers
3rd trophic level s
secondary consumers
4th trophic level
teritary consumers
top of trophic levels
apex predators
100 energy at ____then goes to 1 percent at
1 trophic level
2nd trophic level
autotrophs include
chemoautotrophs and photoautotrophs
chemoautotroph is
an organism that uses chemicals (methane) to make organic compounds
ex. bacteria
photoautotroph is
an organism that uses sunlight to make organic compoounds
ex. bacteria, plants, algae
heterotrophs include
consumers and decomposers
Plants are considered to be
autotrophs
animals are considered
heterotrophs
Which of the following cellular processes require ATP
cell division,
digestion
dna replication
making proteins
cell growth
nerve impulses
protein pumps like the sodium potassium pump
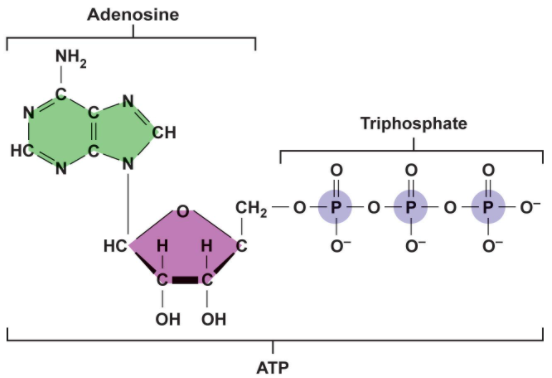
what is the green molecule?
adenosine
The main source of energy for autotrophs is inorganic compounds and the main source of energy for heterotrophs is organic compounds.
true
venus fly trap is a
autotroph
spiders are
heterotrophs
The energy that ATP carries is stored in
the bonds that connect the phosphates to each other
How is ADP able to "recharge" and transform back into ATP?
adding another phosphate
When the last phosphate is removed from an ATP molecule …
a large amount of energy is released
What is another term for autotroph?
producer
what is ATP
an organic molecule that carries energy that cells can use
Atp contains
one adenine, one ribose sugar and THREE phosphate groups
Where is the greatest amount of energy contained in ATP
between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups (This is why ADP has less energy because it doesn’t have that 3rd group).
What is ADP?
an organic molecule that lost a phosphate group when the last phosphate bond was broken by a hydrolysis reaction
what does adp contain?
one adiene, one ribose sugar and TWO phosphate groups
How and when is energy released in ADP
When the last phosphate bond is broken, energy is released for cellular work
ADP needs to be recharged, another phosphate is added (creating ATP in this process)
ENERGY IS NOT RELEASED WHEN BONDS ARE BROKEN; ENERGY IS RELEASED WHEN BONDS ARE FORMED
Phosphorylation means
adding a phosphate to a molecule
what are the processes that make ATP
cellular respiration and photosynthesis
what pigment is found in chloroplasts
chlorophyll
what is a stack of thylakoids called?
granum
What is the space surrounding the granum called
stroma
chlorophyll absorbs
blue/violet/red
chlorophyll reflects
green and yellow light
Process of photosynthesis is divided into
light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions
How are electrons transported between the different reactions
NADP+ (a transport molecule)
light-dependent reactions occur in
the thylakoids
photosystems collect sunlight and use it to energize electrons, releasing energy as they go throughout molecules
This is called the electron transport chain
What happens in light-dependent reactions
h20 molecules are broken apart in a process called photolysis
chlorophyll B helps plants absorb
violet, blue, orange and red
what color absorbs the least
green because it is reflective