Science wave - Sec 3
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are wave
a disturbance that carries energy through matter
Transverse waves
a wave that disturbs the particles in the medium perpendicular to the direction of the
Longitudinal Waves
A wave that disturbs the particles in the medium parallel to the direction of the energy transfer.
Crest
the highest point of the wave
Trough
the lowest point of the wave
Compression
where the particles are close together
Rarefaction
where the particles are spread apart
Wavelength
The distance between one point on a wave and the exact same place on the next wave.
Phase
Any two points on a wave that are one or more
whole wavelengths apart are said to be “in phase”.
Frequency
Is the number of complete wavelengths a point on that wave makes each second.
Amplitude
The greatest distance from equilibrium.
wavelengths get smaller
frequencies get higher.
Radio waves
Have the longest wavelengths and the
lowest frequencies
Infrared waves
Have a shorter wavelength, from .001 m to 700 nm, and therefore, a higher frequency.
Visible light
Wavelengths range from 700 nm (red light) to 30 nm (violet light) with frequencies higher than infrared waves.
Ultraviolet Light:
Wavelengths range from 400 nm to
10 nm
What can Ultraviolet Lights do to a person
the frequency is high enough with UV rays to penetrate living cells and cause them damage.
X-Rays
Wavelengths from 10 nm to .001 nm.
What can X-Rays do to a person
These rays have enough energy to penetrate
deep into tissues and cause damage to cells
What can Gamma Rays do
have enough energy to go through most materials easily
Gamma Rays
Carry the most energy and have the shortest wavelengths, less than one trillionth of a meter (10-12).
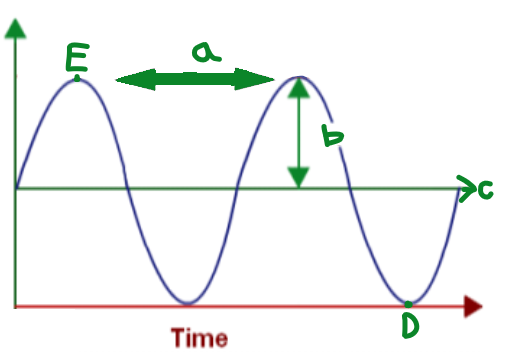
A
Wavelength
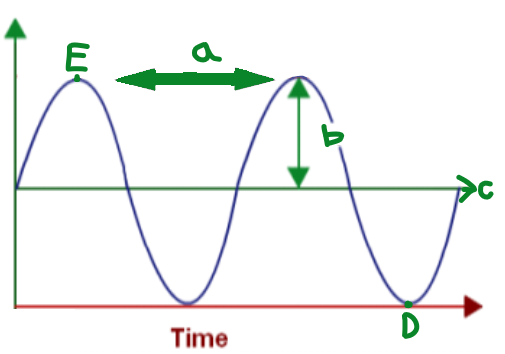
B
Amplitude
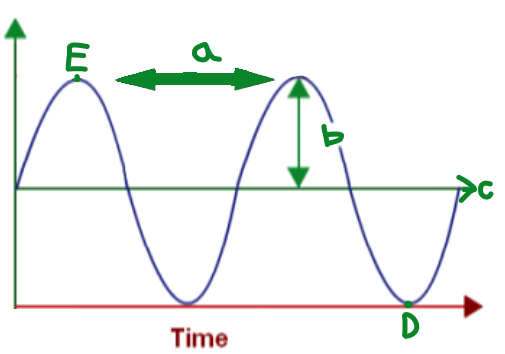
C
Equilibrium
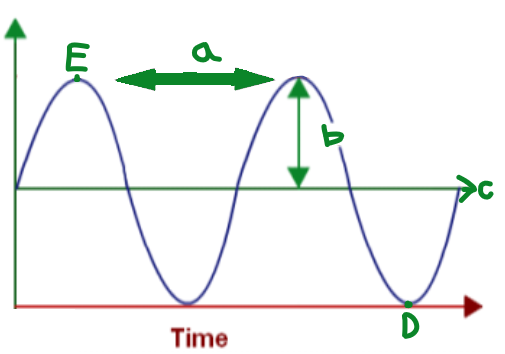
D
Trough
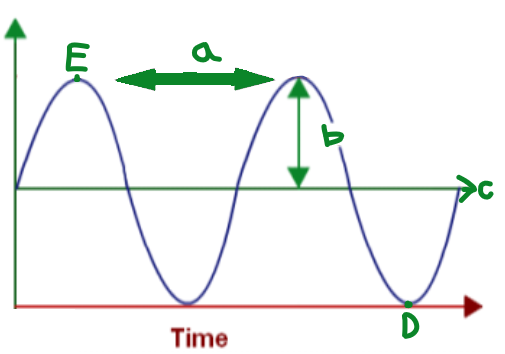
E
Crest