HINF 461: Quality Improvement Exam Preparation Guide
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
Quality Improvement (QI)
A structured organizational process for involving personnel in planning and executing a continuous flow of improvements to provide quality health care that meets or exceeds expectations.
What is the goal of QI
to improve organizational process and outcomes
Total Quality Improvement (TQI)
A management philosophy and method; in the industry, QI is referred to as TQI.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
In healthcare, QI is referred to as CQI.
What are the other names of QI
Quality Assurance (QA), Quality, Quality Control, Total Quality Management, and Continuous Quality Improvement
What does QI involve?
providing customers with products and services that constantly meet customer needs and expectations
How does QI differ from the management methods?
Recognizes the importance of customer needs in quality and that those needs will change over time due to education, economics, technology, and culture.
Importance of Quality Improvement
A way of achieving product, process, and service perfection.
Ongoing Process of QI
Patient care continually undergoes change, including new research, guidelines, clinical procedures, and technologies.
Localized Improvements
An ad hoc team is developed to look at specific process problems or opportunities.
Organizational Learning in TQI
Occurs when TQI is documented and results in the development of policies and procedures that are implemented.
Reasons for TQI in Healthcare Organizations
Accreditation, cost control, competition, and pressure from employers.
Basic TQI Strategies
Conformance to requirements, competitive advantage, and true process improvement.
Kaizen
Dynamic change, changing expectations, and continuous efforts to address change.
Philosophical Elements of QI
Process optimization, continuing improvement, organizational learning, and data-driven analysis.
Structural Elements of QI
Top management commitment, statistical measures, customer satisfaction measures, benchmarking, and redesign of processes from scratch.
Deming's 14 Points for QI
A set of principles aimed at improving quality in organizations, including creating a statement of aims, learning new philosophies, and driving out fear.
Point 1 of Deming's 14 Points
Create and publish a statement of the aims and purposes of the company for all employees to see.
Point 2 of Deming's 14 Points
Learn the new philosophy.
Point 3 of Deming's 14 Points
Inspect to improve processes and reduce costs.
Point 4 of Deming's 14 Points
Do not award business on the basis of price tag alone.
Point 5 of Deming's 14 Points
Improve the system of production and service.
Point 6 of Deming's 14 Points
Train.
Point 7 of Deming's 14 Points
Team leadership.
Point 8 of Deming's 14 Points
Drive out fear. Create trust. Create a climate of innovation.
Point 9 of Deming's 14 Points
Optimize company team, group and staff purposes
Point 10 of Deming's 14 Points
Eliminate numerical goals, poster and slogans asking for new productivity.
Point 11 of Deming's 14 Points
Eliminate work standards that prescribe numerical goals.
Point 12 of Deming's 14 Points
Eliminate management by objective
Point 13 of Deming's 14 Points
Remove barriers that rob people of pride in workmanship.
Point 14 of Deming's 14 Points
Encourage education and self-improvement for everyone.
Point 15 of Deming's 14 Points
Take action to accomplish transformation
Walter Shewhart
Father of quality control who introduced control charts.
Feigenbaum
Introduced total quality control. Developed a system of integration on the function of QI from: conception, planning, design, and set-up.
Juran
Developed a quality trilogy consisting of quality planning, quality control, and quality improvement.
Crosby
Focused on changing corporate culture and attitudes with the zero defects theory.
Ishikawa
Promoted total organizational participation and introduced the fish bone diagram and just in time process.
Total Quality Improvement (TQI)
A systematic approach to improving quality in healthcare that focuses on customer satisfaction, profitability, employee satisfaction, reduced costs, improved patient survival, and better continuity of care.
Benefits of TQI
Includes customer satisfaction, profitability, employee satisfaction, reduced costs, improved patient survival, and better continuity of care.
Advantages of TQI
Improves quality of care while empowering healthcare professionals, enhances worker motivation and accountability, leverages staff knowledge and skills, and strengthens organizational effectiveness.
Quality and organizational survival
Healthcare organizations address gross inefficiencies and cost containment.
There were two key components that devised the path forward, that was creating:
A system to standardize and make transparent all EHR change requests and the
processes. And, a governance structure that could be relied upon by both EHR users and EHR
stewards within IMIT
EHR change requests
A system to standardize and make transparent all electronic health record change requests and processes.
Governance structure for EHR
A reliable structure for both EHR users and EHR stewards within IMIT.
Quality Improvement (QI)
The extent to which healthcare services are provided to individuals and patient outcomes, requiring safety, effectiveness, timeliness, efficiency, equity, and people-centeredness.
Components of Health (WHO)
Includes safety, effectiveness, timeliness, efficiency, equity, and people-centeredness.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
A structured organizational process for involving personnel in planning and executing continuous improvements to provide quality healthcare.

Characteristics of CQI in healthcare
Includes a link to the strategic plan, a quality council of top leadership, training programs, mechanisms for selecting improvement opportunities, process improvement teams, staff support for analysis and redesign, personnel policies that motivate participation, and application of scientific methods and statistical process control.
Characteristic/Functions of Health Care CQI
1. Understanding and adapting to the external environment.
2.Empowering clinicians and managers to analyze and improve processes.
3. Adopting a planned, articulated philosophy of ongoing change and adaptation.
4. Developing a multidisciplinary approach that goes beyond conventional
departmental and professional lines;
5. Adopting a planned, articulated philosophy of ongoing change and adaptation;
6. setting up mechanisms to ensure implementation of best practices through
planned organizational learning
7. providing the motivation for a rational, data-based, cooperative approach to
process analysis and change; and developing a culture that promotes all of the
above.
CQI
CQI is simultaneously two things: a management philosophy and a management method.
Elements of CQI
Philosophical elements, Structural elements, Healthcare elements.
PDSA
PDSA cycles help test changes in small steps to improve systems. They allow quick feedback and adjustments, making sure solutions are practical and effective.
FOCUS
Find, Organize, Clarify, Understand, Select.
Need for CQI
The safety and quality of care has shown improvement since 2000 but further improvement is needed. External forcers are are increasing the demand for higher quality: Accreditation, legislation.
Dynamic character of CQI
CQI methodology is constantly being refined and tested: it is an evolutionary quality improvement mechanism.
Current state of CQI in healthcare
Improvement in quality and safety remains limited despite best efforts.
Diffusion theory
Provides one way of understanding the barriers and facilitators of CQI in healthcare.
Economic case for an innovation
Includes the returns to all the actors, not just the individual investing business unit.
Social case for an innovation
Involves measuring benefits, but not requiring positive returns on the investment.
Motivational Factors
Intrinsic motivation, capturing the intellectual capital of the workforce, reducing managerial overhead, lateral linkages.
Culture of excellence
Ensures excellence and high quality at every customer interface, shared by all in the organization.
Three types of leaders
Opinion, Champion, Boundary spanners.
Implementation definition
(A) specified set of activities designed to put into practice, an activity, or program.
Implementation science definition
The scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of research findings and other evidence-based practices into routine practice.
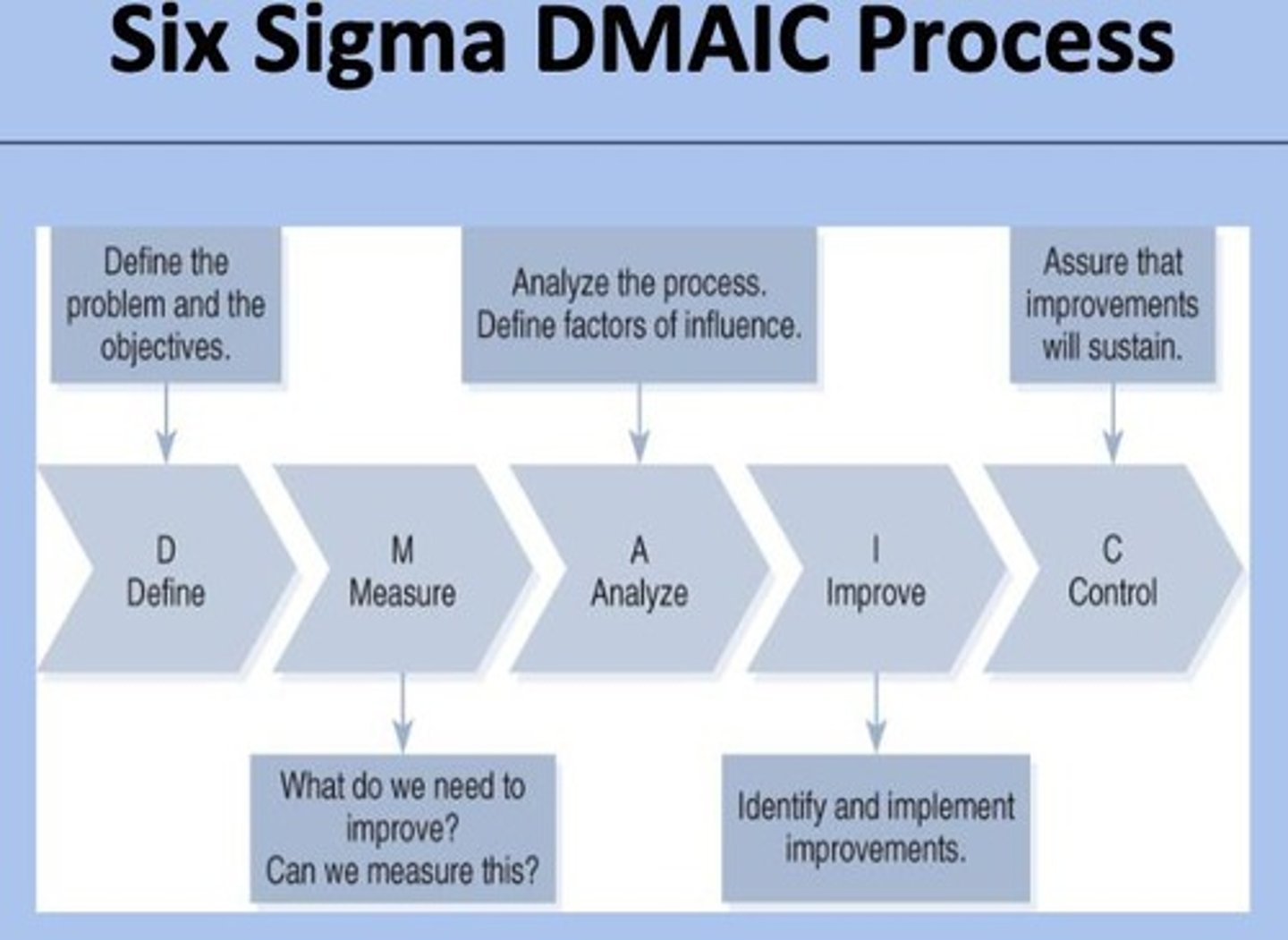
Six Sigma's DMAIC process
Moves directly from the Improve step to the Control step without any mention of context-specific details.
Key ingredients for achieving outcomes
Integrating improvement and implementation.
Model for improvement and implementation
A framework that guides the process of improving and implementing health care practices.
Consolidated Framework for Implementation
A structured approach to ensure effective implementation of health care practices.
Active Implementation Frameworks
Definitions and strategies that promote effective implementation in health care settings.
Implementation Drivers
Factors that influence the successful implementation of health care practices.
Implementation strategies
○ Engage consumers
○ Use evaluative and iterative strategies
○ Provide technical assistance
○ Adapt and tailor to the context
○ Develop stakeholder relationships
○ Train and educate stakeholders
○ Support clinicians (and service providers)
○ Utilize financial strategies
○ Change infrastructure
QI in Digital Transformation
A concept discussed by Guest Lecturer Ruonan Lou, focusing on five blocks of digital transformation.
Understanding root cause analysis
A method for identifying the fundamental reasons for problems in health care.
Data Harmonization
The process of standardizing data from different sources to create a cohesive dataset.
Student Synthetic Dataset
An outline discussed by Guest Lecturer Sheraz Cheema, focusing on data for educational purposes.
BC PSLS
The Patient Safety and Learning System, a web-based tool used by BC's health authorities to report and learn from patient safety incidents.
PSLS Handler
A leadership role responsible for reviewing reported incidents and conducting evaluations.
PSLS Training Duration
About 1 hour, scheduled at your convenience and eligible for CPD credits.
Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale
CTAS has five levels of urgency in medical conditions.
Level 1: Resuscitation
Conditions that are threats to life or limb.
Level 2: Emergent
Conditions that are a potential threat to life, limb or function.
Level 3: Urgent
Serious conditions that require emergency intervention.
Level 4: Less urgent
Conditions that relate to patient distress or potential complications that would benefit from intervention.
Level 5: Non-urgent
Conditions that are non-urgent or that may be part of a chronic problem.
Quality Improvement (QI)
A systematic approach to improve health care services through measurement and analysis.
Data can be used to...
Used to evaluate the current situation, analyze, improve processes, and track progress.
Methods used for analyzing data in QI draws from:
biostatistics, economics, epidemiology
Industrial Statistical Tools
- widely tested in healthcare
- transferrable
-meaningful
-easy to understand
-easy to use
- help point of sources of error and variation
-indicate where improvements can be made most effectively
-should be used on a continuous basis
-different tools may be useful at different stages of QI projects
QI Measurement Tools
Includes flowcharts, cause and effect diagrams, check sheets, Pareto diagrams, histograms, run charts, regression analyses, and control charts.
Stages of QI
1. Describe the process 2. Identify the source of variation 3. Perform in-depth analyses 4. Weigh alternatives (opportunities for further investigation and aid with making choices for change) 5. Measure improvement (in response to change)
Attribute data
Describes categories or qualities (e.g., yes/no, pass/fail, colors).
Variable data
Measures quantities on a scale (e.g., height, weight, temperature).
CQI requires knowledge about the behaviour of systems, which is obtained from:
- data and other sources of information
- the application of tools and techniques that have been proven to be effective throughout the evolution of CQI
Process capability
Studies to understand the expected output of a process and its predictability.
Benefits of stable process
Includes productivity, greater speed, and reliability.
Process behavior chart
The most effective way to measure, document, analyze, and understand the capability of a process.
Turnaround time (TAT)
Turnaround time
- is what acceptable variation is dependent on
Statistical control
The basis of CQI activities to ensure processes are stable or 'in control'.
Voice of the process
Listening to the data and variation to inform improvement actions.
Understanding Variation
understanding the nature of process variation and measurement/statistical analysis