Endocrine System
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Describe the anatomical relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland.
→ Hypothalamus is connected to pituitary gland underneath by infundibulum
→ Infundibulum contains neural tracts that carry hormones from the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary (neural tissue)
→ Hypothalamus connects to anterior pituitary via hypophyseal portal system (glandular tissue)
→ Capillaries in the hypothalamus are connected to capillaries in the anterior pituitary via the infundibulum
How do cells in the hypothalamus control the secretion of the cells of the anterior pituitary?
By releasing hormones into capillaries serving the anterior pituitary
Where are the hormones of the posterior pituitary produced and how do they get to the posterior pituitary?
In the hypothalamus and travel down nerve axons to the posterior pituitary
What is meant by an antagonist?
Antagonists reverse or oppose the reaction of certain effects
Why is the nervous system like ‘SMS’ while the endocrine system is like ‘Email’ in terms of speed?
Nervous signals are electrical (impulses); Endocrine signals are liquids (bloodstream)
What is a target organ?
Organ responding to a particular hormone in a specific way
If hormones travel in the bloodstream, explain why not all tissues respond
The proper hormone receptors must be present on the cells of the target organ
Compare the location of receptors for protein based and steroid-based hormones.
→ Protein-based (polar) hormone receptors located on cell membranes (work with second messengers)
→ Steroid-based (non-polar) hormones diffuse through cell membranes (receptors located in cytoplasm or nucleus)
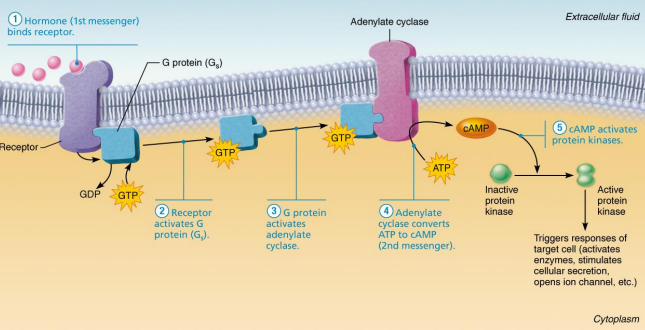
How do first messengers differ from second messengers?
→ First messengers are protein-based (polar) hormones traveling to target cells
→ Cannot diffuse through cell membrane lipids thus attach to cell membrane receptors
→ On contact, receptors activate a second chemical messenger inside the cell
→ Message is forwarded to nucleus chemically
Which hormones produced in inadequate amounts result in the following?
• Excessive urination
• Loss of glucose in the urine
• Abnormally small stature
• Mental and physical sluggishness
→ ADH
→ Insulin
→ Growth hormone
→ Thyroid hormone
Which hormones produced in excessive amounts result in the following?
• Large hands and feet
• Nervousness and sweating
• Spontaneous fractures
• Reduction of pain and swelling
→ Growth hormone
→ Adrenaline
→ PTH
→ Cortisol
Explain the thyroxine feedback loop
→ Blood thyroxine ↓
→ Hypothalamus detects ↓
→ Releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
→ TRH stimulates anterior pituitary
→ Releases thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
→ TSH stimulates thyroid gland
→ Thyroid gland releases thyroxine
→ Blood thyroxine ↑
→ Inhibits hypothalamus
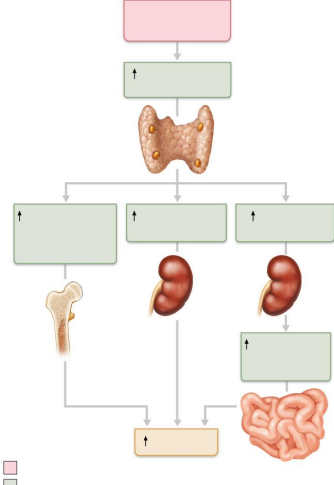
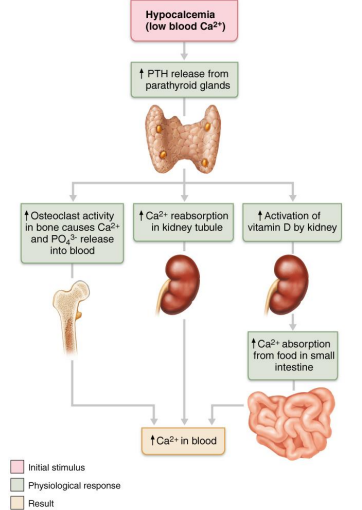
Explain PTH and calcitonin antagonism using the diagram as a guide
→ Blood Ca2+ ↓ = ↑ PTH = ↓ Bone Ca2+
→ Blood Ca2+ ↑ = ↑ Calcitonin = ↑ Bone Ca2+
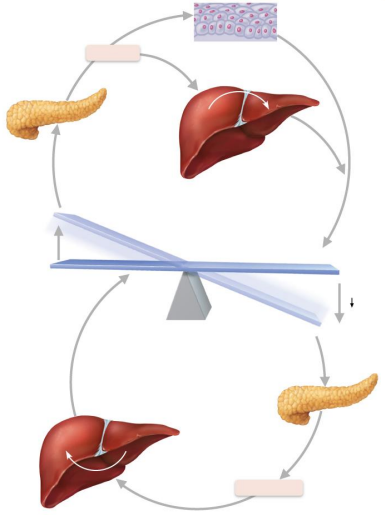
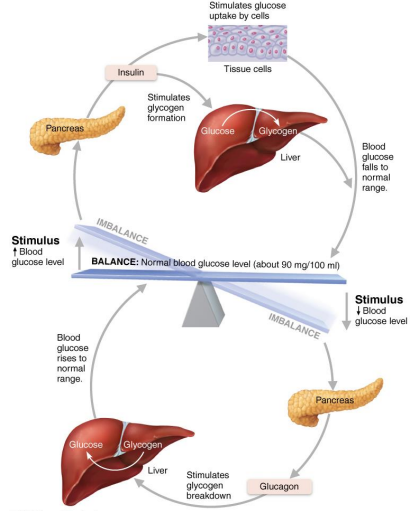
Explain insulin and glucagon antagonism using the diagram as a guide
→ Blood glucose ↓ = ↑ glucagon
→ Blood glucose ↑ = ↑ insulin
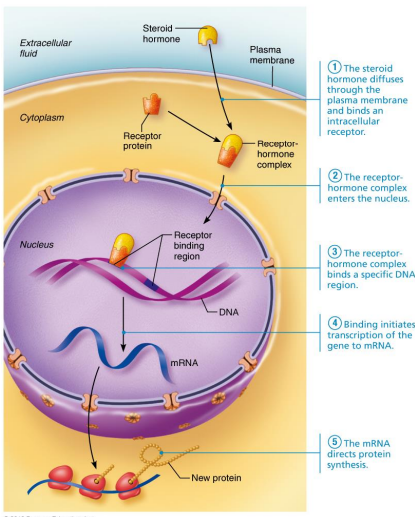
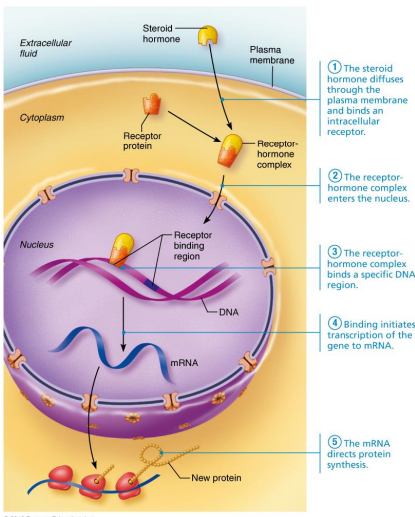
Is this an example of a protein-based or steroid based hormone?
Steroid-based
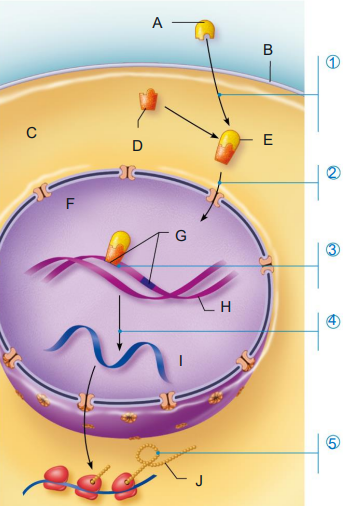
Identify structures (A-J)

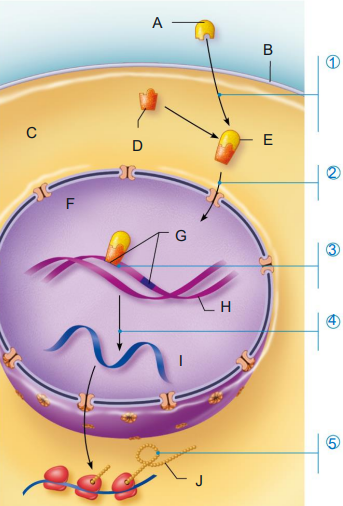
Identify processes (1-5)
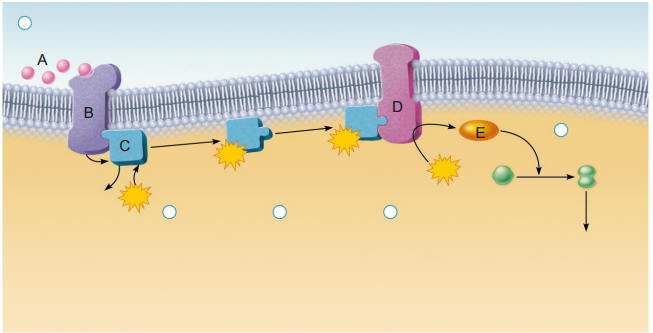
Is this an example of a protein-based or steroid based hormone?
Protein-based hormone
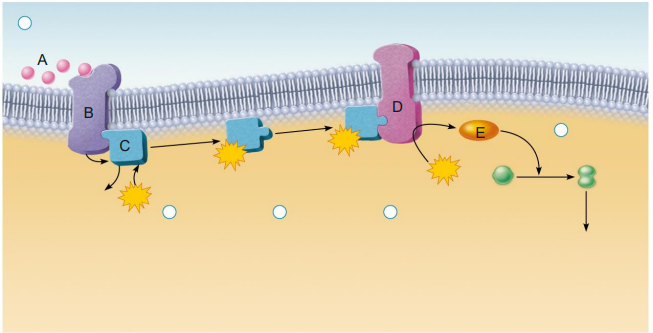
Identify items (A-E)