Biology final exam STUDY HARD!!
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Biosphere
All parts of Earth where life can survive.
Omnivore
An organism that eats both plants and animals, such as a raccoon.
Decomposer
Organisms that break down dead material and return nutrients to the soil.
Autotroph
An organism that collects energy from sunlight or inorganic substances to produce food.
Food web
A complex network of feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem.
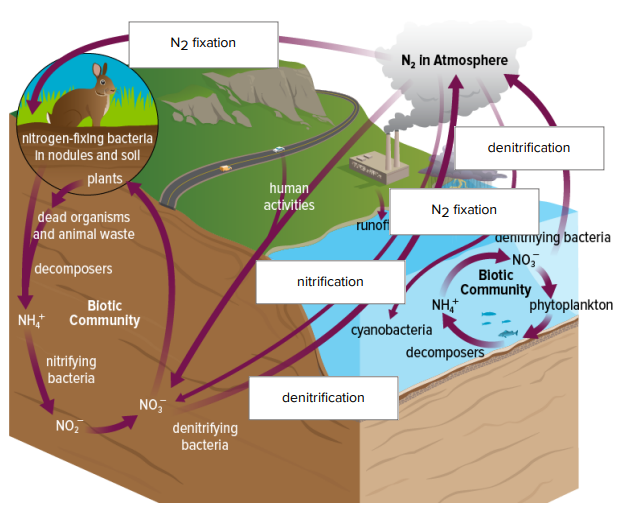
Nitrogen cycle
The cycle by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms, involving processes such as fixation and denitrification.
Abiotic factor
Non-living components of the environment, such as water and temperature.
Population
A group of organisms of the same species that occupy the same geographic area at the same time.
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass.
Homeostasis
The ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment.
Carnivore
An organism that primarily eats other animals.
Herbivore
An organism that primarily eats plants.
Detritivore
An organism that feeds on dead organic matter and helps with decomposition.
Commensalism
A relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
N2 fixation
The process of converting nitrogen gas from the atmosphere into ammonia or related compounds.
Denitrification
The process by which bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas, releasing it back into the atmosphere.
Nitrification
The process of converting ammonia into nitrates by soil bacteria.
Ecosystem
A biological community interacting with its physical environment.
Biogeochemical cycle
The movement of chemical elements between living and non-living components of the ecosystem.
Heterotroph
An organism that obtains its food by consuming other organisms.
Producer
An organism that can make its own food, typically green plants.
Trophic level
The position an organism occupies in a food chain.
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from the atmosphere, including rain, snow, sleet, and hail.
Condensation
The process where water vapor cools and changes back to liquid, forming clouds.
Evaporation
The process of water turning into vapor and entering the atmosphere.
Transpiration
The process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts.
Succession
The process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time.
Nutrients
Substances that provide nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life.
Cellular respiration
The process by which organisms convert glucose and oxygen into energy.
Autotrophic bacteria
Bacteria that can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Microbial decomposer
Microorganisms that break down dead organic matter.
Polar covalent bond
A type of chemical bond where electrons are shared unequally between atoms, resulting in partial charges.
Phosphorus cycle
The cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Water cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Energy pyramid
A graphical representation used to show the energy flow through an ecosystem.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Eutrophication
The excessive growth of algae in water bodies caused by high nutrient levels.
Limiting factor
Any environmental condition that limits the growth, abundance, or distribution of an organism.
Carbon cycle
The cycle through which carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, land, water, and living organisms.
Cellular organization
The hierarchical structure of cells in living organisms.
Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment.
Genetic variation
Differences in DNA among individuals within a population.
Mutualism
A symbiotic relationship where both species benefit from the interaction.
Acid-base reaction
A chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base.
Ionic bond
A chemical bond formed between two ions with opposite charges.
Covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a catalyst to accelerate a chemical reaction in a biological process.
Macromolecule
A large, complex molecule, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Biomolecule
Any molecule that is produced by living organisms, including proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
a
a
Homeostatic regulation
The mechanisms that maintain stable conditions within an organism.
Nutrient cycling
The movement and exchange of organic and inorganic matter back into the production of living matter.
Gene expression
The process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize functional gene products.
Cell membrane
The biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment.
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll.
Cellular differentiation
The process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell.
Hormone
A signaling molecule produced by glands in multicellular organisms.
Exponential growth
Growth that occurs when the resources are unlimited and the population increases rapidly.
Carbohydrate
Organic molecules consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, typically in a 1:2:1 ratio.
Lipid
A diverse group of hydrophobic molecules including fats, oils, and waxes.
Protein synthesis
The process by which cells generate new proteins.
Nucleotide
The building block of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Gene
A segment of DNA that contains the code for a specific protein.
Chromosome
A condensed structure of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.