MLT 111 (Ch. 8, 9, 10-17)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
CLSI recommends synovial fluid to be collected in:
1 tube
3 tubes
4 tubes
2 tubes
3 tubes
CSF stands for…?
Cerebral Spinal Fluid
Chemical analysis of CSF shows that the fluid contains:
a. Plasma chemicals in the same concentration as in the plasma
b. Fewer chemicals than are found in plasma
c. More chemicals than are found in plasma
d. Plasma chemicals in concentrations different from those in the plasma
d. Plasma chemicals in concentrations different from those in the plasma
Differentiation of Exudate Vs Transudates is important, if it is transudate little further testing is required. This statement is:
Incorrect or Correct
Correct
Semen analysis on post-vasectomy patients should be performed:
Within 1 week post-vasectomy
Until two consecutive monthly specimens show no sperm
Until two consecutive monthly specimens show no viable sperm
Within 1 month post-vasectomy
Until two consecutive monthly specimens show no sperm
The function of serous fluid is to:
Provide lubrication for the serous membranes
Remove excess fluid from body cavities
Provide nutrients to the serous membranes
Protect organs from trauma
Provide lubrication for the serous membranes
The third tube of CSF collected from a lumbar puncture should be used for:
Cytology examination
Hematology tests
Chemistry tests
Microbiology tests
Hematology tests
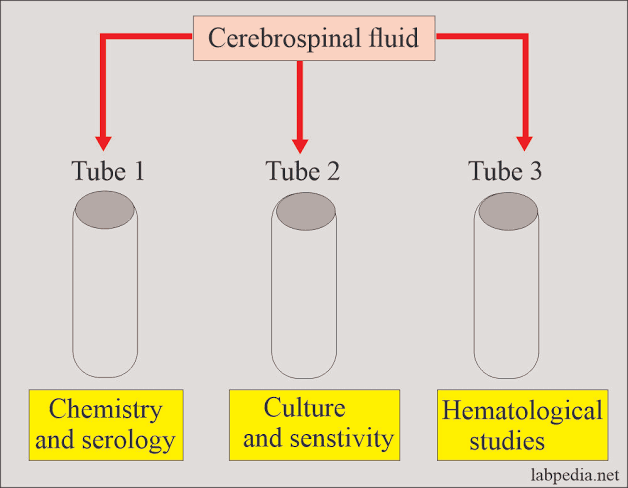
Which of the following body fluid and collection procedure WRONGLY matched
Peritoneal fluid - Paracentesis
Pleural fluid - Thoracentesis
CSF – Lumbar puncture
Pericardial fluid - Asciticentesis
Pericardial fluid - Asciticentesis
Which of the following is most often associated with the formation of a transudate?
Pancreatitis
Congestive heart failure
Peritonitis
Malignancy
Congestive heart failure
Which is not a true statement describing synovial fluid?
It acts as a lubricant.
It supplies nourishment to cartilage.
It is found only in the knee.
It surrounds all joints in the body.
It is found only in the knee.
If CSF tubes numbered 2 and 3 cannot be analyzed within 1 hour, the correct procedure is to:
Leave both tubes at room temperature
Refrigerate tube 2 and freeze tube 3
Refrigerate both tubes
Refrigerate tube 3 and leave tube 2 at room temperature
Refrigerate tube 3 and leave tube 2 at room temperature
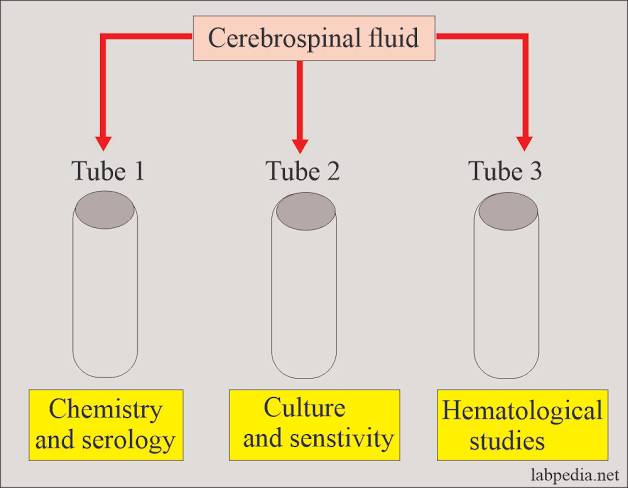
CSF Tube collection; order, department and preservation method…
Hematology, Chemistry/Serology and Microbiology
Chemistry/Serology; freeze it
Microbiology; room temperature
Hematology; refrigerate
Which of the following disorders is caused by the failure to inherit the gene for producing phenylalanine hydroxylase?
porphyria
Phenylketonuria
Alkaptonuria
Maple syrup Urine Disease
Phenylketonuria
What is a common cause of end-stage renal disease?
polysystic kidney disease
Acute kidney injury
Nephrolithiasis
Chronic glomerulonephritis
Chronic glomerulonephritis
Which of the following amino acids is not associated with Maple Syrup Urine Disease?
Valine
Tyrosine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Tyrosine
Which of the following is a common symptom of Maple Syrup Urine Disease in newborns?
Hyperactivity and rapid weight gain
Seizures and mental retardation
A strong odor of maple syrup in urine
Darkening of urine on exposure to air
A strong odor of maple syrup in urine
Which of the following tests is used for newborn screening of Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
Guthrie blood test
Ferric chloride test
Watson-Schwartz test
Silver nitrate test
Guthrie blood test
Which of the following diseases primarily affects the glomerulus?
Glomerulonephritis
Pyelonephritis
Urethritis
Cystitis
Glomerulonephritis
Upon micrscopic examination you are likely to see WBCs, RBCs, bacteria, and WBC casts in pyelonephritis.
True
False
True
Membranous glomerulonephritis is defined as thickening of the glomerulus membrane caused by immune complex deposits.
True
False
True
Which test uses ferric chloride to produce a blue-green color for detecting phenylpyruvic acid in urine?
Ferric Chloride test
Silver nitrate test
DNPH test
Guthrie test
DNPH test
The presence of oval fat bodies in urine sediment and 3+ protein on the chemical analysis is significant for:
chronic kidney disease
Acute kidney injury
Nephrotic syndrome
chronic glomerulonephritis
Nephrotic syndrome
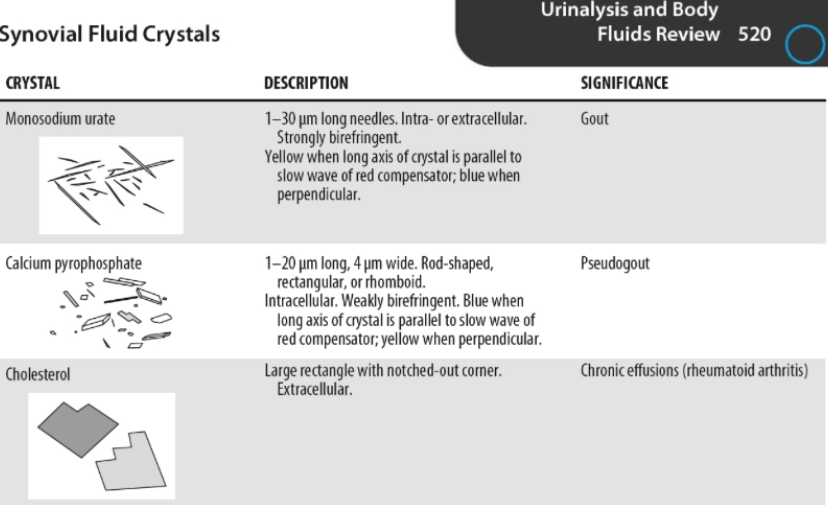
what crystal would you find in a synovial fluid if the patient has gout?
monosodium urate(MSU)
Synovial fluid is found where?
in joints
A transudate is a clear serous fluid with a SG <1.015 and a WBC count <1000/ul. Associated with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome and requires no further testing.
True
Extrudates affect membranes and cause inflammation, infection, malignancy and require further testing—- SG of >1.015. Fluid is yellow, red, brown or green in color. Is this true?
True
What is described?
colorless and clear
<1.015 sg
Non-inflammatory; no further testing
Transudate
What is described?
yellow, brown, green, red in color ; cloudy
>1.015 sg
inflammatory and requires further testing
Extrudates
What am I describing?
colorless/pale yellow ; clear
No crystals
average viscosity
It’s found in all joints
synovial fluid (normal)
Monosodium urate crystals is found in what illnesses?
Gout
Cholesterol crystals is found in what illness?
Chronic effusions — rheumatoid arthritis
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals is found in what illness?
Pseudogout