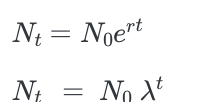Midterm Definitions
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for something that researchers have observed.
Sugar maples do not grow well in grassy fields because sugar maples and grass experience intense competition for nitrogen in the soil.
Prediction
A statement of an outcome that should occur if a hypothesis is correct.
Removing the grass from Johnston Green will increase the survival of sugar maples planted there.
Null hypothesis:
A hypothesis that represents the "not" or "no-effect" contrast to the hypothesis being tested.
What can happen when competitors overlap
1) Temporary co-existence (at reduced carrying capacity)
2) Competitive exclusion
3) Niche partitioning
Niche Partitioning
both species continue to co-exist, but they diverge to occupy slightly different ecological niches within the shared habitat.
i.e., a change in the realized niche
Competitive exclusion:
one of the species disappears from that area.
Co-existence at reduced carrying capacity:
both species continue to live in the area, but at lower numbers.
But this tends to only last in the short term.
• i.e., temporary
Treatment (or experimental) group:
A group that experiences experimental conditions that conform to the mechanism proposed in the hypothesis.
Control group:
A comparison group that represents the normal or no-treatment condition to contrast with groups that experience experimental manipulation.
Controlled conditions:
Aspects of an experimental design that are used in both control and experimental treatments to eliminate bias among treatments and reduce influence from confounding factors.
Outcome variable:
The variable that is measured in an experimental or observational study. It represents a quantity that is relevant to the hypothesis being tested.
Ecosystem services:
Goods and services provided to humans by the natural environment such as oxygen, high-quality and abundant water, productive soils, food and fiber, and recreational and spiritual resources.
Humus:
Soil organic matter originating in decaying plants roots, leaves, and stems.
Niche:
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions that a species lives in.
Fundamental niche:
The possible range that a species can tolerate, which defines the types of habitats where a species can potentially occur.
Realized niche:
The actual range that a species occupies, given the constraints of biotic and abiotic factors.
Acclimation:
a phenotypic change that helps an individual cope with a change in conditions.
Adaptation:
a change in allele frequencies that increases average fitness in a population in a particular environment.
Evolution:
a change in allele frequencies across generations.
Biotic factors:
interactions, such as predation, parasitism, mutualism, or competition, that influence whether a species is found in a given area.
Abiotic factors:
physical conditions, such as temperature, moisture availability, and soil chemistry, that influence whether a species is found in a given area.
Independent Variable
(also known as the predictor or explanatory variable): A variable whose value does not depend on the value of another variable. Common examples include the treatment groups in an experimental study or time.
Dependent Variable
(also known as the response variable): A measured quantity whose value depends on the value of another variable.
Discrete Variable
A quantity that can only take certain, discrete values.
Continuous Variable
A quantity that can take a continuous range of values.
Scatterplot
A type of graph where individual datapoints from two continuous variables are plotted to assess whether the variables are correlated in any way.
Histogram:
A type of graph where a range of possible values is plotted along the x-axis and the frequency of datapoints in each interval in the range is plotted on the y-axis.
Organisms
focuses on how individuals of the same species interact with each other and the environment.
Populations
a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area at the same time, and interact with each other via competition, cooperation, and/or sexual reproduction.
Species
an evolutionary unit in nature. comprised of one or more populations that evolve as a unit and share genetic and physical characteristics.
Community
The collection of species found in the same area at the same time.
Ecosystems
The interacting biotic and abiotic components present in a geographic area.
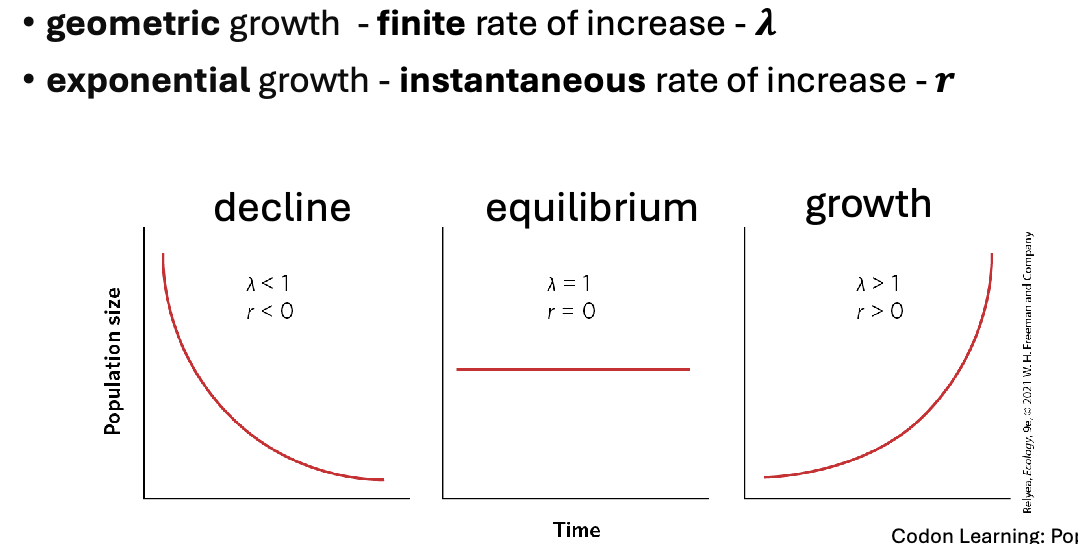
Finite Rate of increase (lambda):
The growth rate over a defined time period (how quickly population is growing or declining)
Usually one year for organisms that breed once per year.
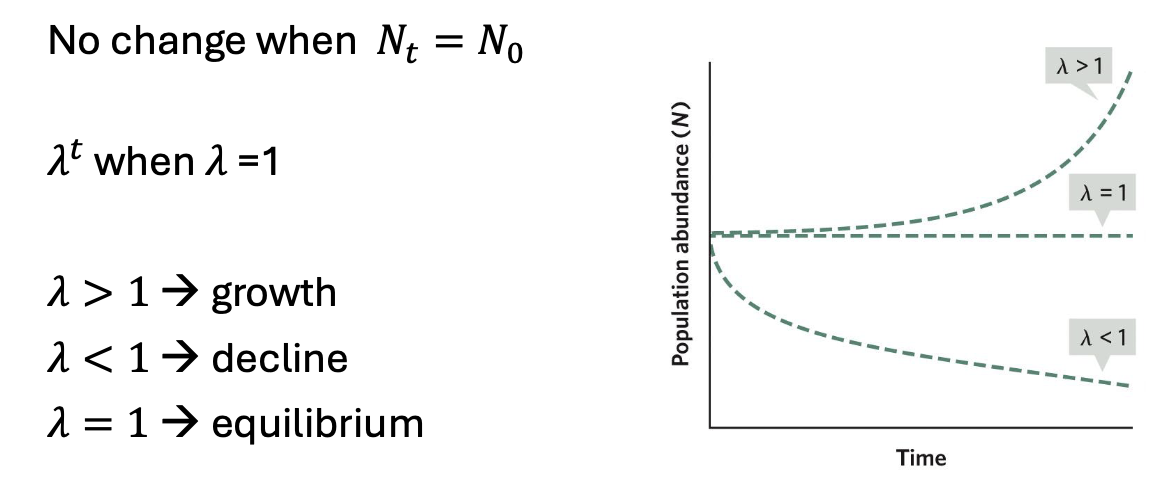
Instantaneous rate of increase ( r )
The growth rate at any moment, indicates growth, decline, or equilibrium
Density-dependent growth
Population growth that is limited by density dependent factors such as disease, predation, and access to food or other resources.
Carrying Capacity
The population size that can be sustained over time in a particular habitat.
Disturbance
an event that removes biomass
Biomass
The total mass of living organisms in a specific area.
Habitat fragmentation
The conversion of large, contiguous areas of native plant and animal communities to small fragments separated by tracts of human development.
Keystone species:
A species that has a disproportionately large impact on a community relative to its numbers.
Foundation Species
provide an ecological foundation for many other species, even though they might not benefit from the interactions
Food Web
A diagram showing the trophic relationships among species in a community.
Tropic Cascade
A change in a food web-usually caused by a change in an important predator-that causes changes in the abundance of other species in the web.
Primary Productivity
In most ecosystems, the amount of light energy captured by photosynthetic organisms.
Gross Primary Production
The total amount of primary productivity in an area, often reported as a rate with units of g/m²/ year.
Net primary productivity (NPP):
The amount of primary productivity present in biomass, often reported as a rate with units of g/m?/year. NPP=GPP-respiration
Direct interactions
occur between two species where one directly affects the other
• Predation or mutualism
Indirect interactions
occur when the relationship between two species is mediated by one or more additional species
• ‘Trophic cascade’
Human appropriation of net primary productivity (HANPP):
The amount of primary productivity used by humans, often reported as a rate with units of gigatons of carbon per year.
Tropic Level
The level at which a particular species feeds, starting with primary producers and moting on to primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on.
Limiting Factor
any environmental or ecological factor that restricts the growth, distribution, or abundance of organisms within that ecosystem
5 examples of limiting factors
• light
• temperature
• space
• energy
• nutrient availability
competitive exclusion principle
states that if two species with identical niches compete, then one will inevitably drive the other to extinction.
Apparent competition
occurs when two or more prey species are indirectly linked through a shared predator
Interference competition
refers to direct interactions between individuals or species that impede the access of competitors to essential resources.
intra vs. inter specific
Interspecific – between species
Intraspecific – within a species
Fitness trade-off
An inevitable compromise between traits that can't all be optimized by natural selection.
Life history
The sequence of life events involving growth and reproduction—essentially, how species allocate energy and other resources to survival and reproduction.
Succession:
The changing sequence of species that occupy a site after a disturbance.
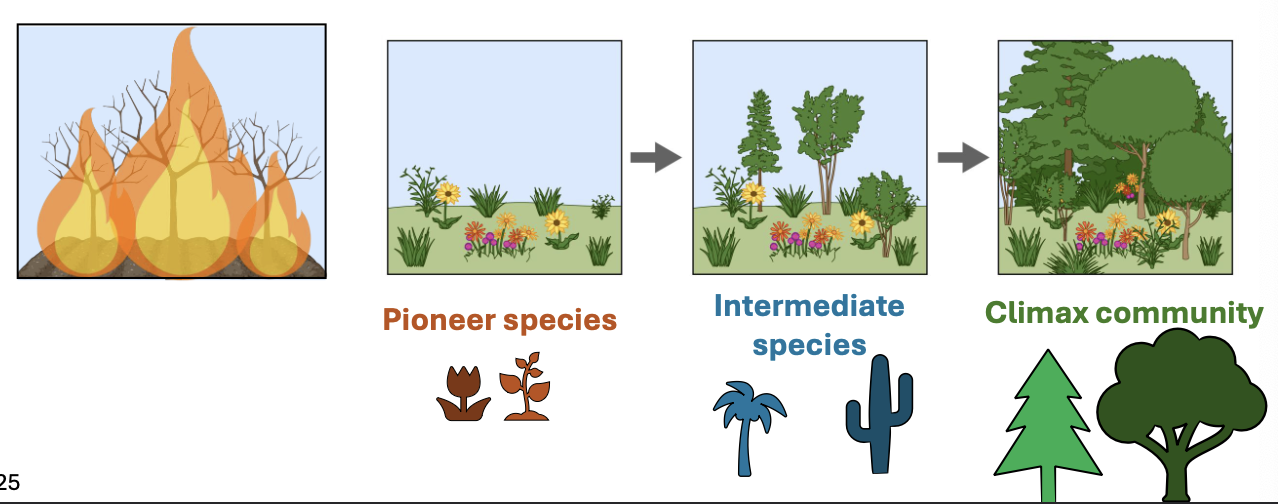
Disturbance:
An event that removes biomass from a community and changes both physical and biotic conditions.
Weed:
A species that is adapted to thrive in disturbed sites.
Sink:
A long-term repository where a particular atom or molecule may remain for millions to hundreds of millions of years.
Denitrification:
A collection of metabolic processes in different bacteria and archaea species that results in the release of N2 as an end-product. Analogous reactions release N2 when biomass burns during wildfires.
Flux:
The rate that a substance moves—its direction and amount per unit time.
Dead zone:
A region of oxygen-free (anoxic) ocean water created by a chain of events that starts with over-fertilization with nitrogen.
Carbon sink:
A long-term repository for reduced carbon atoms (carbon atoms not in CO2).
Negative feedback (in the context of climate change):
An event or process that causes greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere to drop, making climate change less extreme.
Positive feedback (in the context of climate change):
An event or process that causes even more greenhouse gases to be released into the atmosphere, making climate change even more extreme.
Phenology:
The study of the timing or seasonality of life events in organisms.
Phenological mismatch:
Changes in phenology that change the way that two species interact.
Ecology
study of the processes influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms and how they intereact with one another and their physical environment
Individual
a single organism
range of tolerance
refers to the range of environmental conditions within which an organism can survive, grow, and reproduce
exponential vs geometric graph
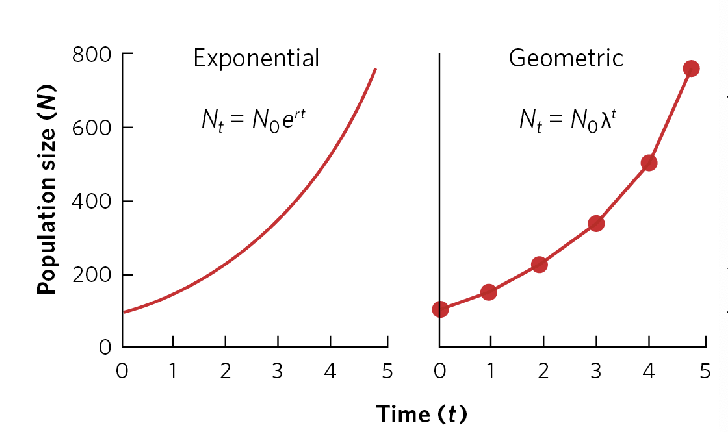
Geometric
growth is a pattern of population increase where the growth rate is constant with constant time (no .5) 𝜆

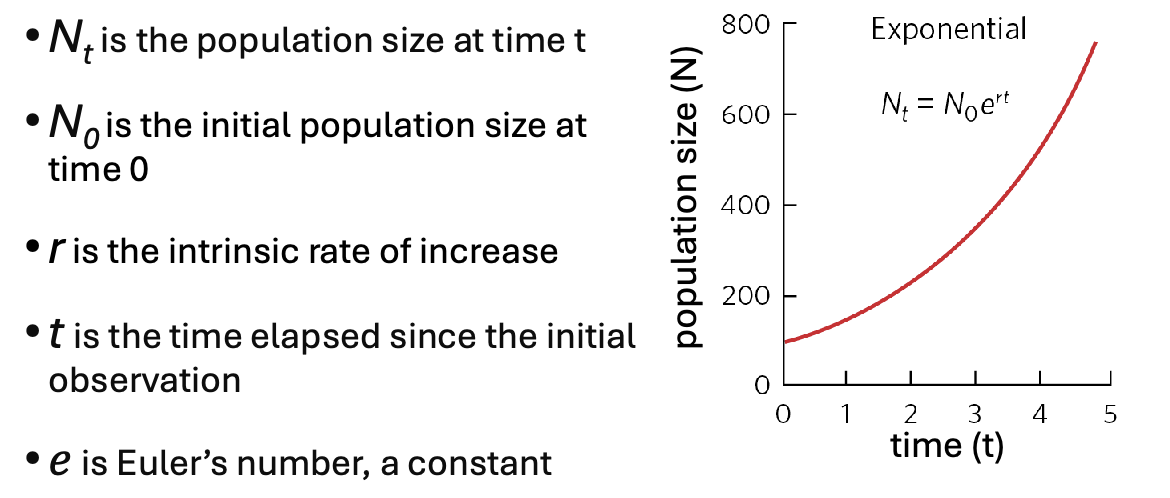
continuous exponential growth
occurs when a population increases at a constant rate over time, leading to rapid growth described by a smooth curve. population increase by unit r
exponential vs geometric values
density-independent
factors are environmental events that affect population sizes regardless of density, such as natural disasters or climate changes.
types of competition
exploitive- when individuals compete for shared resources, leading to decreased availability. (indirect)
interference- when individuals directly compete, actively preventing one another from accessing resources. (direct)
apparent- occurs when two species share a resource, causing an increase in the population of one and a decrease in the other due to predation or parasitism.
exclusion- is the principle that two species competing for the same resource cannot coexist indefinitely; one species will outcompete the other.
Trophic levels
are the hierarchical levels in an ecosystem, comprising producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on, that indicate the flow of energy and nutrients.

Energy Transfer
is the process by which energy moves through an ecosystem from one trophic level to another, primarily through feeding relationships. often 10% of efficiency is transferred to the next level due to energy loss.
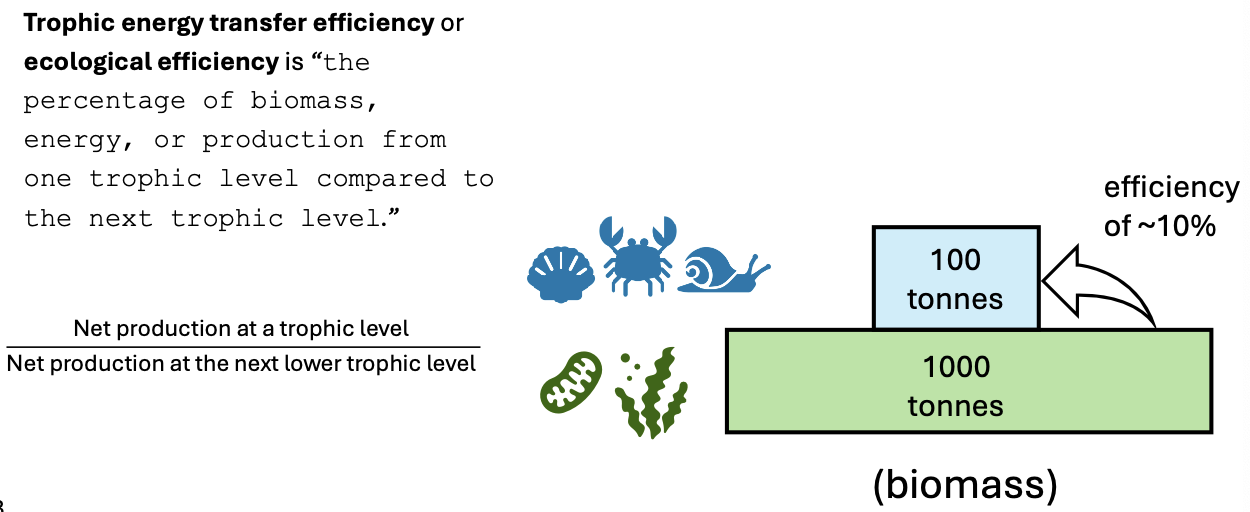
productivity
the rate at which energy is converted into organic matter 1kg/C/m²/yr
Production
the biomass produced by organisms in an ecosystem over a given period of time 1kg/C/m² in 2005
standing biomass or standing crop
is the total mass of living matter present in a specific area at a given time, usually expressed in kg/C/m². standing crop on the field is 1000kg C
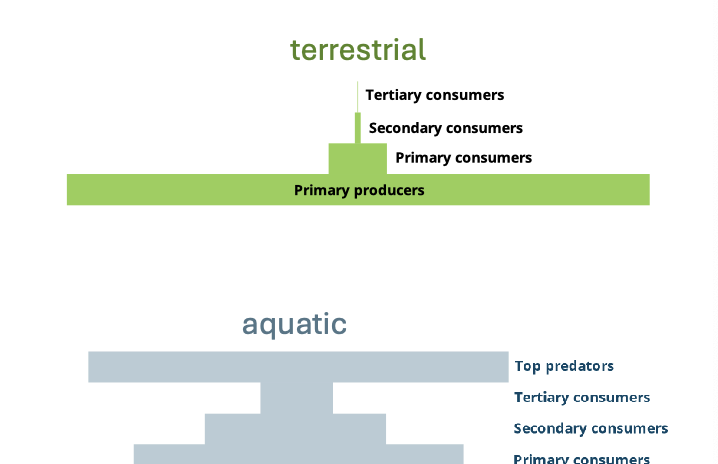
Trophic pyramid
is a graphical representation that shows the distribution of biomass or energy among different trophic levels in an ecosystem. usually wide at bottom narrow at top, wide at top and bottom for aquatic
trade off
is a balancing act between two competing factors where an increase in one factor results in a decrease in another. In ecology, it often refers to the choices organisms make to optimize their survival and reproduction.
life history
is the series of changes that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction and death, encompassing growth, development, and reproductive strategies.
slow growth→large body→late reproduction→few offspring→high investment→long lifespan→ low growth rate+abundance
rapid growth→small body→early reproduction→more offspring→low investment→ short lifespan→high growthrate+abundance
pioneer species
are the first organisms to colonize barren or disturbed environments, initiating ecological succession and contributing to soil development.
intermediate species
need some soil nutrients, grow fast+high, moderate lifespan+dispersal, builds soil
climax community species
slow dispersal, grow slow_tall, long life, require rich soil, good competitors
succession as graph
pool
storage or reservoirs
populations graph
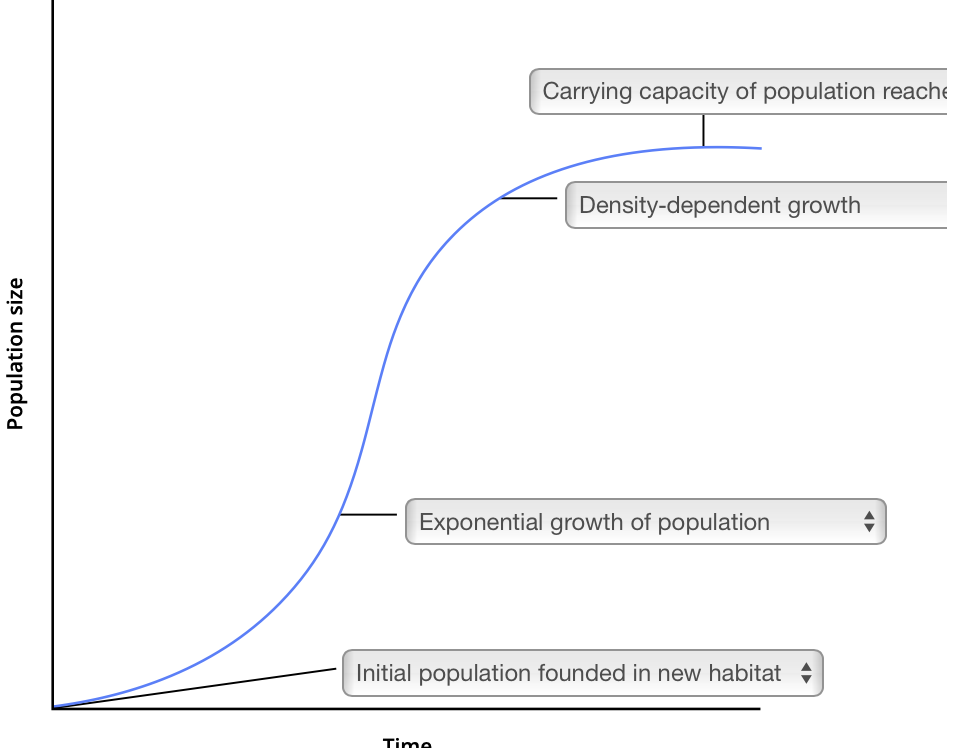
population rate equation