(27.9.10.11) Ovaries, Uterine Tubes, Uterus, & Vagina
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Describe the location, structure, and function of the ovaries
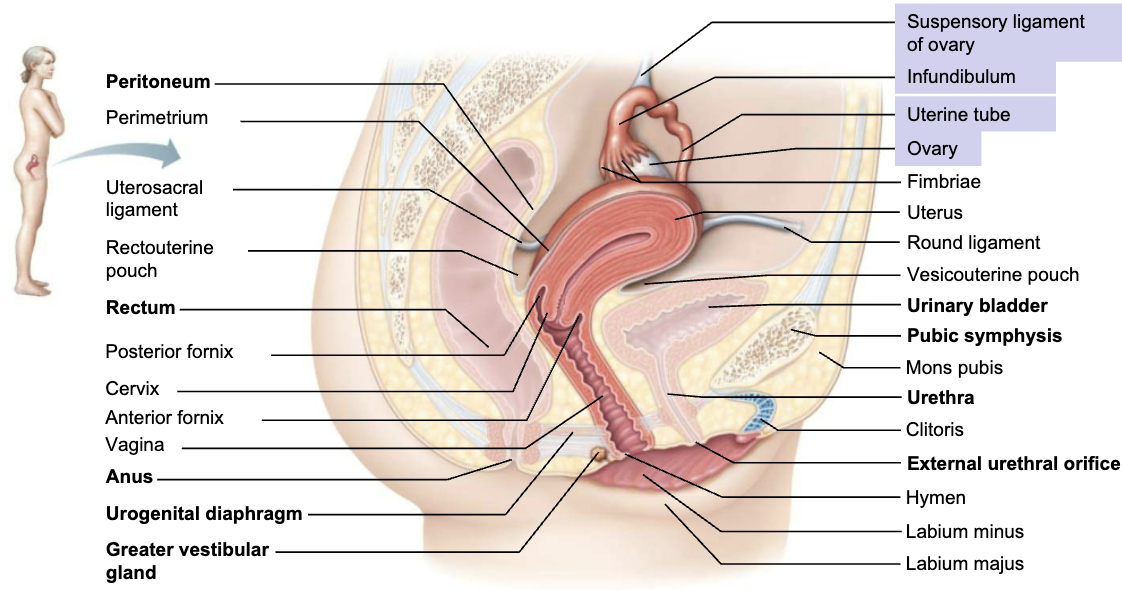
Internal genitalia
STRUCUTRE
Female gonads
The paired ovaries are found on either side of the uterus and
are held in place by several ligaments
FUNCTION
Produce female gametes (ova)
Secrete female sex hormones, estrogen (estradiol, estrone, estriol), and progesterone
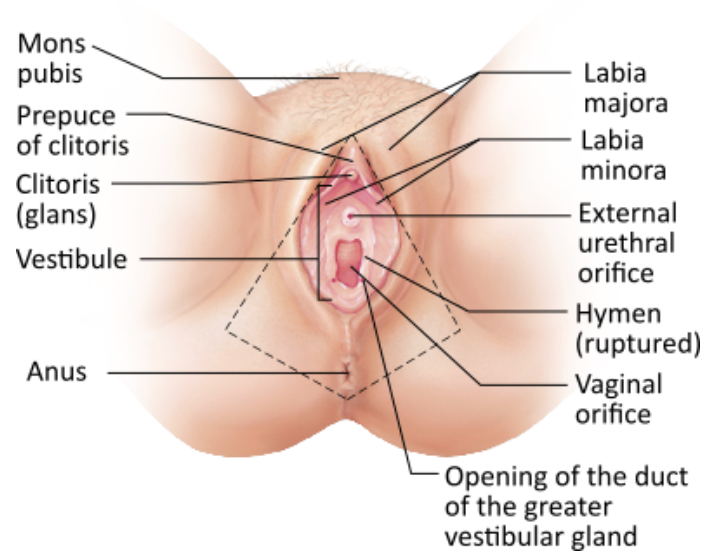
Define Internal genitalia
Located in pelvic cavity
Include ovaries and duct system (uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina)
Define External genitalia
External sex organs
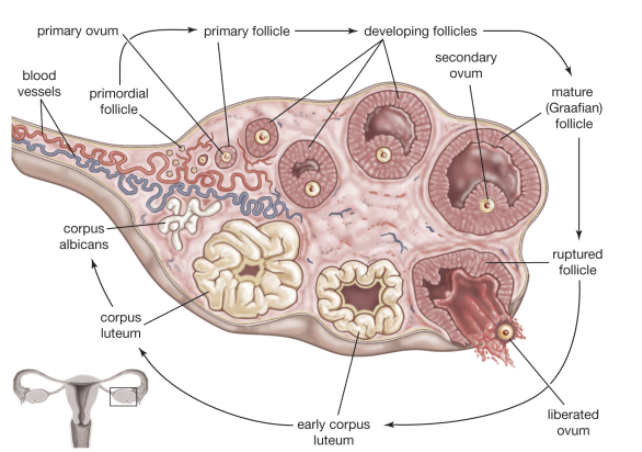
Describe Structure and Function of Ovarian follicles
STRUCTURE
Tiny saclike structures embedded in cortex
FUNCTION
Contain immature egg (oocyte) surrounded by:
Follicle cells (if only one cell layer is present)
Granulosa cells (if more than one layer present)
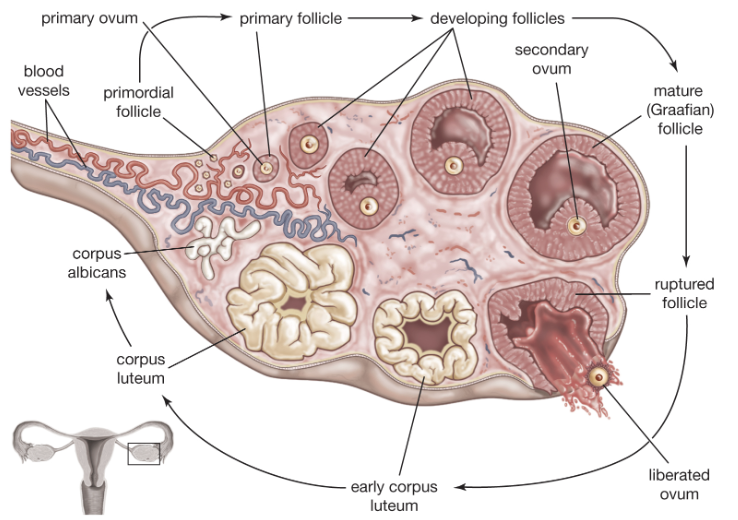
Describe Follicles Stages of Development
Primordial follicle
Single layer of follicle cells plus oocyte
More mature follicles
Several layers of granulosa cells plus oocyte
Vesicular (antral or tertiary) follicle
Fully mature follicle
Fluid-filled antrum forms; follicle bulges$$ from ovary surface
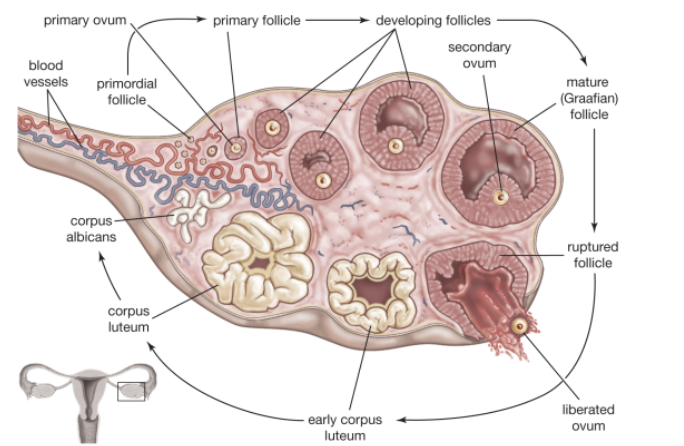
Define Ovulation
Ejection of oocyte from ripening follicle
Corpus luteum develops from ruptured follicle after ovulation
T/F: Uterine tube system has direct contact with ovaries
→ FALSE
Uterine tube system DOES NOT have direct contact with ovaries
List Tube System of Female Reproductive System
Uterine tubes
Uterus
Vagina
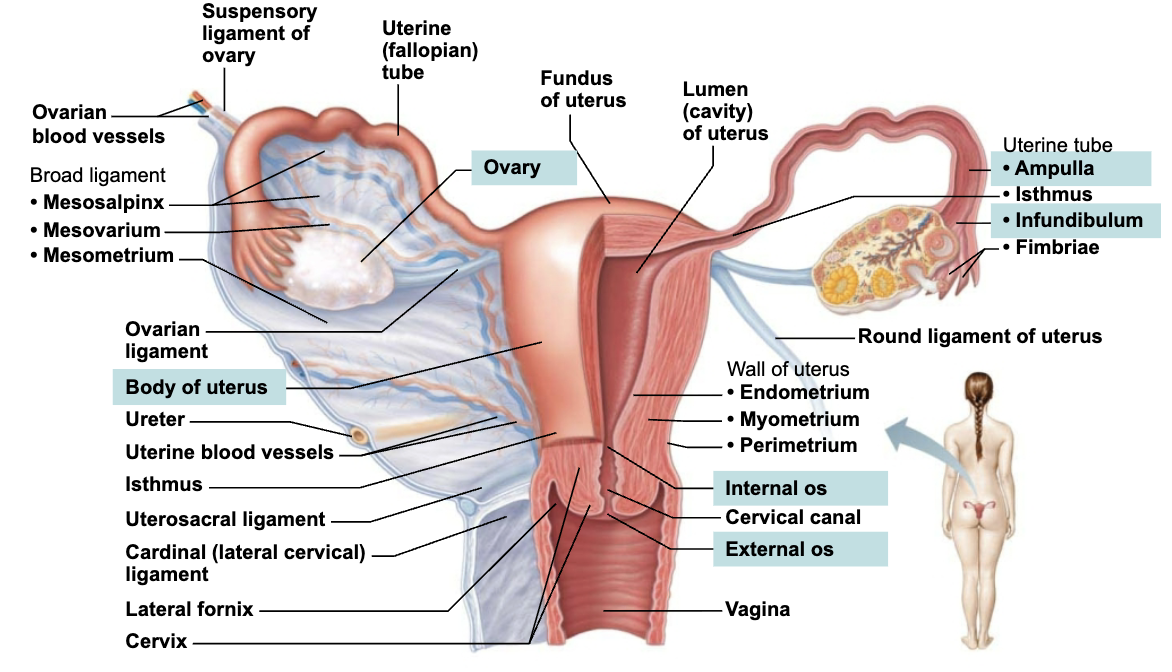
Describe Structure and Function of Uterine Tubes
Fallopian tubes or Oviducts
STUCTURE
Each tube ~10cm (4in) long and extends from area of ovary to superolateral region of uterus
FUNCTION
Receive ovulated oocyte and are usual site of fertilization
Oocyte is carried along toward uterus by smooht muscle peristalsis and ciliary action
Non-ciliated cells of tube function to nourish oocyte and sperm
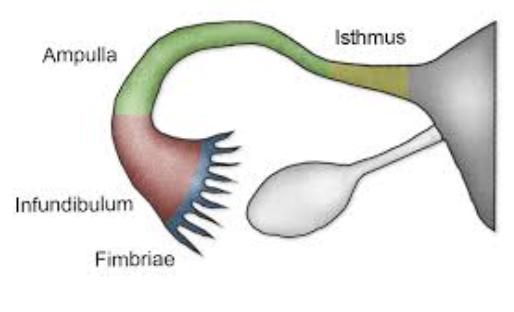
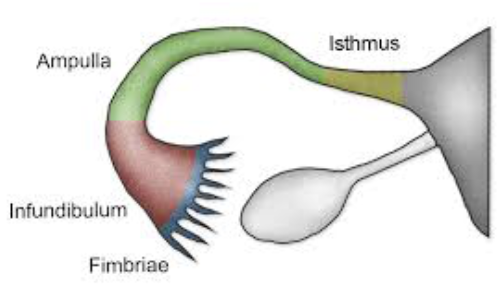
List and Describe the Regions of Uterine Tube
Isthmus
Constricted area where tube joins uterus
Ampulla
Distal end of tube that curves around ovary
Infundibulum
Distal expansion near ovary
Contains fimbriae that creates current to move oocyte into uterine tube
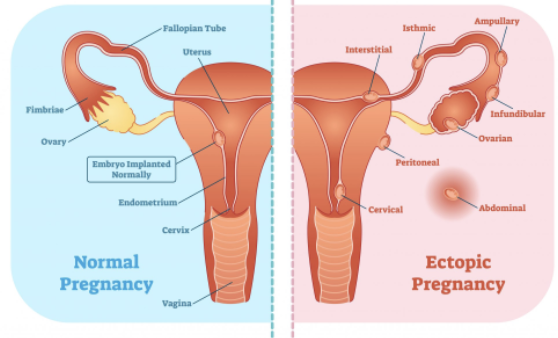
Effect of Ectopic pregnancy
EFFECT
Oocyte is fertilized in peritoneal cavity or distal uterine tube and begins developing there
Normally abort naturally with substantial bleeding
Describe Structure and Function of Uterus
STRUCTURE
Hollow, thick-walled, muscular organ
FUNCTION
To receive, retain, and nourish fertilized ovum
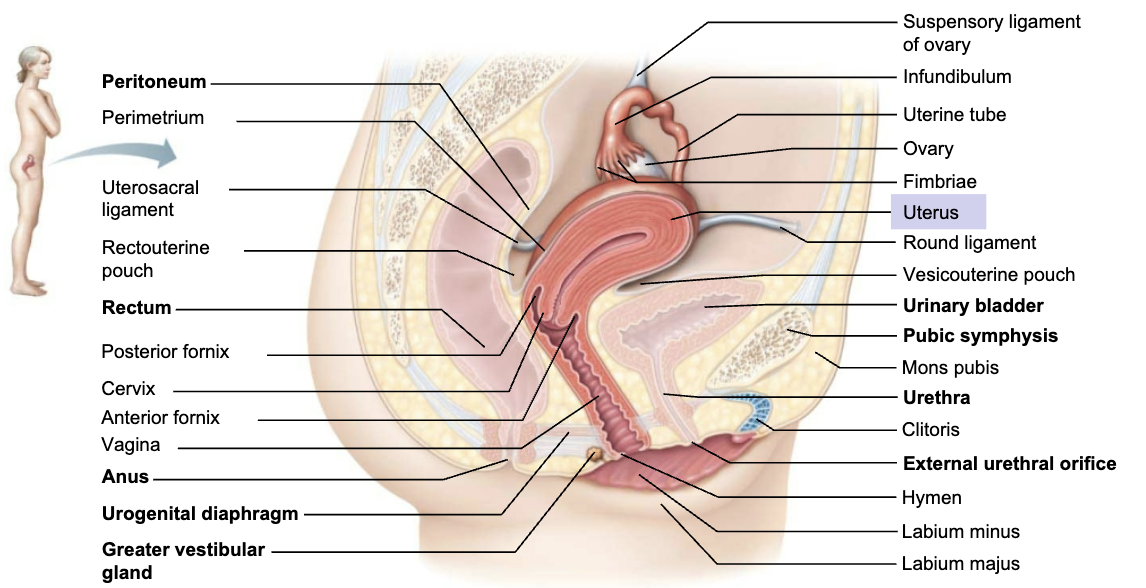
List and Describe the Regions of Uterus
Body
Major portion
Fundus
Rounded superior region
Isthmus
Narrowed inferior region
Role of Cervical glands
Secrete mucus that blocks sperm entry except during midcycle
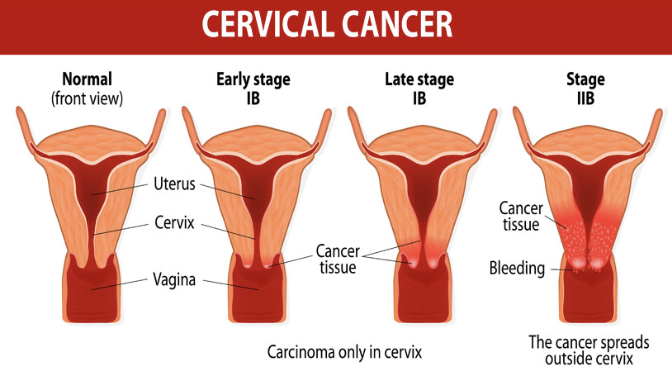
Effect and Risk of Cervical Cancer
EFFECT
Affects 450,000 women worldwide each year, killing half
Most common between ages 30 and 50
RISK
Frequent cervical inflammation
STIs, including HPV
List and Describe the Three Layers of the Uterine Wall
Perimetrium
Outermost serous layer (visceral peritoneum)
Myometrium
Bulky middle layer consisting interlacing layers of smooth muscle
Contracts rhythmically during childbirth
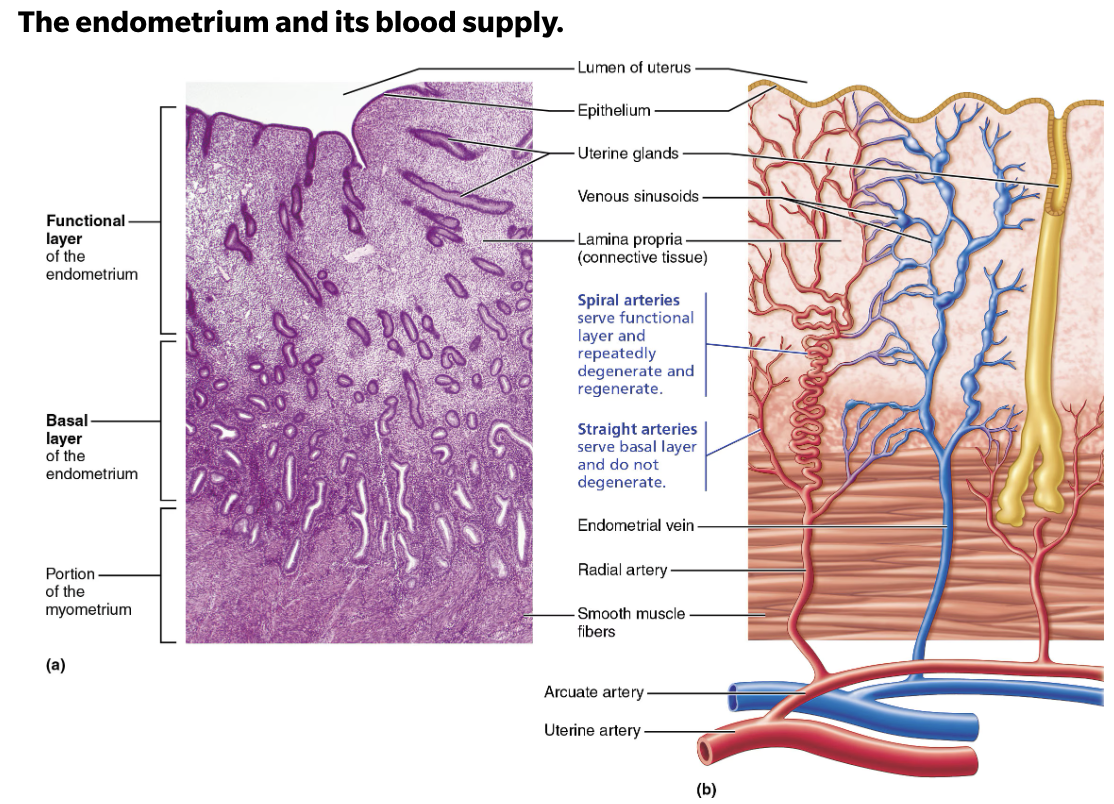
Endometrium
Mucosal lining
Simple columnar epithelium
Fertilized egg burrows into endometrium and resides there during development
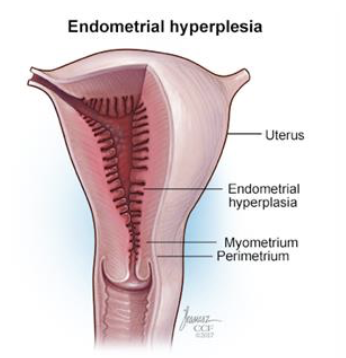
Name and describe Layers of the Endometrium
Endometrium has two chief layers (strata)
Stratum functionalis (functional layer)
Changes in response to ovarian hormone cycles
Shed during menstruation
Stratum basalis (basal layer)
Forms new stratum functionalis after menstruation
Unresponsive to ovarian hormones
Describe Structure and Function of Vagina
STRUCTURE
Thin-walled tube 8-10cm (3-4 in) in length
Extends between bladder and rectum from cervix to exterior
Epithelial cells of the vaginal mucosa produce a
glycogen-rich fluid that is metabolized by bacteria to lactic
acid, producing a highly acidic environment that protects
from infection.
FUNCTION
Birth canal
Passageway for menstrual flow
Organ of copulation
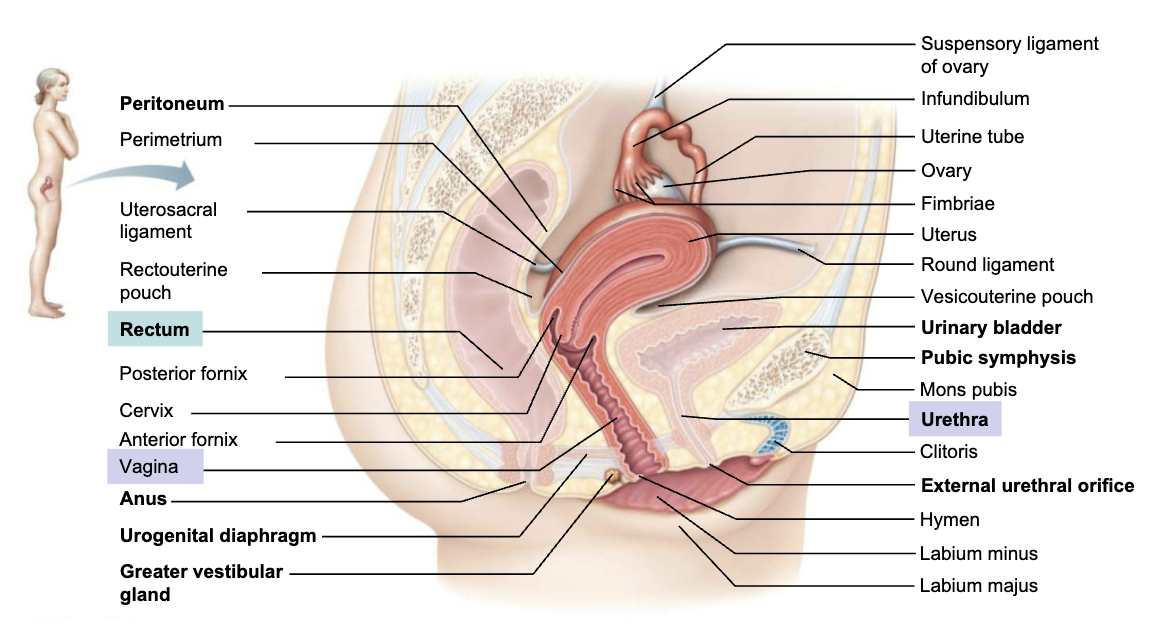
T/F: Urethra runs parallels to vagina anteriorly
→ TRUE
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) associated with untreated gonorrheal infections results in fallopian tube scarring and infertility. What other disorder would a female with PID be at high risk for?
→ Ectopic Pregnancy
What part of the female system is the usual site of fertilization of the ovulated oocyte?
→ Uterine (fallopian) tube
Eggs that successfully implant in the uterus are first fertilized in the uterine tube. This does not imply a "tubal pregnancy," where the zygote implants in the uterine tube
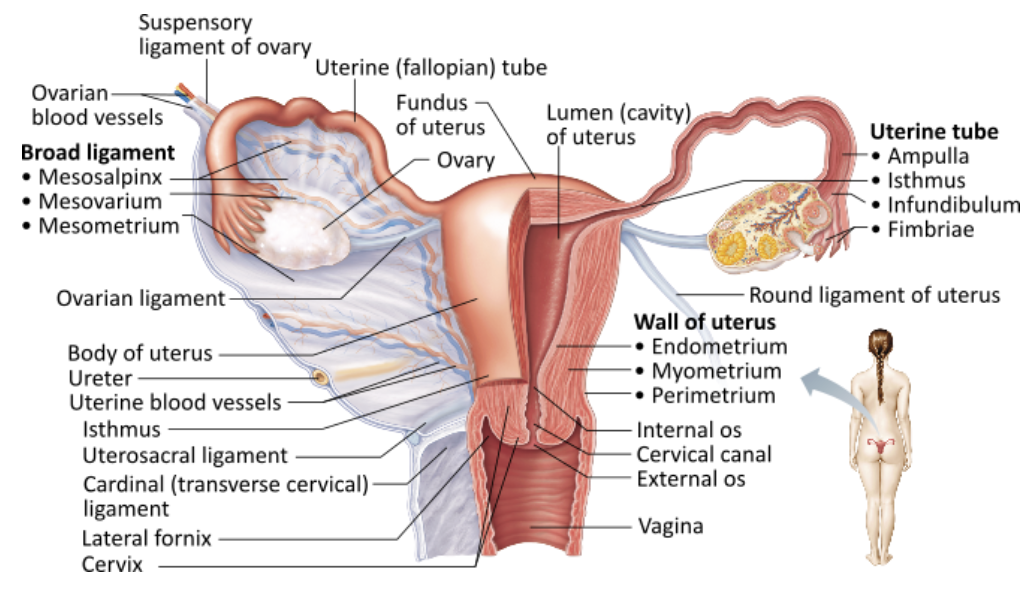
Which layer of the uterus is made of smooth muscle?
→ Myometrium
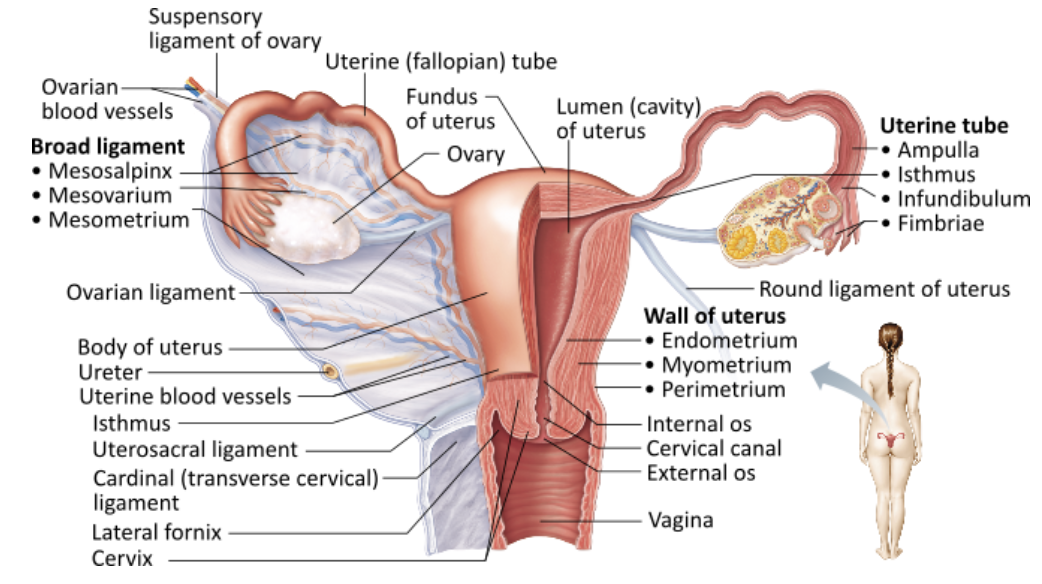
Which of these structures directly encloses the vestibule?
→ Labia minora
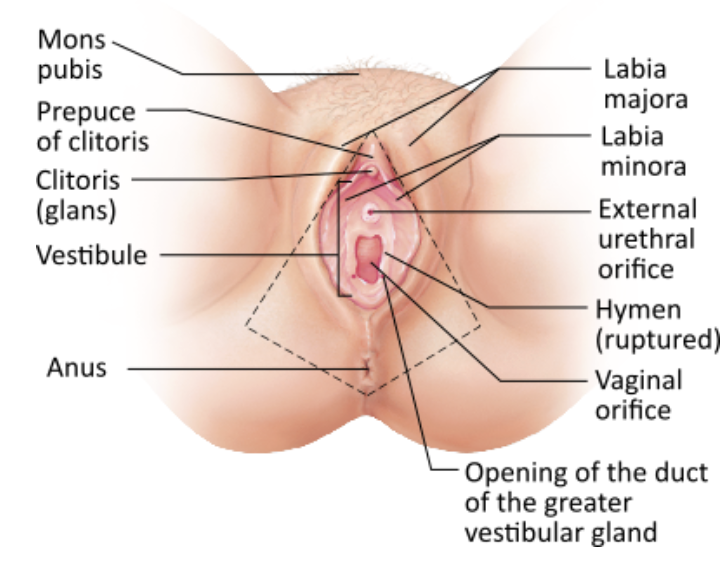
Which structure(s) of the female's external genitalia has/have erectile tissue?
→ Clitoris