Topic 5 - chemical and fuel cells
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
5.25 What is a chemical cell?
A store of chemical energy that can be transferred to electrical energy
A chemical cell produces electricity from a chemical redox reaction
Chemical cell are also called electrochemical cells
5.25 What is a simple cell?
A store of electrical energy.
5.25 What are simple cells made from?
From dipping 2 different metals of different reactivities into an electrolyte.
The metals are the electrodes
Draw a diagram of a simple chemical cell
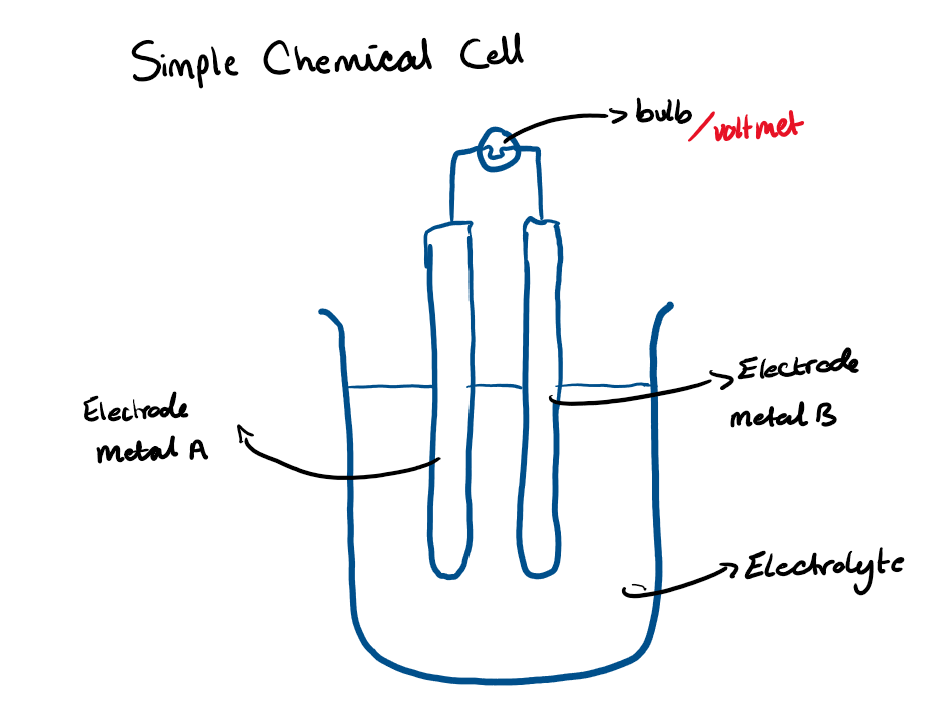
5.25 What are the four main components of a very simple chemical cell?
Electrodes: Two different metals of different reactivities
Electrolyte: Must contain ions that can move, usually aqueous compounds eg NaCl (aq)
External wires: As conductors
Voltmeter / bulb: To measure flow of electricity
5.25 How do you know that the circuit is complete?
because there is a difference in reactivity between the 2 metals that are the electrodes the cell starts to produce a voltage
5.25 Which metal will lose electrons ?
the more reactive metal (the anode)
These electrons will flow through the wires to the least reactive metal electrode
5.25 when will the cell stop producing a voltage?
the cell will stop producing a voltage when one of the reactant gets used up.
Or the bulb will eventually get dimmer and go out
5.25 which direction does electricity always flow in
from the anode to the cathode
5.25 which electrode is the more reactive metal and which is the least reactive metal?
The anode is the more reactive metal
The cathode is the less reactive metal
5.25 give an example of two metals which are often used in simple chemical cells
The anode is often zinc zn
The cathode is often copper cu
5.25 the greater the voltage…
the greater the difference in reactivity of the metals
5.25 what causes a voltage to be produced?
The difference in the ability of the electrode to release electrons (how reactive the metal is)
5.26 what is a fuel cell?
A fuel cell is a type of chemical cell
They convert the chemical energy into electrical energy by a redox reaction between fuel and oxygen
5.26 how does the fuel cell work?
The fuel enters the cell and it is oxidised. This sets up a potential difference across the cell. - a voltage
5.26 What happens in a hydrogen-fuel cell?
electricity is produced through a chemical reaction between oxygen and hydrogen
5.26 which cell is oxidised and which is reduced? What is the waste products?
The hydrogen us oxidised (gains oxygen) and loses electrons
The oxygen is reduced (loses oxygen) and gains electrons
Water is the only waste product
5.26 What is the overall equation for the reaction that takes place in the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
hydrogen + oxygen → water
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) (the H2O that is produced is a gas)
5.26 Draw out a diagram of a hydrogen fuel cell with labels
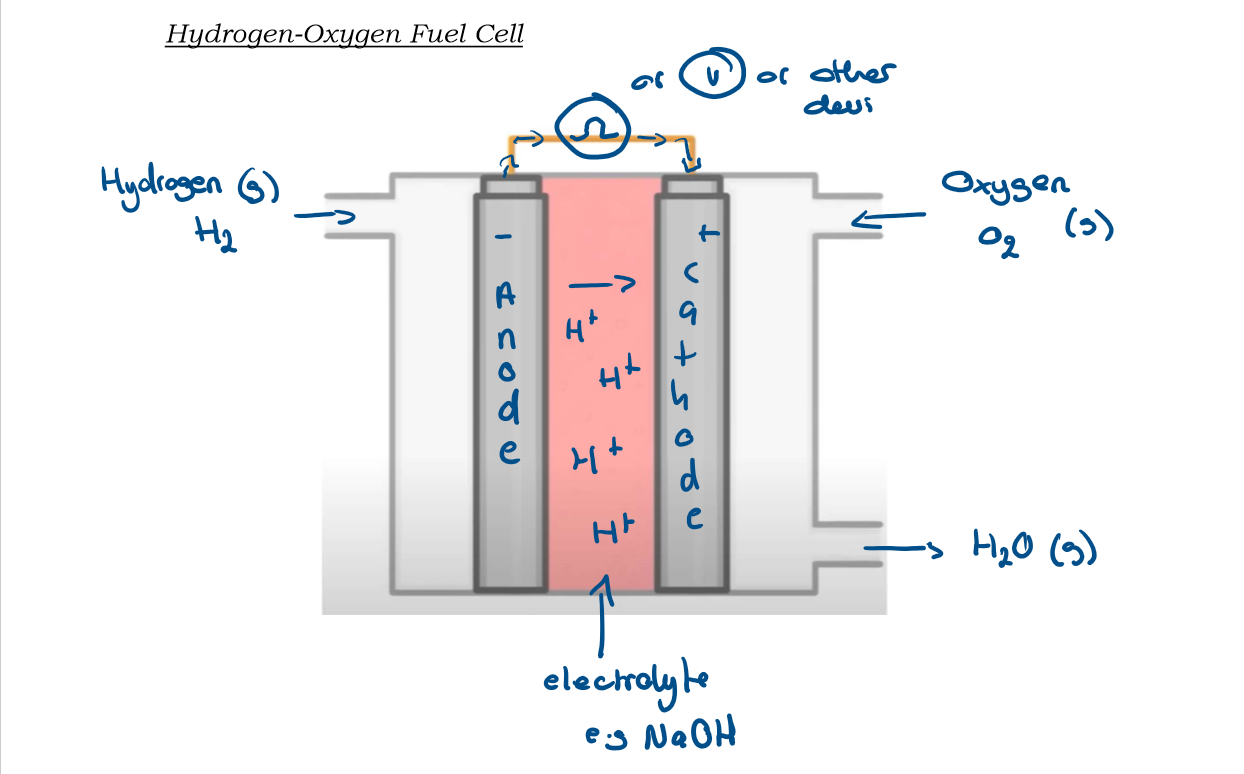
5.26 Explain what happens on the left side of the hydrogen fuel cell
-on the left hand side hydrogen gas is fed into the left of the fuel cell
-the hydrogen ions produced at the anode then travel through the electrolyte to the cathode
-the electrons travel around the wires from the anode to the cathode, producing the electrical current.
5.26 What is the reaction at the anode + half equation
oxidation
H2 → 2H+ + 2e-
5.26 Explain what happens on the right side of the hydrogen fuel cell
-The hydrogen ions (from the left side) combine with the oxygen that comes from the top right side to the fuel cell to produce water.
-The waste product H2O leaves as a gas from the bottom right side of the fuel cell.
5.26 What is the reaction at the cathode + half equation?
Reduction
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O
5.26 what is the energy transfer?
chemical energy to electrical energy
The fuel cell needs to be kept in supply for the fuel or it will stop producing electricity
5.26 What is the overall equation for the hydrogen fuel cell?
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
5.27 what are a use for hydrogen fuel cells? Why is this use beneficial?
they can be used in vehicles to produce the electricity that is used to power the car.
This means that fuel cells can be used instead of car engines which burn petrol and diesel, lead batteries and chemical cells
5.27 What are some advantages of using hydrogen fuel cells?
produces only h2o (g) as waste, therefore no co2 nor greenhouse gases'
Renewable source of H2 and O2(water), (though it needs to be electrolysed)
Conserves non renewable fuels such as crude oil
Can refuel when using in vehicles, this is fast and there is no need to recharge battery
The cell itself is simple and lasts a long time.
5.27 what are some disadvantage of fuel cells?
-H2 is very dangerous, expensive and very combustible (burns easily)
Storage, transport and refuelling of H2 as a gas is difficult